Prevalence of Osteosynthesis Hardware Removal Due to Surgical Site Infections Following Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
- Inclusion Criteria: Patients aged over 18 years with dentofacial deformities.
- Inclusion Criteria: Patients undergoing SSRO, either as a standalone procedure or in combination with other orthognathic surgeries.
- Exclusion Criteria: Patients undergoing alternative mandibular orthognathic procedures (e.g., IVRO) [14,15,16], patients undergoing reoperation, patients solely with specific comorbidity, studies where the surgical procedure was not well-defined [17], studies including multiple fixation methods within the same cohort.
- Inclusion Criteria: Hardware removal due to SSI.
- Inclusion Criteria: Observational studies written in English.
- Exclusion Criteria: Case reports and case series with fewer than 30 patients, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, narrative reviews, and other review articles, interventional studies, including randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-RCTs, conference abstracts, letters to the editor, expert opinion, retracted articles, articles with no full text available, and articles written in languages other than English [23].
2.2. Information Source
2.3. Search Strategy
- Medline/PMC Central: (mandib* OR lower jaw) AND (orthognathic OR corrective jaw OR bilateral sagittal split osteotom* OR osteotom*) AND (infect* OR sequal* OR complicat*), Filters: None
- Scopus: ((mandib* OR (lower AND jaw)) AND (orthognathic OR (corrective AND jaw) OR (bilateral AND sagittal AND split AND osteotom*) OR osteotom*) AND (infect* OR sequal* OR complicat*)), Filters: Title-Abstract-Keywords
- Web of Science: ((mandib* OR (lower AND jaw)) AND (orthognathic OR (corrective AND jaw) OR (bilateral AND sagittal AND split AND osteotom*) OR osteotom*) AND (infect* OR sequal* OR complicat*)), Filters: Articles, English language
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Effect Measure
2.8. Statistical Analysis
- 0–40%: Not significant
- 30–60%: Moderate
- 50–90%: Significant
- 75–100%: Substantial heterogeneity [25]
3. Results
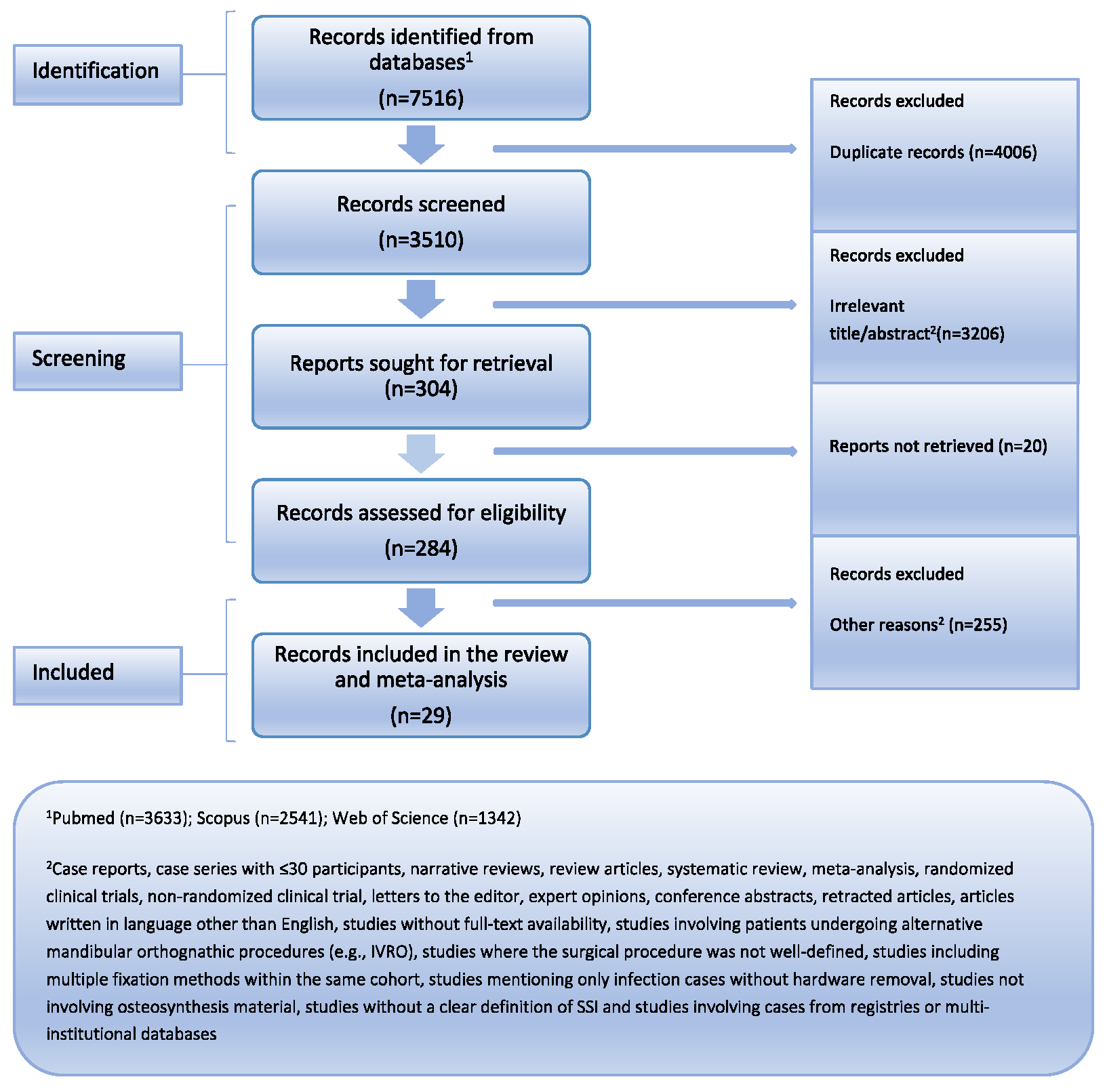
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
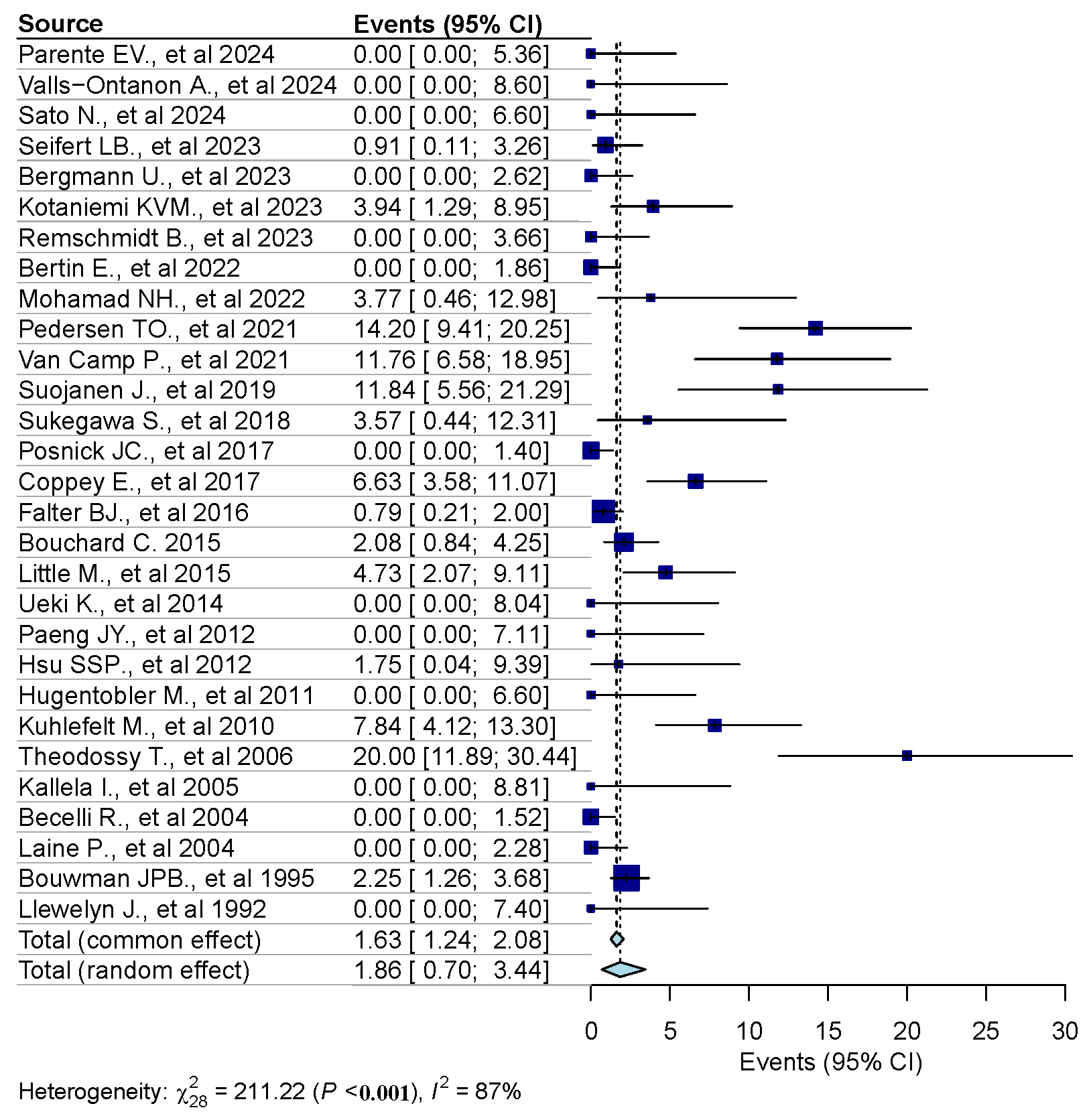
3.3. Results of Syntheses
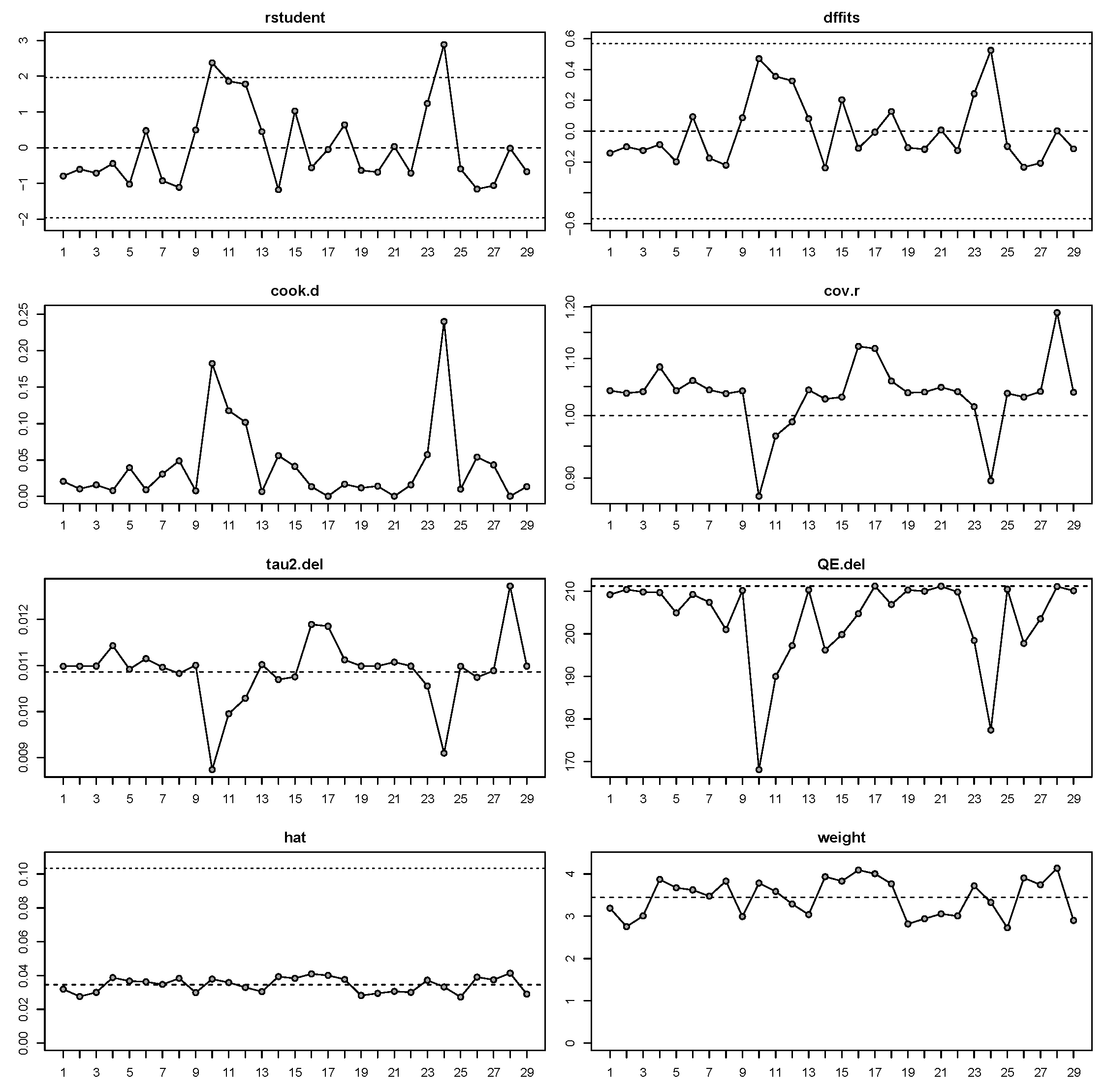
3.4. Meta-Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSRO | Sagittal split ramus osteotomy |
| SSI | Surgical site infection |
| IVRO | Intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy |
| RR | Risk ratio |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trials |
| ORIF | Open reduction and internal fixation |
| OIA | Osteosynthesis-associated infections |
References
