Evaluation of Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Growth Hormone (GH)-Deficient Children After 6 Months of Recombinant Human GH Replacement Therapy: Anti-Ageing GH vs. Pro-Ageing Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Protocol
2.2. Metabolic Variables
2.3. Determination of the Epigenetic Age
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Parameters Before and After rhGH Treatment
3.2. Chronological vs. Biological Ages Before and After rhGH Treatment
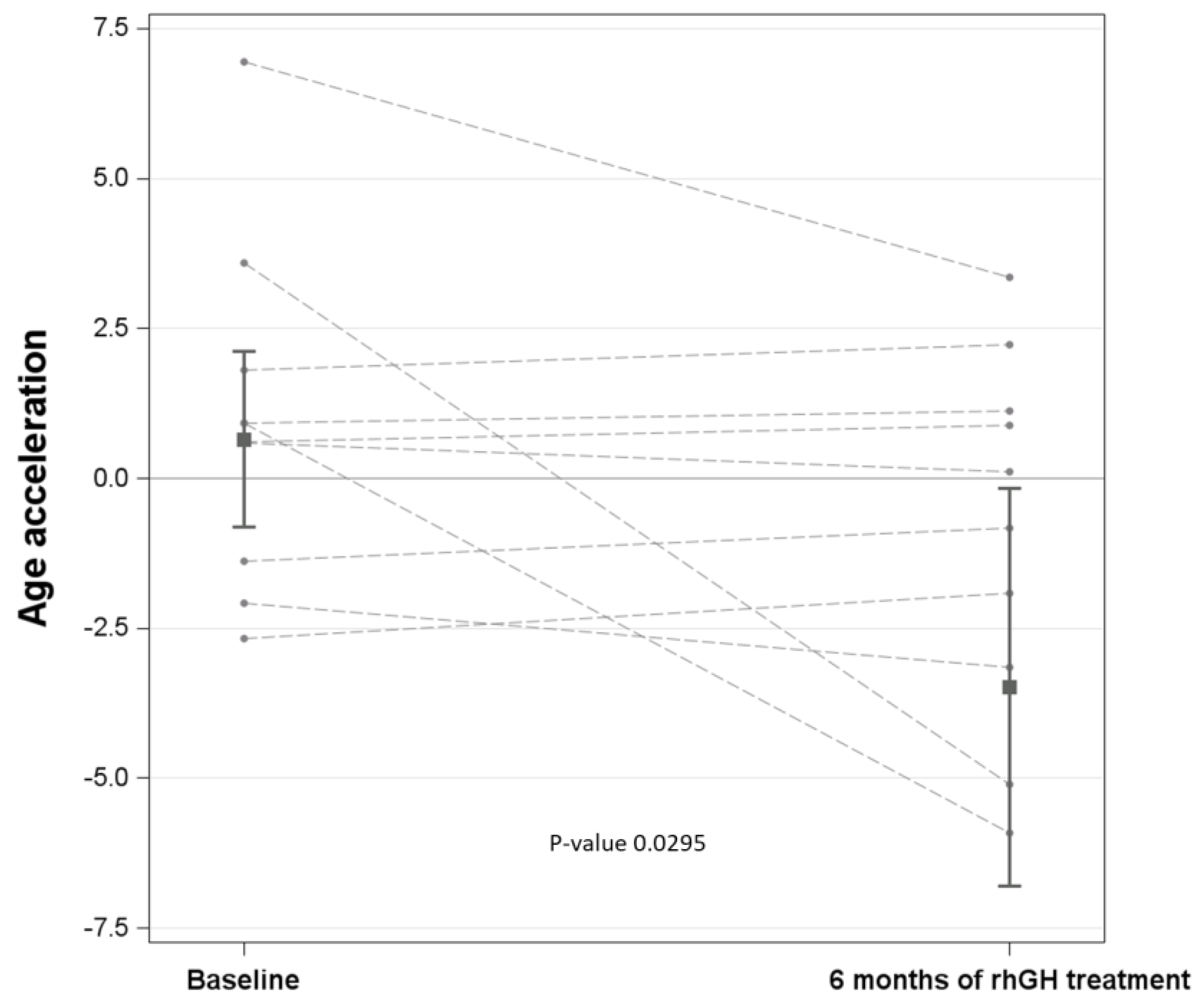
3.3. Association of Age Acceleration with Each Parameter: Effect of rhGH Treatment
3.4. Association of Age Acceleration with Each Parameter: Adjustment for rhGH Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Junnila, R.K.; List, E.O.; Berryman, D.E.; Murrey, J.W.; Kopchick, J.J. The GH/IGF-1 axis in ageing and longevity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, S.A.; Hoffman, A.R. The somatopause: Should growth hormone deficiency in older people Be treated? Clin. Geriatr. Med. 1997, 13, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Werder, K. The somatopause is no indication for growth hormone therapy. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1999, 22 (Suppl. S5), 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar-Oliveira, M.H.; Bartke, A. Growth Hormone Deficiency: Health and Longevity. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 575–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Darcy, J. GH and ageing: Pitfalls and new insights. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, H.; Laron, Z. Insulin-like growth factors and aging: Lessons from Laron syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1291812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, D.E.; Christiansen, J.S.; Johannsson, G.; Thorner, M.O.; Kopchick, J.J. Role of the GH/IGF-1 axis in lifespan and healthspan: Lessons from animal models. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2008, 18, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.A.; Lamberts, S.W. Igf-1 and longevity. Horm. Res. 2004, 62 (Suppl. S3), 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bartke, A. Can growth hormone (GH) accelerate aging? Evidence from GH-transgenic mice. Neuroendocrinology 2003, 78, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritvonen, E.