Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Series and Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Selection
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Age ≥ 70 years;
- International prostate symptom score (IPSS) > 18;
- Maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) < 12 mL/s;
- Prostate volume > 45 cc, measured by transrectal ultrasound (TRUS);
- Resistance to medical therapy for ≥ 6 months;
- Acceptance of potential risks, including post-treatment sexual dysfunction.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Prostate cancer diagnosis or suspicion;
- Previous prostate surgery;
- Severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2);
- Active urinary tract infection;
- Contraindications to embolization, such as severe atherosclerosis.
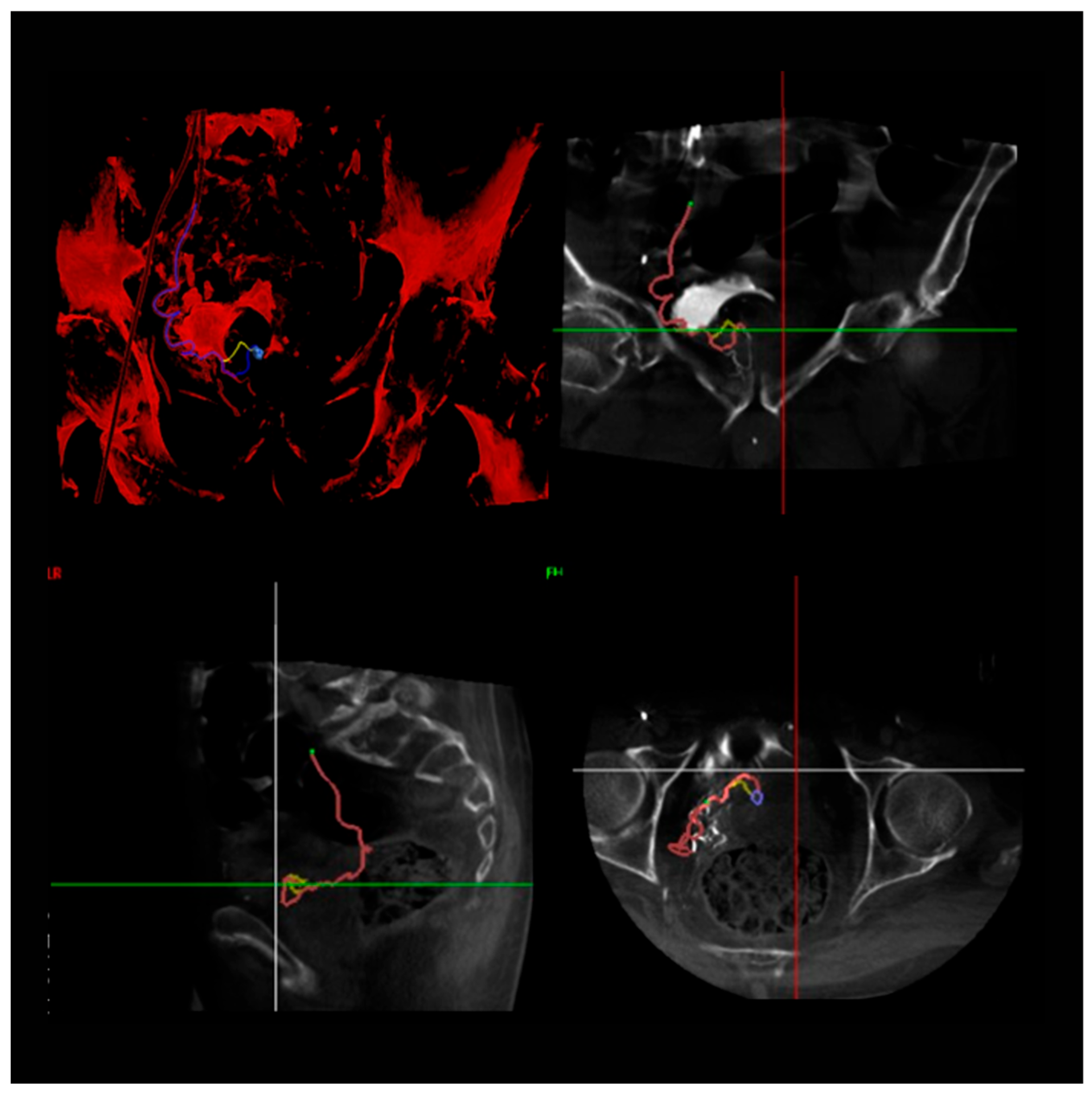
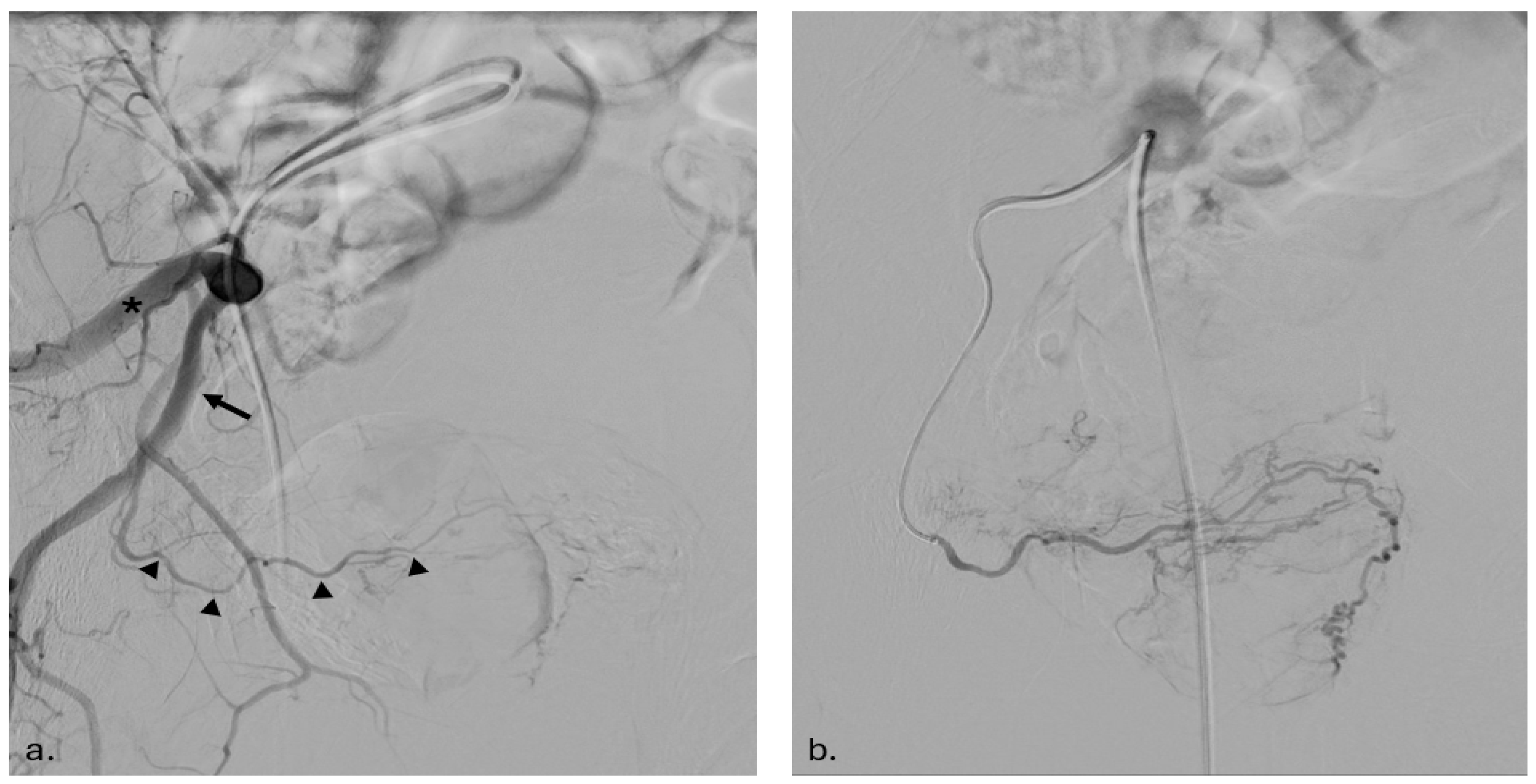
2.3. Embolization Procedure
2.3.1. Arterial Access and Imaging
2.3.2. Catheterization and Embolization
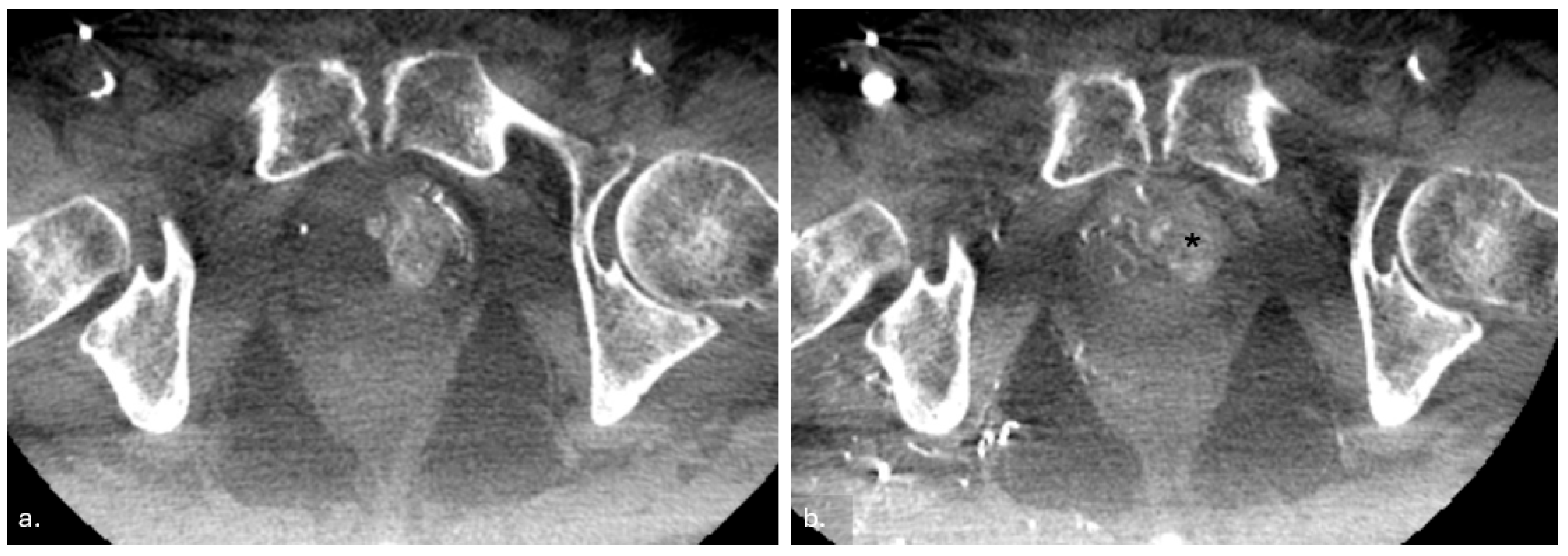
2.3.3. Post-Procedure Imaging and Verification
2.3.4. Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion and Literature Context
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delazar, S.; Azadnajafabad, S.; Firouznia, K.; Nowroozi, M.R.; Amini, E.; Fotouhi, M.; Ghanaati, H. Outcomes of Prostatic Artery Embolization for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Symptoms: A Prospective Single-Center Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, N.; Yamoah, K.; Johnstone, P.; Torres-Roca, J.; Pow-Sang, J.; Fernandez, D.; Rishi, A.; Grass, G.D. Prostate Artery Embolization in the Setting of Prostate Cancer: Review and Opinion. Cancer Control 2025, 32, 10732748251317691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Crisóstomo, V.; Báez-Díaz, C.; Sánchez, F.M. Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE) for Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Part 2, Insights into the Technical Rationale. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakhur, A.; McWilliams, J.P. Prostate Artery Embolization for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Current Status. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2017, 68, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, J.S.; Froelich, M.F.; McWilliams, J.P.; Gratzke, C.; Huber, T.; Gresser, E.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Diehl, S.J.; Nörenberg, D. Prostatic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Markov Model–Based Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2022, 19, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocerossa, F.; Cantiello, F.; Bagalá, L.; Sicoli, F.; Carbonara, U.; Manfredi, C.; Falagario, U.; Veccia, A.