- Monson, L. Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2013, 27, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, J.P.; Houppermans, P.N.W.J.; Gooris, P.; Mensink, G.; Van Merkesteyn, J.P.R. Risk Factors for Common Complications Associated with Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostares, E.; Kostares, M.; Kostare, G.; Kantzanou, M. Prevalence of lingual sensory impairment following bilateral sagittal split osteotomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 28, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, B.B.; Da Silveira, M.L.M.; Dantas, W.R.M.; Almeida, R.A.C.; Germano, A.R. Does the Presence of Third Molars during Sagittal Split Mandibular Ramus Osteotomy Favour Complications? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaglo, A.; Leslie, S.W.; Sharman, T. Postoperative Wound Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560533/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Borchardt, R.A.; Tzizik, D. Update on surgical site infections: The new CDC guidelines. J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2018, 31, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friscia, M.; Sbordone, C.; Petrocelli, M.; Vaira, L.A.; Attanasi, F.; Cassandro, F.M.; Paternoster, M.; Iaconetta, G.; Califano, L. Complications after Orthognathic Surgery: Our Experience on 423 Cases. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 21, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.M.; Sargeant, J.M. Meta-Analyses Including Data from Observational Studies. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmar, C.L.; Humphries, L.S.; Zimmerman, C.E.; Vu, G.H.; Swanson, J.W.; Bartlett, S.P.; Taylor, J.A. Orthognathic Hardware Complications in the Era of Patient-Specific Implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 609e–621e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.R.-F.; Chuang, K.-T.; Hsu, S.S.-P.; Chen, Y.-R.; Chen, C.-T. Modification of Sagittal Split Osteotomy in Class II Asymmetry: Optimizing Bone Contact between Proximal and Distal Segments. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 153, 1142e–1151e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Moroi, A.; Yoshizawa, K. Stability of the Chin after Advancement Genioplasty Using Absorbable Plate and Screws with Template Devices. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariña, R.; Valladares-Pérez, S.; Navarro-Cuellar, C.; Torrealba, R.; Fariña-Silva, A.; Fariña-Silva, G. M-Shaped Genioplasty: New Findings after 10 Years of Experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2023, 11, e4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, O.; Mahmoud, R.; Shuster, A.; Arbel, S.; Kleinman, S.; Mijiritsky, E.; Ianculovici, C. Vertical Ramus Osteotomy, Is It Still a Valid Tool in Orthognathic Surgery? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi Claus, J.D.; Almeida, M.S.; Correia Lopes, H.J.; Bustos Aguilera, L.M.; Soto, J. Angled Screws With Locking Plates—An Alternative Fixation for Minimally Invasive Mandibular Orthognathic Surgery. