Disproportionality Analysis of Renal Adverse Events Associated with a Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Acid-Suppressing Agents—A Pharmacovigilance Study Based on the FAERS Database
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Sources
2.2. Identification of Target AE Reports
2.3. Signal Mining
2.4. Descriptive Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Reporting Guidelines
3. Results
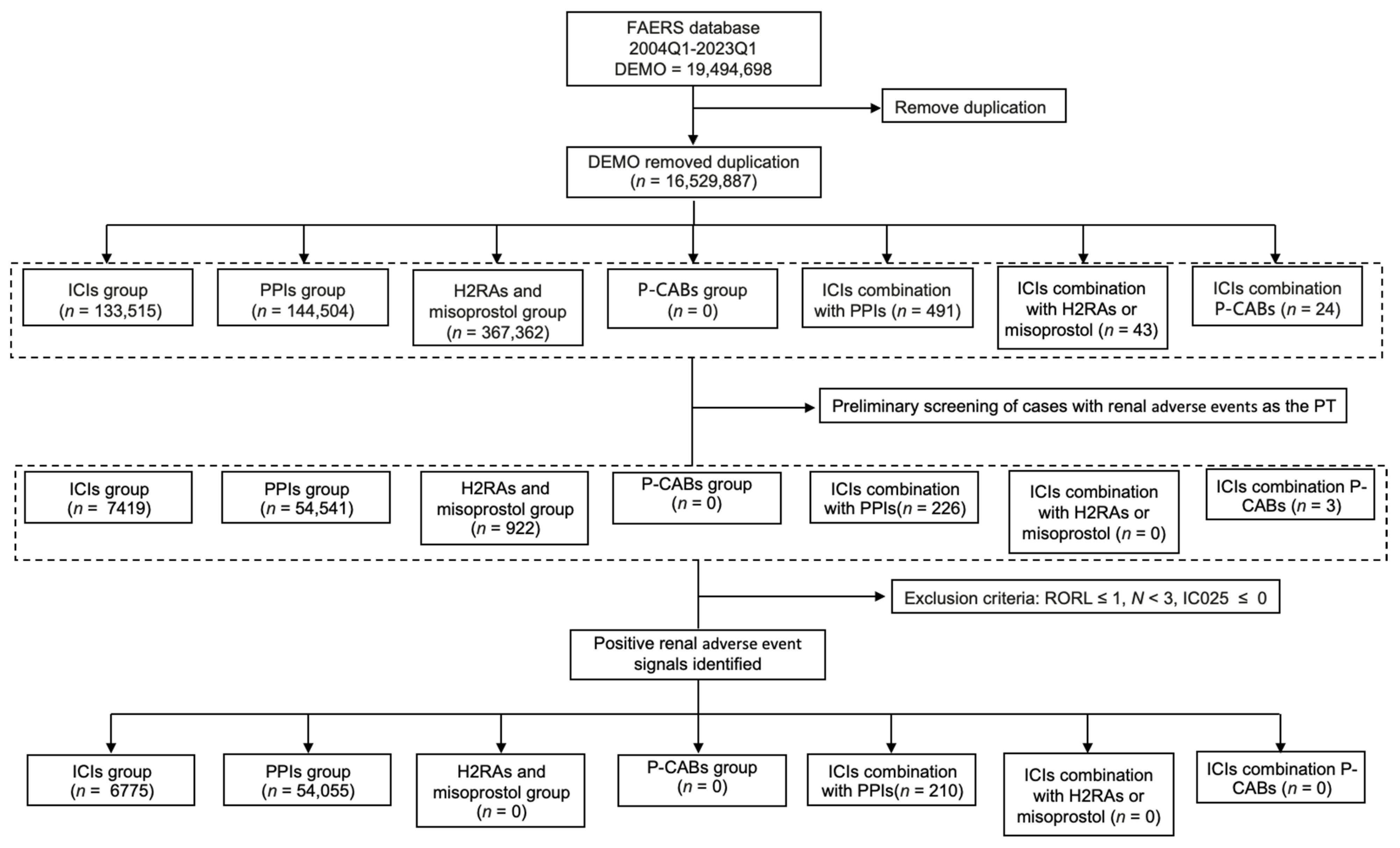
3.1. Scanning for rAEs in the FAERS Database
3.2. Descriptive Analysis of Cases with Renal AEs Under Different Treatments from the FAERS
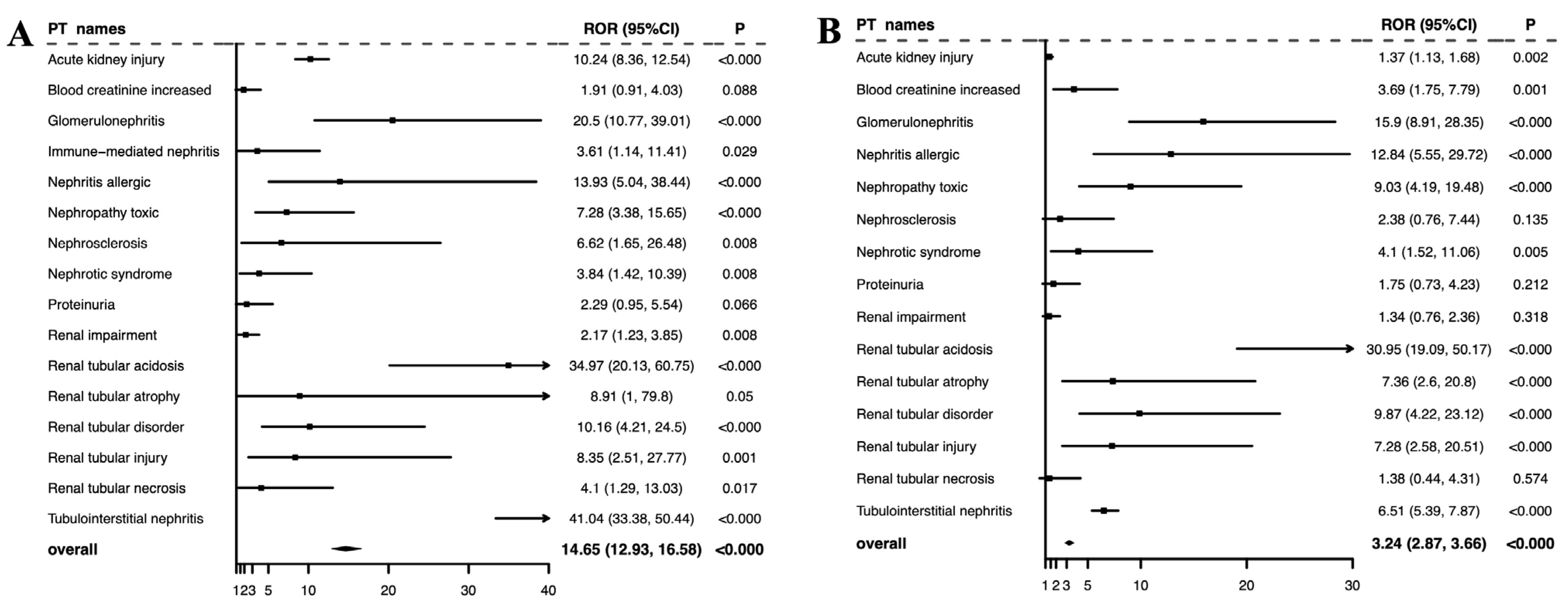
3.3. Signals of Disproportionate Reporting for ICI–PPI Combination Therapy Against Monotherapy
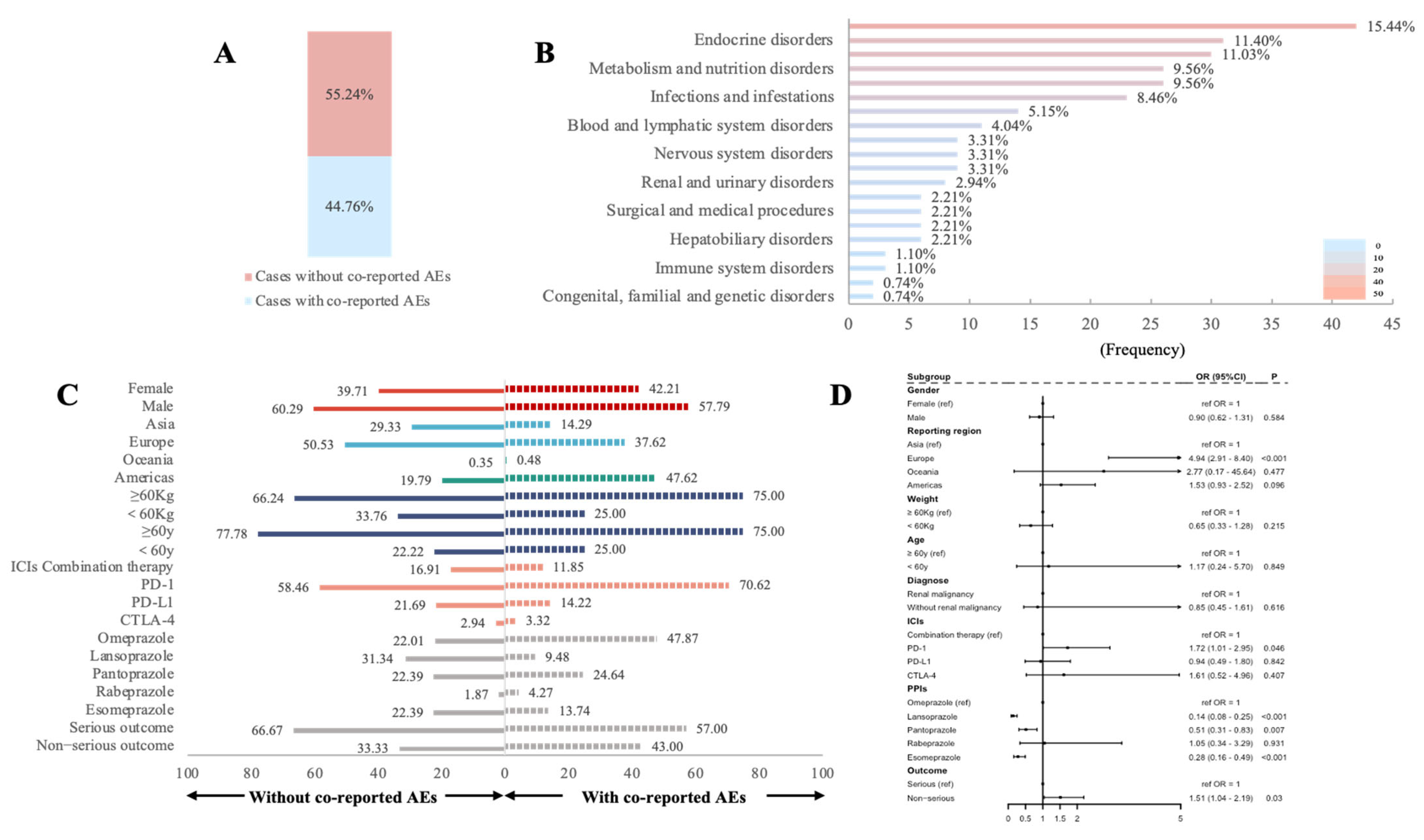
3.4. Influencing Factors for rAEs in PPIs Combined with ICIs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICIs | immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| PPIs | proton pump inhibitors |
| rAEs | renal adverse events |
| ASAs | acid-suppressing agents |
| H2RAs | histamine-2 receptor antagonists |
| P-CABs | potassium-competitive acid blockers |
| FAERS | the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| PS | primary suspect |
| PT | preferred term |
| SOC | System organ class |
| ROR | reporting odds ratio |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| IQR | interquartile range |
References
- Naimi, A.; Mohammed, R.N.; Raji, A.; Chupradit, S.; Yumashev, A.V.; Suksatan, W.; Shalaby, M.N.; Thangavelu, L.; Kamrava, S.; Shomali, N.; et al. Tumor immunotherapies by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); the pros and cons. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okiyama, N.; Tanaka, R. Immune-related adverse events in various organs caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Marrone, K.A.; Troxell, M.L.; Ralto, K.M.; Hoenig, M.P.; Brahmer, J.R.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Glezerman, I.G.; Wolchok, J.; et al. Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espi, M.; Teuma, C.; Novel-Catin, E.; Maillet, D.; Souquet, P.J.; Dalle, S.; Koppe, L.; Fouque, D. Renal adverse effects of immune checkpoints inhibitors in clinical practice: ImmuNoTox study. Eur. J. Cancer. 