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Napolitano, L.; et al. Clinical Effects of Oral Supplementation of Gamma-Cyclodextrin Curcumin Complex in Male Patients with Moderate-To-Severe Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia-Related Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Urol. Int. 2023, 107, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisco, J.M.; Bilhim, T.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Fernandes, L.; Pereira, J.; Costa, N.V.; Duarte, M.; Oliveira, A.G. Medium- and Long-Term Outcome of Prostate Artery Embolization for Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Results in 630 Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapping, C.R.; Macdonald, A.; Hadi, M.; Mortensen, C.; Crew, J.; Protheroe, A.; Little, M.W.; Boardman, P. Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE) for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) with Haematuria in the Absence of an Upper Urinary Tract Pathology. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantiello, F.; Crocerossa, F.; Alba, S.; Carbonara, U.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Falagario, U.; Veccia, A.; Ucciero, G.; Ferro, M.; Mondaini, N.; et al. Refining Surgical Strategies in ThuLEP for BPH: A Propensity Score Matched Comparison of En-bloc, Three Lobes, and Two Lobes Techniques. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditonno, F.; Manfredi, C.; Licari, L.C.; Bologna, E.; Franco, A.; Pandolfo, S.D.; De Sio, M.; De Nunzio, C.; Fiori, C.; Cherullo, E.E.; et al. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Surgery: A Snapshot of Trends, Costs, and Surgical Retreatment Rates in the USA. Eur. Urol. Focus 2024, 10, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finati, M.; Cindolo, L.; Busetto, G.M.; Arcaniolo, D.; Perdonà, S.; Lucarelli, G.; Veccia, A.; Aveta, A.; Autorino, R.; Pandolfo, S.D. Ejaculation Preservation in BPH: A Question of Size? Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2025, 76, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westwood, J.; Geraghty, R.; Jones, P.; Rai, B.P.; Somani, B.K. Rezum: A New Transurethral Water Vapour Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2018, 10, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, C.; Spirito, L.; Quattrone, C.; Bottone, F.; Romano, L.; Balsamo, R.; Trama, F.; Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Napolitano, L.; et al. Rezūm Water Vapor Therapy vs. Thulium Laser Enucleation for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Patients with Large Prostates: A Multicenter Prospective Comparative Study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025. epub ahead of printing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallè, M.; Giulioni, C.; Papaveri, A.; Mengoni, F.; Orciani, R.