Obesity and Comorbidities in HFpEF: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis in a University Hospital Setting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection and Analysis of the Study Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Data Statement
3. Results
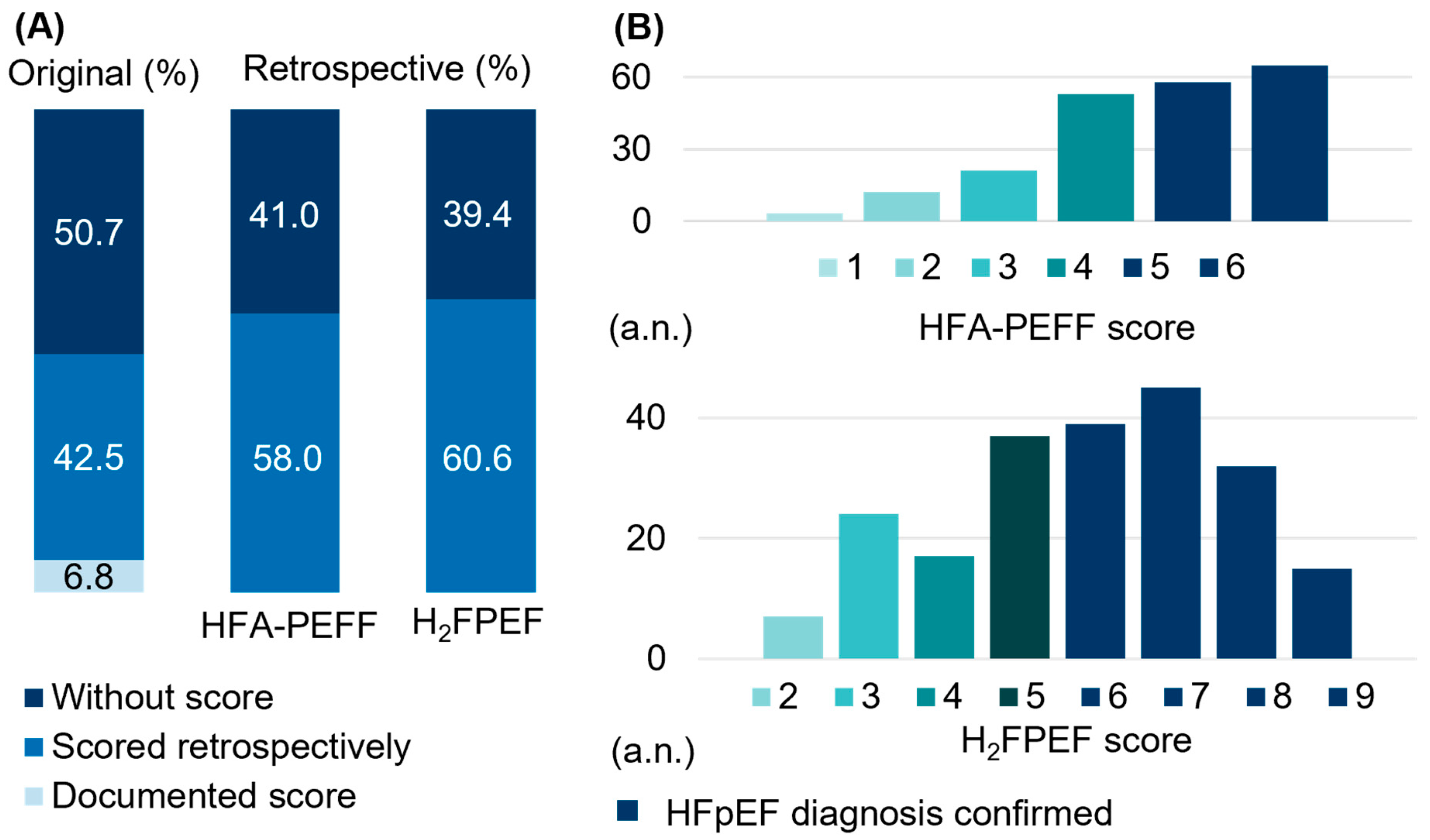
3.1. Limited HFpEF Case Identification with the Need for Methodological Adjustments
3.2. Obesity and Comorbidities
3.3. Female Vs. Male Sex in HFpEF Symptom Severity
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACEi | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor |
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| AHT | Arterial Hypertension |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ARB | Angiotensin Receptor Blocker |
| ARNI | Angiotensin Receptor–Neprilysin Inhibitor |
| ASA | Acetylsalicylic Acid |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CCB | Calcium Channel Blocker |
| CHD | Coronary Heart Disease |
| CI | Cardiac Index |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CVD | Cerebrovascular Disease |
| EF | Ejection Fraction |
| eGFR | estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| HFA-PEFF | Heart Failure Association Pre-test Assessment Echo, Function, and Final Etiology |
| HFpEF | Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction |
| IASD | Interatrial Shunt Device |
| LAVI | Left Atrial Volume Index |
| LV | Left Ventricular |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| MRA | Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| OACs | Oral Anticoagulants |
| PAD | Peripheral Artery Disease |
| PAH | Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension |
| PCWP | Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure |
| TIA | Transient Ischemic Attack |
| SGLT-2i | Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
References
- Pieske, B.; Tschöpe, C.; De Boer, R.A.; Fraser, A.G.; Anker, S.D.; Donal, E.; Edelmann, F.; Fu, M.; Guazzi, M.; Lam, C.S.; et al. How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm: A consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3297–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieske, B.; Tschöpe, C.; De Boer, R.A.; Fraser, A.G.; Anker, S.D.; Donal, E.; Edelmann, F.; Fu, M.; Guazzi, M.; Lam, C.S.; et al. How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm: A consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. J. Heart Fail 2020, 22, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitzman, D.W.; Brubaker, P.; Morgan, T.; Haykowsky, M.; Hundley, G.; Kraus, W.E.; Eggebeen, J.; Nicklas, B.J. Effect of caloric restriction or aerobic exercise training on peak oxygen consumption and quality of life in obese older patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenchaiah, S.; Evans, J.C.; Levy, D.; Wilson, P.W.; Benjamin, E.J.; Larson, M.G.; Kannel, W.B.; Vasan, R.S. Obesity and the risk of heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, M.; Trummer-Herbst, V.; Koser, F.; Durand, S.; Adão, R.; Vasques-Nóvoa, F.; Freundt, J.K.; Voglhuber, J.; Pricolo, M.R.; Kasa, M.; et al. Nicotinamide for the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koser, F.; Hobbach, A.J.; Abdellatif, M.; Herbst, V.; Türk, C.; Reinecke, H.; Krüger, M.; Sedej, S.; Linke, W.A. Acetylation and phosphorylation changes to cardiac proteins in experimental HFpEF due to metabolic risk reveal targets for treatment. Life Sci. 2022, 309, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, M.; Stavropoulou, E.; Nikolaidou, A.; Dividis, G.; Peteinidou, E.; Tsioufis, P.; Kamperidis, N.; Dimitriadis, K.; Karamitsos, T.; Giannakoulas, G.; et