A Proposal for a New Lung Ultrasound Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Reliability of Lung Ultrasound for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
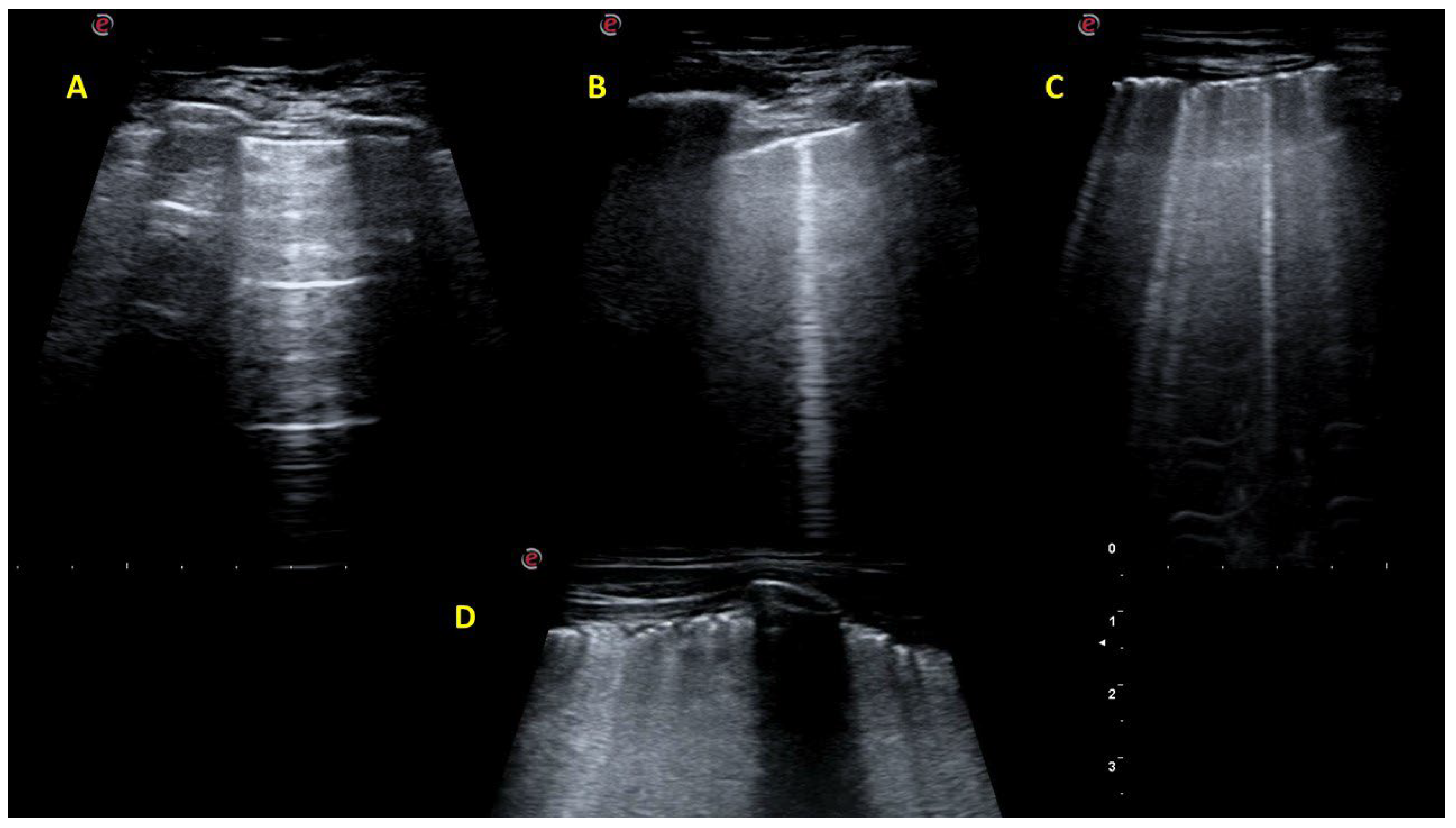
2.2. Lung Ultrasound Investigation
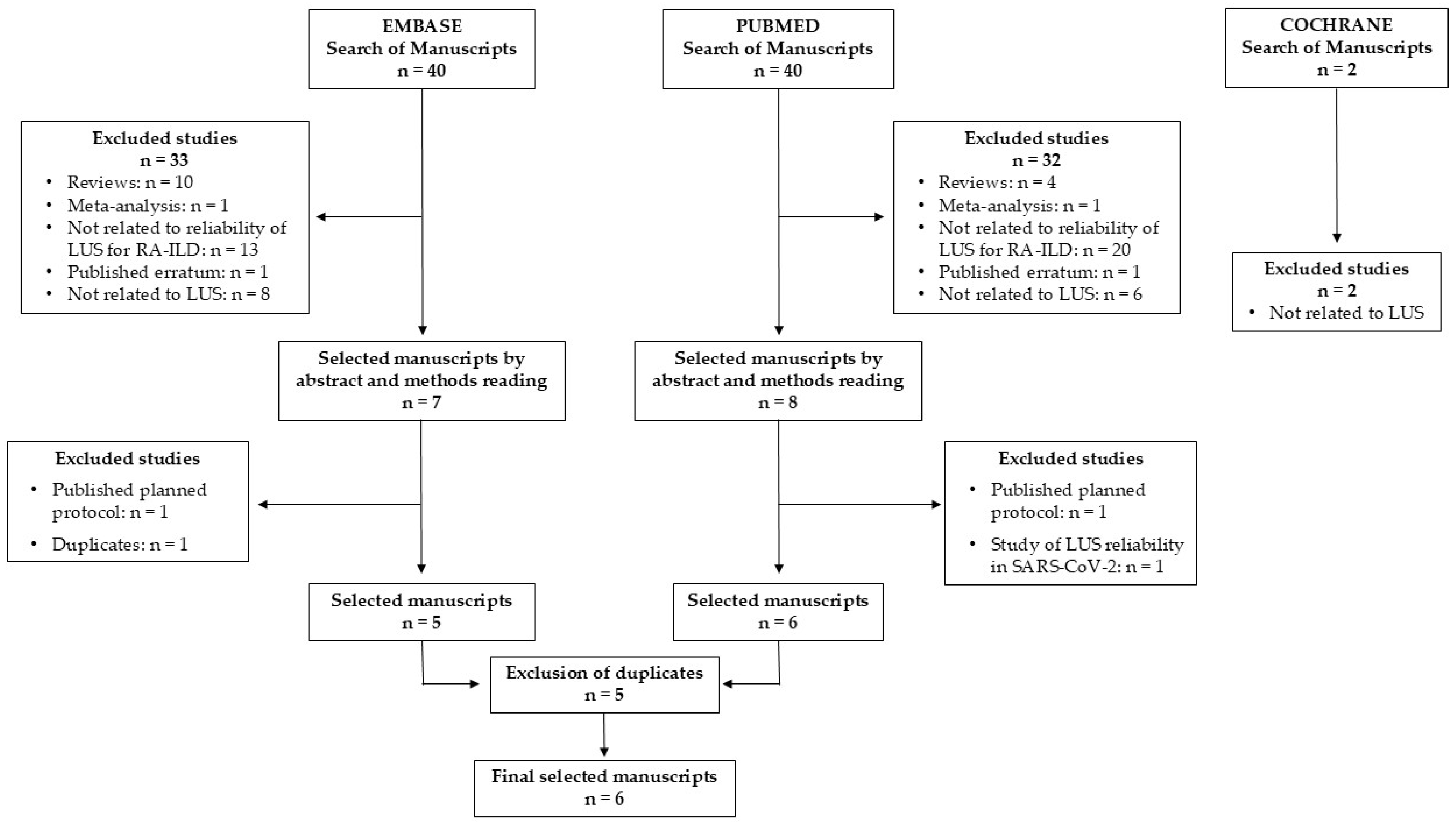
2.3. Systematic Review of the Literature
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reliability of the B-Line Scores
3.2. Reliability of the Pleural Line Scores
3.3. Diagnostic Performance of the Proposed LUS Scores
3.4. Systematic Literature Review
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACPA | Anti-citrullinated peptide antibody |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| BLs | B lines |
| CHEST | American College of Chest Physicians |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| csDMARDs | Conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs |
| CTDs | Connective tissue diseases |
| CTD-ILD | Connective tissue diseases associated with interstitial lung disease |
| DAS28 | Disease Activity Score of 28 joints |
| EULAR | European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology |
| HAQ | Health Assessment Questionnaire |
| HCs | Healthy controls |
| HRCT | High-resolution chest computed tomography |
| ICC-LUS | International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound |
| ICL-LUS | International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| ICSs | Intercostal spaces |
| ĸ | Kappa |
| LFTs | lung function tests |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RA-ILD | RA associated with interstitial lung disease |
| SSc-ILD | Systemic sclerosis associated with interstitial lung disease |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, G.; Jing, Z.; Lv, L.; Nan, K.; Dang, X. The Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Diseases Study and Forecasts for 2030 by Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.; Collins, B.F.; Ho, L.A.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, K.; Solomon, J.J.; Olson, A.L.; Kong, A.M.; Cole, A.L.; Fischer, A.; Swigris, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis–Interstitial Lung Disease in the United States: Prevalence, Incidence, and Healthcare Costs and Mortality. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Lee, J.S.; Sverzellati, N.; Rossi, G.; Cottin, V. The Lung in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focus on Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongartz, T.; Nannini, C.; Medina-Velasquez, Y.F.; Achenbach, S.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Vassallo, R.; Gabriel, S.E.; Matteson, E.L. Incidence and Mortality of Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.M.; Bell, C.L.; Shinki, K.; Rosenthal, A.; Bridges, A.J. Changing Trends in Serious Extra-Articular Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis among United State Veterans over 20 Years. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, A.L.; Swigris, J.J.; Sprunger, D.B.; Fischer, A.; Fernandez-Perez, E.R.; Solomon, J.; Murphy, J.; Cohen, M.; Raghu, G.; Brown, K.K. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease-Associated Mortality. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.A.; Rodriguez-Nieto, M.J.; Sanchez-Pernaute, O.; Romero-Bueno, F.; Leon, L.; Vadillo, C.; Freites-Nuñez, D.D.; Jover, J.A.; Álvarez-Sala, J.L.; Abasolo, L. Mortality Rate in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: The Role of Radiographic Patterns. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Jiménez, E.; Vázquez Rodríguez, T.; Martín-Robles, I.; Castillo Villegas, D.; Juan García, J.; Bollo de Miguel, E.; Robles-Pérez, A.; Ferrer Galván, M.; Mouronte Roibas, C.; Herrera Lara, S.; et al. Diagnostic Delay of Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Increases Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Blanco, R.; Cavagna, L.; Ancochea, J.; Castañeda, S.; González-Gay, M.