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2025, 36, e77–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeberger, R.; Asi, Y.; Thiele, O.C.; Hoffmann, J.; Stucke, K.; Engel, M. Neurosensory Alterations and Function of the Temporomandibular Joint after High Oblique Sagittal Split Osteotomy: An Alternative Technique in Orthognathic Surgery. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høgevold, H.E.; Mobarak, K.A.; Espeland, L.; Krogstad, O.; Skjelbred, P. Plate Fixation of Extra-Oral Subcondylar Ramus Osteotomy for Correction of Mandibular Prognathism: Clinical Aspects and Short Term Stability. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 29, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velich, N.; Németh, Z.; Suba, C.; Szabó, G. Removal of Titanium Plates Coated with Anodic Titanium Oxide Ceramic: Retrospective Study. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2002, 13, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widar, F.; Afshari, M.; Rasmusson, L.; Dahlin, C.; Kashani, H. Incidence and Risk Factors Predisposing Plate Removal Following Orthognathic Surgery. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017, 124, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Wahab, P.U.; Senthil Nathan, P.; Madhulaxmi, M.; Muthusekhar, M.R.; Loong, S.C.; Abhinav, R.P. Risk Factors for Post-Operative Infection Following Single Piece Osteotomy. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2017, 16, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpha, C.; O’Ryan, F.; Silva, A.; Poor, D. The Incidence of Postoperative Wound Healing Problems Following Sagittal Ramus Osteotomies Stabilized with Miniplates and Monocortical Screws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoedler, S.; Baecher, H.; Hoch, C.C.; Obed, D.; Matar, D.Y.; Rendenbach, C.; Kim, B.-S.; Harhaus, L.; Kauke-Navarro, M.; Hundeshagen, G.; et al. Early Outcomes and Risk Factors in Orthognathic Surgery for Mandibular and Maxillary Hypo- and Hyperplasia: A 13-Year Analysis of a Multi-Institutional Database. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.K.; Silverstein, M.; Cevallos, P.; Johnstone, T.; Wu, R.; Nazerali, R.; Bruckman, K. Risk Factors for Hardware Removal Following Bimaxillary Surgery: A National Database Analysis. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2024, 35, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Oh, J.-S.; Shin, S.-H.; Kim, S.-G. Removal of miniplates following facial trauma and orthognathic surgery: A 3-year study. Oral Biol. Res. 2018, 42, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y. Using Freeman-Tukey Double Arcsine Transformation in Meta-Analysis of Single Proportions. