Spinal Anesthesia Results in Lower Costs Compared to General Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion—A Matched Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Cohort Development and Data Collection
2.3. Cost Data Collection
- Anesthesia care costs (including anesthesiologist fees)
- Implant costs (rods, screws, cages, grafts, etc.)
- Inpatient costs (recovery support staff, medical supplies, drugs, etc.)
- OR supplies/medications (staff, medical supplies, sterilization, drugs, etc.)
- OR time fees
- PACU time fees
2.4. Anesthetic Technique
2.5. Cohort Development Variables and Outcome Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demograohics and Non-Cost Outcomes
3.2. Comparative Cost Analysis
3.2.1. Total Cost Differences
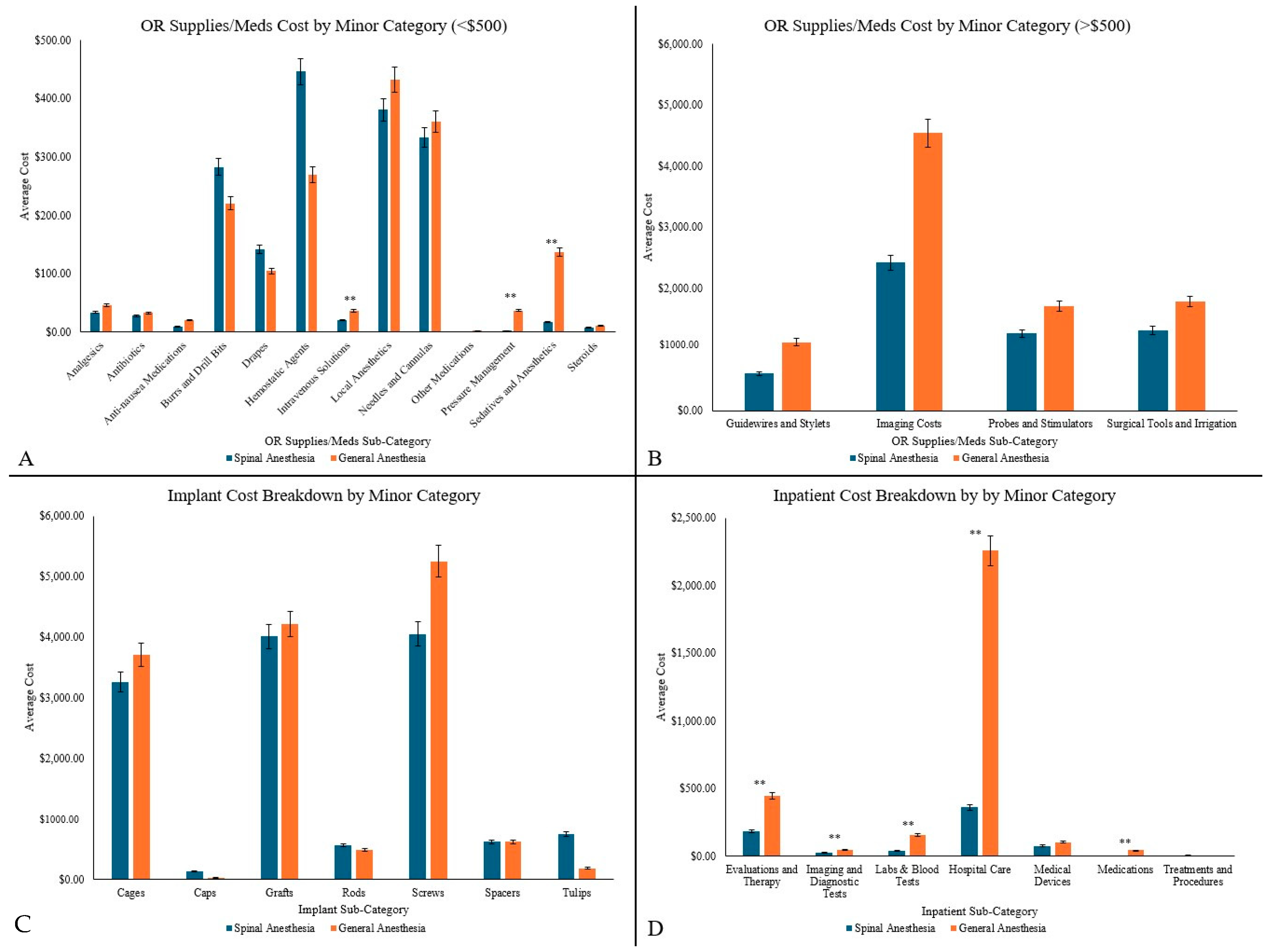
3.2.2. Operating Room (OR) Supplies/Medications
3.2.3. In-Patient Costs
3.2.4. Implant Costs
3.2.5. Anesthesia Care Costs
3.2.6. OR Time Costs
3.2.7. Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) Time
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Key Findings
4.2. Interpretation of Results
4.3. Comparison with Existing Literature
4.4. Clinical Relevance
4.5. Future Research Directions
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravindra, V.M.; Senglaub, S.S.; Rattani, A.; Dewan, M.C.; Härtl, R.; Bisson, E.; Park, K.B.; Shrime, M.G. Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease: Estimating Global Incidence and Worldwide Volume. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Park, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Yeom, J.S. Recent Updates on Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Techniques, Technologies, and Indications. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.; Idris, Z.; Beng, T.B.; Young, T.Y.; Chek, W.C.; Abdullah, J.M.; Hieng, W.S. Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Surgery Compared to Open Posterior Lumbar Instrumentation and Fusion. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2017, 12, 620–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessing, N.L.; Edwards, C.C.; Brown, C.H.; Ledford, E.C.; Dean, C.L.; Lin, C. Spinal Anesthesia in Elderly Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spine Surgery. Orthopedics 2017, 40, e317–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.D.; Alomari, S.; Khalifeh, J.M.; Ahmed, A.K.; Musharbash, F.N.; Mo, K.; Lubelski, D.; Witham, T.F.; Bydon, A.; Theodore, N. Adoption of awake spine surgery—Trends from a national registry over 14 years. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiani, B.; Reardon, T.; Selvage, J.; Dahan, A.; El-Farra, M.H.; Endres, P.; Taka, T.; Suliman, Y.; Rose, A. Awake spine surgery: An eye-opening movement. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biase, G.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Abode-Iyamah, K.O. Spine Surgery Under Spinal vs. General Anesthesia: Prospective Analysis of Quality of Life, Fatigue, and Cognition. Neurosurgery 2022, 90, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waguia, R.; Touko, E.K.; Sykes, D.A.W.; Kelly-Hedrick, M.; Hijji, F.Y.; Sharan, A.D.; Foster, N.