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Imbimbo, C.; Crocetto, F.; Castellani, D.; Herrmann, T.; et al. Influence of Preoperative Indwelling Urinary Catheter on Outcomes of High-Power Holmium Laser Enucleation for Very Large Prostate (≥200 mL). World J. Urol. 2025, 43, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouli, S.; Salem, R.; McClure, T.D. Prostate Artery Embolization for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2024, 212, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, F.C.; Moreira, A.M.; Antunes, A.A. The “PErFecTED Technique”: Proximal Embolization First, Then Embolize Distal for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 37, 1602–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilhim, T.; Pisco, J.; Rio Tinto, H.; Fernandes, L.; Campos Pinheiro, L.; Duarte, M.; Pereira, J.A.; Oliveira, A.G.; O’Neill, J. Unilateral Versus Bilateral Prostatic Arterial Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Patients with Prostate Enlargement. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autorino, R.; Amparore, D.; Loizzo, D.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Checcucci, E.; Porpiglia, F. Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy Is Better than Endoscopic Enucleation of the Prostate. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara-Lopes, G.; Mattedi, R.; Antunes, A.A.; Carnevale, F.C.; Cerri, G.G.; Srougi, M.; Alves, V.A.; Leite, K.R.M. The Histology of Prostate Tissue Following Prostatic Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2013, 39, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, A.M.; Maciel, M.S.; Moreira, A.M.; De Paula Rodrigues, V.C.; Antunes, A.A.; Srougi, M.; Cerri, G.G.; Carnevale, F.C. Prostate Zonal Volumetry as a Predictor of Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Artery Embolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisco, J.; Campos Pinheiro, L.; Bilhim, T.; Duarte, M.; Rio Tinto, H.; Fernandes, L.; Vaz Santos, V.; Oliveira, A.G. Prostatic Arterial Embolization for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Short- and Intermediate-Term Results. Radiology 2013, 266, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, F.C.; Da Motta-Leal-Filho, J.