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/chapter_9/9_5_2_identifying_and_measuring_heterogeneity.htm (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/chapter_9/9_6_4_meta_regression.htm (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Barker, T.H.; Migliavaca, C.B.; Stein, C.; Colpani, V.; Falavigna, M.; Aromataris, E.; Munn, Z. Conducting Proportional Meta-Analysis in Different Types of Systematic Reviews: A Guide for Synthesisers of Evidence. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, E.V.; Silvares, M.G.; Zerbinatti, D.C.Z.; Da Silva Pinto, S. Minimally Invasive Sagittal Osteotomy—Technical Note. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 53, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posnick, J.C.; Choi, E.; Chavda, A. Method of Osteotomy Fixation and Need for Removal Following Bimaxillary Orthognathic, Osseous Genioplasty, and Intranasal Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlefelt, M.; Laine, P.; Suominen-Taipale, L.; Ingman, T.; Lindqvist, C.; Thorén, H. Risk Factors Contributing to Symptomatic Miniplate Removal: A Retrospective Study of 153 Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy Patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodossy, T.; Jackson, O.; Petrie, A.; Lloyd, T. Risk Factors Contributing to Symptomatic Plate Removal Following Sagittal Split Osteotomy. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.H.; Murugesan, R.; Soh, C.L.; Singh, J. A 7-Year Retrospective Analysis of Titanium Plates Removal Following Orthognathic Surgery. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2022, 21, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Ontañón, A.; Kesmez, Ö.; Starch-Jensen, T.; Triginer-Roig, S.; Neagu-Vladut, D.; Hernández-Alfaro, F. Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy with or without Concomitant Removal of Third Molars: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Related Complications and Bone Healing. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 28, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Denadai, R.; Hung, Y.-T.; Chung, K.H.; Chou, P.-Y.; Pai, B.C.J.; Lo, L.-J.; Lin, H.-H. Single-Splint, 2-Jaw Orthognathic Surgery for Correction of Facial Asymmetry: 3-Dimensional Planning and Surgical Execution. J. Craniofacial. Surg. 2023, 35, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, L.B.; Langhans, C.; Berdan, Y.; Zorn, S.; Klos, M.; Landes, C.; Sader, R. Comparison of Two Surgical Techniques (HOO vs. BSSO) for Mandibular Osteotomies in Orthognathic Surgery—A 10-Year Retrospective Study. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 27, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Camp, P.; Verstraete, L.; Van Loon, B.; Scheerlinck, J.; Nout, E. Antibiotics in Orthognathic Surgery: A Retrospective Analysis and Identification of Risk Factors for Postoperative Infection. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suojanen, J.; Järvinen, S.; Hodzic, Z.; Reunanen, J.; Leikola, J.; Stoor, P. No Differences in Infections between Patient-Specific Implants and Conventional Mini-Plates in Mandibular Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy—Up to 3-Year Follow-Up. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falter, B.; Abeloos, J.; De Clercq, C.; Neyt, N.; Lamoral, P.; Swennen, G.R.J. Transoral Fixation of Bicortical Screws Is Safe and Feasible for Lower Jaw Osteotomies. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 2285.e1–2285.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Okabe, K.; Marukawa, K.; Mukozawa, A.; Moroi, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Sotobori, M.; Ishihara, Y.; Yoshizawa, K.; Ooi, K. Skeletal Stability after Mandibular Setback Surgery: Comparison between the Hybrid Technique for Fixation and the Conventional Plate Fixation Using an Absorbable Plate and Screws. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paeng, J.-Y.; Hong, J.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, M.-J. Comparative Study of Skeletal Stability between Bicortical Resorbable and Titanium Screw Fixation after Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy for Mandibular Prognathism. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becelli, R.; Fini, G.; Renzi, G.; Giovannetti, F.; Roefaro, E. Complications of Bicortical Screw Fixation Observed in 482 Mandibular Sagittal Osteotomies. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2004, 15, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, U.; Jónsdóttir, O.H.; Bergmann, J.B.; Björnsson, G.Á. In-Office Outpatient Orthognathic Surgery: Review of 254 Cases Where the Patients Were Discharged the Same Day. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaniemi, K.V.M.; Suojanen, J.; Palotie, T. Complications and Associated Risk Factors for Bimaxillary Osteotomies: A 15-Year Single-Center Retrospective Study. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2023, 34, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remschmidt, B.; Schwaiger, M.; Gaessler, J.; Wallner, J.; Zemann, W.; Schwaiger, M. Surgical Site Infections in Orthognathic Surgery: Prolonged versus Single-Dose Antibiotic Prophylaxis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, E.; Meyer, C.; Chatelain, B.; Barrabé, A.; Weber, E.; Louvrier, A. Does Penicillin Allergy Increase the Risk of Surgical Site Infection after Orthognathic Surgery? A Multivariate Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, T.Ø.; Haaberg, V.; Løes, S. Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Mandibular Advancement with Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Comparison of Three versus Four Doses Penicillin V. Oral Surg. 2021, 14, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Manabe, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Sukegawa-Takahashi, Y.; Masui, M.; Furuki, Y. Is the Removal of Osteosynthesis Plates after Orthognathic Surgery Necessary? Retrospective Long-Term Follow-up Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppey, E.; Mommaerts, M.Y. Early Complications From the Use of Calcium Phosphate Paste in Mandibular Lengthening Surgery. A Retrospective Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1274.e1–1274.