Á. Efficacy and Safety of Abatacept in Interstitial Lung Disease of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bes, C. Comprehensive Review of Current Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches to Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 6, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narváez, J.; Aburto, M.; Seoane-Mato, D.; Bonilla, G.; Acosta, O.; Candelas, G.; Cano-Jiménez, E.; Castellví, I.; González-Ruiz, J.M.; Corominas, H.; et al. Screening Criteria for Interstitial Lung Disease Associated to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Expert Proposal Based on Delphi Methodology. Reumatol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.A.; Saravanan, V.; Nisar, M.; Arthanari, S.; Woodhead, F.A.; Price-Forbes, A.N.; Dawson, J.; Sathi, N.; Ahmad, Y.; Koduri, G.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: Associations, Prognostic Factors and Physiological and Radiological Characteristics--a Large Multicentre UK Study. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, G.C.; Doyle, T.J.; Sparks, J.A. Interstitial Lung Disease throughout the Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Course. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.R.; Bernstein, E.J.; Bolster, M.B.; Chung, J.H.; Danoff, S.K.; George, M.D.; Khanna, D.; Guyatt, G.; Mirza, R.D.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. 2023 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) Guideline for the Screening and Monitoring of Interstitial Lung Disease in People with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederer, J.; Schnabel, A.; Muhle, C.; Gross, W.L.; Heller, M.; Reuter, M. Correlation between HRCT Findings, Pulmonary Function Tests and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Bong, D.A.; Castañeda, S.; Möller, I. Use of Ultrasound to Diagnose and Monitor Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatic Diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3547–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Long, S.; Gutierrez, M.; Clavijo-Cornejo, D.; Alfaro-Rodríguez, A.; González-Sámano, K.; Cortes-Altamirano, J.L.; Muñoz-Louis, R.; Cruz-Arenas, E.; Camargo, K.; Gonzalez, F.; et al. Intersticiopatía pulmonar subclínica en pacientes con esclerosis sistémica. Estudio piloto sobre el papel del ultrasonido. Reumatol. Clínica 2021, 17, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Acebes, C.; Castañeda, S. Usefulness of Extra-Articular Ultrasound Applied to Systemic Inflammatory Diseases in Clinical Practice. Reumatol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 17, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Moreno, P.; Linares-Contreras, M.F.; Rodríguez-Vargas, G.-S.; Rodríguez-Linares, P.; Mata-Hurtado, A.; Ibatá, L.; Martínez, S.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Diaz, M.; Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; et al. Usefulness of Lung Ultrasound as a Method for Early Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2024, 16, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Soto-Fajardo, C.; Pineda, C.; Alfaro-Rodriguez, A.; Terslev, L.; Bruyn, G.; Iagnocco, A.; Bertolazzi, C.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Delle Sedie, A. Ultrasound in the Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Literature Review by the OMERACT Ultrasound Group. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogliati, C.; Antivalle, M.; Torzillo, D.; Birocchi, S.; Norsa, A.; Bianco, R.; Costantino, G.; Ditto, M.C.; Battellino, M.; Sarzi Puttini, P.C.; et al. Standard and Pocket-Size Lung Ultrasound Devices Can Detect Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazedi-Fuerst, F.C.; Kielhauser, S.M.; Scheidl, S.; Tripolt, N.J.; Lutfi, A.; Yazdani-Biuki, B.; Dejaco, C.; Graninger, W.B. Ultrasound Screening for Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Lung Ultrasound for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.Q.; Zhang, W.W.; Sun, D.S.; Chen, X.M.; Yuan, S.F.; Gong, Z.H.; Liu, L. A Simplified Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in Connective Tissue Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotoh, D.S.; Helal, A.; Rizk, M.S.; Esaily, H.A. Serum Krebs von Den Lungen-6 and Lung Ultrasound B Lines as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Vázquez, N.; Jimenez-Núñez, F.G.; Godoy-Navarrete, F.J.