Balance or Strength? Reconsidering Muscle Metrics in Sagittal Malalignment in Adult Sagittal Deformity Patients
Abstract
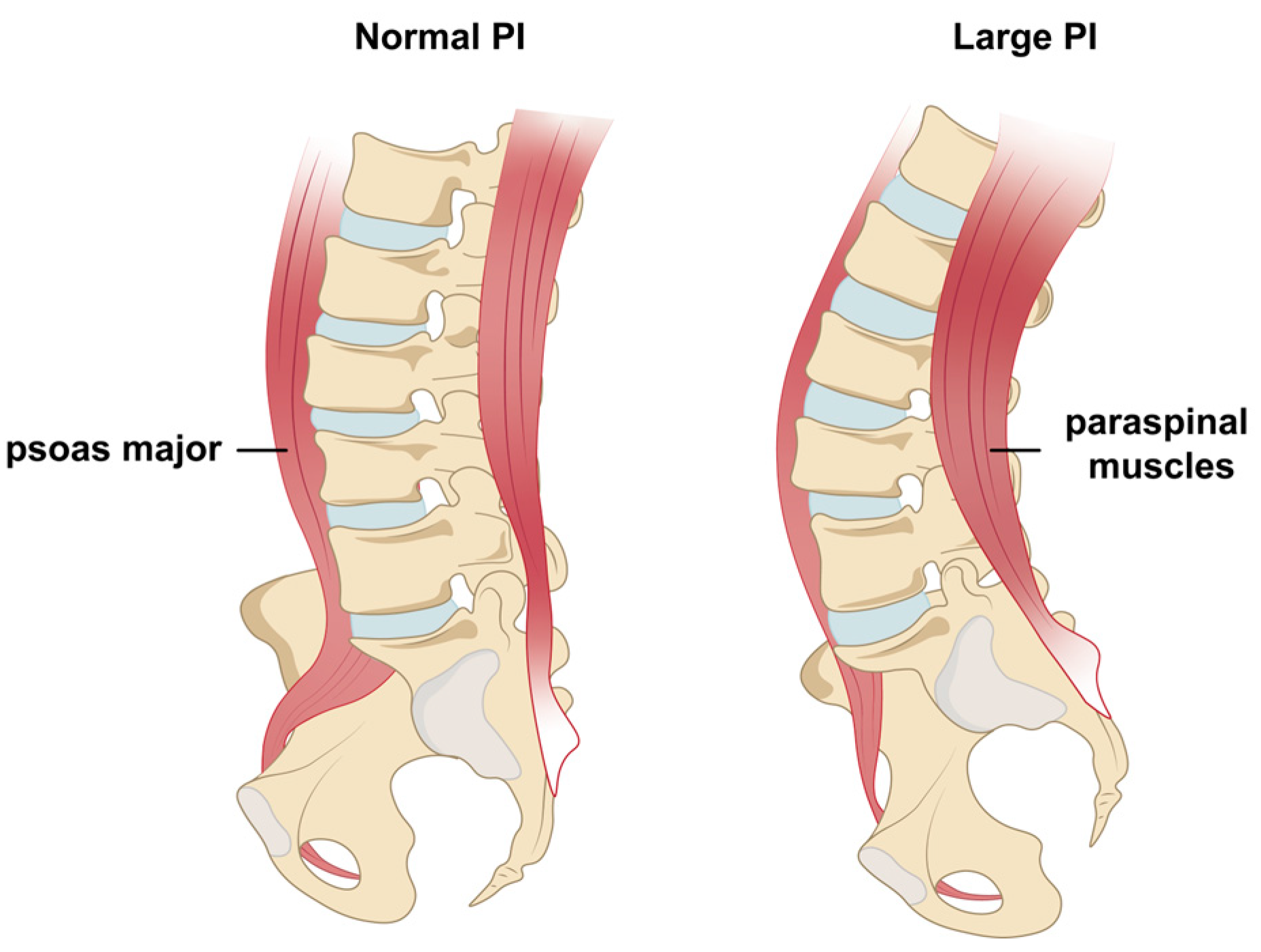
1. Introduction
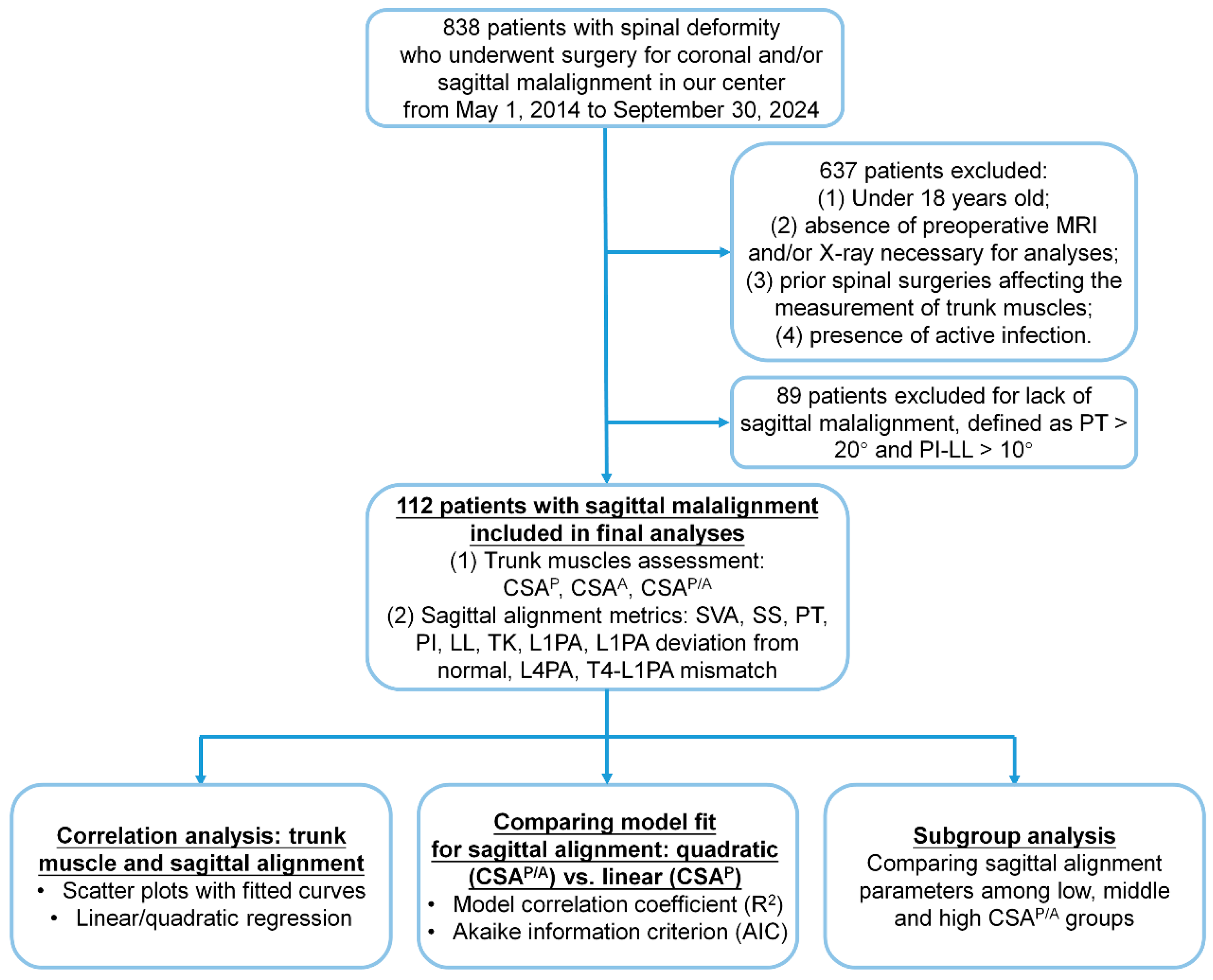
2. Materials and Methods
- Patient Enrollment
- Data Collection and Radiographic Analysis
- Spinal Alignment Assessment
- Trunk Muscle Assessment
- Ethical Approval
- Statistical Analysis
3. Results
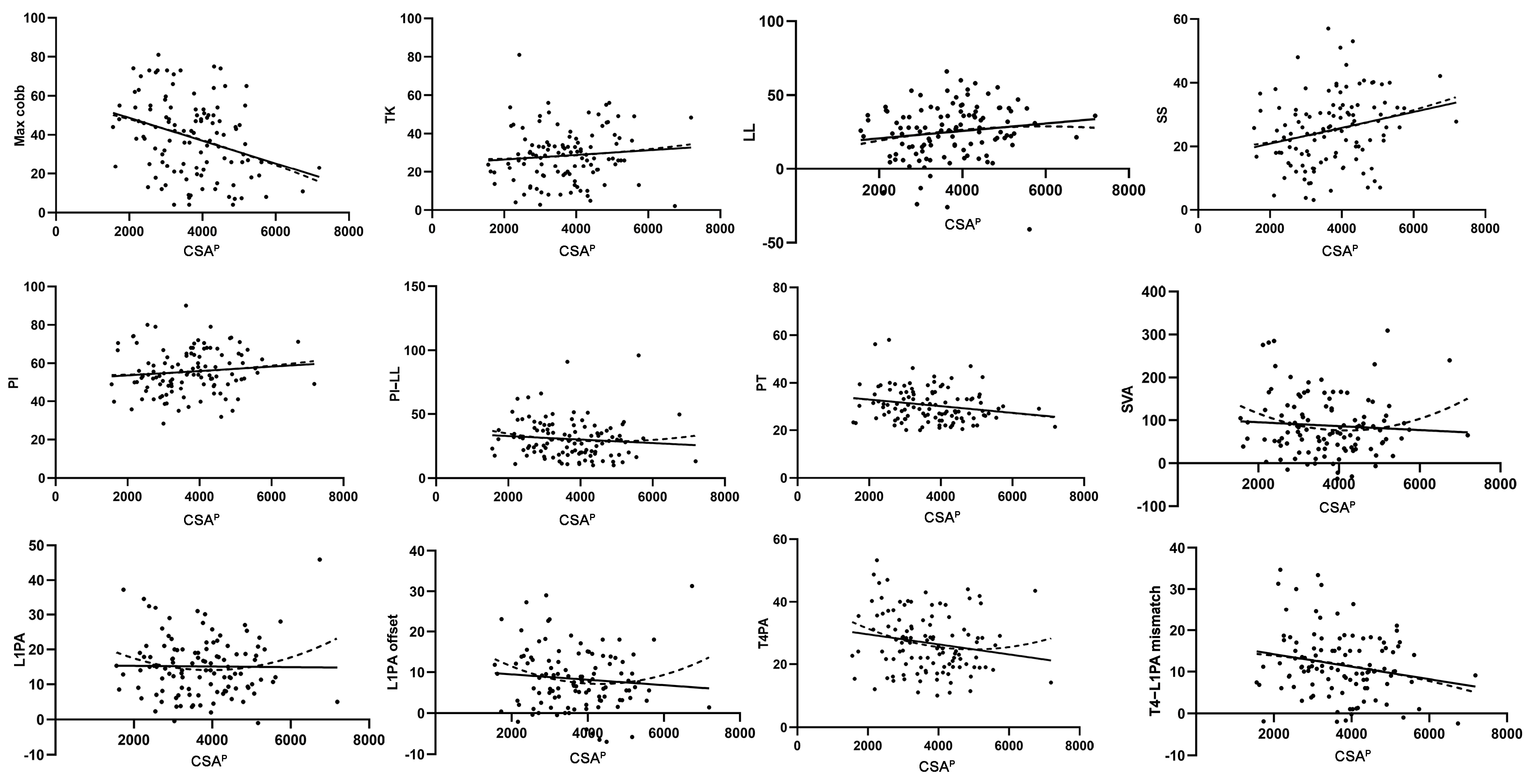
3.1. Simple Linear Regression Analysis of the Relationship Between Trunk Muscles and Sagittal Alignment
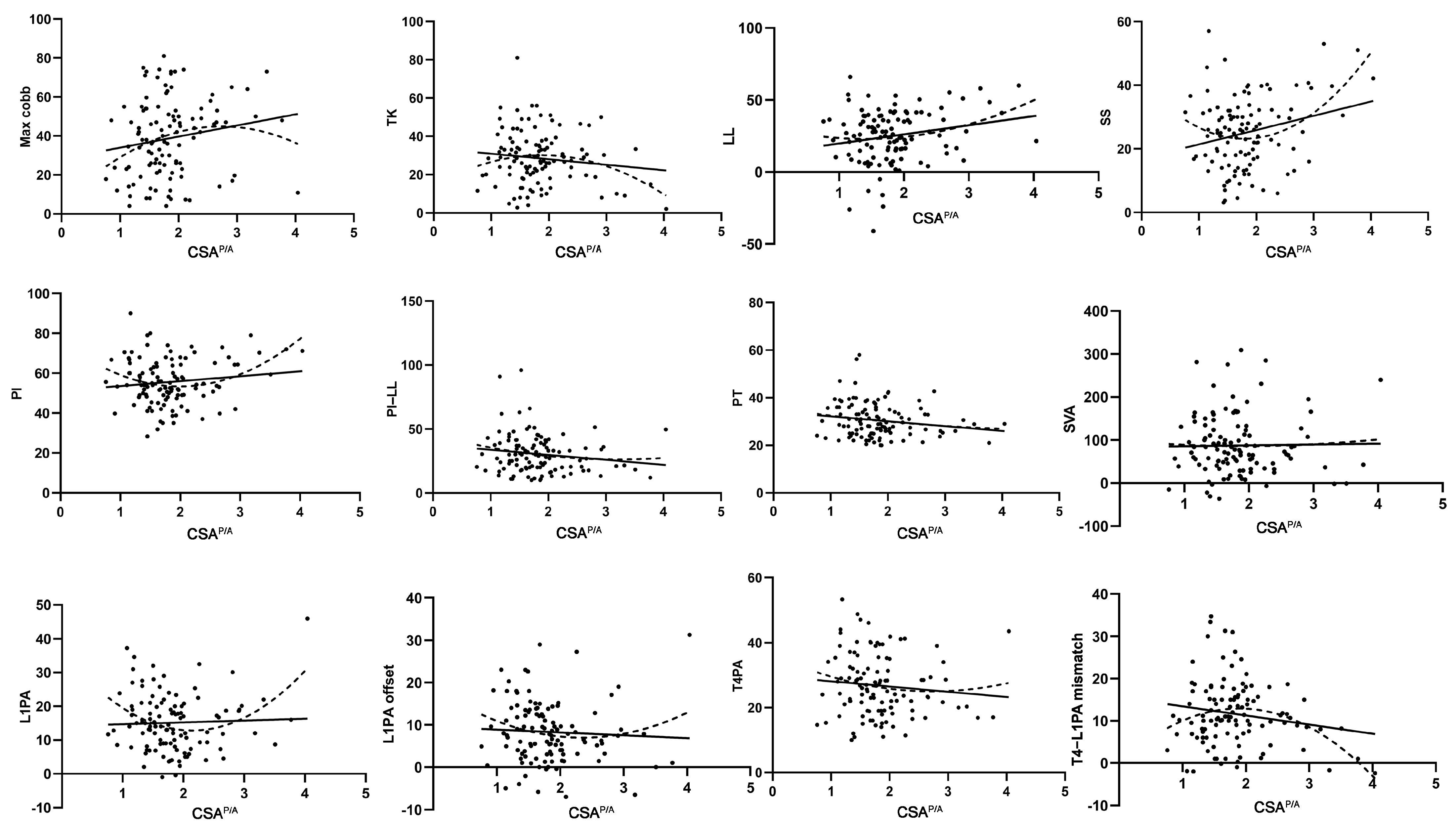
3.2. Quadratic Regression Analysis of the Relationship Between Trunk Muscles and Sagittal Alignment
3.3. Comparison of Quadratic (CSAP/A) and Linear (CSAP) Models for Sagittal Alignment
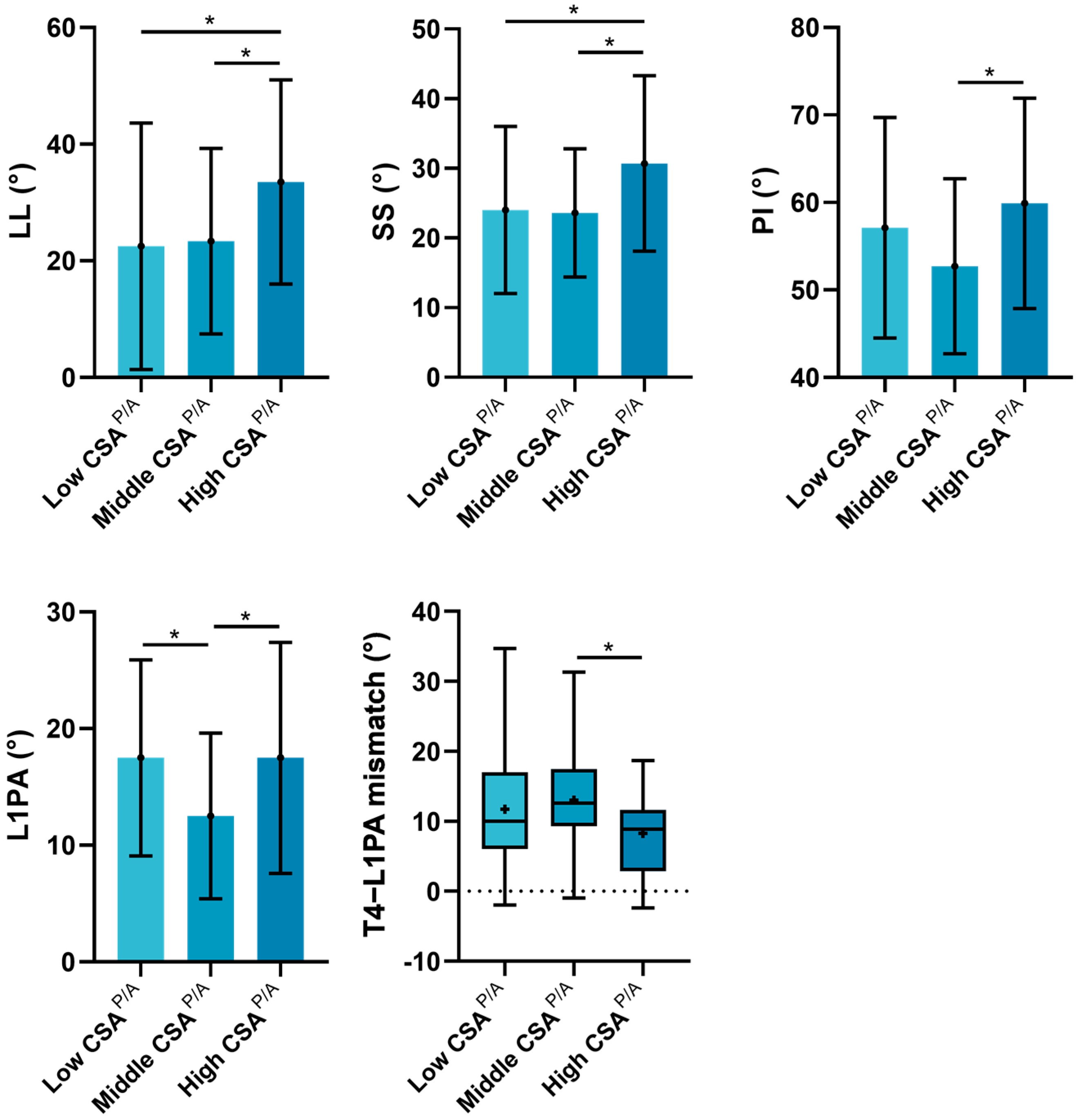
3.4. Subgroup Analyses of the Influence of CSAP/A on Sagittal Alignment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| ASD | Adult spinal deformity |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CSA | Cross-sectional area |
| CSAA | Cross-sectional area of anterior muscles |
| CSAP | Cross-sectional area of posterior muscles |
| CSAP/A | Cross-sectional area ratio of posterior to anterior muscles |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| FI | Fat infiltration |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LL | Lumbar lordosis |
| L1PA | L1 pelvic angle |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NS | No significance |
| PA | Posteroanterior |
| PI | Pelvic incidence |
| PT | Pelvic tilt |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SS | Sacral slope |
| SVA | Sagittal vertical axis |
| T4PA | T4 pelvic angle |
| TK | Thoracic kyphosis |
References