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M. How to start an awake spine program: Protocol and illustrative cases. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 13, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.P.; Bonin, B.; Quinones, C.; Kumbhare, D.; Guthikonda, B.; Hoang, S. Spinal Anesthesia for Awake Spine Surgery: A Paradigm Shift for Enhanced Recovery after Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urick, D.; Sciavolino, B.; Wang, T.Y.; Gupta, D.K.; Sharan, A.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M. Perioperative outcomes of general versus spinal anesthesia in the lumbar spine surgery population: A systematic review and meta-analysis of data from 2005 through 2021. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 30, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehab, Z.; Tabarestani, T.Q.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M.; Husain, A.M. Intraoperative Electromyography in Awake Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Case Study on Nerve Activation Under the Effects of Local Anesthesia. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 39, e26–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, D.A.W.; Tabarestani, T.Q.; Chaudhry, N.S.; Salven, D.S.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Bullock, W.M.; Guinn, N.R.; Gadsden, J.; Berger, M.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M. Awake Spinal Fusion Is Associated with Reduced Length of Stay, Opioid Use, and Time to Ambulation Compared to General Anesthesia: A Matched Cohort Study. World Neurosurg. 2023, 176, e91–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorrilla-Vaca, A.; Healy, R.J.; Mirski, M.A. A Comparison of Regional Versus General Anesthesia for Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Studies. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2017, 29, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Pierce, J.; Welch, W.C. Cost Analysis of Spinal Versus General Anesthesia for Lumbar Diskectomy and Laminectomy Spine Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2016, 89, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcott, B.P.; Khanna, A.; Yanamadala, V.; Coumans, J.V.; Peterfreund, R.A. Cost analysis of spinal and general anesthesia for the surgical treatment of lumbar spondylosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekerak, R.; Mostafa, E.; Morris, M.T.; Nessim, A.; Vira, A.; Sharan, A. Comparative outcome analysis of spinal anesthesia versus general anesthesia in lumbar fusion surgery. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 13, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerji, A.; Chattopadhyaya, A.; Banerjee, S. Lumbar spine instrumented fusion surgery under spinal anaesthesia versus general anaesthesia-A retrospective study of 239 cases. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 18, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterwald, M.; Muster, M.; Farshad, M.; Saporito, A.; Brada, M.; Aguirre, J.A. Spinal versus general anesthesia for lumbar spine surgery in high risk patients: Perioperative hemodynamic stability, complications and costs. J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 46, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, K.; Doger, C.; Ornek, D.; Gokcinar, D.; Aydemir, S.; Ozay, R. Perioperative outcome and cost-effectiveness of spinal versus general anesthesia for lumbar spine surgery. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2014, 48, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.T.; Morris, J.; Wallace, C.; Cho, W.; Sharan, A.; Abouelrigal, M.; Joseph, V. An Analysis of the Cost-Effectiveness of Spinal Versus General Anesthesia for Lumbar Spine Surgery in Various Hospital Settings. Glob. Spine J. 2019, 9, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Jonayed, S.; Alam, M.S.; Al Mamun Choudhury, A.; Akter, S.; Chakraborty, S. Efficacy, safety, and reliability of surgery on the lumbar spine under general versus spinal anesthesia—An analysis of 64 cases. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 16, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vural, C.; Yorukoglu, D. Comparison of patient satisfaction and cost in spinal and general anesthesia for lumbar disc surgery. Turk. Neurosurg. 2014, 24, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Roman, R.J.; Govindarajan, V.; Bryant, J.P.; Wang, M.Y. Spinal anesthesia in awake surgical procedures of the lumbar spine: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 3709 patients. Neurosurg. Focus. 2021, 51, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulutas, M.; Secer, M.; Taskapilioglu, O.; Karadas, S.; Akyilmaz, A.A.; Baydilek, Y.; Kocamer, B.; Ozboz, A.; Boyaci, S. General versus epidural anesthesia for lumbar microdiscectomy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, O.; Tariq, R.; Akhtar Khan, S.; Hussain, M.; Ahmed, U. Degenerative Lumbar Spine Surgeries Under Regional Anesthesia in a Developing Country: An Initial Case Series. Cureus 2023, 15, e34065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, E.T.; Naderi, S. Effects of Anesthesia Protocol on Perioperative Outcomes and Costs of Lumbar Microdiscectomies. Turk. Neurosurg. 2019, 29, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, T.; Kortlever, J.T.P.; Shapiro, L.M.; Baker, L.; Harris, A.H.S.; Kamal, R.N. The Influence of Cost Information on Treatment Choice: A Mixed-Methods Study. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2020, 45, 899–908.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, A.A.; Steinmetz, M.P. Evolution of Minimally Invasive Lumbar Spine Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2020, 140, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossopoulos, P.N.; Ononogbu-Uche, F.C.; Tabarestani, T.Q.; Huang, C.-C.; Paturu, M.; Bardeesi, A.; Ray, W.Z.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Goodwin, C.R.; Erickson, M.; et al. Evolution of the Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF): From Open to Percutaneous to Patient-Specific. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, C. General anaesthesia: Practical recommendations and recent advances. Drugs 1999, 58, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, I.; Stieger, A.; Luedi, M.M.; Romero, C.S. Spinal anesthesia in ambulatory patients. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2024, 37, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouz, K.; Hoppe, P.; Briesenick, L.; Saugel, B. Intraoperative hypotension: Pathophysiology, clinical relevance, and therapeutic approaches. Indian J. Anaesth. 2020, 64, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.M.; Hasanin, A.; ElSayed, O.S.; Mostafa, M.; Khaled, D.; Arafa, A.S.; Hassan, A. Comparison of the hemodynamic effects of opioid-based versus lidocaine-based induction of anesthesia with propofol in older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2023, 42, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauro, K.M.; Smith, C.; Ibadin, S.; Thomas, A.; Ganshorn, H.; Bakunda, L.; Bajgain, B.; Bisch, S.P.; Nelson, G. Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Guidelines and Hospital Length of Stay, Readmission, Complications, and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2417310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, S.; Rücker, G.; Eberhart, L.H.; Pace, N.L.; Hartl, H.M.; Jordan, O.L.; Mayer, D.; Riemer, M.; Schaefer, M.S.; Raj, D.; et al. Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 10, CD012859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajjoub, R.; Ghaith, A.K.; El-Hajj, V.G.; Rios-Zermano, J.; De Biase, G.; Atallah, E.; Tfaily, A.; Saad, H.; Akinduro, O.O.; Elmi-Terander, A.; et al. Comparative outcomes of awake spine surgery under spinal versus general anesthesia: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, M.C.; Hale, S.D.; White-Dzuro, C.; Pierce, K.E.; Naessig, S.A.; Ahmad, W.; Passias, P.G. Ambulatory spine surgery. J. Spine Surg. 2019, 5 (Suppl. S2), S147–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Major Category | Minor Category | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Anesthesia Time | Anesthesia Room Fee and Per Minute | ||
| Implants | Cages | Caps | Grafts |
| Rods | Screws | Spacers | |
| Tulips | |||
| In-Patient Costs | Evaluations and Therapy | Imaging and Diagnostic Tests | Labs and Blood Tests |
| Hospital Care | Medical Devices | Medications | |
| Treatments and Procedures | |||
| OR Supplies | Analgesics | Anti-nausea Medications | Antibiotics |
| Burrs and Drill Bits | Drapes | Guidewires and Stylets | |
| Hemostatic Agents | Imaging Costs | Intravenous Solutions | |
| Local Anesthetics | Needles and Cannulas | Other Medications | |
| Pressure Management | Probes and Stimulators | Sedatives and Anesthetics | |
| Steroids | Surgical Tools and Irrigation | ||
| OR Time | OR Fee and Per Minute | ||
| PACU Time | Time spent in PACU | ||
| Spinal Anesthesia (n = 9) | General Anesthesia (n = 9) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.8 ± 6.8 | 67.2 ± 7.9 | p = 0.37 |
| Gender | p = 0.63 | ||
| Male (%n) | 5 (55.6%) | 6 (66.7%) | |
| Female (%n) | 4 (44.4%) | 3 (33.3%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.7 ± 3.3 | 29.0 ± 5.1 | p = 0.36 |
| History of Smoking | 3 (33.3%) | 4 (44.4%) | p = 0.58 |
| History of Hypertension | 5 (55.6%) | 9 (100.0%) | p = 0.09 |
| History of Diabetes | 3 (33.3%) | 5 (55.6%) | p = 0.46 |
| History of Heart Disease | 3 (33.3%) | 6 (66.7%) | p = 0.25 |
| History of Pulmonary Disease | 5 (55.6%) | 5 (55.6%) | p = 1.00 |