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Aguilar-Hurtado, M.C.; Romero-Barco, C.M.; Ureña-Garnica, I.; Espildora, F.; Padin-Martín, M.I.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Utility of Pulmonary Ultrasound to Identify Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, M.; Tardella, M.; Filippucci, E.; Carotti, M.; Salaffi, F. Lung Ultrasound in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Definition of Significant Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Ruta, S.; Clavijo-Cornejo, D.; Fuentes-Moreno, G.; Reyes-Long, S.; Bertolazzi, C. The Emerging Role of Ultrasound in Detecting Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2022, 89, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L. Lung Ultrasound: A New Tool for the Cardiologist. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2011, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, L.; Frassi, F.; Soldati, G.; Tesorio, P.; Gheorghiade, M.; Picano, E. Ultrasound Lung Comets for the Differential Diagnosis of Acute Cardiogenic Dyspnoea: A Comparison with Natriuretic Peptides. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Mussa, A.; Garofalo, G.; Cardinale, L.; Casoli, G.; Perotto, F.; Fava, C.; Frascisco, M. Bedside Lung Ultrasound in the Assessment of Alveolar-Interstitial Syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 24, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G. Lung Sonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G. Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2020, 158, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Tardella, M.; Pineda, C.; Bertolazzi, C.; Bichisecchi, E.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W. Utility of a Simplified Ultrasound Assessment to Assess Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis in Connective Tissue Disorders—Preliminary Results. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L.; Volpicelli, G. How I Do It: Lung Ultrasound. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2014, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for the International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (ICC-LUS); Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; et al. International Evidence-Based Recommendations for Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. An Application of Hierarchical Kappa-Type Statistics in the Assessment of Majority Agreement among Multiple Observers. Biometrics 1977, 33, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandinelli, F.; Benucci, M.; Mallia, I.; Mauro, I.; Pecani, N.; Li Gobbi, F.; Manfredi, M.; Guiducci, S.; Lari, B.; Grossi, V.; et al. Do Ultrasound Lung Abnormalities Correlate to Biomarkers and Male Gender in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanten Zabaleta, R.; Marín, J.; Zacariaz Hereter, J.B.; Maritano, J.; Fullana, M.; Alvarado, N.; Soriano, E.R.; Rosa, J.E. Clinical Utility of Lung Ultrasound for the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Reumatismo 2024, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Yomono, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Suzuki, M.; Gono, T.; Kuwana, M. Lung Ultrasound in the Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Connective Tissue Disease: Performance in Comparison with High-Resolution Computed Tomography. Mod. Rheumatol. 2024, 35, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, N.; Kosiak, W.; Wełnicki, M.; Skoczylas, A.; Olszewski, R.; Piotrkowski, J.; Skoczyński, S.; Radzikowska, E.; Jassem, E.; Grabczak, E.M.; et al. Recommendations for Lung Ultrasound in Internal Medicine. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L.; Doveri, M.; D’Errico, L.; Frassi, F.; Bazzichi, M.L.; Delle Sedie, A.; Scali, M.C.; Monti, S.; Mondillo, S.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. Ultrasound Lung Comets in Systemic Sclerosis: A Chest Sonography Hallmark of Pulmonary Interstitial Fibrosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barskova, T.; Gargani, L.; Guiducci, S.; Randone, S.B.; Bruni, C.; Carnesecchi, G.; Conforti, M.L.; Porta, F.; Pignone, A.; Caramella, D.; et al. Lung Ultrasound for the Screening of Interstitial Lung Disease in Very Early Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Sedie, A.; Doveri, M.; Frassi, F.; Gargani, L.; D’Errico, G.; Pepe, P.; Bazzichi, L.; Riente, L.; Caramella, D.; Bombardieri, S. Ultrasound Lung Comets in Systemic Sclerosis: A Useful Tool to Detect Lung Interstitial Fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, S54. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Bong, D.A.; Busquets-Pérez, N.; Möller, I. Ultrasound Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Diseases. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2024, 11, S316–S322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sperandeo, M.; Varriale, A.; Sperandeo, G.; Filabozzi, P.; Piattelli, M.L.; Carnevale, V.; Decuzzi, M.; Vendemiale, G. Transthoracic Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Our Experience. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazedi-Fuerst, F.; Kielhauser, S.; Brickmann, K.; Tripolt, N.; Meilinger, M.; Lutfi, A.; Graninger, W. Sonographic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S87–S91. [Google Scholar]
- Buda, N.; Masiak, A.; Zdrojewski, Z. Utility of Lung Ultrasound in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis with Lung Involvement. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, N.; Piskunowicz, M.; Porzezińska, M.; Kosiak, W.; Zdrojewski, Z. Lung Ultrasonography in the Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Connective Tissue Diseases: Criteria and Severity of Pulmonary Fibrosis—Analysis of 52 Patients. Ultraschall Med. 2015, 37, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Pallisa-Nuñez, E.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Castella-Fierro, E. Pleural Irregularity, a New Ultrasound Sign for the Study of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis and Antisynthetase Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S136–S141. [Google Scholar]
- Sperandeo, M.; De Cata, A.; Molinaro, F.; Trovato, F.; Catalano, D.; Simeone, A.; Varriale, A.; Martines, G.; Trovato, G. Ultrasound Signs of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis as Timely Indicators for Chest Computed Tomography. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L.; Romei, C.; Bruni, C.; Lepri, G.; El-Aoufy, K.; Orlandi, M.; D’Errico, L.; Bandini, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Guiducci, S.; et al. Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Systemic Sclerosis: Cut-off Values and Methodological Indications for Interstitial Lung Disease Screening. Rheumatology 2022, 61, SI56–SI64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, R.; Chung, M.; Yang, D.; Sharpless, L.; Li, S.; Chung, L. Development and Assessment of Novel Lung Ultrasound Interpretation Criteria for the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermant, M.; Kalkanis, A.; Goos, T.; Cypers, H.; De Crem, N.; Neerinckx, B.; Taelman, V.; Verschueren, P.; Wuyts, W.A. Ultrasonographic Presentation and Anatomic Distribution of Lung Involvement in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doveri, M.; Frassi, F.; Consensi, A.; Vesprini, E.; Gargani, L.; Tafuri, M.; Picano, E.; Della Rossa, A.; Delle Sedie, A.; d’Ascanio, A.; et al. Ultrasound lung comets: New echographic sign of lung interstitial fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Reumatismo 2008, 60, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, A.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Lucci, S.; Barilaro, G.; Quarta, S.; Barbano, B.; Giovannetti, A.; Amoroso, A.; Rosato, E. Lung Ultrasound in Systemic Sclerosis: Correlation with High-Resolution Computed Tomography, Pulmonary Function Tests and Clinical Variables of Disease. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2016, 11, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M.L.; Gigante, A.; Iacolare, A.; Pellicano, C.; Lucci, S.; Rosato, E. The Predictive Role of Lung Ultrasound in Progression of Scleroderma Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazedi-Fuerst, F.C.; Zechner, P.M.; Tripolt, N.J.; Kielhauser, S.M.; Brickmann, K.; Scheidl, S.; Lutfi, A.; Graninger, W.G. Pulmonary Echography in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A. Comparison of a New, Modified Lung Ultrasonography Technique with High-Resolution CT in the Diagnosis of the Alveolo-Interstitial Syndrome of Systemic Scleroderma. Med. Ultrason. 2014, 16, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdashi, M.; Broofeh, B.; Mohammadi, A. Diagnostic Performances of High Resolution Trans-Thoracic Lung Ultrasonography in Pulmonary Alveoli-Interstitial Involvement of Rheumatoid Lung Disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 562–566. [Google Scholar]