2021, 147, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraz-Muñoz, A.; Amir, E.; Ng, P.; Avila-Casado, C.; Ragobar, C.; Chan, C.; Kim, J.; Wald, R.; Kitchlu, A. Acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: Incidence, risk factors and outcomes. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethapathy, H.; Zhao, S.; Chute, D.F.; Zubiri, L.; Oppong, Y.; Strohbehn, I.; Cortazar, F.B.; Leaf, D.E.; Mooradian, M.J.; Villani, A.-C.; et al. The Incidence, Causes, and Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Cortazar, F.B.; Riella, L.V.; Leaf, D.E. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Nephrotoxicity: Update 2020. Kidney360 2020, 1, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wei, W.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Yi, C.; Pu, Y.; Yin, T.; Na, F.; Zhang, L.; Fu, P.; et al. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1173952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champiat, S.; Lambotte, O.; Barreau, E.; Belkhir, R.; Berdelou, A.; Carbonnel, F.; Cauquil, C.; Chanson, P.; Collins, M.; Durrbach, A.; et al. Management of immune checkpoint blockade dysimmune toxicities: A collaborative position paper. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Gao, Y.; Kong, Z.; Wang, J.; Si, S.; Han, W.; Li, J.; Lv, Z.; Wang, R. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and acute kidney injury. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1353339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chute, D.F.; Zhao, S.; Strohbehn, I.A.; Rusibamayila, N.; Seethapathy, H.; Lee, M.; Zubiri, L.; Gupta, S.; Leaf, D.E.; Rahma, O.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of CKD and Estimated GFR Decline in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Abudayyeh, A.; Gupta, S.; Gudsoorkar, P.; Klomjit, N.; Motwani, S.S.; Karam, S.; Costa, E.S.V.T.; Khalid, S.B.; Anand, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated nephrotoxicity: A position statement from the American Society of Onco-nephrology. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.; Obeid, M.; Spain, L.; Carbonnel, F.; Wang, Y.; Robert, C.; Lyon, A.R.; Wick, W.; Kostine, M.; Peters, S.; et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Xu, M.; Patel, S.; Johns, A.; Grogan, M.; Li, M.; Lopez, G.; Miah, A.; Hoyd, R.; Liu, Y.; et al. Proton pump inhibitor use (PPI) in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) for advanced cancer: Survival and prior therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawachi, H.; Yamada, T.; Tamiya, M.; Negi, Y.; Goto, Y.; Nakao, A.; Shiotsu, S.; Tanimura, K.; Takeda, T.; Okada, A.; et al. Concomitant Proton Pump Inhibitor Use With Pembrolizumab Monotherapy vs Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Plus Chemotherapy in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2322915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.; Merza, N.; Qatani, A.; Rahim, M.; Varughese, T.; Mohammad, A.; Masood, F.; Reza, F.Z.; Wan, S.; Almas, T. Impact of proton-pump inhibitors on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 78, 103752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahim, M.; Mamlouk, O.; Lin, H.; Lin, J.; Page, V.; Abdel-Wahab, N.; Swan, J.; Selamet, U.; Yee, C.; Diab, A.; et al. Incidence, predictors, and survival impact of acute kidney injury in patients with melanoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A 10-year single-institution analysis. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1927313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Herrmann, S.M. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and their interaction with proton pump inhibitors-related interstitial nephritis. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; You, R. Hepatitis-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients: An observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study using the FAERS database. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1383212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaroli, M.; Raschi, E.; Poluzzi, E.; Hauben, M. The evolving role of disproportionality analysis in pharmacovigilance. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2024, 23, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, A.; Edwards, I.R. Data mining in spontaneous reports. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 98, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, J.E.; Manouchehri, A.; Moey, M.