- Cerpa, M.; Lenke, L.G.; Fehlings, M.G.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Cheung, K.M.C.; Carreon, L.Y. Evolution and Advancement of Adult Spinal Deformity Research and Clinical Care: An Overview of the Scoli-RISK-1 Study. Glob. Spine J. 2019, 9 (Suppl. S1), 8s–14s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, A.; Hah, R.J. Postoperative complications in adult spinal deformity surgery: An overview of timing, risk factors, and management strategies. Semin. Spine Surg. 2023, 35, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Shin, H.M.; Song, D.G.; Lee, J.W.; Park, K.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Bae, J.H.; Choy, W.S. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes and Complications of Primary and Revision Surgery Using a Combined Anterior and Posterior Approach in Patients with Adult Spinal Deformity and Sagittal Imbalance. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.J.; Kim, B.; Kang, J.; Choi, J.; Moon, B.J.; Ryu, D.S.; Yoon, S.H.; Chin, D.K.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, K.N.; et al. Clinical, Radiographic, and Genetic Analyses in a Population-Based Cohort of Adult Spinal Deformity in the Older Population. Neurospine 2021, 18, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, K.C.; Oh, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, H. Overcorrection of lumbar lordosis for adult spinal deformity with sagittal imbalance: Comparison of radiographic outcomes between overcorrection and undercorrection. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, C.S. Comparison of Surgical Burden, Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes According to the Severity of Baseline Sagittal Imbalance in Adult Spinal Deformity Patients. Neurospine 2024, 21, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Bourghli, A.; Larrieu, D.; Boissiere, L.; Pizones, J.; Alanay, A.; PelIise, F.; Kleinstück, F.; Obeid, I. Sagittal alignment of diverse mechanical complications following adult spinal deformity surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramoto, A.; Imagama, S.; Ito, Z.; Hirano, K.; Ishiguro, N.; Hasegawa, Y. Spinal sagittal balance substantially influences locomotive syndrome and physical performance in community-living middle-aged and elderly women. J. Orthop. Sci. 2016, 21, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, J.; Mundis, G.M.; Klineberg, E.O.; Smith, J.S.; Line, B.; Gum, J.L.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Hamilton, D.K.; Soroceanu, A.; Eastlack, R.; et al. The T4-L1-Hip Axis: Sagittal Spinal Realignment Targets in Long-Construct Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: Early Impact. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2024, 106, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhni, M.C.; Shillingford, J.N.; Laratta, J.L.; Hyun, S.J.; Kim, Y.J. Restoration of Sagittal Balance in Spinal Deformity Surgery. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2018, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurube, T. Impacts of Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery on Coronal Malalignment: Commentary on “Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Patients with Mild Scoliosis and Age-Appropriate Sagittal Alignment with Minimum 2-Year Follow-up”. Neurospine 2023, 20, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Sathe, A.; Lee, S.M.; Theologis, A.A.; Deviren, V.; Lee, S.H. Correlation of Paraspinal Muscle Mass with Decompensation of Sagittal Adult Spinal Deformity After Setting of Fatigue Post 10-Minute Walk. Neurospine 2021, 18, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Hyun, S.J.; Kim, K.J. Reciprocal Changes in the Whole-Body Following Realignment Surgery in Adult Spinal Deformity. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo Totera, J.I.; Fleiderman Valenzuela, J.G.; Garrido Arancibia, J.A.; Pantoja Contreras, S.T.; Beaulieu Lalanne, L.; Alvarez-Lemos, F.L. Sagittal balance: From theory to clinical practice. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Sun, J. Erector Spinae Atrophy Correlates with Global Sagittal Imbalance and Postoperative Proximal Junctional Kyphosis Incidence in Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis. Asian Spine J. 2024, 18, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Tang, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Luo, F. Correlation between strength/endurance of paraspinal muscles and sagittal parameters in patients with degenerative spinal deformity. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.J.; Shin, H.M.; Lee, J.S.; Song, D.G.; Lee, J.W.; Chang, S.H.; Park, K.Y.; Choy, W.S. Sarcopenia and Back Muscle Degeneration as Risk Factors for Degenerative Adult Spinal Deformity with Sagittal Imbalance and Degenerative Spinal Disease: A Comparative Study. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e547–e555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Li, K.; Chen, C.; Dai, W.; Rong, Z.; Luo, F. Isokinetic strength assessment of trunk muscle and its relationship with spinal-pelvic parameters in patients with degenerative spinal deformity. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2023, 36, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Chiba, H.; Jimbo, S.; Senoo, I.; Shimizu, M.; Atsuta, Y.; Ito, H.; Sugisawa, H.; Sugawara, T.; Habaguchi, T. Clinical, physical, and radiographic analyses of lumbar degenerative kyphosis and spondylolisthesis among community-based cohort. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.S.; Shinn, J.K.; Kim, B.W.; Moon, B.J.; Ha, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, K.N.; Chin, D.K.; Yoon, S.H. Prospective Observational Cohort Study of Health-related Quality of Life: Marked Adult Sagittal Deformity (ASD) in Comparison with Mild to Moderate ASD. Spine 2019, 44, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewicki, J.; Panjabi, M.M.; Khachatryan, A. Stabilizing function of trunk flexor-extensor muscles around a neutral spine posture. Spine 1997, 22, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanishima, S.; Hagino, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Tanimura, C.; Nagashima, H. Relationship among Osteoporosis, Sarcopenia, Locomotive Syndrome, and Spinal Kyphosis in Older Individuals Living in a Local Mountain Area. Asian Spine J. 2023, 17, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomov, M.; Alvi, M.A.; Elminawy, M.; Currier, B.; Yaszemski, M.; Nassr, A.; Huddleston, P.; Sebastian, A.; Bydon, M.; Freedman, B. An Objective and Reliable Method for Identifying Sarcopenia in Lumbar Spine Surgery Patients: Using Morphometric Measurements on Computed Tomography Imaging. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Chang, I.B.; Song, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Park, M.S.; Chan Kim, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Oh, J.K.; et al. The Effect of Lumbar Spinal Muscle on Spinal Sagittal Alignment: Evaluating Muscle Quantity and Quality. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Kuroki, T.; Nagai, T.; Kawano, K.; Higa, K.; Kurogi, S.; Hamanaka, H.; Chosa, E. Sarcopenia, Ectopic Fat Infiltration into the Lumbar Paravertebral Muscles, and Lumbo-Pelvic Deformity in Older Adults Undergoing Lumbar Surgery. Spine 2022, 47, E46–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banno, T.; Yamato, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Togawa, D.; Oe, S.; Mihara, Y.; Kurosu, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Matsuyama, Y. Assessment of the Cross-Sectional Areas of the Psoas Major and Multifidus Muscles in Patients with Adult Spinal Deformity: A Case-Control Study. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E968–E973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Fu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Xu, S.; Liu, H. Association between back muscle degeneration and spinal-pelvic parameters in patients with degenerative spinal kyphosis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paalanne, N.P.; Korpelainen, R.; Taimela, S.P.; Remes, J.; Salakka, M.; Karppinen, J.I. Reproducibility and reference values of inclinometric balance and isometric trunk muscle strength measurements in Finnish young adults. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyytiäinen, K.; Salminen, J.J.; Suvitie, T.; Wickström, G.; Pentti, J. Reproducibility of nine tests to measure spinal mobility and trunk muscle strength. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1991, 23, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropponen, A.; Videman, T.; Battié, M.C. The reliability of paraspinal muscles composition measurements using routine spine MRI and their association with back function. Man. Ther. 