- Fehr, A.; Baghdady, S.; Ghaleb, R.; Maklad, S. Transthoracic Ultrasound in the Detection of Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis in Patients with Rheumatic Connective Tissue Diseases. Bull. Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2018, 76, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Vasco, P.G.; de Luna Cardenal, G.; Garrido, I.M.; Pinilla, J.M.L.; Rodríguez, G.F.; Mateo, J.J.N.; Ruiz, D.C. Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Sjögren’s Syndrome by Lung Ultrasound: A Pilot Study of Correlation with High-Resolution Chest Tomography. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardella, M.; Gutierrez, M.; Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Ariani, A.; Bertolazzi, C.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W. Ultrasound in the Assessment of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Connective Tissue Disorders: Correlation with High-Resolution Computed Tomography. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trezzi, M.; Torzillo, D.; Ceriani, E.; Costantino, G.; Caruso, S.; Damavandi, P.T.; Genderini, A.; Cicardi, M.; Montano, N.; Cogliati, C. Lung Ultrasonography for the Assessment of Rapid Extravascular Water Variation: Evidence from Hemodialysis Patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofíudóttir, B.K.; Harders, S.; Laursen, C.B.; Lage-Hansen, P.R.; Nielsen, S.M.; Just, S.A.; Christensen, R.; Davidsen, J.R.; Ellingsen, T. Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Thoracic Ultrasound: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2024, 76, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Weng, Y.; Graglia, S.; Chung, S.; Duanmu, Y.; Lalani, F.; Gandhi, K.; Lobo, V.; Jensen, T.; Nahn, J.; et al. Interobserver Agreement of Lung Ultrasound Findings of COVID-19. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofíudóttir, B.K.; Harders, S.M.W.; Lage-Hansen, P.R.; Christensen, R.; Munk, H.L.; Sorensen, G.L.; Davidsen, J.R.; Ellingsen, T. Using Thoracic Ultrasound to Detect Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Protocol for the Diagnostic Test Accuracy AURORA Study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e067434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| B-Line Evaluations | B-Line Global Count | B-Line Binary Count | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | |
| Intercostal Spaces | ||||
| Anterolateral Thorax | ||||
| 2nd right parasternal line | E1: 0.86 (0.49–1.00) | E1: 94.4 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.59 (−0.03–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 2nd left parasternal line | E1: 0.61 (−0.13–1.00) | E1: 83.3 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.87 (0.52–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.40 (−0.33–1.00) | E3: 72.2 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th right mid-clavicular line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E2: 91.7 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th left mid-clavicular line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th right anterior axillary line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th left anterior axillary line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.60 (−0.15–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | E2: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 0.73 (0.23–1.00) | E3: 88.9 | E3: 0.25 (−0.91–1.00) | E3: 66.7 | |
| 4th right mid-axillary line | E1: 0.86 (0.49–1.00) | E1: 94.4 | E1: 0.86 (0.49–1.00) | E1: 94.4 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.86 (0.48–1.00) | E3: 94.4 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th left mid-axillary line | E1: 0.61 (−0.08–1.00) | E1: 83.3 | E1: 0.33 (−0.47–1.00) | E1: 66.7 |
