Preserving Esthetics: Interventional Radiotherapy (Brachytherapy) as a Potential Alternative to Surgery for Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Midface
Abstract
1. Introduction
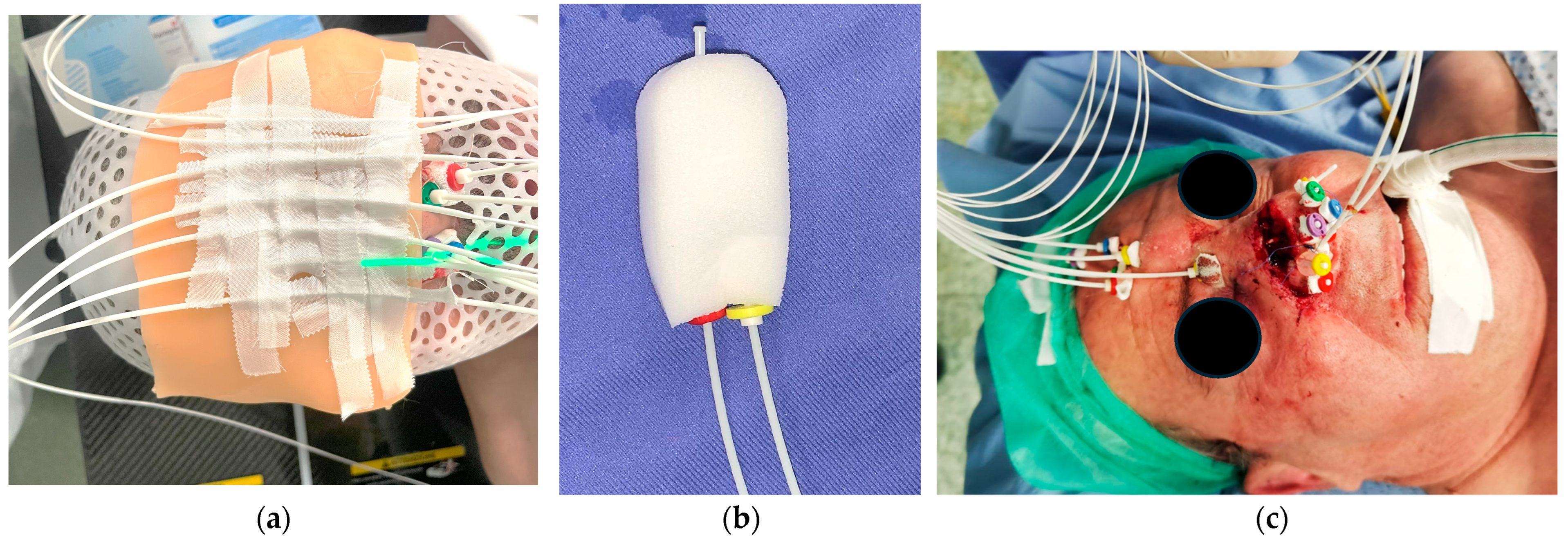
2. Materials and Methods
- For tumors located on the cheeks and lips, patients received 45 Gy in 9 fractions, delivered twice in a day (bis in die, BID), with at least 6 h between doses.