al. Diagnosing Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in Obese Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y.N.V.; Carter, R.E.; Obokata, M.; Redfield, M.M.; Borlaug, B.A. A simple, evidence-based approach to help guide diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 2018, 138, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Kreouzi, M.; Hitas, C.; Anagnostou, D.; Nikolaou, M. Adipokines and Cardiometabolic Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Jensen, M.D.; Kitzman, D.W.; Lam, C.S.P.; Obokata, M.; Rider, O.J. Obesity and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: New insights and pathophysiological targets. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3434–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C. A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.A.; Couch, L.S.; Rider, O.J. Myocardial metabolism in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scantlebury, D.C.; Borlaug, B.A. Why are women more likely than men to develop heart failure with preserved ejection fraction? Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2011, 26, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Redfield, M.M. Diastolic and systolic heart failure are distinct phenotypes within the heart failure spectrum. Circulation 2011, 123, 2006–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.E.; Enserro, D.; Brouwers, F.P.; Kizer, J.R.; Shah, S.J.; Psaty, B.M.; Bartz, T.M.; Santhanakrishnan, R.; Lee, D.S.; Chan, C.; et al. Predicting heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction: The international collaboration on heart failure subtypes. Circ. Heart Fail 2016, 9, e003116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.J.; Taylor, K.S.; Ordonez-Mena, J.M.; Jones, N.R.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Hobbs, F.D.R. ESC Heart Failure Association age-adjusted natriuretic peptide thresholds for a new diagnosis of heart failure: Diagnostic accuracy study. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, ehae666-949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, F.; Brimicombe, J.; Cheriyan, J.; Edwards, D.; Hobbs, F.R.; Jalaludeen, N.; Mant, J.; Pilling, M.; Schiff, R.; Taylor, C.J.; et al. Diagnosis of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in primary care: Cohort study. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 4562–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlay, S.M.; Roger, V.L.; Redfield, M.M. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciomer, S.; Moscucci, F.; Salvioni, E.; Marchese, G.; Bussotti, M.; Corrà, U.; Piepoli, M.F. Role of gender, age and BMI in prognosis of heart failure. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbach, A.J.; Feld, J.; Linke, W.A.; Sindermann, J.R.; Dröge, P.; Ruhnke, T.; Günster, C.; Reinecke, H. BMI-stratified exploration of the ’obesity paradox’: Heart failure perspectives from a large German insurance database. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, R.; McAlister, F.A.; McMurray, J.J.; Cowie, M.R.; Rich, M.; Pocock, S.; Swedberg, K.; Maggioni, A.; Gamble, G.; Ariti, C.; et al. Meta-analysis Global Group in Chronic Heart Failure (MAGGIC). The obesity paradox in heart failure patients with preserved versus reduced ejection fraction: A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, P.; Zhu, W. The “Obesity Paradox” in Patients With HFpEF With or Without Comorbid Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 743327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysohoou, C.; Konstantinou, K.; Tsioufis, K. The Role of NT-proBNP Levels in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction-It Is Not Always a Hide-and-Seek Game. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, A.A.; Rich, J.D.; Shah, S.J. The Emerging Epidemic of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2013, 10, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Hamo, C.E.; Udelson, J.E.; Pitt, B.; Yancy, C.; Shah, S.J.; Desvigne-Nickens, P.; Bernstein, H.S.; Clark, R.L.; Depre, C.; et al. Exploring new endpoints for patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e003358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Rasmussen, S.; Davies, M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Lindegaard, M.L.; Møller, D.V.; et al. Semaglutide in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Petrie, M.C.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Davies, M.J.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Møller, D.V.; Treppendahl, M.B.; Verma, S.; et al. STEP-HFpEF DM Trial Committees and Investigators. Semaglutide in Patients with Obesity-Related Heart Failure and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Zile, M.R.; Kramer, C.M.; Baum, S.J.; Litwin, S.E.; Menon, V.; Ge, J.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Ou, Y.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. SUMMIT Trial Study Group. Tirzepatide for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, D. GLP-1RA may have varying effects on cardiac structure in patients with ASCVD depending on BMI. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1355540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, L.; Han, S.; Yang, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Ping, F.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; et al. Sex Differences in the Efficacy of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Weight Reduction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes 2025, 17, e70063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (N = 219) | |
|---|---|
| Demographic data | |
| Age—years—mean ± SD | 75.03 ± 9.16 (N = 217) |
| Female—% (a.n) | 50.0 (109) (N = 218) |
| Outpatients—% (a.n.) | 60.5 (130) (N = 215) |
| BMI—kg/m2—mean ± SD | 28.80 ± 6.01 (N = 216) |
| BMI category-median | II (N = 216) |
| BMI category—% (a.n.) | |
| I | 28.7 (62) |
| II | 30.1 (65) |
| III | 41.2 (89) |
| BP (sys.)—mmHg—mean ± SD | 138.22 ± 26.01 (N = 140) |
| BP (dias.)—mmHg—mean ± SD | 78.76 ± 12.78 (N = 137) |
| Comorbidities | |
| AF—% (a.n.) | 74.3 (162) (N = 218) |
| AHT—% (a.n.) | 93.6 (205) (N = 218) |
| Diabetes—% (a.n.) | 35.6 (78) (N = 218) |
| (ex-) nicotine abuse—% (a.n.) | 33.0 (72) (N = 218) |
| CVD—% (a.n.) | 12.4 (27) (N = 218) |
| PAD—% (a.n.) | 18.3 (40) (N = 218) |
| CHD—% (a.n.) | 43.6 (95) (N = 218) |
| MI—% (a.n.) | 12.8 (28) (N = 218) |
| Stroke/TIA—% (a.n.) | 13.3 (29) (N = 218) |
| COPD—% (a.n.) | 18.3 (40) (N = 218) |
| Sleep apnea—% (a.n.) | 14.7 (32) (N = 218) |
| PAH—% (a.n.) | 21.6 (47) (N = 218) |
| CKD—% (a.n.) | 55.7 (122) (N = 219) |
| Comorbidities—No.—mean ± SD | 4.02 ± 1.72 (N = 218) |
| Clinical performance | |
| NYHA class median | II–III (N = 205) |
| NYHA class—% (a.n.) | |
| I | 6.8 (14) |
| I–II | 3.4 (7) |
| II | 27.3 (56) |
| II–III | 16.1 (33) |
| III | 32.2 (66) |
| III–IV | 6.3 (13) |
| IV | 7.8 (16) |
| Edema—% (a.n.) | 37.1 (73) (N = 197) |
| HFA-PEFF scoring total—median (IQR) | 5.00 [2] (N = 212) |
| HFA-PEFF scoring—% (a.n.) | |
| 1 | 1.4 (3) |
| 2 | 5.6 (12) |
| 3 | 9.9 (21) |
| 4 | 24.2 (53) |
| 5 | 27.2 (58) |