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Baroni, R.H.; Marcelino, A.S.Z.; Cerri, L.M.O.; Yoshinaga, E.M.; Cerri, G.G.; Srougi, M. Quality of Life and Clinical Symptom Improvement Support Prostatic Artery Embolization for Patients with Acute Urinary Retention Caused by Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, F.C.; Antunes, A.A.; Da Motta Leal Filho, J.M.; De Oliveira Cerri, L.M.; Baroni, R.H.; Marcelino, A.S.Z.; Freire, G.C.; Moreira, A.M.; Srougi, M.; Cerri, G.G. Prostatic Artery Embolization as a Primary Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Preliminary Results in Two Patients. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amouyal, G.; Thiounn, N.; Pellerin, O.; Yen-Ting, L.; Del Giudice, C.; Dean, C.; Pereira, H.; Chatellier, G.; Sapoval, M. Clinical Results After Prostatic Artery Embolization Using the PErFecTED Technique: A Single-Center Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagla, S.; Martin, C.P.; Van Breda, A.; Sheridan, M.J.; Sterling, K.M.; Papadouris, D.; Rholl, K.S.; Smirniotopoulos, J.B.; Van Breda, A. Early Results from a United States Trial of Prostatic Artery Embolization in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurbatov, D.; Russo, G.I.; Lepetukhin, A.; Dubsky, S.; Sitkin, I.; Morgia, G.; Rozhivanov, R.; Cimino, S.; Sansalone, S. Prostatic Artery Embolization for Prostate Volume Greater Than 80 cm3: Results from a Single-Center Prospective Study. Urology 2014, 84, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, M.; Balderi, A.; Arnò, M.; Sortino, D.; Antonietti, A.; Pedrazzini, F.; Giovinazzo, G.; Vinay, C.; Maugeri, O.; Ambruosi, C.; et al. Prostatic Artery Embolization in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Preliminary Results in 13 Patients. La Radiol. Med. 2015, 120, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, B.K.; Hacking, N.; Bryant, T.; Coyne, J.; Flowers, D.; Harris, M.; Dyer, J. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int. 2014, 114, 639–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, L.; Duan, F.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, G.; Li, K.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H. Prostatic Arterial Embolization for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Caused by Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Comparative Study of Medium- and Large-Volume Prostates. BJU Int. 2016, 117, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, A.M.; Moreira, A.M.; De Paula Rodrigues, V.C.; Yoshinaga, E.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Harward, S.H.; Srougi, M.; Carnevale, F.C. Prostatic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Patients with Prostates >90 g: A Prospective Single-Center Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampoldi, A.; Barbosa, F.; Secco, S.; Migliorisi, C.; Galfano, A.; Prestini, G.; Harward, S.H.; Di Trapani, D.; Brambillasca, P.M.; Ruggero, V.; et al. Prostatic Artery Embolization as an Alternative to Indwelling Bladder Catheterization to Manage Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Poor Surgical Candidates. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, O.M.; Carnevale, F.C.; Moreira, A.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Rodrigues, V.C.; Srougi, M. Comparative Study Using 100–300 Versus 300–500 μm Microspheres for Symptomatic Patients Due to Enlarged-BPH Prostates. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, A.H.; Gabr, M.F.; Elmohamady, B.N.; Ahmed, A. Prostatic Artery Embolization: A Promising Technique in the Treatment of High-Risk Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urol. Int. 2016, 97, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M.; Abd El Tawab, K.A.; Abd El Tawab, K.H.; El-Gharib, M. Role of Prostatic Artery Embolization in Management of Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2016, 47, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, M.; Wang, Y. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Prostatic Arterial Embolization versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate—A Prospective, Randomized, and Controlled Clinical Trial. Radiology 2014, 270, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Duan, F.; Wang, M.-Q.; Zhang, G.-D.; Yuan, K. Prostatic Arterial Embolization with Small Sized Particles for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Large Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Preliminary Results. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapping, C.R.; Little, M.W.; Macdonald, A.; Mackinnon, T.; Kearns, D.; Macpherson, R.; Crew, J.; Boardman, P. The STREAM Trial (Prostatic Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) 24-Month Clinical and Radiological Outcomes. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insausti, I.; Sáez De Ocáriz, A.; Galbete, A.; Capdevila, F.; Solchaga, S.; Giral, P.; Bilhim, T.; Isaacson, A.; Urtasun, F.; Napal, S. Randomized Comparison of Prostatic Artery Embolization versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insausti, I.; Galbete, A.; Lucas-Cava, V.; De Ocáriz, A.S.; Solchaga, S.; Monreal, R.; De La Cuesta, A.M.; Alfaro, R.; Sun, F.; Montesino, M.; et al. Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE) Using Polyethylene Glycol Microspheres: Safety and Efficacy in 81 Patients. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, D.; Hechelhammer, L.; Müllhaupt, G.; Markart, S.; Güsewell, S.; Kessler, T.M.; Schmid, H.