- For tumors on the nose surface, a fractionation scheme of 44 Gy in 14 fractions was used. This regimen consisted of the following:
- The first and last fractions delivering 4 Gy each, administered once daily;
- The remaining 12 fractions delivering 3 Gy each, administered BID with an inter-fraction interval of at least 6 h.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCC | Basal Cell Carcinoma |
| PDEMA | Peripheral Deep En Face Margin Assessment |
| PTS | Patients |
| HDR | High Dose Rate |
| IRT | Interventional Radiotherapy |
| NMSCs | Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers |
| CTV | Clinical Target Volume |
| BID | Bis In Die (twice a day) |
| CTCAE | Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events |
| EBRT | External Beam Radiotherapy |
| EQD2 | Equivalent Dose in 2 Gy fractions |
| OTT | Overall Treatment Time |
References
- Olsen, C.M.; Wilson, L.F.; Green, A.C.; Bain, C.J.; Fritschi, L.; Neale, R.E.; Whiteman, D.C. Cancers in Australia attributable to exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation and prevented by regular sunscreen use. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2015, 39, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepgen, T.L.; Fartasch, M.; Drexler, H.; Schmitt, J. Occupational skin cancer induced by ultraviolet radiation and its prevention. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167 (Suppl. 2), 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Tagliaferri, L.; Mattiucci, G.; Parrilla, C.; Rizzo, D.; Gambacorta, M.A.; Lancellotta, V.; Autorino, R.; Fonnesu, C.; Kihlgren, C.; et al. HDR interventional radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in the treatment of primary and recurrent head and neck malignancies. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rembielak, A.; Mansy, G.; Barnes, E.A.; Licher, J.; Tselis, N. Advances in skin brachytherapy: Cosmesis and function preservation. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 35, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, C.; Ouhib, Z.; Kamrava, M.; Koyfman, S.A.; Campbell, S.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Canavan, J.; Husain, Z.; Barker, C.A.; Cohen, G.N.; et al. The American Brachytherapy society consensus statement for skin brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2020, 19, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, V.; Rembielak, A.; Guinot, J.L.; Jaberi, R.; Lancellotta, V.; Walter, R.; Zuchora, A.; Budrukkar, A.; Kovács, G.; Jürgenliemk-Schulz, I.; et al. H&N and Skin (HNS) GEC-ESTRO Working Group critical review of recommendations regarding prescription depth, bolus thickness and maximum dose in skin superficial brachytherapy with flaps and customized moulds. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bussu, F.; Tagliaferri, L.; De Luca, L.M.; Fionda, B.; Tsatsaris, N.; Crescio, C.; Rizzo, D.; Artuso, A.; Kovacs, G.; Galli, J. A novel approach to interventional radiotherapy (brachytherapy) in nose vestibule. From Paris system rules to anatomic implantation. In Malignancies of the Nasal Vestibule; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tropiano, P.; Tagliaferri, L.; Tondo, A.; Varrucciu, S.; Gallus, R.; Mattiucci, G.C.; De Ridder, M.; Rijken, J.A.; Scheurleer, W.F.J.; D’aviero, A.; et al. From applicator-based (Paris system) implantations to rhinoseptoplasty: The concept of anatomic implantation for interventional radiotherapy in squamous cell carcinoma of the nasal vestibule. Short term results in a monoinstitutional series. Mini-Invasive Surg. 2024, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5.0. Published: 27 November 2017. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Ota, K.; Adar, T.; Dover, L.; Khachemoune, A. Review: The reemergence of brachytherapy as treatment for non-melanoma skin cancer. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2018, 29, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Lehrer, E.J.; Aphale, A.; Lango, M.; Galloway, T.J.; Zaorsky, N.G. Surgical excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, external-beam radiotherapy, or brachytherapy for indolent skin cancer: An international meta-analysis of 58 studies with 21,000 patients. Cancer 2019, 125, 3582–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliscia, C.; Fuentes, T.; Coccia, N.; Mattioni, R.; Perrone, F.; Paiar, F. High-dose-rate brachytherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer using tailored custom moulds—A single-centre experience. Contemp. Oncol. 