Clinical Effectiveness of Surgical Marginal Resection with Piezoelectric Device on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
Piezoelectric Devices in Medical–Dental Applications
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Success Criteria
2.3. Statistical Analysis
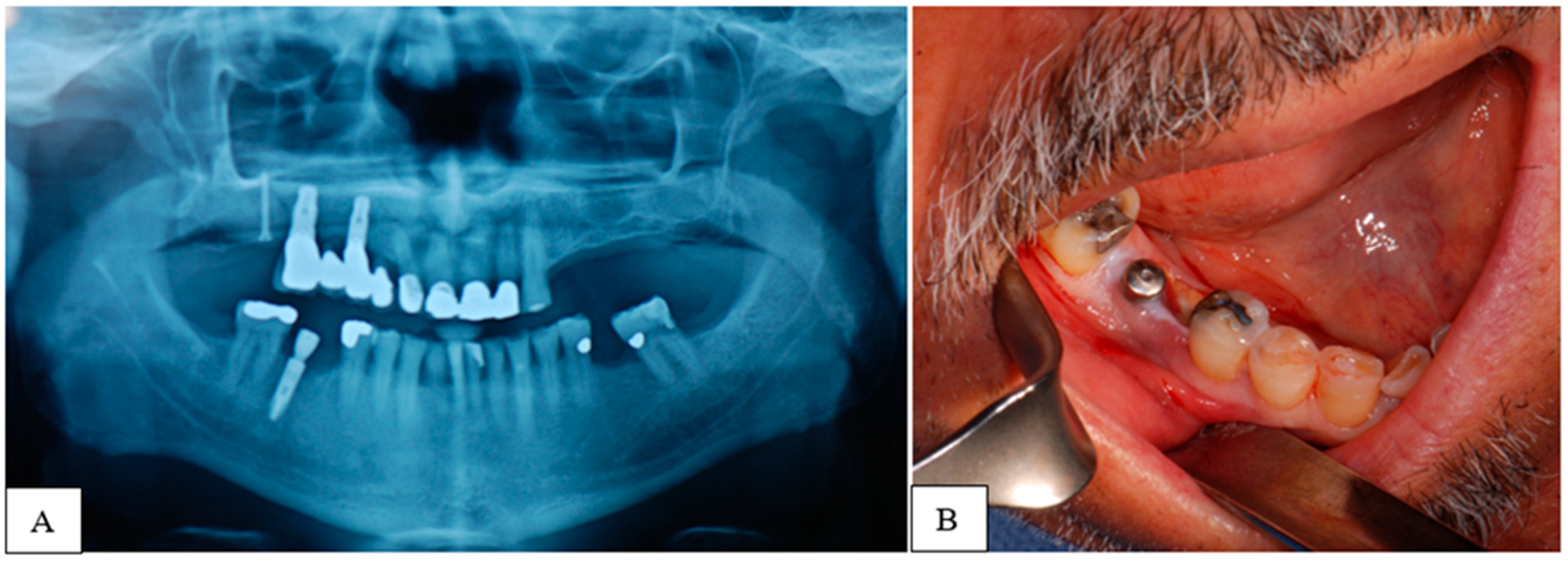
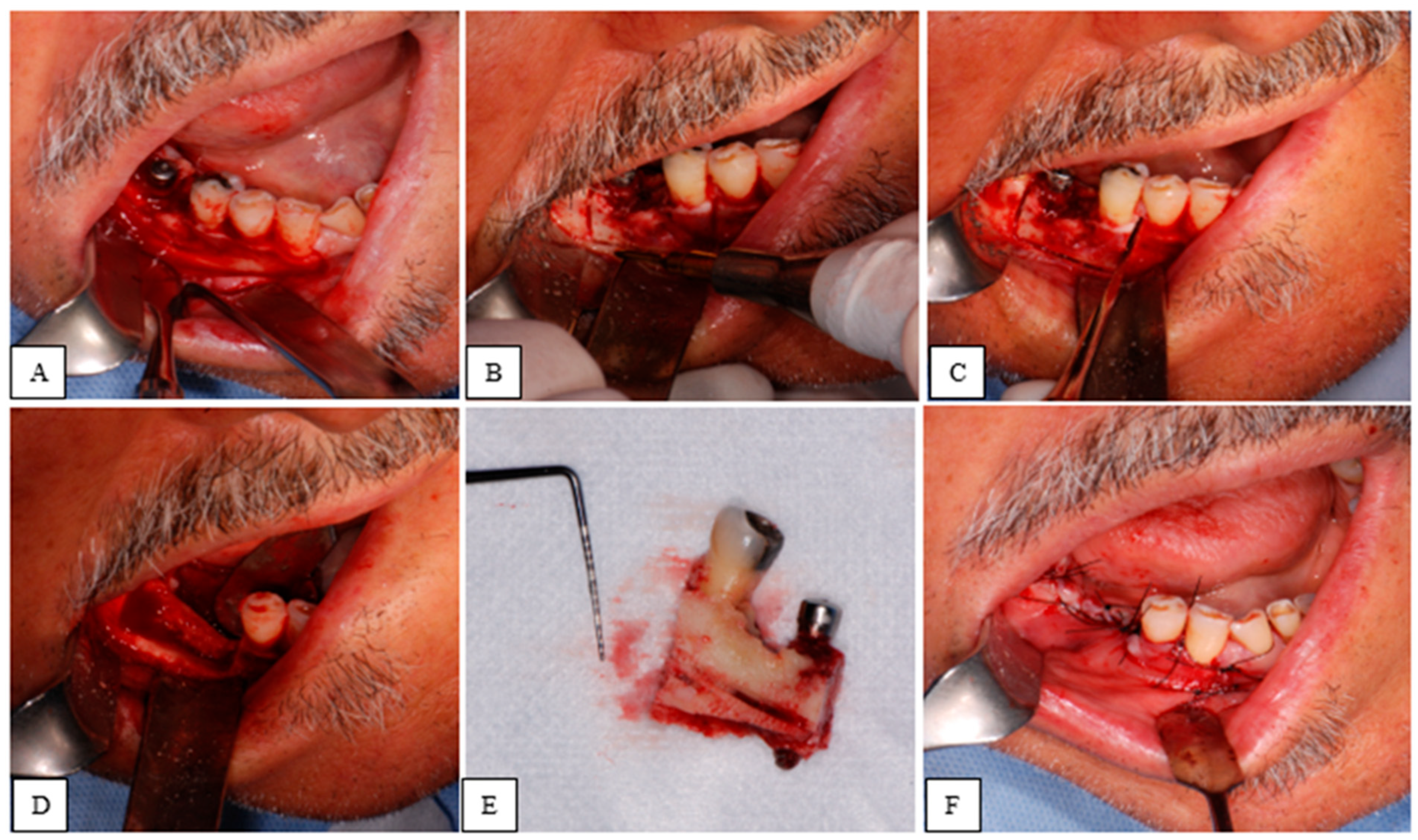
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OPG | Orthopantomography |
| CBCT | Cone Beam Computed Tomography |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ZOL | Zoledronic acid |
| ALE | Alendronate |
| IBA | Ibandronate |
References
- Bedogni, A.; Mauceri, R.; Fusco, V.; Bertoldo, F.; Bettini, G.; Di Fede, O.; Lo Casto, A.; Marchetti, C.; Panzarella, V.; Saia, G.; et al. Italian Position Paper (SIPMO-SICMF) on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ). Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 3679–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Morrison, A.; Hanley, D.A.; Felsenberg, D.; McCauley, L.K.; O’Ryan, F.; Reid, I.R.; Ruggiero, S.L.; Taguchi, A.; Tetradis, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of osteonecrosis of the jaw: A systematic review and international consensus. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Schiødt, M.; Mendes, R.A.; Ripamonti, C.; Hope, S.; Drudge-Coates, L.; Niepel, D.; Van den Wyngaert, T. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Definition and best practice for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 127, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarom, N.; Shapiro, C.L.; Peterson, D.E.; Van Poznak, C.H.; Bohlke, K.; Ruggiero, S.L.; Migliorati, C.A.; Khan, A.; Morrison, A.; Anderson, H.; et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: MASCC/ISOO/ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2270–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, A.; Fusco, V.; Agrillo, A.; Campisi, G. Learning from experience. Proposal of a refined definition and staging system for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ). Oral Dis. 2012, 18, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, G.; Mauceri, R.; Bertoldo, F.; Bettini, G.; Biasotto, M.; Colella, G.; Consolo, U.; Di Fede, O.; Favia, G.; Fusco, V.; et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) prevention and diagnosis: Italian consensus update 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fede, O.; Panzarella, V.; Mauceri, R.; Fusco, V.; Bedogni, A.; Lo Muzio, L.; Sipmo Onj Board Campisi, G. The dental management of patients at risk of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: New paradigm of primary prevention. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2684924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristow, O.; Otto, S.; Troeltzsch, M.; Hohlweg-Majert, B.; Pautke, C. Treatment perspectives for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; Bennardo, F.; Barone, S.; Antonelli, A.; Figliuzzi, M.M.; Fortunato, L. Surgical management of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaloo, T.; Hazboun, R.; Tetradis, S. Pathophysiology of osteonecrosis of the jaws and its management. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 27, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebe, T. Pathophysiology of BRONJ: Drug-related osteoclastic disease of the jaw. Oral Sci. Int. 2013, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Singh, S.; Chen, Y.; Hamadeh, I.S.; Langaee, T.; McDonough, C.W.; Gong, Y.