| E2: 0.85 (0.47–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 0.78 (0.20–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| Posterior Thorax | ||||
| 8th right paravertebral line | E1: 0.86 (0.49–1.00) | E1: 94.4 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.85 (0.47–1.00) | E3: 94.4 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 8th left paravertebral line | E1: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E1: 91.2 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.85 (0.47–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.78 (0.20–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 8th right subscapular line | E1: 0.71 (0.18–1.00) | E1: 88.9 | E1: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 0.86 (0.47–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.78 (0.20–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 8th left subscapular line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.85 (0.47–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 0.74 (0.07–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 8th right posterior axillary line | E1: 0.71 (−0.03–1.00) | E1: 88.9 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.86 (0.48–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.86 (0.49–1.00) | E3: 94.4 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 8th left posterior axillary line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| Global and Binary Scores of B Lines, Respectively | E1: 0.73 (0.39–1.00) | E1: 88.9 | E1: 0.90 (0.39–1.00) | E1: 95.8 |
| E2: 0.80 (0.55–1.00) | E2: 91.7 | E2: 0.84 (0.56–1.00) | E2: 93.3 | |
| E3: 0.82 (0.56–1.00) | E3: 92.9 | E3: 0.80 (0.45–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | |
| B-Line Evaluations | B-Lines Global Score | B-Line Binary Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | |
| Intercostal Spaces | ||||
| Anterolateral Thorax | ||||
| 2nd right parasternal line | 0.84 (0.62–1.00) | 93.7 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 2nd left parasternal line | 0.75 (0.45–1.00) | 90.5 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 4th right mid-clavicular line | 0.95 (0.83–1.00) | 98.4 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 4th left mid-clavicular line | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 4th right anterior axillary line | 0.96 (0.85–1.00) | 98.4 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 4th left anterior axillary line | 0.79 (0.46–1.00) | 93.7 | 0.69 (0.21–1.00) | 90.5 |
| 4th right mid-axillary line | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 4th left mid-axillary line | 0.93 (0.77–1.00) | 97.6 | 0.83 (0.44–1.00) | 95.2 |
| Posterior Thorax | ||||
| 8th right paravertebral line | 0.85 (0.65–1.00) | 94.0 | 0.88 (0.62–1.00) | 95.2 |
| 8th left paravertebral line | 0.97 (0.89–1.00) | 98.8 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 8th right subscapular line | 0.91 (0.75–1.00) | 96.4 | 0.84 (0.53–1.00) | 95.2 |
| 8th left subscapular line | 0.69 (0.37–1.00) | 88.1 | 0.61 (0.16–1.00) | 85.7 |
| 8th right posterior axillary line | 0.81 (0.55–1.00) | 92.9 | 0.87 (0.58–1.00) | 95.2 |
| 8th left posterior axillary line | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| Global and Binary Scores of B Lines, Respectively | 0.93 (0.86–1.00) | 97.1 | 0.90 (0.76–1.00) | 96.0 |
| Pleural Line Evaluations | Semiquantitative Score | Binary Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | |
| Intercostal Spaces | ||||
| Anterolateral Thorax | ||||
| 2nd right parasternal line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.54 (−0.42–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | E2: 0.25 (−0.91–1.00) | E2: 66.7 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 2nd left parasternal line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.57 (−0.21–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | E3: 0.33 (−0.47–1.00) | E3: 66.7 | |
