Prosthetic Heart Valves: More than Half a Century of Innovation—An Overview
Abstract
1. Background
2. Mechanical Prostheses
2.1. Ball-in-Cage (Starr–Edwards)
2.2. Monoleaflet
2.3. Bileaflet
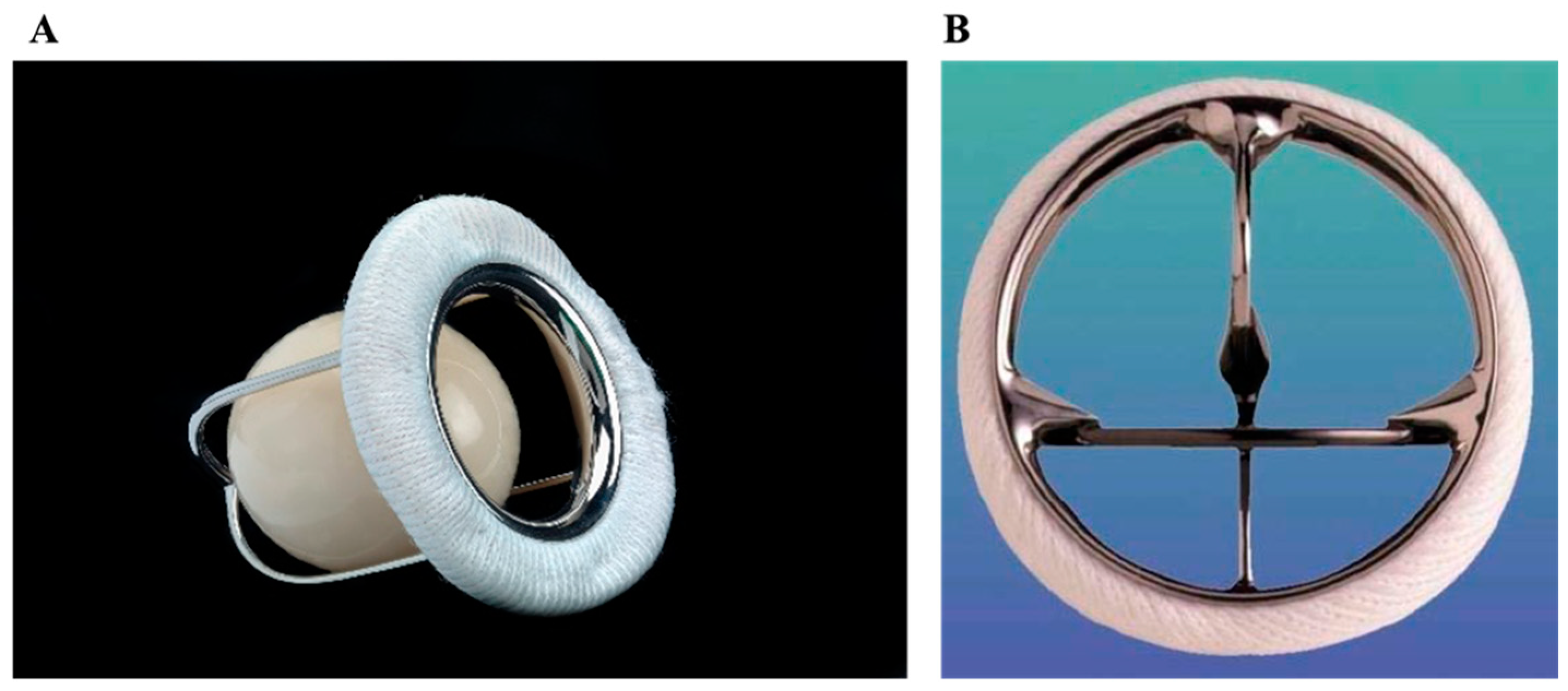
2.3.1. St. Jude Medical (SJM) and Sorin (CarboMedics–CM)
2.3.2. ATS Medical
2.3.3. On-X
3. Biologic Prostheses
3.1. Stented
3.1.1. Stented Porcine
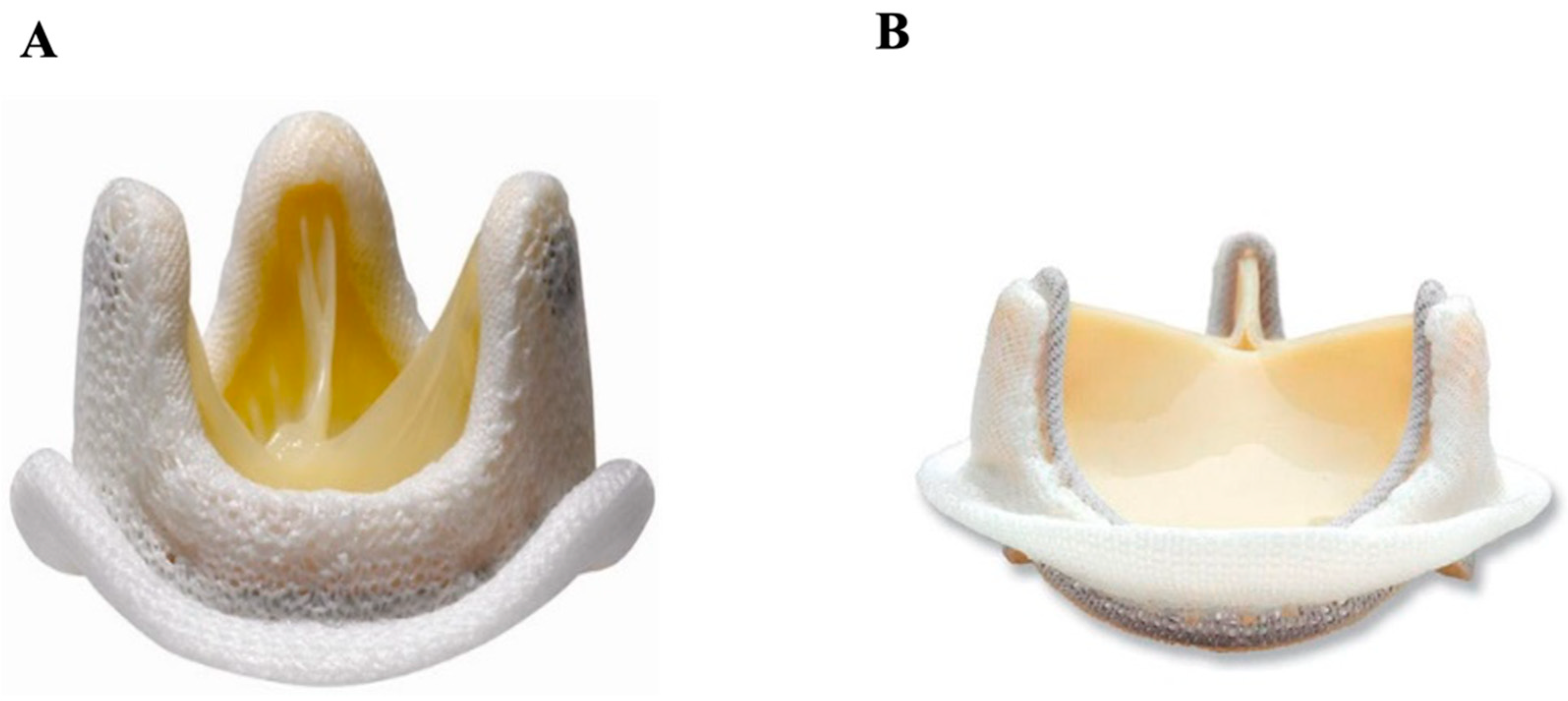
3.1.2. Stented Pericardial Bovine
3.2. Stentless
3.2.1. Stentless Pericardial Bovine
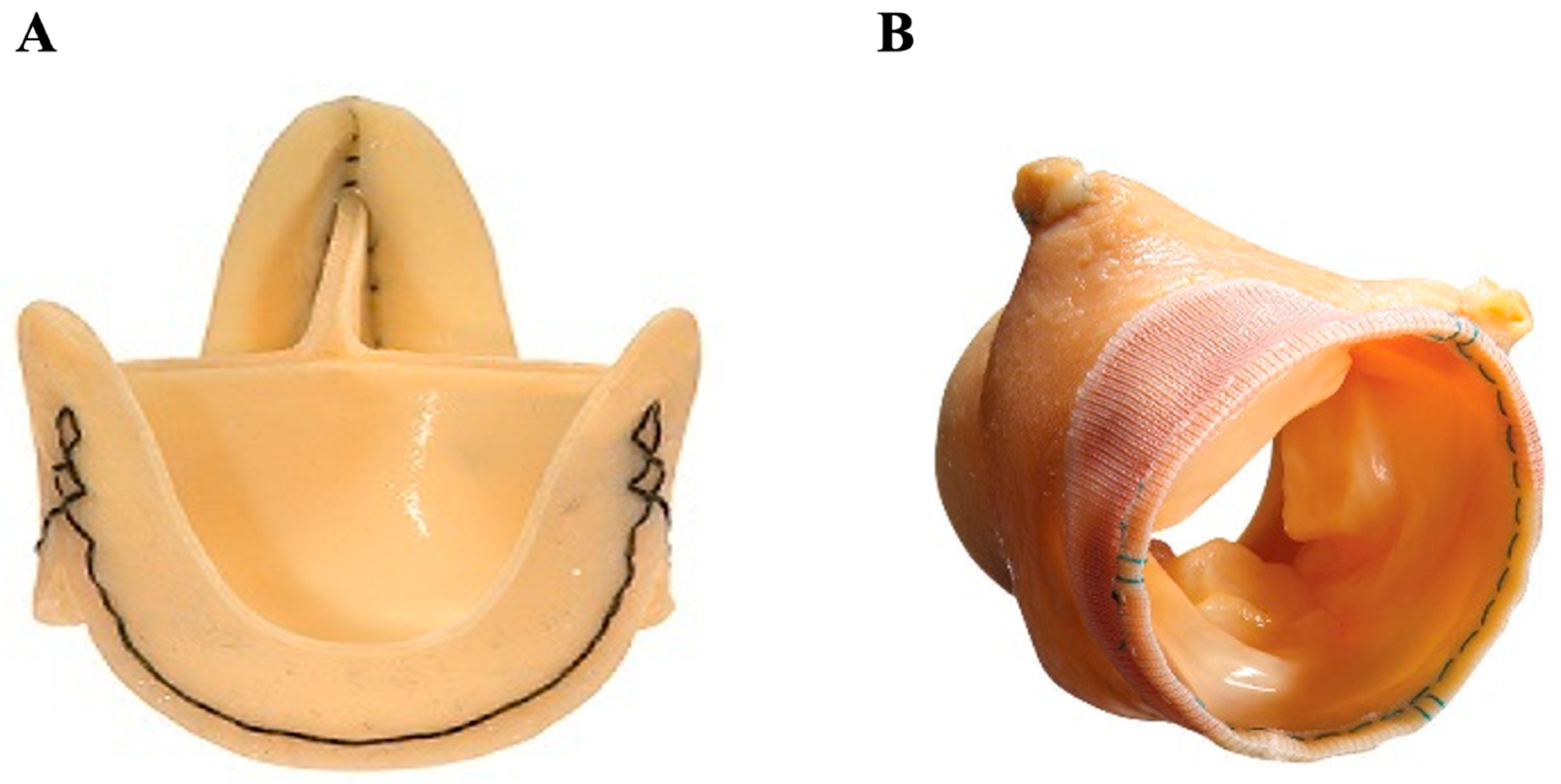
3.2.2. Stentless Porcine
3.3. Sutureless
4. Other Prostheses
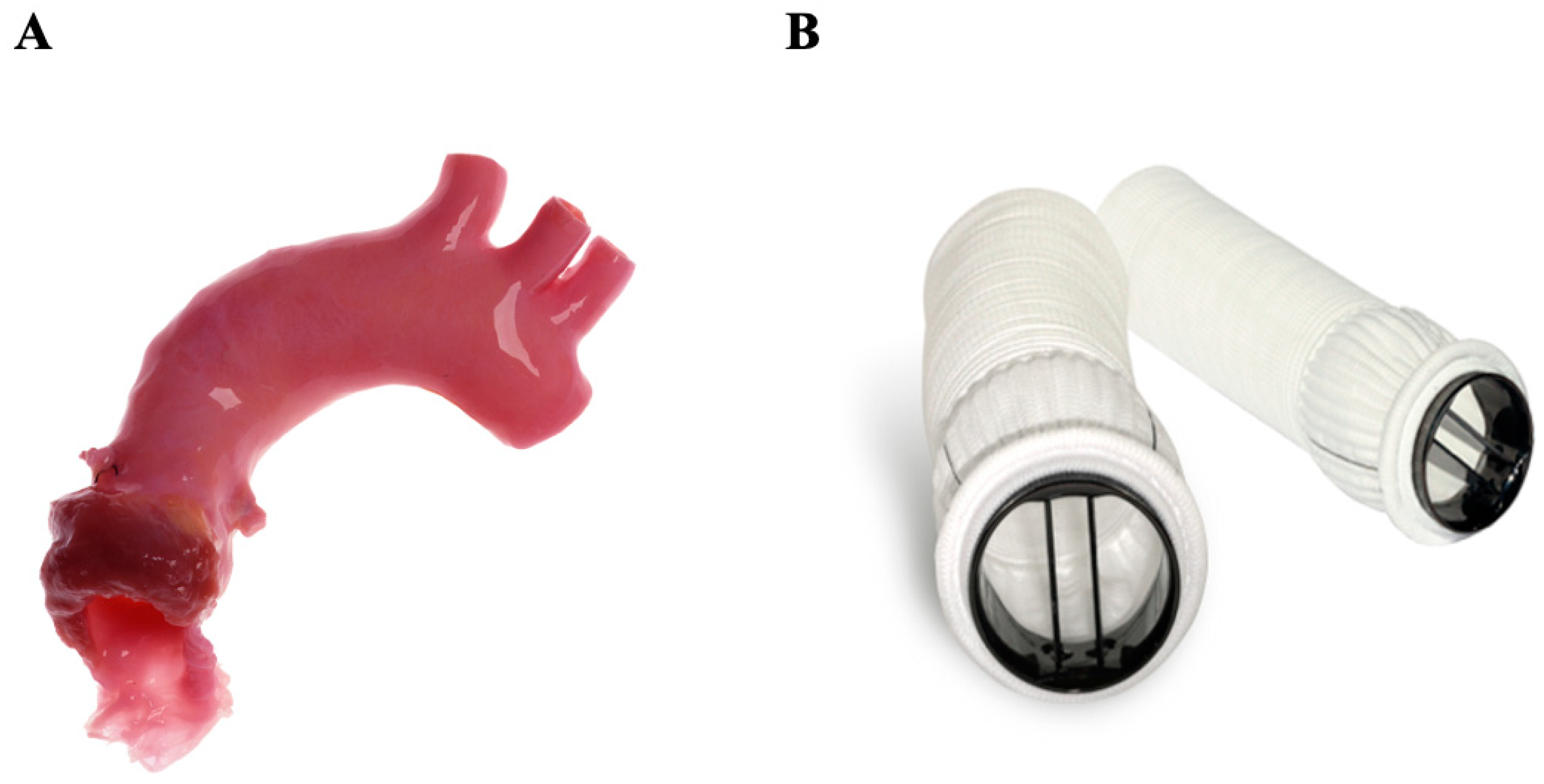
4.1. Homograft
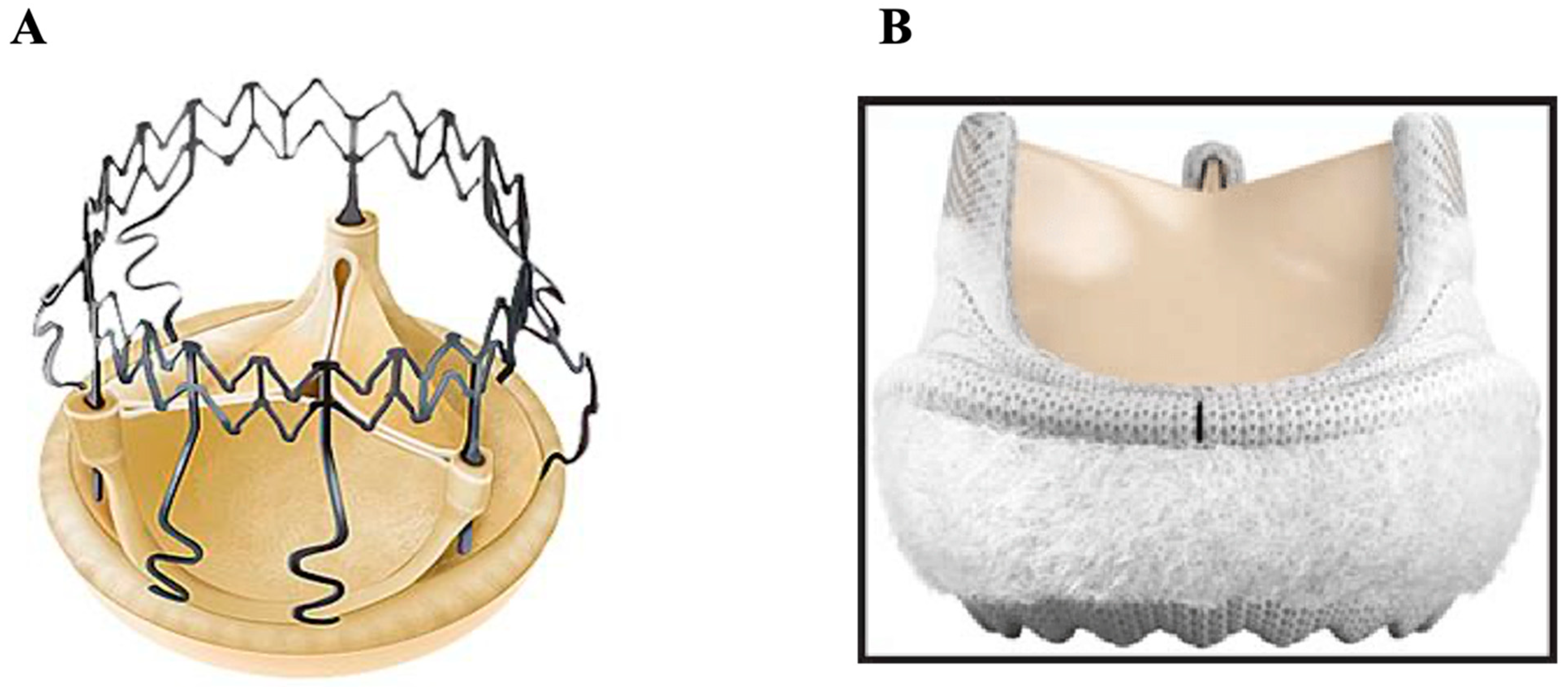
4.2. Composite Valve (On-X Ascending Aortic Prosthesis)
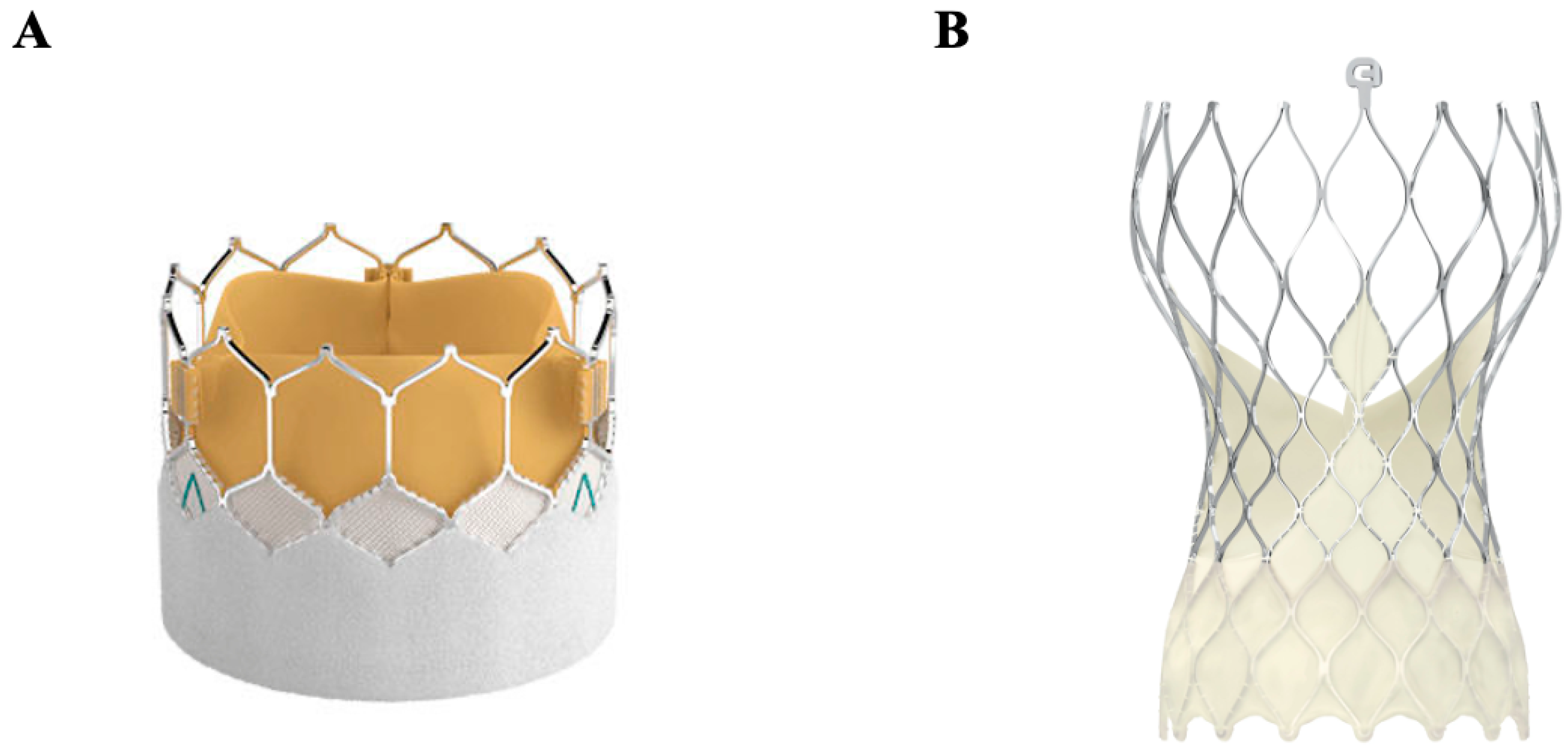
4.3. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
4.4. Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement (TMVR)
4.5. Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement (TPVR) and Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Replacement (TTVR)
4.6. Tissue-Engineered Heart Valves
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eveborn, G.W.; Schirmer, H.; Heggelund, G.; Lunde, P.; Rasmussen, K. The evolving epidemiology of valvular aortic stenosis. Tromsø Study Heart 2013, 99, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikof, E.L. The development of prosthetic heart valves—Lessons in form and function. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannegieter, S.C.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Briët, E. Thromboembolic and bleeding complications in patients with mechanical heart valve prostheses. Circulation 1994, 89, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Connolly, S.J.; Brueckmann, M.; Granger, C.B.; Kappetein, A.P.; Mack, M.J.; Blatchford, J.; Devenny, K.; Friedman, J.; Guiver, K.; et al. Dabigatran versus Warfarin in Patients with Mechanical Heart Valves. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenaeken, T.; Vanoppen, A.; Janssens, F.; Tanghe, L.; Verbrugghe, P.; Rega, F.; Meuris, B. DOACs in the Anticoagulation of Mechanical Valves: A Systematic Review and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammermeister, K.E.; Sethi, G.K.; Henderson, W.G.; Oprian, C.; Kim, T.; Rahimtoola, S. A Comparison of Outcomes in Men 11 Years after Heart-Valve Replacement with a Mechanical Valve or Bioprosthesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pop, A.; Dasi, L.P.; George, I. Lifetime Management for Aortic Stenosis: Strategy and Decision-Making in the Current Era. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2025, 119, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Lu, X.; McKean, S.; Warnock, R.; Laschinger, J.; Loyo-Berríos, N.; Marinac-Dabic, D. Selection of prosthetic aortic valves in the United States among elderly Medicare patients from 2006 to 2015. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr-Edwards Heart Valve: National Museum of American History. Available online: https://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/search/object/nmah_1726277 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Pibarot, P.; Dumesnil, J.G. Prosthetic Heart Valves. Circulation 2009, 119, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Taramasso, M.; Guidotti, A.; Pozzoli, A.; Nietilspach, F.; Von Segesser, L.; Maisano, F. The evolution of surgical valves. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 20, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Oyer, P.E.; Stinson, E.B.; Griepp, R.B.; Shumway, N.E. Valve replacement with the Starr-Edwards and Hancock prostheses. Ann. Surg. 1977, 186, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, J.; Kremkau, E. Hemodynamic changes after valve replacement with Starr-Edwards prostheses. Am. J. Cardiol. 1975, 35, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahakes, G.J. Mechanical Heart Valves. Circulation 2007, 116, 1759–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouni, M.A.; Baumeister, R.H.; Traverse, P. 49 years of normal functioning Starr-Edwards aortic valve prosthesis. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, omz141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Head, S.J.; Ko, J.; Singh, R.; Roberts, W.C.; Mack, M.J. 43.3-Year Durability of a Smeloff-Cutter Ball-Caged Mitral Valve. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 91, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impact of an Aortic Valve Implant on Body Surface UWB Propagation: A Preliminary Study—Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Medtronic-Hall-Aortic-Heart-Valve_fig3_224234205 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Kleine, P.; Hasenkam, M.J.; Nygaard, H.; Perthel, M.; Wesemeyer, D.; Laas, J. Tilting disc versus bileaflet aortic valve substitutes: Intraoperative and postoperative hemodynamic performance in humans. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2000, 9, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Meuris, B.; Verbeken, E.; Flameng, W. Mechanical valve thrombosis in a chronic animal model: Differences between monoleaflet and bileaflet valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2005, 14, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.T.; Healy, T.M.; Fontaine, A.A.; Saxena, R.; Yoganathan, A.P. Velocity measurements and flow patterns within the hinge region of a Medtronic Parallel bileaflet mechanical valve with clear housing. J. Heart Valve Dis. 1996, 5, 591–599. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.L.; Schaff, H.V.; Lahr, B.D.; Mullany, C.J.; Sundt, T.M.; Dearani, J.A.; McGregor, C.G.; Orszulak, T.A. Aortic valve replacement in patients aged 50 to 70 years: Improved outcome with mechanical versus biologic prostheses. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 135, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Jude Medical Heart Valve Demonstration 31M Unit National Museum of American History. Available online: https://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/search/object/nmah_735416 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Copeland, J.G.; Sethi, G.K. Four-year experience with the CarboMedics valve: The North American experience. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1994, 58, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandemir, O.; Tokmakoglu, H.; Yildiz, U.; Tezcaner, T.; Yorgancioglu, A.C.; Gunay, L.; Suzer, K.; St. Zorlutuna, Y. Jude Medical and CarboMedics mechanical heart valves in the aortic position: Comparison of long-term results. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2006, 33, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Rosengart, T.K.; O’hara, M.; Lang, S.J.; Ko, W.; Altorki, N.; Krieger, K.H.; Isom, O. Outcome analysis of 245 CarboMedics and St. Jude valves implanted at the same institution. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 66, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.H.; Caputo, M.; Ascione, R.; Wild, J.; West, R.; Angelini, G.D.; Bryan, A.J.; Calafiore, A.M. Prospective randomized comparison of CarboMedics and St Jude Medical bileaflet mechanical heart valve prostheses: An interim report. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 123, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Improved Mechanical Heart Valve Facilitates Implantation: HospiMedica. Available online: https://www.hospimedica.com/surgical-techniques/articles/266720000/improved-mechanical-heart-valve-facilitates-implantation.html (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Sezai, A.; Hata, M.; Niino, T.; Yoshitake, I.; Kasamaki, Y.; Hirayama, A.; Minami, K. Fifteen years of experience with ATS mechanical heart valve prostheses. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 139, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, R.W.; Van Nooten, G.J.; Tesar, P.J. The initial experience with the ATS Medical mechanical cardiac valve prosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 75, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, F.H.; Baykut, D.; Grize, L.; Zerkowski, H.-R. Single-center outcome analysis of 1,161 patients with St. Jude medical and ATS open pivot mechanical heart valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2007, 16, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aortic Valve Prosthesis on-X. Available online: https://www.medicalexpo.com/prod/cryolife/product-106949-975282.html (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Özyurda, U.; Akar, A.R.; Uymaz, O.; Oguz, M.; Ozkan, M.; Yildirim, C.; Aslan, A.; Tasoz, R. Early clinical experience with the On-X prosthetic heart valve. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 4, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.; Jamieson, W.E.; Lam, B.-K.; Ruel, M.; Ling, H.; Fradet, G.; Mesana, T.G. Influence of the On-X mechanical prosthesis on intermediate-term major thromboembolism and hemorrhage: A prospective multicenter study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 140, 1053–1058.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.B.; Pomar, J.L.; Mestres, C.A.; Palatianos, G.M. Clinical event rates with the On-X bileaflet mechanical heart valve: A multicenter experience with follow-up to 12 years. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chung, F.-P.; Chien, K.-L.; Hsu, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-J. Long-Term Outcomes of Bioprosthetic or Mechanical Valve Replacement in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Retrospective Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 745370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Webb, J.G.; Wood, D.A.; Ye, J.; Gurvitch, R.; Masson, J.-B.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Osten, M.; Horlick, E.; Wendler, O.; Dumont, E.; et al. Transcatheter Valve-in-Valve Implantation for Failed Bioprosthetic Heart Valves. Circulation 2010, 121, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, G.W.; Barratt-Boyes, B.G. On stress reduction in bioprosthetic heart valve leaflets by the use of a flexible stent. J. Card. Surg. 1991, 6, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.R.; Pasque, M.K.; Munfakh, N.A.; Melby, S.J.; Lawton, J.S.; Moazami, N.; Codd, J.E.; Crabtree, T.D.; Barner, H.B.; Damiano, R.J. Prosthesis-Patient Mismatch After Aortic Valve Replacement: Impact of Age and Body Size on Late Survival. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 81, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medtronic Bioprostheses for Replacement of Aortic and/or Mitral Heart Valves: Medtronic. Available online: https://www.medtronic.com/ca-en/healthcare-professionals/products/cardiovascular/heart-valves-surgical/mosaic-mosaic-ultra-bioprostheses.html (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Zuhdi, N.; Hawley, W.; Voehl, V.; Hancock, W.; Carey, J.; Greer, A. porcine aortic valves as replacements for human heart valves. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1974, 17, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botzenhardt, F.; Gansera, B.; Kemkes, B.M. Mid-term hemodynamic and clinical results of the stented porcine medtronic mosaic valve in aortic position. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 52, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PERIMOUNT—Aortic Valve Bioprosthesis by Edwards Lifesciences: MedicalExpo. Available online: https://www.medicalexpo.com/prod/edwards-lifesciences/product-77962-473632.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Gerosa, G.; Tarzia, V.; Rizzoli, G.; Bottio, T. Small aortic annulus: The hydrodynamic performances of 5 commercially available tissue valves. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 131, 1058–1064.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, J.B.; Rajani, R.; Parkin, D.; Rimington, H.M.; Blauth, C.I.; Venn, G.E.; Young, C.P.; Roxburgh, J.C. Bovine pericardial versus porcine stented replacement aortic valves: Early results of a randomized comparison of the Perimount and the Mosaic valves. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 136, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banbury, M.K.; Cosgrove, D.M.; White, J.A.; Blackstone, E.H.; Frater, R.W.M.; Okies, J. Age and valve size effect on the long-term durability of the Carpentier-Edwards aortic pericardial bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 72, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathi, A.M.; Englum, B.R.; Keenan, J.E.; Schechter, M.A.; Wang, H.; Smith, P.K.; Glower, D.D.; Hughes, G.C. Long-Term Survival After Bovine Pericardial Versus Porcine Stented Bioprosthetic Aortic Valve Replacement: Does Valve Choice Matter? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Zagorski, B.; Christakis, G.T.; Joyner, C.D.; Vincent, J.; Sever, J.; Harbi, S.; Feder-Elituv, R.; Moussa, F.; Goldman, B.S.; et al. Are stentless valves hemodynamically superior to stented valves? Long-term follow-up of a randomized trial comparing Carpentier–Edwards pericardial valve with the Toronto Stentless Porcine Valve. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, J.; Schöttler, J.; Petzina, R.; Hoffmann, G. Stented bioprostheses in aortic position. HSR Proc Intensive Care Cardiovasc Anesth. 2012, 4, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bach, D.S.; Kon, N.D.; Dumesnil, J.G.; Sintek, C.F.; Doty, D.B. Ten-year outcome after aortic valve replacement with the freestyle stentless bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kesteren, F.; Wollersheim, L.W.; Baan, J., Jr.; Nederveen, A.J.; Kaya, A.S.; Boekholdt, M.; de Mol, B.A.; van Ooij, P.; Planken, R.N. Four-dimensional flow MRI of stented versus stentless aortic valve bioprostheses. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, G.; Diken, A.I.; Hanedan, O.; Yurdakok, O.; Ozyalcin, S.; Kucuker, S.A.; Ozatik, M.A. The Sorin Freedom SOLO stentless tissue valve: Early outcomes after aortic valve replacement. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2013, 40, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stanger, O.; Tevaearai, H.; Carrel, T. The Freedom SOLO bovine pericardial stentless valve. Res. Rep. Clin. Cardiol. 2014, 2014, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, A.; Rusinaru, D.; Petitprez, B.; Marticho, P.; Vaida, I.; Tribouilloy, C.; Caus, T. Thrombocytopenia after aortic valve replacement with freedom solo bioprosthesis: A propensity study. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repossini, A.; Fischlein, T.; Santarpino, G.; Schäfer, C.; Claus, B.; Passaretti, B.; Di Bacco, L.; Giroletti, L.; Bisleri, G.; Muneretto, C.; et al. Pericardial Stentless Valve for Aortic Valve Replacement: Long-Term Results. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.; Dodge-Khatami, A.; Fraser, C., Jr.; Calhoon, J.; Ebeid, M.; Taylor, M.; Salazar, J. Systemic Semilunar Valve Replacement in Pediatric Patients Using a Porcine, Full-Root Bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, T.E.; Pollick, C.; Bos, J. Aortic valve replacement with stentless porcine aortic bioprosthesis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1990, 99, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, K.L.; Sintek, C.F.; Fletcher, A.D.; Pfeffer, T.A.; Kochamba, G.S.; Hyde, M.R.; Torpoco, J.O.; Khonsari, S. Aortic valve replacement with the freestyle stentless bioprosthesis: Five-year experience. Circulation 1999, 100, II17–II23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrandecic, M.; Fantini, F.A.; Filho, B.G.; de Oliveira, O.C.; Júnior, I.M.d.C.; Vrandecic, E. Retrospective clinical analysis of stented vs. stentless porcine aortic bioprostheses. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2000, 18, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Halstead, J.C.; Cafferty, F.; Sharples, L.; Rose, F.; Lee, E.; Rusk, R.; Dunning, J.; Argano, V.; Tsui, S. Early clinical and hemodynamic outcomes after stented and stentless aortic valve replacement: Results from a randomized controlled trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 83, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borger, M.A.; Prasongsukarn, K.; Armstrong, S.; Feindel, C.M.; David, T.E. Stentless aortic valve reoperations: A surgical challenge. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolo, B.; Di Eusanio, M. Aortic valve replacement with sutureless and rapid deployment aortic valve prostheses. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2016, 13, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Expert Consensus on Sutureless and Rapid Deployment Valves in Aortic Valve Replacement Using Minimally Invasive Approaches—Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/EDWARDS-INTUITY-Reprinted-from-Barnhart-et-al-Current-clinical-evidence-on-rapid_fig2_306328601 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Flameng, W.; Herregods, M.-C.; Hermans, H.; Van der Mieren, G.; Vercalsteren, M.; Poortmans, G.; Van Hemelrijck, J.; Meuris, B. Effect of sutureless implantation of the Perceval S aortic valve bioprosthesis on intraoperative and early postoperative outcomes. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 142, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhart, G.R.; Shrestha, M.L. Current Clinical Evidence on Rapid Deployment Aortic Valve Replacement: Sutureless Aortic Bioprostheses. Innov. Technol. Tech. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 11, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liakopoulos, O.J.; Gerfer, S.; Weider, S.; Rahmanian, P.; Zeriouh, M.; Eghbalzadeh, K.; Sabashnikov, A.; Choi, Y.-H.; Wippermann, J.; Wahlers, T. Direct Comparison of the Edwards Intuity Elite and Sorin Perceval S Rapid Deployment Aortic Valves. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Eusanio, M.; Phan, K. Sutureless aortic valve replacement. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surgery 2015, 4, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Santarpino, G.; Pfeiffer, S.; Jessl, J.; Dell’aquila, A.M.; Pollari, F.; Pauschinger, M.; Fischlein, T. Sutureless replacement versus transcatheter valve implantation in aortic valve stenosis: A propensity-matched analysis of 2 strategies in high-risk patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perceval S Sutureless Valve for Aortic Valve Replacement: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness, Safety, and Cost-Effectiveness; CADTH Rapid Response Reports; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2015.