| 6 | 30.5 (65) |
| H2FPEF scoring total—median (IQR) | 6.00 [2] (N = 216) |
| H2FPEF scoring—% (a.n.) | |
| 1 | 0.0 (0) |
| 2 | 3.2 (7) |
| 3 | 11.1 (24) |
| 4 | 7.9 (17) |
| 5 | 17.1 (37) |
| 6 | 18.1 (39) |
| 7 | 20.8 (45) |
| 8 | 14.8 (32) |
| 9 | 6.9 (15) |
| Laboratory findings | |
| Sodium—mmol/L—mean ± SD | 139.78 ± 7.26 (N = 194) |
| Potassium—mmol/L—mean ± SD | 4.40 ± 0.57 (N = 194) |
| Urea—mg/dL—mean ± SD | 26.62 ± 15.21 (N = 156) |
| Creatinine—mg/dL—mean ± SD | 1.44 ± 0.96 (N = 194) |
| eGFR—mL/min/1.73 m2—mean ± SD | 50.28 ± 20.33 (N = 186) |
| NT-proBNP—pg/mL—median (IQR) | 1261.00 (1776) (N = 186) |
| Hemoglobin—g/dL—mean ± SD | 12.31 ± 1.95 (N = 194) |
| Hematocrit—%—mean ± SD | 37.69 ± 6.43 (N = 194) |
| HbA1c—%—mean ± SD | 8.6 ± 1.80 (N = 3) |
| Medical therapy | |
| ACEi—% (a.n.) | 29.8 (65) (N = 218) |
| ARB—% (a.n.) | 40.1 (87) (N = 217) |
| ARNI—% (a.n.) | 6.0 (13) (N = 218) |
| ARNI/ACEi/ARB—% (a.n.) | 75.1 (163) (N = 217) |
| Beta blockers—% (a.n.) | 79.8 (174) (N = 218) |
| CCB—% (a.n.) | 36.2 (79) (N = 218) |
| Diuretics—% (a.n.) | 79.8 (174) (N = 218) |
| MRA—% (a.n.) | 23.4 (51) (N = 218) |
| SGLT-2i—% (a.n.) | 12.4 (27) (N = 218) |
| ASA—% (a.n.) | 21.2 (46) (N = 217) |
| Statins—% (a.n.) | 58.3 (127) (N = 218) |
| OAC—% (a.n.) | 72.0 (157) (N = 218) |
| Sys. HF treatment—% (a.n.) | 17.5 (38) (N = 217) |
| Device therapy | |
| IASD—% (a.n.) | 6.4 (14) (N = 218) |
| Echocardiographic findings | |
| LVEF—%—mean ± SD | 56.54 ± 5.41 (N = 218) |
| LAVI—mL/m2—mean ± SD | 48.77 ± 18.92 (N = 185) |
| E/e’—mean ± SD | 14.07 ± 5.35 (N = 135) |
| E/A— ± SD | 1.78 ± 0.98 (N = 135) |
| e’ septal—cm/s—mean ± SD | 7.10 ± 3.78 (N = 80) |
| e’ lateral—cm/s—mean ± SD | 9.46 ± 3.31 (N = 86) |
| TR velocity—m/s—mean ± SD | 3.12 ± 0.51 (N = 51) |
| Degree dias. dys.—total—median | II (N = 132) |
| Degree dias. dys.—% (a.n.) | |
| I | 22.0 (29) |
| I–II | 0.8 (1) |
| II | 40.9 (54) |
| II–III | 3.0 (4) |
| III | 33.3 (44) |
| Invasive hemodynamics | |
| CI—L/min/m2—mean ± SD | 2.35 ± 0.71 (N = 65) |
| PCWP—mmHg—mean ± SD | 20.21 ± 7.28 (N = 61) |
| BMI Category | I (N = 62) | II (N = 65) | III (N = 89) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I vs. II | I vs. III | II vs. III | ||||
| Demographic data | ||||||
| BMI—kg/m2—mean ± SD | 22.37 ± 2.23 (N = 62) | 27.29 ± 1.30 (N = 65) | 34.39 ± 4.61 (N = 89) | |||
| Age—years—mean ± SD | 77.27 ± 7.60 (N = 62) | 74.20 ± 10.41 (N = 65) | 74.10 ± 9.05 (N = 88) | 0.176 | 0.111 | 1.000 |
| Female—% (a.n.) | 58.1 (36) (N = 62) | 47.7 (31) (N = 65) | 46.1 (41) (N = 89) | 0.734 | 0.447 | 1.000 |
| Outpatients—% (a.n.) | 59.7 (37) (N = 62) | 57.1 (36) (N = 63) | 65.5 (57) (N = 87) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.906 |
| BP (sys.)—mmHg—mean ± SD | 135.42 ± 25.44 (N = 38) | 137.65 ± 17.96 (N = 40) | 138.92 ± 29.70 (N = 60) | 0.394 | 0.868 | 0.437 |
| BP (dias.)—mmHg—mean ± SD | 77.53 ± 14.12 (N = 38) | 81.51 ± 11.04 (N = 39) | 77.24 ± 11.94 (N = 58) | 0.085 | 0.901 | 0.077 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| AF—% (a.n.) | 79.0 (49) (N = 62) | 66.2 (43) (N = 65) | 77.5 (69) (N = 89) | 0.291 | 1.000 | 0.332 |
| AHT—% (a.n.) | 90.3 (56) (N = 62) | 92.3 (60) (N = 65) | 97.8 (87) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.179 | 0.483 |
| Diabetes—% (a.n.) | 17.7 (11) (N = 62) | 30.8 (20) (N = 65) | 50.6 (45) (N = 89) | 0.337 | <0.001 * | 0.027 * |
| (ex-)nicotine abuse—% (a.n.) | 30.7 (19) (N = 62) | 35.3 (23) (N = 65) | 32.5 (29) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| CVD—% (a.n.) | 16.1 (10) (N = 62) | 12.3 (8) (N = 65) | 10.1 (9) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.824 | 1.000 |