2021, 25, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, L.; Ciardo, F.G.; Fionda, B.; Casà, C.; DI Stefani, A.; Lancellotta, V.; Placidi, E.; Macchia, G.; Capocchiano, N.D.; Morganti, A.G.; et al. Non-melanoma skin cancer treated by contact high-dose-rate radiotherapy (brachytherapy): A mono-institutional series and literature review. Vivo 2021, 35, 2313–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicheł, A.; Chyrek, A.J.; Kluska, A.; Burchardt, W.M. Advanced non-melanoma skin cancer in elderly patients: When surgery says NO, interventional radiotherapy (brachytherapy) says YES. J. Contemp. Brachyther 2023, 15, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzysztofiak, T.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Tukiendorf, A.; Suchorzepka, M.; Wojcieszek, P. Basal cell carcinoma treated with high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy-early evaluation of clinical and dermoscopic patterns during irradiation. Cancers 2021, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadavalli, P.; Pareek, V.; Barthwal, M.; Bharat, R.; Mullassery, S.; Aashita; Patil, P.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, D.N.; Mallick, S. Clinical and toxicity outcomes with 3D based-HDR surface mold brachytherapy in skin cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2024, 20, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaorsky, N.G.; Lee, C.T.; Zhang, E.; Galloway, T.J. Skin CanceR Brachytherapy vs External beam radiation therapy (SCRiBE) meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brovchuk, S.; Shepil, Z.; Venkat, P.; Vaskevych, O.; Park, S.-J. High dose rate brachytherapy for lip cancer with interstitial, surface, or a combination of interstitial and surface mold technique. Brachytherapy 2025, 24, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzysztofiak, T.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Pilśniak, A.; Wojcieszek, P. High dose rate brachytherapy in nonmelanoma skin cancer-Systematic review. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaghchi, B.; Esmati, E.; Ghalehtaki, R.; Gomar, M.; Jaberi, R.; Gholami, S.; Babaloui, S.; Nabavi, M.; Sotoudeh, S.; Khanjani, N.; et al. High-dose-rate brachytherapy in treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of head and neck region: Preliminary results of a prospective single institution study. J. Contemp. Brachyther. 2018, 10, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinot, J.L.; Bacorro, W.; Budrukkar, A.; Bussu, F.; Gonzalez-Perez, V.; Jaberi, R.; Martinez-Monge, R.; Rembielak, A.; Rovirosa, A.; Strnad, V.; et al. GEC-ESTRO recommendations for head & neck cancer brachytherapy (interventional radiotherapy): 2nd update with focus on HDR and PDR. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 201, 110533. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, S.; Arenas, M.; Gutierrez, C.; Richart, J.; Perez-Calatayud, J.; Celada, F.; Santos, M.; Rovirosa, A. Recommendations of the Spanish brachytherapy group (GEB) of Spanish Society of Radiation Oncology (SEOR) and the Spanish Society of Medical Physics (SEFM) for high-dose rate (HDR) non melanoma skin cancer brachytherapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-Y.; Tang, J.-Y.; Hu, S.C.-S.; Ke, K.C.-L.; Cheng, S.-T. Electronic brachytherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer in Asians: Experience from a Taiwan medical center. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherf, C.; Licher, J.; Mletzko, C.; Trommel, M.; Tselis, N.; Chatzikonstantinou, G.; Diefenhardt, M.; Rödel, C.; Köhn, J.; Ramm, U. Individualized mould-based high-dose-rate brachytherapy for perinasal skin tumors: Technique evaluation from a dosimetric point of view. J. Contemp. Brachyther. 2021, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyrek, A.J.; Chicheł, A.; Burchardt, W.M.; Bielęda, G.; Jankowska, M.; Moczko, J.; Roszak, A. Superficial high-dose-rate brachytherapy for primary tumors and relapses after surgery in patients with basal cell carcinoma of the head and neck region: Results of a retrospective comparative cohort study. J. Contemp. Brachyther. 