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Jaatinen, P.; Ebeling, T.; Moilanen, L.; Nuutila, P.; Kauppinen-Mäkelin, R.; Schalin-Jäntti, C. Mortality in acromegaly: A 20-year follow-up study. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2016, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukama, T.; Srour, B.; Johnson, T.; Katzke, V.; Kaaks, R. IGF-1 and Risk of Morbidity and Mortality from Cancer, Cardiovascular Diseases, and All Causes in EPIC-Heidelberg. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e1092–e1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Song, Q.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cui, Y.T.; Fu, J.X.; Feng, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. IGF-1 Accelerates Cell Aging by Inhibiting POLD1 Expression. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Growth hormone treatment in children: Review of safety and efficacy. Paediatr. Drugs. 2004, 6, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.L.; Merriam, G.R.; Kargi, A.Y. Adult growth hormone deficiency—Benefits, side effects, and risks of growth hormone replacement. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savine, R.; Sönksen, P. Growth hormone—Hormone replacement for the somatopause? Horm. Res. 2000, 53 (Suppl. S3), 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Hascup, E.; Hascup, K.; Masternak, M.M. Growth Hormone and Aging: New Findings. World J. Mens Health. 2021, 39, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Taurin, S.; Alshammary, S. New insights into methods to measure biological age: A literature review. Front. Aging. 2024, 5, 1395649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Le Stunff, C.; Cheung, W.; Kwan, T.; Lathrop, M.; Pastinen, T.; Bougnères, P. Differentially methylated CpGs in response to growth hormone administration in children with idiopathic short stature. Clin. Epigenet. 2022, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, V.L.; Rakoczy, S.; Rojanathammanee, L.; Brown-Borg, H.M. Expression of DNA methyltransferases is influenced by growth hormone in the long-living Ames dwarf mouse in vivo and in vitro. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, E.; Targher, G.; Alberiche, M.