| PAD—% (a.n.) | 22.6 (14) (N = 62) | 21.5 (14) (N = 65) | 13.5 (12) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.476 | 0.617 |
| CHD—% (a.n.) | 48.4 (30) (N = 62) | 47.7 (31) (N = 65) | 37.1 (33) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.509 | 0.547 |
| MI—% (a.n.) | 12.9 (8) (N = 62) | 16.9 (11) (N = 65) | 10.1 (9) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.651 |
| Stroke/TIA—% (a.n.) | 12.9 (8) (N = 62) | 13.8 (9) (N = 65) | 13.5 (12) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| COPD—% (a.n.) | 21.0 (13) (N = 62) | 18.5 (12) (N = 65) | 14.6 (13) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.948 | 1.000 |
| Sleep apnea—% (a.n.) | 4.8 (3) (N = 62) | 9.2 (6) (N = 65) | 25.8 (23) (N = 89) | 1.000 | <0.001 * | 0.011 * |
| PAH—% (a.n.) | 22.6 (14) (N = 62) | 16.9 (11) (N = 65) | 23.6 (21) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.963 | 1.000 |
| CKD—% (a.n.) | 58.1 (36) (N = 62) | 49.2 (32) (N = 65) | 58.4 (52) (N = 89) | 0.958 | 1.000 | 0.779 |
| Comorbidities—No.—mean ± SD | 3.94 ± 1.62 (N = 62) | 3.78 ± 1.68 (N = 65) | 4.22 ± 1.80 (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.927 | 0.352 |
| Clinical performance | ||||||
| NYHA class median | II–III (N = 58) | II–III (N = 59) | III (N = 87) | 0.962 | 0.065 | 0.652 |
| NYHA class—% (a.n.) | ||||||
| I | 17.2 (10) | 3.4 (2) | 2.3 (2) | |||
| I–II | 1.7 (1) | 8.5 (5) | 1.1 (1) | |||
| II | 27.6 (16) | 33.9 (20) | 23.0 (20) | |||
| II–III | 10.3 (6) | 11.9 (7) | 23.0 (20) | |||
| III | 31.0 (18) | 27.1 (16) | 26.8 (32) | |||
| III–IV | 5.2 (3) | 5.1 (3) | 8.0 (7) | |||
| IV | 6.9 (4) | 10.2 (6) | 5.7 (5) | |||
| Edema—% (a.n.) | 19.0 (11) (N = 58) | 38.6 (22) (N = 57) | 47.5 (38) (N = 80) | 0.079 | 0.002 * | 0.827 |
| HFA-PEFF scoring total-median (IQR) | 5.00 [2] (N = 61) | 5.00 [2] (N = 63) | 5.00 [2] (N = 87) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| HFA-PEFF sc.—% (a.n.) | ||||||
| 1 | 1.6 (1) | 1.6 (1) | 1.1 (1) | |||
| 2 | 4.9 (3) | 3.2 (2) | 8.0 (7) | |||
| 3 | 6.6 (4) | 15.9 (10) | 8.0 (7) | |||
| 4 | 27.9 (17) | 15.9 (10) | 29.9 (26) | |||
| 5 | 29.5 (5) | 31.7 (20) | 21.8 (19) | |||
| 6 | 29.5 (18) | 31.7 (20) | 29.9 (26) | |||
| H2FPEF scoring total—median (IQR) | 5.00 [2] (N = 61) | 5.00 [4] (N = 64) | 8.00 [2] (N = 89) | 1.000 | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| H2FPEF scoring—% (a.n.) | ||||||
| 1 | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | |||
| 2 | 4.9 (3) | 6.3 (4) | 0.0 (0) | |||
| 3 | 14.8 (9) | 21.9 (14) | 1.1 (1) | |||
| 4 | 4.9 (3) | 10.9 (7) | 7.9 (7) | |||
| 5 | 29.5 (18) | 15.6 (10) | 10.1 (9) | |||
| 6 | 26.2 (16) | 20.3 (13) | 9.0 (8) | |||
| 7 | 19.7 (12) | 21.9 (14) | 21.3 (19) | |||
| 8 | 0.0 (0) | 1.6 (1) | 34.8 (8) | |||
| 9 | 0.0 (0) | 1.6 (1) | 15.7 (14) | |||
| Laboratory findings | ||||||
| Sodium—mmol/L—mean ± SD | 140.55 ± 11.31 (N = 56) | 138.58 ± 5.73 (N = 55) | 140.06 ± 3.88 (N = 81) | 0.466 | 1.000 | 0.738 |
| Potassium—mmol/L—mean ± SD | 4.35 ± 0.56 (N = 56) | 4.38 ± 0.51 (N = 55) | 4.45 ± 0.61 (N = 81) | 1.000 | 0.824 | 1.000 |
| Urea—mg/dL—mean ± SD | 24.80 ± 14.52 (N = 46) | 25.41 ± 15.80 (N = 43) | 28.55 ± 15.38 (N = 66) | 1.000 | 0.610 | 0.889 |
| Creatinine—mg/dL—mean ± SD | 1.33 ± 0.79 (N = 56) | 1.51 ± 1.39 (N = 55) | 1.47 ± 0.69 (N = 81) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| eGFR—mL/min/1.73 m2—mean ± SD | 53.39 ± 19.41 (N = 56) | 51.76 ± 20.02 (N = 54) | 47.31 ± 21.13 (N = 74) | 0.707 | 0.066 | 0.156 |