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, C.; Lalancette, M. Infections After Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Retrospective Analysis of 336 Patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.; Langford, R.J.; Bhanji, A.; Farr, D. Plate Removal Following Orthognathic Surgery. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.S.-P.; Huang, C.-S.; Chen, P.K.-T.; Ko, E.W.-C.; Chen, Y.-R. The Stability of Mandibular Prognathism Corrected by Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomies: A Comparison of Bi-Cortical Osteosynthesis and Mono-Cortical Osteosynthesis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugentobler, M.; Lenoir, V.; Scolozzi, P. Mandibular Sagittal Split Osteotomy: Is a Bicortical 2-Screw Osteosynthesis Adequate? J. Craniofacial Surg. 2011, 22, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallela, I.; Laine, P.; Suuronen, R.; Lindqvist, C.; Iizuka, T. Assessment of Material- and Technique-Related Complications Following Sagittal Split Osteotomies Stabilized by Biodegradable Polylactide Screws. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2005, 99, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, P.; Kontio, R.; Lindqvist, C.; Suuronen, R. Are There Any Complications with Bioabsorbable Fixation Devices? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, J.P.B.; Husak, A.; Putnam, G.D.; Becking, A.G.; Tuinzing, D.B. Screw Fixation Following Bilateral Sagittal Ramus Osteotomy for Mandibular Advancement—Complications in 700 Consecutive Cases. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1995, 33, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewelyn, J.; Sugar, A. Lag Screws in Sagittal Split Osteotomies: Should They Be Removed? Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 30, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirk, M.; Markewitsch, W.; Peters, F.; Kröger, N.; Lentzen, M.-P.; Zoeller, J.E.; Zinser, M. Osteosynthesis-Associated Infection in Maxillofacial Surgery by Bacterial Biofilms: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 11 Years. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 4401–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal; Rohit; Prajapati, V.; Shahi, A.; Prakash, O. Significance of Microbial Analysis during Removal of Miniplates at Infected Sites in the Craniomaxillofacial Region—An Evaluative Study. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostares, E.; Kostare, G.; Kostares, M.; Kantzanou, M. Prevalence of Surgical Site Infections after Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Mandibular Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareb, B.; Van Bakelen, N.B.