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Saggiani, F.; Zenere, M.B.; Monauni, T.; Muggeo, M. Homeostasis model assessment closely mirrors the glucose clamp technique in the assessment of insulin sensitivity: Studies in subjects with various degrees of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbieć-Piekarska, R.; Spólnicka, M.; Kupiec, T.; Parys-Proszek, A.; Makowska, Ż.; Pałeczka, A.; Kucharczyk, K.; Płoski, R.; Branicki, W. Development of a forensically useful age prediction method based on DNA methylation analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 17, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciari, E.; Milani, S.; Balsamo, A.; Spada, E.; Bona, G.; Cavallo, L.; Cerutti, F.; Gargantini, L.; Greggio, N.; Tonini, G.; et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (2 to 20 yr). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, S.A.; Cohen, P. The somatomedin hypothesis 2007: 50 years later. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yang, W.; De Luca, F. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Independent Effects of Growth Hormone on Growth Plate Chondrogenesis and Longitudinal Bone Growth. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.J. Classical and novel GH receptor signaling pathways. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, H. The IGF1 Signaling Pathway: From Basic Concepts to Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Nava, F.; Lanes, R. GH/IGF-1 Signaling and Current Knowledge of Epigenetics; a Review and Considerations on Possible Therapeutic Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
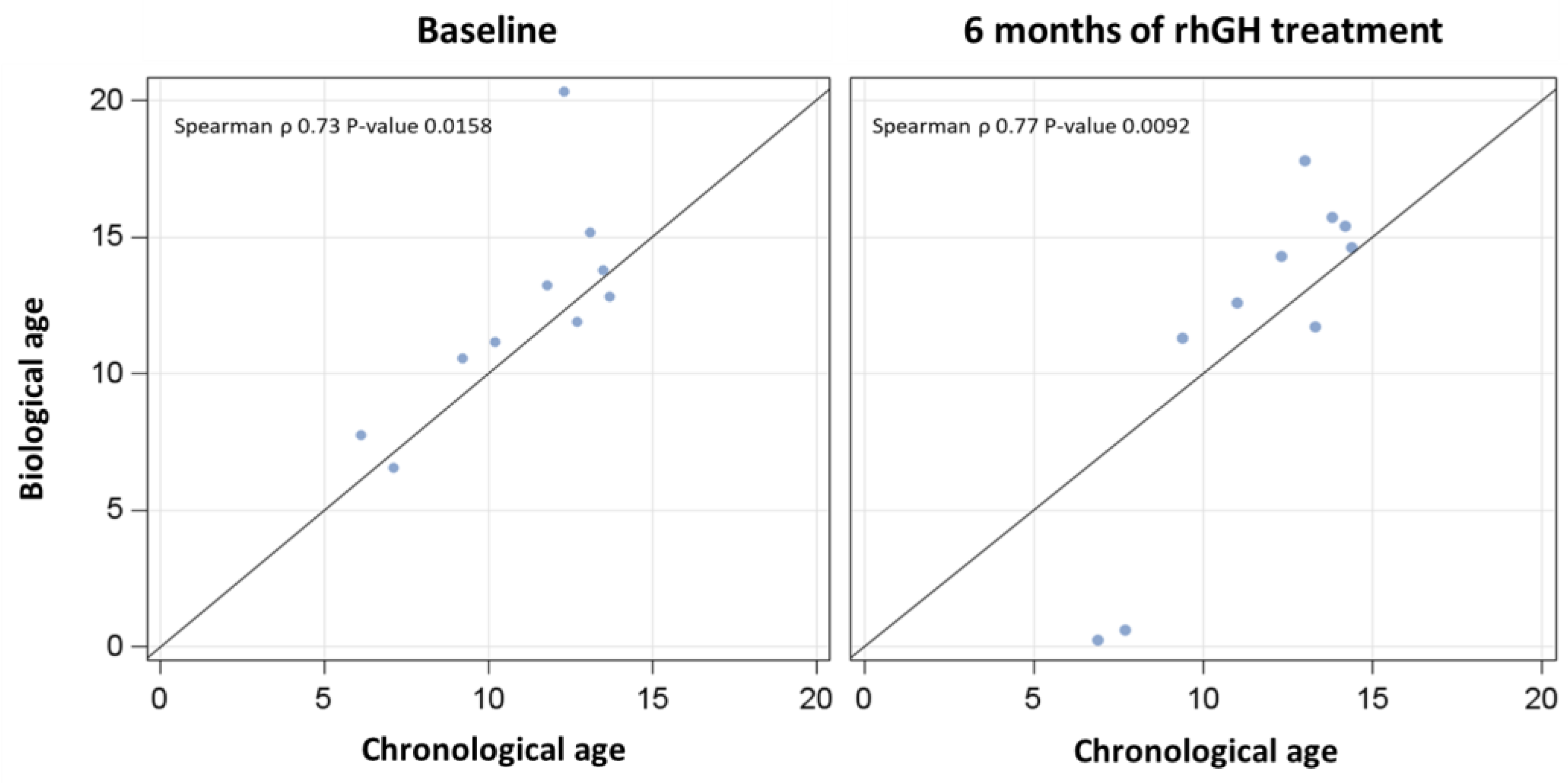
| Parameter | Baseline | 6 Months of rhGH Treatment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 11.0 ± 2.7 | 11.6 ± 2.6 | 0.6961 |
| DNAm age, years | 12.3 [10.6;13.8] | 13.4 [11.3;15.4] | 0.6822 |
| Age acceleration, years | 0.92 ± 2.8 | −0.92 ± 3.1 | 0.1790 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 5 (50%) | 5 (50%) | - |
| Female | 5 (50%) | 5 (50%) | |
| Height, cm | 133 [113;139] | 138 [119;147] | 0.2556 |
| Height SDS | −2.5 ± 0.3 | −2.2 ± 0.4 | 0.0712 |
| Weight, kg | 32.0 [19.1;40.1] | 35.4 [20.0;45.1] | 0.4814 |
| Weight SDS | −2.2 [−2.4;−1.2] | −1.9 [−2.4;−0.8] | 0.6288 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 17.0 [14.9;20.3] | 17.7 [14.7;22.6] | 0.9109 |
| BMI SDS | −0.8 [−1.5;−0.1] | −0.9 [−1.5;0.5] | 1 |
| FM, % | 22.7 [15.4;31.2] | 21.9 [16.9;28.5] | 0.7941 |
| FFM, kg | 23 [18.5;27.1] | 28.9 [16.4;32.7] | 0.2274 |
| HV, cm/year | 3.9 ± 1.4 | 8.7 ± 2.6 | <0.0001 |
| HV SDS | −2.8 [−3.8;−1.8] | 1.7 [0.1;4.1] | 0.0014 |