| NT-proBNP—pg/mL—median (IQR) | 1464.50 (1757) (N = 54) | 1139.50 (1542) (N = 56) | 1215.00 (1973) (N = 74) | 0.179 | 1.000 | 0.561 |
| Hemoglobin—g/dL—mean ± SD | 12.27 ± 1.78 (N = 56) | 12.18 ± 1.82 (N = 55) | 12.48 ± 2.13 (N = 81) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Hematocrit—%—mean ± SD | 37.31 ± 4.85 (N = 56) | 37.70 ± 8.33 (N = 55) | 38.13 ± 5.93 (N = 81) | 0.620 | 0.360 | 0.147 |
| HbA1c—%—mean ± SD | 0.00 (N = 0) | 0.00 (N = 0) | 8.6 ± 1.80 (N = 3) | |||
| Medical therapy | ||||||
| ACEi—% (a.n.) | 33.9 (21) (N = 62) | 36.9 (24) (N = 65) | 21.3 (19) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.291 | 0.110 |
| ARB—% (a.n.) | 29.0 (18) (N = 62) | 38.5 (25) (N = 65) | 48.9 (43) (N = 88) | 0.828 | 0.044 * | 0.577 |
| ARNI—% (a.n.) | 4.8 (3) (N = 62) | 0.0 (0) (N = 65) | 11.2 (10) (N = 89) | 0.740 | 0.303 | 0.011 * |
| ARNI/ACEi/ARB—% (a.n.) | 66.1 (41) (N = 62) | 75.4 (49) (N = 65) | 80.7 (71) (N = 88) | 0.688 | 0.131 | 1.000 |
| Beta blockers—% (a.n.) | 79.0 (49) (N = 62) | 80.0 (52) (N = 65) | 80.9 (72) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| CCB—% (a.n.) | 25.8 (16) (N = 62) | 32.3 (21) (N = 65) | 47.2 (42) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.021 * | 0.17 |
| Diuretics—% (a.n.) | 72.6 (45) (N = 62) | 72.3 (47) (N = 65) | 89.9 (80) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.027 * | 0.021 * |
| MRA—% (a.n.) | 14.5 (9) (N = 62) | 23.1 (15) (N = 65) | 29.2 (26) (N = 89) | 0.758 | 0.107 | 1.000 |
| SGLT-2i—% (a.n.) | 0.0 (0) (N = 62) | 15.4 (10) (N = 65) | 18.0 (16) (N = 89) | 0.021 * | 0.002 * | 1.000 |
| ASA—% (a.n.) | 24.2 (15) (N = 62) | 20.0 (13) (N = 65) | 19.3 (17) (N = 88) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Statins—% (a.n.) | 58.1 (36) (N = 62) | 55.4 (36) (N = 65) | 61.8 (55) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| OAC—% (a.n.) | 67.7 (42) (N = 62) | 69.2 (45) (N = 65) | 77.5 (69) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.567 | 0.775 |
| Sys. HF treatment—% (a.n.) | 6.5 (4) (N = 62) | 18.4 (12) (N = 65) | 23.9 (21) (N = 88) | 0.135 | <0.001 * | 0.128 |
| Device therapy | ||||||
| IASD—% (a.n.) | 4.8 (3) (N = 62) | 4.6 (3) (N = 65) | 9.0 (8) (N = 89) | 1.000 | 0.933 | 0.837 |
| Echocardiographic findings | ||||||
| LVEF—%—mean ± SD | 56.50 ± 4.40 (N = 62) | 56.93 ± 5.62 (N = 65) | 56.21 ± 5.89 (N = 89) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| LAVI—mL/m2—mean ± SD | 51.76 ± 21.09 (N = 53) | 46.78 ± 16.34 (N = 57) | 48.25 ± 19.23 (N = 74) | 0.511 | 0.914 | 1.000 |
| E/e’—mean ± SD | 14.21 ± 5.80 (N = 45) | 14.22 ± 4.92 (N = 54) | 13.75 ± 5.42 (N = 64) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| E/A—mean ± SD | 1.59 ± 0.75 (N = 33) | 1.77 ± 0.88 (N = 45) | 1.88 ± 1.16 (N = 56) | 1.000 | 0.517 | 1.000 |
| e’ septal—cm/s—mean ± SD | 5.85 ± 2.33 (N = 29) | 6.53 ± 2.28 (N = 25) | 9.20 ± 5.33 (N = 25) | 1.000 | 0.003 * | 0.029 * |
| e’ lateral—cm/s—mean ± SD | 8.81 ± 3.13 (N = 31) | 8.84 ± 2.72 (N = 25) | 10.74 ± 3.71 (N = 29) | 1.000 | 0.069 | 0.102 |
| TR velocity—m/s—mean ± SD | 3.00 ± 0.50 (N = 15) | 3.08 ± 0.54 (N = 16) | 3.17 ± 0.42 (N = 19) | 1.000 | 0.985 | 1.000 |
| Degree dias. dys.—total median | II (N = 38) | II (N = 40) | II (N = 53) | 0.359 | 1.000 | 0.839 |
| Degree dias. dys.—% (a.n.) | ||||||
| I | 26.3 (10) | 15.5 (7) | 22.6 (12) | |||
| I–II | 2.6 (1) | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | |||
| II | 42.1 (16) | 35.0 (14) | 45.3 (24) | |||
| II–III | 2.6 (1) | 7.5 (3) | 0.0 (0) | |||
| III | 26.3 (10) | 40.0 (16) | 32.1 (17) | |||
| Invasive hemodynamics | ||||||
| CI—L/min/m2—mean ± SD | 2.24 ± 0.57 (N = 14) | 2.58 ± 1.21 (N = 14) | 2.28 ± 0.46 (N = 36) | 0.655 | 1.000 | 0.551 |