| 4th right mid-clavicular line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E2: 91.7 | E2: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th left mid-clavicular line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th right anterior axillary line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | E3: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 4th left anterior axillary line | E1: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E1: 91.7 | E1: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 0.57 (−0.21–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | E2: 0.33 (−0.47–1.00) | E2: 66.7 | |
| E3: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | E3: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 4th right mid-axillary line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.78 (0.16–1.00) | E2: 91.7 | E2: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| 4th left mid-axillary line | E1: 0.78 (0.70–1.00) | E1: 91.7 | E1: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E2: 91.7 | E2: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| Posterior Thorax | ||||
| 8th right paravertebral line | E1: 0.78 (0.16–1.00) | E1: 91.7 | E1: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 0.78 (0.20–1.00) | E2: 91.7 | E2: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 8th left paravertebral line | E1: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E1: 91.7 | E1: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 8th right subscapular line | E1: 0.78 (0.20–1.00) | E1: 91.7 | E1: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 0.71 (0.18–1.00) | E2: 88.9 | E2: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 8th left subscapular line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.75 (0.04–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.57 (−0.42–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 8th right posterior axillary line | E1: 0.78 (0.20–1.00) | E1: 91.7 | E1: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E1: 83.3 |
| E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | E2: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E2: 100 | |
| E3: 0.78 (0.21–1.00) | E3: 91.7 | E3: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E3: 83.3 | |
| 8th left posterior axillary line | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 | E1: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E1: 100 |
| E2: 0.71 (0.18–1.00) | E2: 88.9 | E2: 0.67 (−0.14–1.00) | E2: 83.3 | |
| E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | E3: 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | E3: 100 | |
| Semiquantitative and Binary Pleural Line Scores, Respectively | E1: 0.91 (0.27–1.00) | E1: 96.7 | E1: 0.84 (0.56–1.00) | E1: 93.3 |
| E2: 0.86 (0.23–1.00) | E2: 94.4 | E2: 0.77 (0.44–1.00) | E2: 90.0 | |
| E3: 0.88 (0.24–1.00) | E3: 95.4 | E3: 0.77 (0.44–1.00) | E3: 90.0 | |
| Pleural Line Evaluations | Semiquantitative Score | Binary Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | Kappa (95%CI) | Agreement % | |
| Intercostal Spaces | ||||
| Anterolateral Thorax | ||||
| 2nd right parasternal line | 0.73 (0.48–1.00) | 92.1 | 0.70 (0.35–1.00) | 85.7 |
| 2nd left parasternal line | 0.89 (0.72–1.00) | 96.8 | 0.78 (0.47–1.00) | 90.5 |
| 4th right mid-clavicular line | 0.81 (0.57–1.00) | 95.2 | 0.87 (0.58–1.00) | 95.2 |
| 4th left mid-clavicular line | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 100 |
| 4th right anterior axillary line | 0.78 (0.56–1.00) | 93.7 | 0.89 (0.64–1.00) | 95.2 |
| 4th left anterior axillary line | 0.71 (0.39–1.00) | 92.1 | 0.75 (0.37–1.00) | 90.5 |
| 4th right mid-axillary line | 0.77 (0.54–1.00) | 93.7 | 0.78 (0.47–1.00) | 90.5 |
| 4th left mid-axillary line | 0.77 (0.51–1.00) | 92.9 | 0.77 (0.43–1.00) | 90.5 |
| Posterior Thorax | ||||
| 8th right paravertebral line | 0.82 (0.56–1.00) | 95.2 | 0.66 (0.28–1.00) | 85.7 |
| 8th left paravertebral line | 0.94 (0.79–1.00) | 98.4 | 0.88 (0.62–1.00) | 95.2 |
| 8th right subscapular line | 0.89 (0.70–1.00) | 96.8 | 0.80 (0.51–1.00) | 90.5 |
| 8th left subscapular line | 0.80 (0.57–1.00) | 93.6 | 0.62 (0.26–1.00) | 80.9 |
| 8th right posterior axillary line | 0.92 (0.78–1.00) | 96.8 | 0.81 (0.53–1.00) | 90.5 |
| 8th left posterior axillary line | 0.96 (0.90–1.00) | 98.4 | 0.90 (0.69–1.00) | 95.2 |