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M.; Johnson, J.A. Pharmacogenomics of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 64, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Sun, S.; Aghaloo, T.; Oh, J.E.; McKenna, C.E.; Kang, M.K.; Shin, K.H.; Tetradis, S.; Park, N.H.; Kim, R.H. Genetic factors associated with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, P.M.; Schiodt, M. Dentoalveolar trauma and minor trauma as precipitating factors for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ): A retrospective study of 149 consecutive patients from the Copenhagen ONJ Cohort. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 119, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limones, A.; Sáez-Alcaide, L.M.; Díaz-Parreño, S.A.; Helm, A.; Bornstein, M.M.; Molinero-Mourelle, P. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) in cancer patients treated with denosumab vs. zoledronic acid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2020, 25, e326–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Kastritis, E.; Bamia, C.; Melakopoulos, I.; Gika, D.; Roussou, M.; Migkou, M.; Eleftherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; Christoulas, D.; Terpos, E.; et al. The role of supportive care in the era of novel therapies for multiple myeloma. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94 (Suppl. S1), S249–S258. [Google Scholar]
- Campisi, G.; Di Fede, O.; Musciotto, A.; Lo Casto, A.; Lo Muzio, L.; Fulfaro, F.; Buscemi, M.; Lo Russo, L.; Tomasello, L. Dental management in patients with bisphosphonates therapy. Dent. Cadmos 2007, 75, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mauceri, R.; Panzarella, V.; Maniscalco, L.; Bedogni, A.; Licata, M.E.; Albanese, A.; Toia, F.; Cumbo, E.M.G.; Mazzola, G.; Di Fede, O.; et al. Conservative surgical treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw with Er,Cr:YSGG laser and platelet-rich plasma: A longitudinal study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3982540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blus, C.; Giannelli, G.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Orru, G. Ultrasonic bone surgery in the treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A case series of 20 patients. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, P.; Manfredi, M.; Merigo, E.; Meleti, M.; Fornaini, C.; Rocca, J.P.; Nammour, S. Surgical approach with Er:YAG laser on osteonecrosis of the jaws (ONJ) in patients under bisphosphonate therapy (BPT). Lasers Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlíková, G.; Foltán, R.; Horká, M.; Hanzelka, T.; Borunská, H.; Sedý, J. Piezosurgery in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curie, J.; Curie, P. Développement par compression de l’électricité polaire dans les cristaux hémièdres à faces inclinées. Comptes Rendus 1880, 91, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, G. Principe de la conservation de l’électricité. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1881, 24, 145–178. [Google Scholar]
- Manbachi, A.; Cobbold, R.S. Development and application of piezoelectric materials for ultrasound generation and detection. Ultrasound 2011, 19, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellotti, T. Technological characteristics and clinical indications of piezoelectric bone surgery. Minerva Stomatol. 2004, 53, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eggers, G.; Klein, J.; Blank, J.; Hassfeld, S. Piezosurgery: An ultrasound device for cutting bone and its use and limitations in maxillofacial surgery. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 42, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, F.; Zhao, P.