| PCWP—mmHg—mean ± SD | 19.57 ± 5.95 (N = 14) | 20.92 ± 12.87 (N = 12) | 20.32 ± 5.16 (N = 34) | 0.900 | 0.555 | 0.480 |
| Female (N = 109) | Male (N = 109) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | |||
| Age—years—mean ± SD | 75.79 ± 9.50 (N = 109) | 74.25 ± 8.78 (N = 108) | 0.212 |
| Outpatients—% (a.n.) | 62.6 (67) (N = 107) | 58.9 (63) (N = 107) | 0.578 |
| BMI—kg/m2—mean ± SD | 28.66 ± 6.86 (N = 108) | 28.94 ± 5.06 (N = 108) | 0.397 |
| BMI category—median | II (N = 108) | II (N = 108) | 0.163 |
| BMI category—% (a.n.) | |||
| I | 33.3 (36) | 24.1 (26) | |
| II | 28.7 (31) | 31.5 (34) | |
| III | 38.0 (41) | 44.4 (48) | |
| BP (sys.)—mmHg—mean ± SD | 137.00 ± 28.36 (N = 69) | 139.41 ± 23.64 (N = 71) | 0.364 |
| BP (dias.)—mmHg—mean ± SD | 78.29 ± 14.20 (N = 68) | 79.22 ± 11.29 (N = 69) | 0.604 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| AF—% (a.n.) | 75.2 (82) (N = 109) | 73.4 (80) (N = 109) | 0.758 |
| AHT—% (a.n.) | 94.5 (103) (N = 109) | 93.6 (102) (N = 109) | 0.776 |
| Diabetes—% (a.n.) | 33.0 (36) (N = 109) | 38.5 (42) (N = 109) | 0.399 |
| (ex-) nicotine abuse—% (a.n.) | 22.0 (24) (N = 109) | 45.0 (48) (N = 109) | <0.001 * |
| CVD—% (a.n.) | 6.4 (7) (N = 109) | 18.3 (20) (N = 109) | 0.007 * |
| PAD—% (a.n.) | 12.8 (14) (N = 109) | 23.9 (26) (N = 109) | 0.036 * |
| CHD—% (a.n.) | 34.9 (38) (N = 109) | 52.3 (57) (N = 109) | 0.009 * |
| MI—% (a.n.) | 9.2 (10) (N = 109) | 16.5 (18) (N = 109) | 0.106 |
| Stroke/TIA—% (a.n.) | 8.3 (9) (N = 109) | 18.3 (20) (N = 109) | 0.028 * |
| COPD—% (a.n.) | 19.3 (21) (N = 109) | 17.4 (19) (N = 109) | 0.728 |
| Sleep apnea—% (a.n.) | 9.2 (10) (N = 109) | 20.2 (22) (N = 109) | 0.022 * |
| PAH—% (a.n.) | 17.4 (19) (N = 109) | 25.7 (28) (N = 109) | 0.140 |
| CKD—% (a.n.) | 56.0 (61) (N = 109) | 56.0 (61) (N = 109) | 1.000 |
| Comorbidities—No.—mean ± SD | 3.67 ± 1.62 (N = 109) | 4.38 ± 1.74 (N = 109) | 0.002 * |
| Clinical performance | |||
| NYHA class—median | III (N = 103) | II–III (N = 102) | 0.066 |
| NYHA class—% (a.n.) | |||
| I | 5.8 (6) | 7.8 (8) | |
| I–II | 1.0 (1) | 5.9 (6) | |
| II | 25.2 (26) | 29.4 (30) | |
| II–III | 16.5 (17) | 15.7 (16) | |
| III | 34.0 (35) | 30.4 (31) | |
| III–IV | 8.7 (9) | 3.9 (4) | |
| IV | 8.7 (9) | 6.9 (7) | |
| Edema—% (a.n.) | 32.0 (31) (N = 97) | 42.0 (42) (N = 100) | 0.146 |
| HFA-PEFF scoring total—median (IQR) | 5.00 [2] (N = 105) | 5.00 [2] (N = 108) | 0.839 |
| HFA-PEFF sc.—% (a.n.) | |||
| 1 | 1.9 (2) | 0.9 (1) | |
| 2 | 5.7 (6) | 5.6 (6) | |
| 3 | 6.7 (7) | 13.0 (14) | |
| 4 | 24.8 (26) | 25.0 (27) | |
| 5 | 29.5 (31) | 25.0 (27) | |
| 6 | 30.5 (32) | 30.6 (33) | |
| H2FPEF scoring total -median (IQR) | 6.00 [2] (N = 107) | 6.00 [2] (N = 107) | 0.850 |
| H2FPEF scoring—% (a.n.) | |||
| 1 | 0.0 (0) | 0.0 (0) | |
| 2 | 4.7 (5) | 1.8 (2) | |
| 3 | 10.3 (11) | 11.9 (13) | |
| 4 | 8.4 (9) | 7.3 (8) | |
| 5 | 13.1 (14) | 21.1 (23) | |
| 6 | 19.6 (21) | 16.5 (18) | |
| 7 | 23.4 (25) | 18.3 (20) | |
| 8 | 15.9 (17) | 13.8 (15) | |
| 9 | 4.7 (5) | 9.2 (10) | |
| Laboratory findings | |||
| Sodium—mmol/L—mean ± SD | 140.19 ± 9.23 (N = 95) | 139.39 ± 4.68 (N = 99) | 0.447 |
| Potassium—mmol/L—mean ± SD | 4.36 ± 0.51 (N = 95) | 4.43 ± 0.62 (N = 99) | 0.440 |
| Urea—mg/dL—mean ± SD | 26.36 ± 17.30 (N = 77) | 26.87 ± 12.97 (N = 79) | 0.836 |
| Creatinine—mg/dL—mean ± SD | 1.28 ± 0.58 (N = 95) | 1.60 ± 1.21 (N = 99) | 0.022 * |
| eGFR—mL/min/1.73 m2—mean ± SD | 48.80 ± 20.73 (N = 92) | 51.73 ± 19.94 (N = 94) | 0.327 |
| NT-proBNP—pg/mL—median (IQR) | 1370.50 (2173) (N = 92) | 1095.00 (1706) (N = 94) | 0.509 |