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Bastarache, L.; Pariente, A.; Gobert, A.; Spano, J.P.; Balko, J.M.; Bonaca, M.P.; et al. Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: An observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaroli, M.; Salvo, F.; Begaud, B.; AlShammari, T.M.; Bate, A.; Battini, V.; Brueckner, A.; Candore, G.; Carnovale, C.; Crisafulli, S.; et al. The Reporting of a Disproportionality Analysis for Drug Safety Signal Detection Using Individual Case Safety Reports in PharmacoVigilance (READUS-PV): Development and Statement. Drug Saf. 2024, 47, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.-S.; Wu, R.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.-D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.-F.; Chen, X.-M.; He, K.-L.; Cai, G.-Y. Incidence, risk factors and prognosis of acute kidney injury in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geevasinga, N.; Coleman, P.L.; Webster, A.C.; Roger, S.D. Proton pump inhibitors and acute interstitial nephritis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, A.O.; Andreani, M.; Fresse, A.; Parassol, N.; Muzzone, M.; Pinel, S.; Bourneau-Martin, D.; Borchiellini, D.; Rocher, F.; Esnault, V.L.M.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced nephropathy: A French national survey. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanchoo, R.; Karam, S.; Uppal, N.N.; Barta, V.S.; Deray, G.; Devoe, C.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Jhaveri, K.D. Adverse Renal Effects of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Narrative Review. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethapathy, H.; Herrmann, S.M.; Sise, M.E. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Kidney Toxicity: Advances in Diagnosis and Management. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, K.; Hao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, Z.; Qi, G.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; et al. Nephrotoxicity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Disproportionality Analysis from 2013 to 2020. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2021, 254, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.; Burtey, S.; Mancini, J.; Pelletier, M.; Sallée, M.; Brunet, P.; Berbis, P.; Grob, J.J.; Honoré, S.; Gaudy, C.; et al. Acute kidney injury in patients treated with anti-programmed death receptor-1 for advanced melanoma: A real-life study in a single-centre cohort. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, D.C.F.; Gasparini, A.; Xu, H.; de Deco, P.; Trevisan, M.; Johansson, A.L.V.; Wettermark, B.; Ärnlöv, J.; Janmaat, C.J.; Lindholm, B.; et al. Association Between Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and Risk of Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Li, T.; Xian, H.; Yan, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Long-term kidney outcomes among users of proton pump inhibitors without intervening acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, D.; Xu, T.; Luo, M.; He, Z.; Li, Y. Proton pump inhibitors associated acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: Data mining of US FDA adverse event reporting system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Mizuno, T.; Koseki, T.; Ito, Y.; Hatano, M.; Takahashi, K.; Yamada, S.; Tsuboi, N. Concomitant Proton Pump Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Increase Nephritis Frequency. Vivo 2021, 35, 2831–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smelick, G.S.; Heffron, T.P.; Chu, L.; Dean, B.; West, D.A.; Duvall, S.L.; Lum, B.L.; Budha, N.; Holden, S.N.; Benet, L.Z.; et al. Prevalence of acid-reducing agents (ARA) in cancer populations and ARA drug-drug interaction potential for molecular targeted agents in clinical development. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4055–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Chesdachai, S.; Panjawatanana, P.; Ungprasert, P.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Associations of Proton-Pump Inhibitors and H2 Receptor Antagonists with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chiou, W.-Y.; Yu, B.-H. Impact of Acid Suppression Therapy on Renal and Survival Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Taiwanese Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, K. Vonoprazan fumarate, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, in the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease: Safety and clinical evidence to date. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756283X17745776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PT Names | rAEs Reported in Full Database | ICI Monotherapy | PPI Monotherapy | ICIs Combined with PPIs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rAEs Reported | ROR (95% CI) | IC025 | rAEs Reported | ROR (95% CI) | IC025 | rAEs Reported | ROR (95% CI) | IC025 | ||
| Acute kidney injury | 160,761 | 2121 | 1.86 (1.79, 1.95) | 0.81 | 22,727 | 16.63 (16.40, 16.87) | 3.77 | 104 | 18.22 (14.94, 22.22) | 3.91 |
| Increased blood creatinine | 55,109 | 708 | 1.81 (1.68, 1.95) | 0.72 | 455 | 0.81 (0.73, 0.88) | −0.46 | 7 | 3.13 (1.49, 6.57) | 0.67 |
| Glomerulonephritis | 1917 | 33 | 2.38 (1.69, 3.36) | 0.71 | 104 | 5.44 (4.46, 6.62) | 2.09 | 13 | 23.88 (13.81, 41.29) | 6.73 |
| Immune-mediated nephritis | 147 | 97 | 113.44 (80.64, 159.57) | 6.20 | 0 | N/A | N/A | 3 | 6.93 (2.21, 21.79) | 7.36 |
| Nephritis allergic | 304 | 8 | 3.23 (1.60, 6.53) | 0.76 | 25 | 7.54 (5.01, 11.35) | 2.37 | 7 | 14.70 (6.94, 31.15) | 8.18 |
| Nephropathy toxic | 8183 | 115 | 1.97 (1.64, 2.37) | 0.67 | 98 | 1.17 (0.96, 1.43) | −0.10 | 7 | 9.60 (4.57, 20.16) | 3.43 |
| Nephrosclerosis | 1055 | 6 | 0.81 (1.80, 0.36) | −1.63 | 287 | 34.11 (29.78, 39.06) | 4.54 | 3 | 6.53 (2.10, 20.29) | 4.51 |
| Nephrotic syndrome | 5491 | 139 | 3.58 (3.02, 4.24) | 1.55 | 177 | 3.21 (2.76, 3.72) | 1.41 | 4 | 6.53 (2.45, 17.42) | 2.80 |
| Proteinuria | 14,321 | 393 | 3.91 (3.54, 4.32) | 1.78 | 781 | 5.57 (5.19, 5.99) | 2.30 | 5 | 5.53 (2.3, 13.32) | 1.91 |
| Renal impairment | 66,302 | 1089 | 2.32 (2.19, 2.47) | 1.10 | 2622 | 4 (3.85, 4.16) | 1.89 | 12 | 4.50 (2.55, 7.94) | 1.47 |
| Renal tubular acidosis | 1609 | 30 | 2.57 (1.79, 3.69) | 0.80 | 68 | 4.17 (3.27, 5.32) | 1.66 | 22 | 40.60 (26.58, 62.01) | 7.95 |
| Renal tubular atrophy | 720 | 1 | 0.26 (0.04, 1.88) | −5.56 | 33 | 4.41 (3.11, 6.25) | 1.61 | 4 | 8.58 (3.21, 22.94) | 5.73 |
| Renal tubular disorder | 2487 | 29 | 1.62 (1.13, 2.34) | 0.11 | 47 | 1.85 (1.38, 2.47) | 0.42 | 6 | 11.10 (4.98, 24.77) | 4.82 |
| Renal tubular injury | 570 | 8 | 1.87 (0.93, 3.76) | −0.15 | 35 | 5.89 (4.18, 8.29) | 2.04 | 4 | 8.66 (3.24, 23.19) | 6.07 |