| IGF-1, µg/L | 120.5 [102;182] | 341 [203;510] | 0.0076 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 81.8 ± 5.9 | 92.5 ± 6.1 | 0.0012 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 0.0226 |
| Insulin, mU/L | 5.0 ± 3.0 | 10.8 ± 4.7 | 0.0039 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.1 [0.7;1.3] | 2.4 [1.7;2.6] | 0.0114 |
| T-C, mg/dL | 153 ± 21 | 177 ± 23 | 0.0258 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 52 ± 14 | 65 ± 19 | 0.0868 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 90 ± 16 | 103 ± 22 | 0.1727 |
| TG, mg/dL | 51 [44;69] | 55.5 [47;87] | 0.5279 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.0 [0.0;0.3] | 0.0 [0.0;0.1] | 0.8796 |
| Univariate Model | Difference | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Acceleration | T6 (6 months of rhGH)–T0 (baseline) | −1.846 | −3.843 | 0.151 | 0.0701 |
| Model adjusted for IGF-1 | Difference | Estimate | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age acceleration | T6 (6 months of rhGH)–T0 (baseline) | −4.137 | −7.862 | −0.412 | 0.0295 |
| Independent Variable | β | SE | 95% CI | p-Value | p-Value of Interaction Term “rhGH Treatment × Variable” | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height, cm | effect at a T0 | −0.113 | 0.034 | −0.180 | −0.047 | 0.0008 | 0.0029 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.057 | 0.068 | −0.076 | 0.190 | 0.3995 | ||
| Height, SDS | effect at a T0 | −7.247 | 2.627 | −12.396 | −2.098 | 0.0058 | 0.4599 |
| effect at a T6 | −5.231 | 2.021 | −9.192 | −1.270 | 0.0096 | ||
| Weight, kg | effect at a T0 | −0.113 | 0.048 | −0.207 | −0.019 | 0.0190 | 0.0272 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.053 | 0.070 | −0.084 | 0.190 | 0.4491 | ||
| Weight, SDS | effect at a T0 | −1.446 | 0.733 | −2.884 | −0.009 | 0.0485 | 0.1313 |
| effect at a T6 | −0.453 | 0.784 | −1.990 | 1.085 | 0.5638 | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | effect at a T0 | −0.212 | 0.125 | −0.458 | 0.033 | 0.0902 | 0.0867 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.174 | 0.218 | −0.253 | 0.602 | 0.4234 | ||
| BMI, SDS | effect at a T0 | −0.629 | 0.425 | −1.462 | 0.204 | 0.1387 | 0.2700 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.083 | 0.691 | −1.270 | 1.437 | 0.9040 | ||
| FM, % | effect at a T0 | −0.029 | 0.024 | −0.076 | 0.017 | 0.2158 | 0.4662 |
| effect at a T6 | −0.078 | 0.062 | −0.200 | 0.044 | 0.2085 | ||
| HV, cm/year | effect at a T0 | −0.385 | 0.592 | −1.546 | 0.775 | 0.5151 | 0.6195 |