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Meng, X.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, S.W. Progress and Perspectives in 2D Piezoelectric Materials for Piezotronics and Piezo-Phototronics. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2411422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubinger, S.; Kuttenberger, J.; Filippi, A.; Sader, R.; Zeilhofer, H.F. Ultrasonic bone cutting in oral surgery: A review of 60 cases. Ultraschall Med. 2008, 29, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.C.; Gealh, W.C.; Nogueira, L.M.; Garcia Junior, I.R.; Okamoto, R. Piezosurgery applied to implant dentistry: Clinical and biological aspects. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robiony, M.; Polini, F.; Costa, F.; Vercellotti, T.; Politi, M. Piezoelectric bone cutting in multipiece maxillary osteotomies. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortino, F.; Pedullà, E.; Masoli, V. Piezoelectric device vs. conventional rotative instruments in impacted third molar surgery: Relationships between surgical difficulty and postoperative pain with histological evaluations. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 36, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zou, J.; Tang, K.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z. From Electricity to Vitality: The Emerging Use of Piezoelectric Materials in Tissue Regeneration. Burn. Trauma 2024, 12, tkae013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, G.; Martinasso, G.; Peirone, B.; Navone, R.; Manzella, C.; Muzio, G.; Russo, C.; Canuto, R.A.; Schierano, G. Cytokines and growth factors involved in the osseointegration of oral titanium implants positioned using piezoelectric bone surgery versus a drill technique: A pilot study in minipigs. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnama, M.; Czupkałło, Ł.; Czajkowski, L.; Grasza, J.; Wallner, J. The use of piezosurgery as an alternative method of minimally invasive surgery in the authors’ experience. Videosurgery Other Miniinvasive Tech. 2013, 8, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivolella, S.; Brunello, G.; Berengo, M.; de Biagi, M.; Bacci, C. Rehabilitation with Implants After Bone Lid Surgery in the Posterior Mandible. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullo, R.; Piccirillo, A.; Femiano, F.; Nastri, L.; Festa, V.M. A Comparison between Piezoelectric Devices and Conventional Rotary Instruments in Bone Harvesting in Patients with Lip and Palate Cleft: A Retrospective Study with Clinical, Radiographical, and Histological Evaluation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2059464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlee, M.; Steigmann, M.; Bratu, E.; Garg, A.K. Piezosurgery: Basics and possibilities. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blus, C.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Vozza, I.; Rispoli, L.; Polastri, C. Split-crest and immediate implant placement with ultrasonic bone surgery: A 3-year life-table analysis with 230 treated sites. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellotti, T.; De Paoli, S.; Nevins, M. The piezoelectric bony window osteotomy and sinus membrane elevation: Introduction of a new technique for simplification of the sinus augmentation procedure. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2001, 21, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Stübinger, S.; Kuttenberger, J.; Filippi, A.; Sader, R.; Zeilhofer, H.F. Intraoral piezosurgery: Preliminary results of a new technique. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labanca, M.; Azzola, F.; Vinci, R.; Rodella, L.F. Piezoelectric Surgery: Twenty Years of Use. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 46, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, G.; Mauceri, R.; Bertoldo, F.; Bettini, G.; Biasotto, M.; Colella, G.; Consolo, U.; Di Fede, O.; Favia, G.; Fusco, V.; et al. Italian Consensus Update on MRONJ Prevention in 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Aghaloo, T.; Carlson, E.R.; Ward, B.B.; Kademani, D. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons’ Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws-2022 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, A.O.; Toth, B.B.; Altundag, K.; Johnson, M.M.; Warneke, C.L.; Hu, M.; Nooka, A.; Sayegh, G.; Guarneri, V.; Desrouleaux, K.; et al. Frequency and Risk Factors Associated with Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Cancer Patients Treated with Intravenous Bisphosphonates. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2008, 23, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estilo, C.L.; van Poznak, C.H.; Williams, T.; Bohle, G.C.; Lwin, P.T.; Zhou, Q.; Riedel, E.R.; Carlson, D.L.; Schoder, H.; Farooki, A.; et al. Osteonecrosis of the Maxilla and Mandible in Patients with Advanced Cancer Treated with Bisphosphonate Therapy. Oncologist 2008, 13, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eckert, A.W.; Maurer, P.; Meyer, L.; Kriwalsky, M.S.; Rohrberg, R.; Schneider, D.; Bilkenroth, U.; Schubert, J. Bisphosphonate-Related Jaw Necrosis—Severe Complication in Maxillofacial Surgery. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumbigere-Math, V.; Tu, L.; Huckabay, S.; Dudek, A.Z.; Lunos, S.; Basi, D.L.; Hughes, P.J.; Leach, J.W.; Swenson, K.K.; Gopalakrishnan, R. A Retrospective Study Evaluating Frequency and Risk Factors of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in 576 Cancer Patients Receiving Intravenous Bisphosphonates. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 35, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Ryan, F.S.; Lo, J.C. Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Patients with Oral Bisphosphonate Exposure: Clinical Course and Outcomes. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliefel, R.; Tröltzsch, M.; Kühnisch, J.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Otto, S. Treatment Strategies and Outcomes of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (BRONJ) with Characterization of Patients: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalay, B.; Yalcin, S.; Emes, Y.; Aktas, I.; Aybar, B.; Issever, H.; Mandel, N.M.; Cetin, O.; Oncu, B. Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis: Laser-Assisted Surgical Treatment or Conventional Surgery? Lasers Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vescovi, P.; Manfredi, M.; Merigo, E.; Meleti, M.; Guidotti, R.; Sarraj, A.; Mergoni, G.; Fornaini, C.; Bonanini, M.; Pizzi, S.; et al. Osteonecrosi dei Masscellari e Bisfosfonati: Terapia e Follow-Up a Lungo Periodo in 160 Pazienti. Dent. Cadmos 2012, 80, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumbigere-Math, V.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Hodges, J.S.; Tsai, M.L.; Swenson, K.K.; Rockwell, L.; Gopalakrishnan, R. Periodontal Disease as a Risk Factor for Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Pérez-Sayáns, M.; Chamorro-Petronacci, C.; Gándara-Vila, P.; López-Jornet, P.; Carballo, J.; García-García, A. Association Between Periodontitis and Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; di Cosola, M.; Copelli, C.; Cantore, S.; Quarta, C.; Nitsch, G.; Sovereto, D.; Spirito, F.; Caloro, G.A.; Cazzolla, A.P.; et al. Oral Bisphosphonate-Induced Osteonecrosis Complications in Patients Undergoing Tooth Extraction: A Systematic Review and Literature Updates. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 6359–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisi, M.; la Ferla, F.; Karapetsa, D.; Gennai, S.; Miccoli, M.; Baggiani, A.; Graziani, F.; Gabriele, M. Risk Factors Influencing BRONJ Staging in Patients Receiving Intravenous Bisphosphonates: A Multivariate Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodem, J.P.; Kargus, S.; Eckstein, S.; Saure, D.; Engel, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Freudlsperger, C. Incidence of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in High-Risk Patients Undergoing Surgical Tooth Extraction. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, D.; Seemann, R.; Matoni, N.; Ewers, R.; Millesi, W.; Wutzl, A. Effect of Dental Implants on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1937.e1–1937.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.; Laviv, A.; Schwartz-Arad, D. Denture-related osteonecrosis of the maxilla associated with oral bisphosphonate treatment. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2007, 138, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Kawabe, M.; Kimura, H.; Kurita, K.; Fukuta, J.; Urade, M. Influence of dentures in the initial occurrence site on the prognosis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A retrospective study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Xiang, Z.-J.; Yang, J.-H.; Wang, W.-J.; Xiang, R.-L. The incidence and relative risk of adverse events in patients treated with bisphosphonate therapy for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919855235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, P.L.; Nicoletti, P.; Shen, Y.; Porter, S.; Fedele, S. Pharmacogenetics of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 27, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apatzidou, D.A. The role of cigarette smoking in periodontal disease and treatment outcomes of dental implant therapy. In Periodontology 2000; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume 90, pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambler, D.; Blincoe, T. Smoking and surgery. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 79, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, C.; Boccuto, M.; Cerrato, A.; Grigoletto, A.; Zanette, G.; Angelini, A.; Sbricoli, L. Safety and efficacy of sectorial resection with piezoelectric device in ONJ. Qeios 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, J.; Shannon, J.; Modelevsky, S.; Grippo, A.A. Bisphosphonates and osteonecrosis of the jaw. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 2350–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.J.; Park, W.-J.; Shin, H.-S.; Choi, M.-G.; Kwon, K.-H.; Choi, E.J. Diseases having an influence on inhibition of angiogenesis as risk factors of osteonecrosis of the jaw. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 42, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molcho, S.; Peer, A.; Berg, T.; Futerman, B.; Khamaisi, M. Diabetes microvascular disease and the risk for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A single center study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1807–E1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarnbring, F.; Kashani, A.; Björk, A.; Hoffman, T.; Krawiec, K.; Ljungman, P.; Lund, B. Role of intravenous dosage regimens of bisphosphonates in relation to other aetiological factors in the development of osteonecrosis of the jaws in patients with myeloma. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anavi-Lev, K.; Anavi, Y.; Chaushu, G.; Alon, D.M.; Gal, G.; Kaplan, I. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: Clinico-pathological investigation and histomorphometric analysis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiranathanagul, S.; Yongchaitrakul, T.; Pattamapun, K.; Pavasant, P. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Lipopolysaccharide activates matrix metalloproteinase-2 and increases receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand expression in human periodontal ligament cells. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelin-Uhlig, S.; Weigel, M.; Ott, B.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Howaldt, H.-P.; Böttger, S.; Hain, T. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw and oral microbiome: Clinical risk factors, pathophysiology and treatment options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennardo, F.; Barone, S.; Vocaturo, C.; Gheorghe, D.N.; Cosentini, G.; Antonelli, A.; Giudice, A. Comparison between Magneto-Dynamic, Piezoelectric, and Conventional Surgery for Dental Extractions: A Pilot Study. Dent. J 2023, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovic, M.; Gabrić, D.; Coleman, N.J.; Slipper, I.J.; Mladenov, M.; Gjorgievska, E. Bone Healing Following Different Types of Osteotomy: Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Three-Dimensional SEM Analyses. Microsc. Microanal. 2016, 22, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, S.; Verma, D.; Bansal, S.; Sutar, S.; Gupta, A.; Kardwal, K. Comparison of Piezosurgery Devices and the Use of Rotatory Devices for the Extraction of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16 (Suppl. S3), S2140–S2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Di Girolamo, M.; Franceschini, C.; Rastelli, S.; Capogreco, M.; D’Amario, M. The Comparative Efficacy of Burs Versus Piezoelectric Techniques in Third Molar Surgery: A Systematic Review Following the PRISMA Guidelines. Medicina 2024, 60, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, S.H.; Kheder, K.A.; Hassan, S.M.A. Histological assessment of potential inferior alveolar nerve injury following osteotomy of the mandibular buccal cortex using a piezoelectric saw. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2024, 70, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seluki, R.; Seluki, M.; Vaitkeviciene, I.; Jagelaviciene, E. Comparison of the effectiveness of conservative and surgical treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2023, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beth-Tasdogan, N.H.; Mayer, B.; Hussein, H.; Zolk, O.; Peter, J.U. Interventions for managing medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 2022, CD012432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fede, O.; Canepa, F.; Panzarella, V.; Mauceri, R.; Bedogni, A.; Lo Muzio, L.; Campisi, G. The treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ): A systematic review with a pooled analysis of only surgery versus combined protocols. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksad, R.A.; Lai, K.-C.; Dodson, T.B.; Woo, S.-B.; Treister, N.S.; Akinyemi, O.; Bihrle, M.; Maytal, G.; August, M.; Gazelle, G.S.; et al. Quality of life implications of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw. Oncologist 2011, 16, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blus, C.