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Vissink, A.; Bos, R.R.M.; Van Minnen, B. Efficacy and Morbidity of Biodegradable versus Titanium Osteosyntheses in Orthognathic Surgery: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 129, e12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Barrachina, R.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; García-Sanz, V.; Almerich-Silla, J.M.; Paredes-Gallardo, V.; Bellot-Arcís, C. Titanium Plate Removal in Orthognathic Surgery: Prevalence, Causes and Risk Factors. A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Year of Publication | Study Design | Continent of Origin | Country | Study Period | Total Patients | Proportion of Males | Mean Age | Osteosynthesis Materials Removal Due to SSI | Removal Rate Due to Infection (%) | Quality Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parente EV., et al. [28] | 2024 | Cross-sectional | South America | Brazil | 2020–2022 | 67 | 28.4 | 34 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Valls-Ontanon A., et al. [33] | 2024 | Cohort | Europe | Spain | 2018–2019 | 41 | 46.3 | 30.8 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Sato N., et al. [34] | 2024 | Cohort | Asia | Taiwan | 2018–2021 | 54 | 33.3 | 22 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Seifert LB., et al. [35] | 2023 | Cohort | Europe | Germany | 2009–2019 | 219 | 42.4 | 25.2 | 2 | 0.9 | Moderate |
| Bergmann U., et al. [42] | 2023 | Cohort | Europe | Iceland | 2010–2022 | 139 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Kotaniemi KVM., et al. [43] | 2023 | Cohort | Europe | Finland | 2006–2020 | 127 | 40.2 | 30 | 5 | 3.9 | Moderate |
| Remschmidt B., et al. [44] | 2023 | Cohort | Europe | Austria | 2017 | 99 | 31.3 | 30.1 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Bertin E., et al. [45] | 2022 | Cohort | Europe | France | 2012–2022 | 197 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Mohamad NH., et al. [32] | 2022 | Cross-sectional | Asia | Malaysia | 2011–2017 | 53 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 2 | 3.8 | Moderate |
| Pedersen TO., et al. [46] | 2021 | Cohort | Europe | Norway | 2013–2019 | 176 | 37.5 | NA 1 | 25 | 14.2 | Moderate |
| Van Camp P., et al. [36] | 2021 | Cohort | Europe | The Netherlands | 2017–2018 | 119 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 14 | 11.8 | Moderate |
| Suojanen J., et al. [37] | 2019 | Cohort | Europe | Finland | NA 1 | 76 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 9 | 11.8 | Moderate |
| Sukegawa S., et al. [47] | 2018 | Cohort | Asia | Japan | 2003–2017 | 56 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 2 | 3.6 | Moderate |
| Posnick JC., et al. [29] | 2017 | Cohort | North America | USA | 2004–2013 | 262 | 48.9 | 25 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Coppey E., et al. [48] | 2017 | Cohort | Europe | Belgium | 2012–2015 | 196 | 41.3 | 26.1 | 13 | 6.6 | Moderate |