| effect at a T6 | −0.086 | 0.274 | −0.624 | 0.451 | 0.7529 | ||
| HV, SDS | effect at a T0 | 0.738 | 0.896 | −1.017 | 2.493 | 0.4099 | 0.3585 |
| effect at a T6 | −0.216 | 0.276 | −0.757 | 0.325 | 0.4346 | ||
| Glucose, mg/dL | effect at a T0 | −0.341 | 0.096 | −0.529 | −0.154 | 0.0004 | 0.0017 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.012 | 0.117 | −0.218 | 0.242 | 0.9180 | ||
| HbA1c, % | effect at a T0 | −1.776 | 3.359 | −8.359 | 4.806 | 0.5969 | 0.0608 |
| effect at a T6 | 5.714 | 1.737 | 2.310 | 9.117 | 0.0010 | ||
| Insulin, mU/L | effect at a T0 | −0.441 | 0.256 | −0.942 | 0.061 | 0.0851 | 0.0197 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.239 | 0.136 | −0.027 | 0.506 | 0.0786 | ||
| HOMA-IR | effect at a T0 | −2.273 | 1.213 | −4.650 | 0.105 | 0.0610 | 0.0139 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.863 | 0.478 | −0.073 | 1.800 | 0.0708 | ||
| T-C, mg/dL | effect at a T0 | 0.049 | 0.041 | −0.032 | 0.129 | 0.2361 | 0.8341 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.043 | 0.039 | −0.034 | 0.119 | 0.2728 | ||
| HDL-C, mg/dL | effect at a T0 | −0.057 | 0.042 | −0.140 | 0.026 | 0.1813 | 0.4983 |
| effect at a T6 | −0.021 | 0.031 | −0.082 | 0.041 | 0.5093 | ||
| LDL-C, mg/dL | effect at a T0 | 0.103 | 0.040 | 0.025 | 0.181 | 0.0099 | 0.3050 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.056 | 0.028 | 0.001 | 0.112 | 0.0475 | ||
| TG, mg/dL | effect at a T0 | 0.082 | 0.046 | −0.008 | 0.173 | 0.0748 | 0.2528 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.004 | 0.047 | −0.088 | 0.097 | 0.9238 | ||
| CRP, mg/dL | effect at a T0 | −2.333 | 2.062 | −6.375 | 1.708 | 0.2578 | 0.8097 |
| effect at a T6 | −0.176 | 10.191 | −20.151 | 19.798 | 0.9862 | ||
| IGF-1, µg/L | effect at a T0 | 0.010 | 0.016 | −0.022 | 0.041 | 0.5483 | 0.9205 |
| effect at a T6 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.021 | 0.0260 | ||
| Independent Variable | β | SE | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height, cm | −0.019 | 0.040 | −0.099 | 0.060 | 0.6332 |
| Height SDS | −5.833 | 1.808 | −9.376 | −2.291 | 0.0013 |
| Weight, kg | −0.011 | 0.043 | −0.096 | 0.073 | 0.7926 |
| Weight SDS | −0.759 | 0.590 | −1.916 | 0.398 | 0.1984 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −0.020 | 0.115 | −0.245 | 0.204 | 0.8594 |
| BMI SDS | −0.239 | 0.420 | −1.062 | 0.584 | 0.5693 |
| FM, % | −0.035 | 0.024 | −0.083 | 0.013 | 0.1496 |