| Renal tubular necrosis | 7893 | 73 | 1.3 (1.03, 1.63) | −0.01 | 600 | 7.93 (7.29, 8.61) | 2.76 | 3 | 4.53 (1.46, 14.08) | 1.61 |
| Tubulointerstitial nephritis | 16,103 | 523 | 4.66 (4.27, 5.08) | 2.04 | 5506 | 50.61 (48.98, 52.29) | 5.02 | 117 | 115.74 (95.87, 139.73) | 7.42 |
| Clinical Characteristics | ICI Monotherapy (n = 6775) | PPI Monotherapy (n = 54,055) | ICIs in Combination with PPIs (n = 210) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reporting region | |||
| Americas | 2177 (32.13) | 51,052 (94.44) | 101 (48.1) |
| Oceania | 103 (1.52) | 120 (0.22) | 1 (0.48) |
| Africa | 15 (0.22) | 8 (0.01) | 0 (0) |
| Europe | 1860 (27.45) | 2415 (4.47) | 77 (36.67) |
| Asia | 2615 (38.6) | 296 (0.55) | 30 (14.29) |
| Missing | 5 (0.07) | 164 (0.3) | 1 (0.48) |
| Reporters | |||
| Healthcare professionals | 5577 (82.32) | 7110 (13.15) | 204 (97.14) |
| Non-healthcare professionals | 1170 (17.27) | 28,700 (53.09) | 4 (1.9) |
| Missing | 28 (0.41) | 18,245 (33.75) | 2 (0.95) |
| Reporting year | |||
| 2004–2008 | 0 (0) | 343 (0.63) | 0 (0) |
| 2009–2013 | 50 (0.74) | 823 (1.52) | 0 (0) |
| 2014–2018 | 1830 (27.01) | 13,349 (24.7) | 32 (15.24) |
| 2019–2023 Q1 | 4895 (72.25) | 39,540 (73.15) | 178 (84.76) |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 4245 (62.66) | 13,313 (24.63) | 115 (54.76) |
| Female | 2052 (30.29) | 18,291 (33.84) | 82 (39.05) |
| Missing | 478 (7.06) | 22,451 (41.53) | 13 (6.19) |
| Age at onset, years | 70 (61−75); n = 737 | 61 (54−68); n = 527 | 60 (59.5−62); n = 16 |
| Diagnosis of renal malignancy | 114 (1.68) | 11 (0.02) | 19 (19.05) |
| Drugs | |||
| ICIs | 5510 (81.33) | N/A | 186 (88.57) |
| Nivolumab | 1896 (27.99) | N/A | 89 (42.38) |
| Pembrolizumab | 2119 (31.28) | N/A | 61 (29.05) |
| Cemiplimab | 70 (1.03) | N/A | 0 (0) |
| Atezolizumab | 961 (14.18) | N/A | 18 (8.57) |
| Avelumab | 74 (1.09) | N/A | 2 (0.95) |
| Durvalumab | 142 (2.1) | N/A | 9 (4.29) |
| Ipilimumab | 247 (3.65) | N/A | 7 (3.33) |
| Tremelimumab | 1 (0.01) | N/A | 0 (0) |
| Combination therapy | 1265 (18.67) | N/A | 24 (11.43) |
| Nivolumab plus ipilimumab | 1238 (18.27) | N/A | 21 (10) |
| Pembrolizumab plus ipilimumab | 15 (0.22) | N/A | 3 (1.43) |
| Tremelimumab plus durvalumab | 10 (0.15) | N/A | 0 (0) |