| Falter BJ., et al. [38] | 2016 | Cohort | Europe | Belgium | 2010–2012 | 509 | 36.3 | 26.3 | 4 | 0.8 | Moderate |
| Bouchard C., et al. [49] | 2015 | Case-series | North America | Canada | 2008–2013 | 336 | 26.5 | 27.2 | 7 | 2.1 | Moderate |
| Little M., et al. [50] | 2015 | Cohort | Europe | United Kingdom | 2004–2012 | 169 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 8 | 4.7 | Moderate |
| Ueki K., et al. [39] | 2014 | Cohort | Asia | Japan | NA 1 | 44 | 36.4 | 29.1 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Paeng JY., et al. [40] | 2012 | Cohort | Asia | Republic of Korea | NA 1 | 50 | 48 | NA 1 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Hsu SSP., et al. [51] | 2012 | Cohort | Asia | Taiwan | 200–2004 | 57 | 45.6 | NA 1 | 1 | 1.8 | Moderate |
| Hugentobler M., et al. [52] | 2011 | Cohort | Europe | Switzerland | NA 1 | 54 | 38.9 | 25.9 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Kuhlefelt M., et al. [30] | 2010 | Cohort | Europe | Finland | 1997–2003 | 153 | 41 | 35.1 | 12 | 7.8 | Moderate |
| Theodossy T., et al. [31] | 2006 | Cohort | Europe | United Kingdom | 2001–2003 | 80 | 26.3 | 25 | 16 | 20 | Moderate |
| Kallela I., et al. [53] | 2005 | Cohort | Europe | Finland | NA 1 | 40 | 27.5 | 29 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Becelli R., et al. [41] | 2004 | Cohort | Europe | Italy | 1996–2001 | 241 | 32.8 | 24 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Laine P., et al. [54] | 2004 | Cohort | Europe | Finland | NA 1 | 160 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
| Bouwman JPB., et al. [55] | 1995 | Cohort | Europe | The Netherlands | NA 1 | 667 | NA 1 | NA 1 | 15 | 2.2 | Moderate |
| Llewelyn J., et al. [56] | 1992 | Cohort | Europe | United Kingdom | NA 1 | 48 | 33 | 23.6 | 0 | 0 | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kantzanou, M.; Kostares, E.; Koumaki, V.; Kostare, G.; Kostares, M.; Tsakris, A. Prevalence of Osteosynthesis Hardware Removal Due to Surgical Site Infections Following Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103558
Kantzanou M, Kostares E, Koumaki V, Kostare G, Kostares M, Tsakris A. Prevalence of Osteosynthesis Hardware Removal Due to Surgical Site Infections Following Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103558
Chicago/Turabian StyleKantzanou, Maria, Evangelos Kostares, Vasiliki Koumaki, Georgia Kostare, Michael Kostares, and Athanasios Tsakris. 2025. "Prevalence of Osteosynthesis Hardware Removal Due to Surgical Site Infections Following Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103558
APA StyleKantzanou, M., Kostares, E., Koumaki, V., Kostare, G., Kostares, M., & Tsakris, A. (2025). Prevalence of Osteosynthesis Hardware Removal Due to Surgical Site Infections Following Sagittal Split Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103558