| HV, cm/year | −0.125 | 0.270 | −0.655 | 0.405 | 0.6440 |
| HV SDS | −0.117 | 0.278 | −0.662 | 0.428 | 0.6740 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | −0.176 | 0.087 | −0.346 | −0.005 | 0.0439 |
| HbA1c, % | 1.809 | 2.080 | −2.269 | 5.886 | 0.3846 |
| Insulin, mU/L | 0.059 | 0.086 | −0.109 | 0.227 | 0.4914 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.257 | 0.320 | −0.371 | 0.884 | 0.4223 |
| T-C, mg/dL | 0.044 | 0.037 | −0.028 | 0.116 | 0.2274 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | −0.031 | 0.026 | −0.082 | 0.021 | 0.2394 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 0.069 | 0.025 | 0.020 | 0.117 | 0.0053 |
| TG, mg/dL | 0.025 | 0.038 | −0.050 | 0.099 | 0.5155 |
| CRP, mg/dL | −2.398 | 1.815 | −5.955 | 1.159 | 0.1864 |
| IGF-1, µg/L | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.021 | 0.0260 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rigamonti, A.E.; Bollati, V.; Favero, C.; Albetti, B.; Bondesan, A.; Marazzi, N.; Cella, S.G.; Sartorio, A. Evaluation of Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Growth Hormone (GH)-Deficient Children After 6 Months of Recombinant Human GH Replacement Therapy: Anti-Ageing GH vs. Pro-Ageing Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113840
Rigamonti AE, Bollati V, Favero C, Albetti B, Bondesan A, Marazzi N, Cella SG, Sartorio A. Evaluation of Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Growth Hormone (GH)-Deficient Children After 6 Months of Recombinant Human GH Replacement Therapy: Anti-Ageing GH vs. Pro-Ageing Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113840
Chicago/Turabian StyleRigamonti, Antonello E., Valentina Bollati, Chiara Favero, Benedetta Albetti, Adele Bondesan, Nicoletta Marazzi, Silvano G. Cella, and Alessandro Sartorio. 2025. "Evaluation of Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Growth Hormone (GH)-Deficient Children After 6 Months of Recombinant Human GH Replacement Therapy: Anti-Ageing GH vs. Pro-Ageing Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113840
APA StyleRigamonti, A. E., Bollati, V., Favero, C., Albetti, B., Bondesan, A., Marazzi, N., Cella, S. G., & Sartorio, A. (2025). Evaluation of Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Growth Hormone (GH)-Deficient Children After 6 Months of Recombinant Human GH Replacement Therapy: Anti-Ageing GH vs. Pro-Ageing Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113840