| Atezolizumab plus Ipilimumab | 2 (0.03) | N/A | 0 (0) |
| PPIs | |||
| Omeprazole | N/A | 4875 (9.02) | 101 (48.1) |
| Lansoprazole | N/A | 15,174 (28.07) | 21 (10) |
| Pantoprazole | N/A | 10,486 (19.4) | 52 (24.76) |
| Rabeprazole | N/A | 867 (1.6) | 9 (4.29) |
| Esomeprazole | N/A | 19,828 (36.68) | 29 (13.81) |
| Dexlansoprazole | N/A | 2825 (5.23) | 0 (0) |
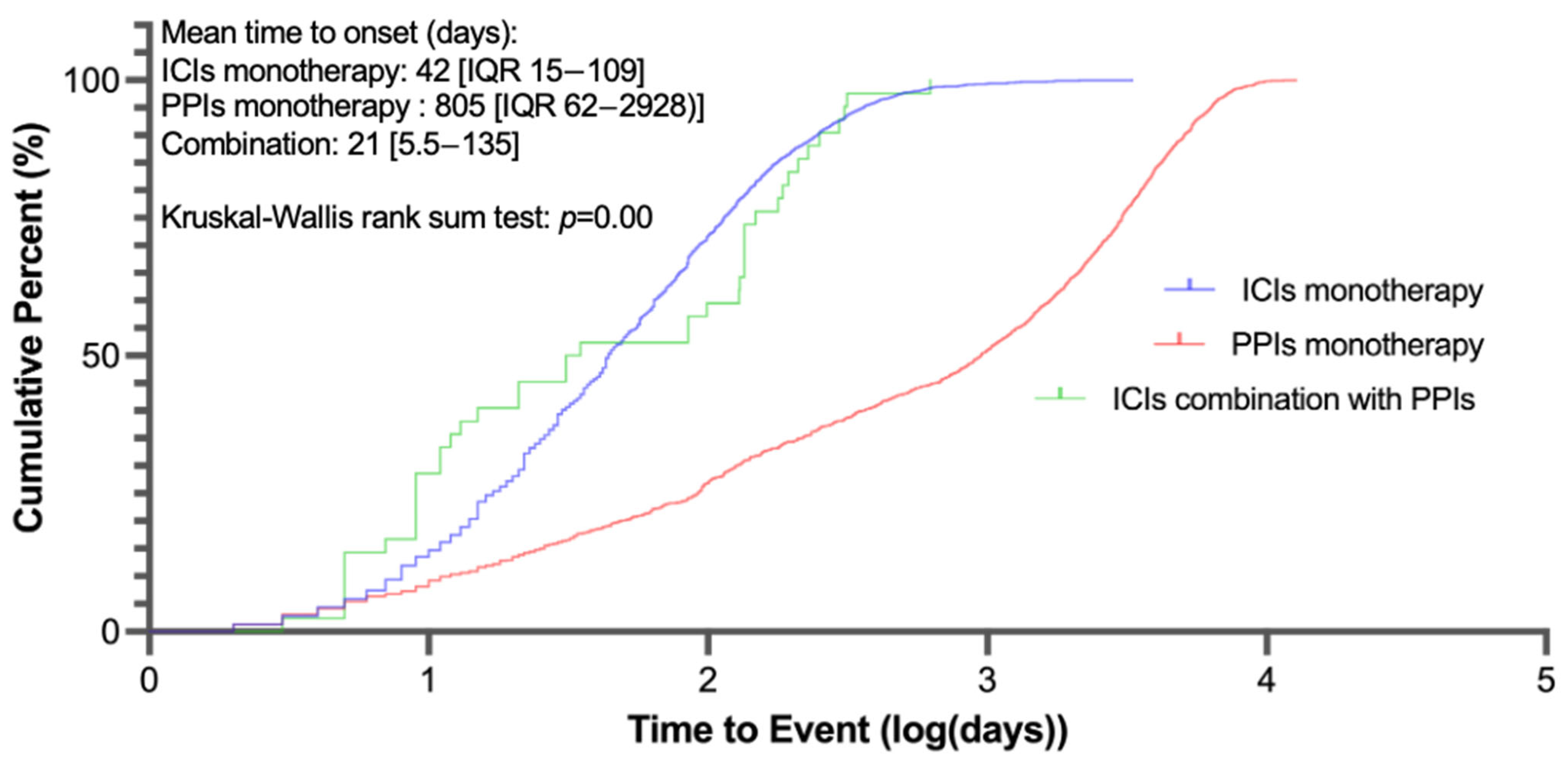
| Time to rAE onset, days | 42(15−109); n = 3033 | 805 (62−2928); n = 3261 | 21 (5.5−135); n = 50 |
| Serious outcome | |||
| Death | 1317 (19.44) | 6000 (11.1) | 9 (4.29) |
| Life-threatening | 766 (11.31) | 632 (1.17) | 24 (11.43) |
| Hospitalization | 4147 (61.21) | 6390 (11.82) | 115 (54.76) |
| Disability | 211 (3.11) | 789 (1.46) | 5 (2.38) |
| Others | 5559 (82.05) | 51,215 (94.75) | 163 (77.62) |
| Missing | 178 (2.63) | 1012 (1.87) | 1 (0.48) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H.; Li, S.; Fu, Z.; You, R. Disproportionality Analysis of Renal Adverse Events Associated with a Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Acid-Suppressing Agents—A Pharmacovigilance Study Based on the FAERS Database. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103581
Liu J, Chen X, Zhang C, Hu H, Li S, Fu Z, You R. Disproportionality Analysis of Renal Adverse Events Associated with a Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Acid-Suppressing Agents—A Pharmacovigilance Study Based on the FAERS Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103581
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinmei, Xu Chen, Cong Zhang, Huiping Hu, Shijun Li, Zhiwen Fu, and Ruxu You. 2025. "Disproportionality Analysis of Renal Adverse Events Associated with a Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Acid-Suppressing Agents—A Pharmacovigilance Study Based on the FAERS Database" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103581
APA StyleLiu, J., Chen, X., Zhang, C., Hu, H., Li, S., Fu, Z., & You, R. (2025). Disproportionality Analysis of Renal Adverse Events Associated with a Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Acid-Suppressing Agents—A Pharmacovigilance Study Based on the FAERS Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103581