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Giannelli, G.; Denotti, G.; Orrù, G. Use of ultrasonic bone surgery (Piezosurgery) to surgically treat bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (BRONJ): A case series report with at least 1 year of follow-up. Open Dent. J. 2013, 7, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blus, C.; Giannelli, G.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Orrù, G. Treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) with ultrasonic piezoelectric bone surgery: A case series of 20 treated sites. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 21, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Malcangi, G.; Ferrara, I.; Viapiano, F.; Netti, A.; Patano, A.; Isacco, C.G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Inchingolo, F. Sixty-month follow-up of clinical MRONJ cases treated with CGF and piezosurgery. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, C.; Maglione, M.; Favero, L.; Perini, A.; Di Lenarda, R.; Berengo, M.; Zanon, E. Management of dental extraction in patients undergoing anticoagulant treatment: Results from a large, multicentre, prospective, case-control study. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, C.; Berengo, M.; Favero, L.; Zanon, E. Safety of dental implant surgery in patients undergoing anticoagulation therapy: A prospective case-control study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, C.; Schiazzano, C.; Zanon, E.; Stellini, E.; Sbricoli, L. Bleeding disorders and dental implants: Review and clinical indications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, C.; Cerrato, A.; Bardhi, E.; Frigo, A.C.; Djaballah, S.A.; Sivolella, S. A retrospective study on the incidence of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) associated with different preventive dental care modalities. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawiec, G.; Niemczyk, W.; Wiench, R.; Niemczyk, S.; Skaba, D. Introduction to amniotic membranes in maxillofacial surgery—A scoping review. Medicina 2024, 60, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manani, G.; Bacci, C.; Zanette, G.; Facco, E. Stato attuale della sedazione cosciente in odontoiatria [Contemporary state of sedation in dentistry]. Dent. Cadmos 2012, 80, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczyk, W.; Żurek, J.; Niemczyk, S.; Kępa, M.; Zięba, N.; Misiołek, M.; Wiench, R. Antibiotic-Loaded Platelet-Rich Fibrin (AL-PRF) as a New Carrier for Antimicrobials: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
|
|
| Stage | Clinical Signs and Symptoms | CT Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1—Focal Mronj The presence of at least 1 clinical sign/symptom and increased bone density limited to the alveolar process at CT, with or without additional radiological signs.
| Abscess, bone exposure, halitosis, intraoral fistula, jaw pain of bone origin, mucosal inflammation, non-healing post-extraction socket, soft tissue swelling, spontaneous loss of bone fragments, sudden dental/implant mobility, purulent discharge, toothache and trismus. | Trabecular thickening and/or focal bone marrow sclerosis, with or without cortical erosion, osteolytic changes, thickening of the alveolar ridge, thickening of the lamina dura, persistent post-extraction socket, periodontal space widening, thickening of the inferior alveolar nerve canal, sequester formation. |
| Stage 2—Diffuse Mronj The presence of at least 1 clinical sign/symptom and increased bone density extending to the basal bone at CT, with or without additional radiological signs.