- Artivion. CryoValve Aortic Allograft. Available online: https://artivion.com/product/cryovalve/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Walter, E.M.D.; De By, T.M.M.H.; Meyer, R.; Hetzer, R. The future of heart valve banking and of homografts: Perspective from the Deutsches Herzzentrum Berlin. HSR Proc. Intensive Care Cardiovasc. Anesth. 2012, 4, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’Brien, M.F.; Harrocks, S.; Stafford, E.G.; Gardner, M.A.; Pohlner, P.G.; Tesar, P.J.; Stephens, F. The homograft aortic valve: A 29-year, 99.3% follow up of 1022 valve replacements. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2001, 10, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ascending Aortic Prosthesis: CryoLife, Inc. Available online: https://cryolifestag.wpengine.com/products/on-x-heart-valves/ascending-aortic-prosthesis/ (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Kalkat, M.S.; Edwards, M.-B.; Taylor, K.M.; Bonser, R.S. Composite Aortic Valve Graft Replacement. Circulation 2007, 116 (Suppl. S11), I-301–I-306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aortic Valve Bioprosthesis SAPIEN 3: MedicalExpo. Available online: https://www.medicalexpo.com/prod/edwards-lifesciences/product-77962-729997.html (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Medtronic’s Evolut TAVR Device Assessed in Results from OPTIMIZE PRO and EVOLUT PRO Studies. Available online: https://citoday.com/news/medtronics-evolut-tavr-device-assessed-in-results-from-optimize-pro-and-evolut-pro-studies (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Fröhlich, G.M.; Lansky, A.J.; Webb, J.; Roffi, M.; Toggweiler, S.; Reinthaler, M.; Wang, D.; Hutchinson, N.; Wendler, O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Local versus general anesthesia for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVR)—Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Makkar, R.R.; Fontana, G.P.; Jilaihawi, H.; Kapadia, S.; Pichard, A.D.; Douglas, P.S.; Thourani, V.H.; Babaliaros, V.C.; Webb, J.G.; Herrmann, H.C.; et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement for inoperable severe aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Sakakibara, M.; Shingu, Y.; Katoh, H.; Wakasa, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Matsui, Y. Characteristics of inoperable patients with severe aortic valve stenosis—In the era of transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 21, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Smith, C.R.; Leon, M.B.; Mack, M.J.; Miller, D.C.; Moses, J.W.; Svensson, L.G.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Webb, J.G.; Fontana, G.P.; Makkar, R.R.; et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, M.J.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Popma, J.J.; Kleiman, N.S.; Søndergaard, L.; Mumtaz, M.; Adams, D.H.; Deeb, G.M.; Maini, B.; Gada, H.; et al. Surgical or Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement in Intermediate-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popma, J.J.; Deeb, G.M.; Yakubov, S.J.; Mumtaz, M.; Gada, H.; O’Hair, D.; Bajwa, T.; Heiser, J.C.; Merhi, W.; Kleiman, N.S.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Replacement with a Self-Expanding Valve in Low-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.M.; Jaluba, K.; Batchelor, W.; Gummipundi, S.; Asch, S.M.; Heidenreich, P. Temporal trends in transcatheter aortic valve replacement use and outcomes by race, ethnicity, and sex. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 99, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogal, S.; Rogers, T.; Aladin, A.; Ben-Dor, I.; Cohen, J.E.; Shults, C.C.; Wermers, J.P.; Weissman, G.; Satler, L.F.; Reardon, M.J.; et al. TAVR in 2023: Who Should Not Get It? Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 193, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terré, J.A.; George, I.; Smith, C.R. Pros and cons of transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 6, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unbehaun, A.; Klein, C.; Buz, S.; Meyer, A.; Wamala, I.; Potapov, E.; Schoenrath, F.; Falk, V.; Kempfert, J. A Novel Technique for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Pure Aortic Regurgitation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, e177–e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Val, D.; Ferreira-Neto, A.N.; Wintzer-Wehekind, J.; Dagenais, F.; Paradis, J.; Bernier, M.; O’Connor, K.; Beaudoin, J.; Freitas-Ferraz, A.B.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Early Experience with Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e013332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, K.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y. Transcatheter mitral valve implantation for degenerated mitral bioprostheses or failed surgical annuloplasty rings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Card. Surg. 2018, 33, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gales, J.; Krasuski, R.A.; Fleming, G.A. Transcatheter Valve Replacement for Right-sided Valve Disease in Congenital Heart Patients. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluchinotta, F.R.; Piekarski, B.L.; Milani, V.; Kretschmar, O.; Burch, P.T.; Hakami, L.; Meyer, D.B.; Jacques, F.; Ghez, O.; Trezzi, M.; et al. Surgical Atrioventricular Valve Replacement with Melody Valve in Infants and Children. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, e007145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, D. Pulmonary Valve Replacement for Tetralogy of Fallot. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2019, 15, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cebotari, S.; Lichtenberg, A.; Tudorache, I.; Hilfiker, A.; Mertsching, H.; Leyh, R.; Breymann, T.; Kallenbach, K.; Maniuc, L.; Batrinac, A.; et al. Clinical Application of Tissue Engineered Human Heart Valves Using Autologous Progenitor Cells. Circulation 2006, 114 (Suppl. S1), I-132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikouch, S.; Horke, A.; Tudorache, I.; Beerbaum, P.; Westhoff-Bleck, M.; Boethig, D.; Repin, O.; Maniuc, L.; Ciubotaru, A.; Haverich, A.; et al. Decellularized fresh homografts for pulmonary valve replacement: A decade of clinical experience. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2016, 50, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bobylev, D.; Sarikouch, S.; Tudorache, I.; Cvitkovic, T.; Söylen, B.; Boethig, D.; Theodoridis, K.; Bertram, H.; Beerbaum, P.; Haverich, A.; et al. Double semilunar valve replacement in complex congenital heart disease using decellularized homografts. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 28, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintas, V.; Fioretta, E.S.; Motta, S.E.; Dijkman, P.E.; Pensalfini, M.; Mazza, E.; Caliskan, E.; Rodriguez, H.; Lipiski, M.; Sauer, M.; et al. Development of a Novel Human Cell-Derived Tissue-Engineered Heart Valve for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: An In Vitro and In Vivo Feasibility Study. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2018, 11, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Valve Type | Features | Common Indications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Durable metal/carbons; designed for lifetime use | Younger patients; pre-existing anticoagulation needs (e.g., atrial fibrillation) | Superior durability; effective in small anatomy | Lifelong warfarin anticoagulation (target INR 2.0–3.0 in aortic, 2.5–3.5 in mitral) |
| Ball-in-cage (Starr–Edwards) | Earliest mechanical valve; silicone ball within a metal cage | Historic (no longer used) | Extremely long lifespan (some > 40 years) | Poor hemodynamics; high gradients; high embolic risk; obsolete |
| Monoleaflet | Single tilting disc design; two asymmetric orifices | Aortic and mitral positions | Better flow than ball-in-cage; simpler design than bileaflet | Older models had fracture risks; lower risk of thrombosis in animal studies |
| Bileaflet | Two semicircular discs; one central and two lateral orifices, symmetric | Most common mechanical design (aortic, mitral, tricuspid) | Excellent hemodynamics; large orifice; reduced target INR of 1.5–2.0 in On-X | Higher flow stagnation and shear stress than in monoleaflet |
| Biologic | Tissue-based; typically bovine or porcine | Age > 50, dialysis patients, or anticoagulation contraindications (pregnancy) | No long-term anticoagulation; expanding transcatheter use | Less durable (10–15 years) due to structural valve deterioration |
| Stented | Biologic valve on a rigid or flexible frame | Aortic, mitral, tricuspid valve replacement | Easier implantation; good mid/long-term safety | Smaller orifice than mechanical; eventual degeneration |
| Stentless | No stent; tubular body and suture ring; greater native-like flow | Aortic valve replacement | Larger orifice and lower gradients than stented; excellent 10-year data | Longer surgery times; complex implantation; difficult reoperation |
| Sutureless | Bovine pericardium on metallic frame; minimal or no suturing required | Less invasive aortic replacement (minithoracotomy) | Rapid deployment; reduced clamp time; favorable survival vs. TAVR | Higher heart block and pacemaker rates than standard surgical replacement |
| Other | Newer innovations | Varied | Varied | Varied |
| Homograft | Human donor valve; often used in Ross procedure (placed in pulmonary position) | Endocarditis, pregnancy, congenital valve disease | Good hemodynamics; no anticoagulation; excellent long-term outcomes in older adults | Technically challenging; limited availability |
| Composite | Mechanical valve with synthetic graft; replaces valve and ascending aorta | Bentall procedure; aneurysms; Marfan syndrome; annuloaortic ectasia; dissection into aortic root | Comprehensive repair in one procedure | High technical complexity; increased early mortality risk |
| Transcatheter (TAVR) | Catheter-delivered biologic valve for aortic position | Aortic stenosis, especially in high-risk groups; valve-in-valve for failed bioprostheses | Minimally invasive; fast recovery; valve-in-valve option | Limited in certain anatomies; associated with heart block, pacemaker, stroke, PVL; uncertain long-term durability |
| Transcatheter (TMVR/TPVR/TTVR) | Catheter-delivered biologic valves for mitral, pulmonary, or tricuspid positions | High-risk mitral regurgitation; congenital heart disease; pediatric cases | Minimally invasive alternative for reoperations; good initial hemodynamics; valve-in-valve option | Limited data; high mortality in TMVR; complications (fracture, endocarditis) in pediatric TPVR |
| Tissue-engineered | Decellularized scaffold reseeded with patient’s cells; mimics native valve growth | Pediatric congenital disease; research settings | Somatic growth potential; reduced risk of immune rejection; strong early durability data | Experimental; long-term outcomes not yet confirmed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabassum, A.; Phillips, K.G.; Hage, F.; Hage, A. Prosthetic Heart Valves: More than Half a Century of Innovation—An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103499
Tabassum A, Phillips KG, Hage F, Hage A. Prosthetic Heart Valves: More than Half a Century of Innovation—An Overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103499
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabassum, Asna, Katherine G. Phillips, Fadi Hage, and Ali Hage. 2025. "Prosthetic Heart Valves: More than Half a Century of Innovation—An Overview" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103499
APA StyleTabassum, A., Phillips, K. G., Hage, F., & Hage, A. (2025). Prosthetic Heart Valves: More than Half a Century of Innovation—An Overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103499