-P.; Engeler, D.S.; Mordasini, L. Comparison of Prostatic Artery Embolisation (PAE) Versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Randomised, Open Label, Non-Inferiority Trial. BMJ 2018, 361, k2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.S.; Mishra, D.K. Transurethral Resection of Prostate. J. Endourol. 2022, 36, S-29–S-34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.F.; Powell, J.; Speakman, M.J.; Longford, N.T.; DasGupta, R.; Bryant, T.; Modi, S.; Dyer, J.; Harris, M.; Carolan-Rees, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Prostate Artery Embolization for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: An Observational Study and Propensity-Matched Comparison with Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (the UK-ROPE study). BJU Int. 2018, 122, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zong, H.-T.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Prostate Artery Embolization on Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Related to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, F.C.; Iscaife, A.; Yoshinaga, E.M.; Moreira, A.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Srougi, M. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Versus Original and PErFecTED Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Preliminary Results of a Single Center, Prospective, Urodynamic-Controlled Analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo, S.D.; Crauso, F.; Aveta, A.; Cilio, S.; Barone, B.; Napolitano, L.; Scarpato, A.; Mirto, B.F.; Serino, F.; Del Giudice, F.; et al. A Novel Low-Cost Uroflowmetry for Patient Telemonitoring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.R.; Kanhai, K.J.K.; Ko, Y.M.; Kim, J.H. Efficacy and Safety of Prostatic Arterial Embolization: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Q.; Guo, L.P.; Zhang, G.D.; Yuan, K.; Li, K.; Duan, F.; Yan, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Wang, Z.J. Prostatic Arterial Embolization for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms due to Large (>80 mL) Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Results of Midterm Follow-Up from Chinese Population. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | PAE n = 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median | 74 | 87 | 76 | 78 | 79 | 77 | 81 | 80 | 85 | 83 | 79.5 |
| Mean IPSS at different time intervals (Pre-PAE—12 mo) | 22–10 | 26–13 | 23–11 | 25–12 | 24–12 | 24–11 | 23–13 | 22–10 | 26–14 | 26–11 | 24–12 |
| Mean maximum urinary flow rate (mL/s) (Pre-PAE—12 mo) | 8.1–11.9 | 7.8–11.6 | 8.9–12.3 | 9.2–13.1 | 8.3–12.2 | 9.0–12.7 | 8.6–12.4 | 8.2–12.0 | 7.5–11.4 | 7.7–11.8 | 8.7–12.6 |
| Mean of prostate volume (cc) (Pre-PAE—12 mo) | 66.4–51.5 | 78.4–53.2 | 62.1–47.2 | 54.2–45.6 | 58.5–46.0 | 69.9–52.0 | 65.2–48.2 | 48.9–43.5 | 75.3–49.1 | 72.8–49.8 | 66.4–49.4 |