| Same as Stage 1, plus mandibular deformation and numbness of the lips. | Diffuse bone marrow sclerosis, with or without cortical erosion, osteolytic changes, thickening of the alveolar ridge, thickening of the lamina dura, persistent post-extraction socket, periodontal space widening, thickening of the inferior alveolar nerve canal, sequester formation, periosteal reaction, and opacified maxillary sinus. |
| Stage 3—Complicated Mronj The presence of at least 1 clinical sign/symptom and increased bone density extended to the basal bone at CT, plus one or more of the following
| Cutaneous fistula, mandible fracture, fluid discharge from the nose. | Osteosclerosis of adjacent bones (zygoma and hard palate), pathologic fracture, osteolysis extending to the maxillary sinus, sinus tract (oroantral, oronasal fistula, oro-cutaneous). |
| Stage | Symptoms | Clinical Findings | Radiographic Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 0 |
|
|
|
| Stage I |
|
|
|
| Stage II |
|
|
|
| Stage III |
|
|
|
| Clinical Signs and Symptoms of BRONJ (T0) | N° of Patients | % |
|---|---|---|
| Exposed bone | 21 | 100 |
| Halitosis | 11 | 52.38 |
| Dental mobility | 7 | 33.33 |
| Pain | 6 | 28.57 |
| Trismus | 5 | 23.81 |
| Failure of post-extraction alveolar mucosa repair | 4 | 19.05 |
| Soft tissue swelling | 3 | 14.29 |
| Lip paresthesia/dysesthesia | 3 | 14.29 |
| Implant mobility | 2 | 9.52 |
| Suppuration | 2 | 9.52 |
| Radiographic Signs of BRONJ (T0) | N° of Patients | % |
|---|---|---|
| Diffuse osteosclerosis | 6 | 28.57 |
| Focal medullary osteosclerosis | 5 | 23.81 |
| Widening of the periodontal space | 5 | 23.81 |
| Persistence of post-extraction alveolus | 4 | 19.05 |
| Sinusitis | 4 | 19.05 |
| Thickening of the alveolar canal | 2 | 9.52 |
| Oro-antral fistulas | 2 | 9.52 |
| Periosteal reaction | 2 | 9.52 |
| No. of Patients | Percentage (%) | Operative Time (min) | Mean (min) | Median (min) | Standard Deviation (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (21 patients) | 100% | 48.81 | 45 | 8.98 | |
| 1 | 4.76% | 75 | |||
| 3 | 14.29% | 60 | |||
| 3 | 14.29% | 55 | |||
| 9 | 42.86% | 45 | |||
| 5 | 23.81% | 40 |
| N° Patient | T1 Clinical Signs and Symptoms of BRONJ | T1 Radiographic Signs of BRONJ | T2 Clinical Signs and Symptoms of BRONJ | T2 Radiographic Signs of BRONJ | T3 Clinical Signs and Symptoms of BRONJ | T3 Radiographic Signs of BRONJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Incomplete epithelialization, Dysesthesia | X-rays not performed | Incomplete epithelialization, Dysesthesia | Trabecular thickening | Exposed bone, Dysesthesia, Pain | Focal medullary osteosclerosis |
| 8 | Incomplete epithelialization | X-rays not performed | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| 13 | Incomplete epithelialization, Trismus | X-rays not performed | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| 14 | Incomplete epithelialization | X-rays not performed | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| 19 | Incomplete epithelialization, Lip Dysesthesia | X-rays not performed | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manera, C.; Tessari, M.L.; Boccuto, M.; Bacci, C. Clinical Effectiveness of Surgical Marginal Resection with Piezoelectric Device on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113792
Manera C, Tessari ML, Boccuto M, Bacci C. Clinical Effectiveness of Surgical Marginal Resection with Piezoelectric Device on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113792
Chicago/Turabian StyleManera, Claudia, Martina Lee Tessari, Mariagrazia Boccuto, and Christian Bacci. 2025. "Clinical Effectiveness of Surgical Marginal Resection with Piezoelectric Device on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113792
APA StyleManera, C., Tessari, M. L., Boccuto, M., & Bacci, C. (2025). Clinical Effectiveness of Surgical Marginal Resection with Piezoelectric Device on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113792