| Semiquantitative and Binary Pleural Scores, Respectively | 0.84 (0.71–1.00) | 94.2 | 0.84 (0.69–1.00) | 93.3 |
| LUS Score | Cut-Off | AUROC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-Line Global Score | ≥3 | 0.74–0.77 | 60–80% | 75% |
| B-Line Binary Score | ≥1 | 0.80 | 60% | 100% |
| Semiquantitative Pleural Line Score | ≥2 | 0.82–0.87 | 90% | 50–75% |
| Binary Pleural Line Score | ≥4 | 0.77–0.81 | 60–80% | 75% |
| Authors, Date | Patients Included | US Machines, Scanning Protocol and Scores | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cogliati et al., 2014 [22] | RA patients with suspected or known ILD | (1) Standard US machine and convex probe
72 ICS: A total BL score > 10 = positive examination (presence of ILD) | Prior to the study, inter-observer variability r = 0.96 for BL quantification (72 ICS) Inter-explorer kappa = 0.78 for the presence of ILD (expert physicians with standard US equipment versus briefly trained physicians with a pocket-sized US machine) |
| Moazedi-Fuerst et al., 2014 [23] | RA patients without clinical or radiographic suspicion of ILD and HC | Standard US machine, convex probe for parenchyma and linear probe for pleural line, 18 ICS Pathology definitions: BL in >2 locations, pleural line thickening (>2.8 mm), pleural line fragmentation, subpleural nodules and negative lung sliding | Inter-observer kappa = 0.92 for the absence/presence of ILD |
| Gutiérrez et al., 2022 [29] | RA patients without a previous history of acute or chronic pulmonary diseases and HC | Standard US machine, 14 ICSs, linear probe Semiquantitative BL score: 0 = normal (≤5 BL), 1 = slight (≥6 and ≤15 BL), 2 = moderate (≤16 and ≥30 BL), and 3 = severe (≥30 BL) | Prior to the study, 8 patients with different CTD-ILD, with inter-observer kappa = 0.82 |
| Bandinelli et al., 2024 [40] | RA patients with mild respiratory symptoms | Standard US machine, 14 ICSs, linear probe and semiquantitative pleural (PLUS) and parenchymal (PAUS) scores # | US examiner: intra-reader ICC > 0.9 for both PLUS and PAUS; Trained residents: inter-reader ICC of 0.82–0.84 for PLUS and 0.86–0.94 for PAUS |
| Zabaleta et al., 2024 [41] | RA patients with chest HRCT in the 12 months prior to inclusion, regardless of symptomatology | Standard US machine, 14 ICSs, linear and convex probes Scores: Total number of BLs and pleural irregularities (PIs) | Prior to the study, inter-observer ICC = 0.97 for BL and ICC = 0.78 for PI and intra-observer ICC = 0.76 for BL ICC = 0.79 for PI |
| Watanabe et al., 2025 [42] | CTD-ILD patients with chest HRCT and LUS within an interval of <3 months | Standard US machine, 14 ICSs and microconvex probe Score: total number of BLs | Inter-rater ICC = 0.93 for the total B-line measurements |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Möller, I.; Mata, A.; Montes, N.; Rodríguez-Vargas, G.-S.; Coronel, L.; Bong, D.; Castañeda, S.; Santos-Moreno, P. A Proposal for a New Lung Ultrasound Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Reliability of Lung Ultrasound for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113701
Vicente-Rabaneda EF, Möller I, Mata A, Montes N, Rodríguez-Vargas G-S, Coronel L, Bong D, Castañeda S, Santos-Moreno P. A Proposal for a New Lung Ultrasound Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Reliability of Lung Ultrasound for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113701
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicente-Rabaneda, Esther Francisca, Ingrid Möller, Abdon Mata, Nuria Montes, Gabriel-Santiago Rodríguez-Vargas, Luis Coronel, David Bong, Santos Castañeda, and Pedro Santos-Moreno. 2025. "A Proposal for a New Lung Ultrasound Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Reliability of Lung Ultrasound for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113701
APA StyleVicente-Rabaneda, E. F., Möller, I., Mata, A., Montes, N., Rodríguez-Vargas, G.-S., Coronel, L., Bong, D., Castañeda, S., & Santos-Moreno, P. (2025). A Proposal for a New Lung Ultrasound Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Reliability of Lung Ultrasound for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113701