| Mean of PSA (ng/mL) (Pre-PAE—12 mo) | 5.1–3.5 | 6.8–4.2 | 4.6–3.1 | 3.3–2.5 | 5.8–3.9 | 2.9–2.1 | 5.5–3.6 | 4.2–3.0 | 7.2–4.7 | 6.5–4.0 | 5.0–3.4 |
| Mean procedure time (min) | 92 | 105 | 87 | 73 | 118 | 95 | 81 | 99 | 68 | 110 | 95 |
| Length of stay (day) | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2.5 |
| Author | Type of Study | No | Age, Mean | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pisco et al. | Retrospective | 630 | 65.1 | [7] |
| Carnevale et al. | Prospective RCT | 30 | 62 | [23] |
| Amouyal et al. | Retrospective | 32 | 65 | [24] |
| Bagla et al. | Retrospective | 78 | 64.7 | [25] |
| Kurbatov et al. | Prospective | 88 | 66.38 | [26] |
| Grosso et al. | Prospective | 13 | 75.9 | [27] |
| Somani et al. | Prospective | 35 | 64 | [28] |
| Wang et al. | Prospective | 115 | 71.5 | [29] |
| de Assis et al. | Prospective | 35 | 64.8 | [30] |
| Rampoldi et al. | Prospective | 43 | 77.9 | [31] |
| Gonçalves et al. | Prospective | 30 | NA | [32] |
| Gabr et al. | Prospective | 22 | 72.5 | [33] |
| Shaker et al. | Prospective | 28 | 68.5 | [34] |
| Gao et al. | Prospective RCT (comparison with TURP) | 57 | 67.7 | [35] |
| Li et al. | Prospective | 24 | 74.5 | [36] |
| Tapping et al. | Prospective | 50 | 67 | [37] |
| Insausti et al. | RCT | 45 | 72.1 | [38] |
| Insausti et al. | Prospective | 81 | 73.87 | [39] |
| Abt et al. | Randomized, open label, and non-inferiority trial | 103 | 65.9 | [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iossa, V.; Punzi, E.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Spena, G.; Russo, P.; Giulioni, C.; Aveta, A.; Spirito, L.; Lombardi, G.; Imperatore, V. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Series and Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113775
Iossa V, Punzi E, Pandolfo SD, Spena G, Russo P, Giulioni C, Aveta A, Spirito L, Lombardi G, Imperatore V. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Series and Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113775
Chicago/Turabian StyleIossa, Vincenzo, Ernesto Punzi, Savio Domenico Pandolfo, Gianluca Spena, Pierluigi Russo, Carlo Giulioni, Achille Aveta, Lorenzo Spirito, Giulio Lombardi, and Vittorio Imperatore. 2025. "Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Series and Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113775
APA StyleIossa, V., Punzi, E., Pandolfo, S. D., Spena, G., Russo, P., Giulioni, C., Aveta, A., Spirito, L., Lombardi, G., & Imperatore, V. (2025). Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Series and Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113775