| Hemoglobin—g/dL—mean ± SD | 12.03 ± 1.78 (N = 95) | 12.58 ± 2.07 (N = 99) | 0.042 * |
| Hematocrit—%—mean ± SD | 36.72 ± 4.82 (N = 95) | 38.63 ± 7.56 (N = 99) | 0.036 * |
| HbA1c—%—mean ± SD | 7.60 ± 0.71 (N = 2) | 10.60 (N = 1) | 0.179 |
| Medical therapy | |||
| ACEi—% (a.n.) | 26.6 (29) (N = 109) | 33.0 (36) (N = 109) | 0.302 |
| ARB—% (a.n.) | 43.5 (47) (N = 108) | 36.7 (40) (N = 109) | 0.308 |
| ARNI—% (a.n.) | 3.7 (4) (N = 109) | 8.3 (9) (N = 109) | 0.154 |
| ARNI/ACEi/ARB—% (a.n.) | 73.1 (79) (N = 108) | 77.1 (84) (N = 109) | 0.507 |
| Beta blockers—% (a.n.) | 80.7 (88) (N = 109) | 78.9 (86) (N = 109) | 0.737 |
| CCB—% (a.n.) | 35.8 (39) (N = 109) | 36.7 (40) (N = 109) | 0.889 |
| Diuretics—% (a.n.) | 83.5 (91) (N = 109) | 76.1 (83) (N = 109) | 0.179 |
| MRA—% (a.n.) | 25.7 (28) (N = 109) | 21.1 (23) (N = 109) | 0.426 |
| SGLT-2i—% (a.n.) | 10.1 (11) (N = 109) | 14.7 (16) (N = 109) | 0.306 |
| ASA—% (a.n.) | 17.6 (19) (N = 108) | 24.8 (27) (N = 109) | 0.198 |
| Statins—% (a.n.) | 47.7 (52) (N = 109) | 68.8 (75) (N = 109) | 0.001 * |
| OAC—% (a.n.) | 71.6 (78) (N = 109) | 72.5 (79) (N = 109) | 0.881 |
| Sys. HF treatment—% (a.n.) | 14.8 (16) (N = 108) | 20.2 (22) (N = 109) | 0.746 |
| Device therapy | |||
| IASD—% (a.n.) | 4.6 (5) (N = 109) | 8.3 (9) (N = 109) | 0.271 |
| Echocardiographic findings | |||
| LVEF—%—mean ± SD | 57.20 ± 5.40 (N = 109) | 55.88 ± 5.36 (N = 109) | 0.072 |
| LAVI—mL/m2—mean ± SD | 47.85 ± 17.93 (N = 91) | 49.66 ± 19.88 (N = 94) | 0.516 |
| E/e’—mean ± SD | 15.34 ± 5.87 (N = 78) | 12.91 ± 4.56 (N = 86) | 0.006 * |
| E/A—mean ± SD | 1.76 ± 0.95 (N = 63) | 1.8 ± 1.02 (N = 72) | 0.792 |
| e’ septal—cm/s—mean ± SD | 7.05 ± 3.40 (N = 36) | 7.15 ± 4.10 (N = 44) | 0.906 |
| e’ lateral—cm/s—mean ± SD | 9.24 ± 3.20 (N = 40) | 9.65 ± 3.43 (N = 46) | 0.565 |
| TR velocity—m/s—mean ± SD | 3.02 ± 0.53 (N = 26) | 3.22 ± 0.49 (N = 25) | 0.174 |
| Degree dias. dys.—total—median | II (N = 63) | II (N = 69) | 0.704 |
| Degree dias. dys.—% (a.n.) | |||
| I | 20.6 (13) | 23.2 (16) | |
| I–II | 0.0 (0) | 1.4 (1) | |
| II | 42.9 (27) | 39.1 (27) | |
| II–III | 1.6 (1) | 4.3 (3) | |
| III | 34.9 (22) | 31.9 (22) | |
| Invasive hemodynamics | |||
| CI—L/min/m2—mean ± SD | 2.37 ± 0.54 (N = 32) | 2.33 ± 0.86 (N = 33) | 0.305 |
| PCWP—mmHg—mean ± SD | 19.36 ± 5.77 (N = 28) | 20.94 ± 8.37 (N = 33) | 0.925 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hobbach, A.J.; Brix, T.J.; Weyer-Elberich, V.; Varghese, J.; Reinecke, H.; Linke, W.A. Obesity and Comorbidities in HFpEF: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis in a University Hospital Setting. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103348
Hobbach AJ, Brix TJ, Weyer-Elberich V, Varghese J, Reinecke H, Linke WA. Obesity and Comorbidities in HFpEF: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis in a University Hospital Setting. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103348
Chicago/Turabian StyleHobbach, Anastasia Janina, Tobias Johannes Brix, Veronika Weyer-Elberich, Julian Varghese, Holger Reinecke, and Wolfgang Albrecht Linke. 2025. "Obesity and Comorbidities in HFpEF: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis in a University Hospital Setting" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103348
APA StyleHobbach, A. J., Brix, T. J., Weyer-Elberich, V., Varghese, J., Reinecke, H., & Linke, W. A. (2025). Obesity and Comorbidities in HFpEF: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis in a University Hospital Setting. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103348