2022, 14, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, S.; Salleron, J.; Py, J.-F.; Cuenin, M.; Buchheit, I.; Marchesi, V.; Huger, S.; Meknaci, E.; Peiffert, D. High-dose-rate brachytherapy for facial skin cancer: Outcome and toxicity assessment for 71 cases. Brachytherapy 2021, 20, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareco, V.; Bujor, L.; Abrunhosa-Branquinho, A.N.; Ferreira, M.R.; Ribeiro, T.; Vasconcelos, A.L.; Ferreira, C.R.; Jorge, M. Interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy in eyelid cancer. Brachytherapy 2015, 14, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge-Cadet, J.; Vairel, B.; Morisseau, M.; Moyal, E.; Ducassou, A.; Chira, C.; Pagès, C.; Sibaud, V.; Brun, T.; Modesto, A. High-dose-rate brachytherapy for treatment of facial skin cancers: Local control, toxicity, and quality of life in 67 patients. Cancers 2024, 16, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, E.; Bardet, E.; Ferron, C.; Peuvrel, P.; Supiot, S.; Campion, L.; De Montreuil, C.B.; Mahe, M.A.; Dreno, B. Interstitial brachytherapy of periorificial skin carcinomas of the face: A retrospective study of 97 cases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| # | Age at Time of Treatment | Sex | Site | Main Involved Side | Hystological Subtypes | Type of Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 68 | M | Nose | Right | Nodular | Primary |
| 2 | 57 | F | Upper Lip | Right | Morpheaform | Primary |
| 3 | 62 | M | Nose | Left | Nodular | Recurrent |
| 4 | 72 | M | Nose | Left | Infiltrative | Recurrent |
| 5 | 90 | M | Nose | Left | Nodular | Recurrent |
| 6 | 84 | M | Nose | Left | Infiltrative | Recurrent |
| 7 | 59 | M | Nose | Left | Nodular | Primary |
| 8 | 77 | M | Nose | Right | Basosquamous | Recurrent |
| # | CTV_cc | CTV Dmean (Gy) | Dose Total (Gy)/#Fractions | Total Number of Plastic Tubes | Endocavitary Tubes | Surface Tubes | Interstitial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.08 | 62.3 | 44/14 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 2 | 13.3 | 93.5 | 45/9 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 6 | 53.08 | 44/14 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 0 |
| 4 | 4.1 | 59.05 | 44/14 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
| 5 | 11.54 | 55.05 | 44/14 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 0 |
| 6 | 3.71 | 62.7 | 44/14 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| 7 | 18.92 | 76.06 | 44/14 | 11 | 4 | 7 | 0 |
| 8 | 23.28 | 78.7 | 44/14 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Re, A.; Lai, S.; Mantione, G.; D’Aviero, A.; Sanna, F.; Pilloni, E.; Menna, S.; Piccari, D.; Boschetti, A.; Fionda, B.; et al. Preserving Esthetics: Interventional Radiotherapy (Brachytherapy) as a Potential Alternative to Surgery for Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Midface. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103305
Re A, Lai S, Mantione G, D’Aviero A, Sanna F, Pilloni E, Menna S, Piccari D, Boschetti A, Fionda B, et al. Preserving Esthetics: Interventional Radiotherapy (Brachytherapy) as a Potential Alternative to Surgery for Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Midface. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103305
Chicago/Turabian StyleRe, Alessia, Sebastiana Lai, Glenda Mantione, Andrea D’Aviero, Fabrizio Sanna, Elisa Pilloni, Sebastiano Menna, Danila Piccari, Althea Boschetti, Bruno Fionda, and et al. 2025. "Preserving Esthetics: Interventional Radiotherapy (Brachytherapy) as a Potential Alternative to Surgery for Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Midface" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103305
APA StyleRe, A., Lai, S., Mantione, G., D’Aviero, A., Sanna, F., Pilloni, E., Menna, S., Piccari, D., Boschetti, A., Fionda, B., Porru, D., Tramaloni, P., Gallus, R., Tagliaferri, L., Montesu, M. A., Rubino, C., Bussu, F., & Mattiucci, G. C. (2025). Preserving Esthetics: Interventional Radiotherapy (Brachytherapy) as a Potential Alternative to Surgery for Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Midface. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103305