| History of Renal Disease | 7 (77.8%) | 4 (44.4%) | p = 0.414 |
| History of Past Spine Surgery | 2 (22.2%) | 4 (44.4%) | p = 0.45 |
| Level of Surgery | p = 1.00 | ||
| L3/L4 | 1 (11.1%) | 1 (11.1%) | |
| L4/L5 | 7 (77.8%) | 7 (77.8%) | |
| L4-S1 | 1 (11.1%) | 1 (11.1%) | |
| Type of Surgery | p = 1.00 | ||
| MIS-TLIF | 5 (55.6%) | 5 (55.6%) | |
| Perc-LIF | 4 (44.4%) | 4 (44.4%) | |
| ASA Grade | p = 0.11 | ||
| 2 | 5 (55.6%) | 1 (11.1) | |
| 3 | 4 (44.4%) | 7 (77.8%) | |
| 4 | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (11.1%) |
| Spinal Anesthesia (n = 9) | General Anesthesia (n = 9) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Blood Loss (mL) | 50.0 ± 21.7 | 81.3 ± 75.3 | p = 0.50 |
| OR time (min) | 181.0 ± 61.4 | 213.0 ± 90.3 | p = 0.50 |
| Length of stay (hours) | 12 ± 11.1 | 78 ± 42.1 | p = 0.04 |
| Post-Op Opioid Use (mg) | 20.1 ± 7.6 | 45.6 ± 11.8 | p = 0.13 |
| 30-day readmission | p = 0.30 | ||
| No Readmission (%n) | 9 (100.0%) | 8 (88.9%) | |
| Readmission (%n) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (11.1%) | |
| Difference in NDI | 0.9 ± 3.5 | 0.18 ± 0.5 | p = 0.60 |
| Difference in ODI | −12.7 ± 42.1 | −20.0 ± 24.7 | p = 0.62 |
| Difference in VAS B | −3.0 ± 4.8 | −3.8 ± 3.2 | p = 0.59 |
| Difference in VAS L | −1.9 ± 5.4 | −3.2 ± 3.7 | p = 0.49 |
| Difference in PROMIS Pain | 1.4 ± 18.5 | −3.7 ± 32.7 | p = 0.75 |
| Difference in PROMIS PF | −7.7 ± 40.5 | −4.6 ± 47.9 | p = 0.99 |
| Difference in PROMIS GH Physical | −4.7 ± 29.7 | −7.8 ± 21.3 | p = 0.82 |
| Difference in PROMIS GH Mental | −5.7 ± 34.0 | −10.7 ± 27.4 | p = 0.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ononogbu-Uche, F.C.; Saleh, A.W.; Toussaint, F.; Wallace, T.; Woo, J.; Morris, M.T.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Bullock, W.M.; Guinn, N.R.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M. Spinal Anesthesia Results in Lower Costs Compared to General Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion—A Matched Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113851
Ononogbu-Uche FC, Saleh AW, Toussaint F, Wallace T, Woo J, Morris MT, Shaffrey CI, Bullock WM, Guinn NR, Abd-El-Barr MM. Spinal Anesthesia Results in Lower Costs Compared to General Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion—A Matched Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113851
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnonogbu-Uche, Favour C., Abdullah Wael Saleh, Felix Toussaint, Taylor Wallace, Joshua Woo, Matthew T. Morris, Christopher I. Shaffrey, William M. Bullock, Nicole R. Guinn, and Muhammad M. Abd-El-Barr. 2025. "Spinal Anesthesia Results in Lower Costs Compared to General Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion—A Matched Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113851
APA StyleOnonogbu-Uche, F. C., Saleh, A. W., Toussaint, F., Wallace, T., Woo, J., Morris, M. T., Shaffrey, C. I., Bullock, W. M., Guinn, N. R., & Abd-El-Barr, M. M. (2025). Spinal Anesthesia Results in Lower Costs Compared to General Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion—A Matched Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113851