2008, 13, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.J.; Zhao, K.L.; Koren, M.; Bentov, I.; Reed, M.J.; Pham, T.N. Thresholds and Mortality Associations of Paraspinous Muscle Sarcopenia in Older Trauma Patients. JAMA Surg. 2020, 155, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadhera, A.S.; Sachdev, R.; Andrade, N.S.; Ren, M.; Zhang, B.; Kebaish, K.M.; Cohen, D.B.; Skolasky, R.L.; Neuman, B.J. Predicting major complications and discharge disposition after adult spinal deformity surgery. Spine J. 2024, 24, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snipes, M.; Taylor, D.C. Model selection and Akaike Information Criteria: An example from wine ratings and prices. Wine Econ. Policy 2014, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Sun, J.; Cui, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, T. Spinal sagittal imbalance in patients with lumbar disc herniation: Its spinopelvic characteristics, strength changes of the spinal musculature and natural history after lumbar discectomy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, H.; Ikemoto, T.; Suzuki, J.; Inoue, M.; Arai, Y.C.; Ushida, T.; Deie, M.; Kamiya, M. Association between Trunk Muscle Strength, Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density, Lumbar Scoliosis Angle, and Skeletal Muscle Volume and Locomotive Syndrome in Elderly Individuals: A Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Study. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2020, 4, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Hoshino, M.; Ohyama, S.; Hori, Y.; Yabu, A.; Kobayashi, A.; Tsujio, T.; Kotake, S.; Nakamura, H. Relationship of back muscle and knee extensors with the compensatory mechanism of sagittal alignment in a community-dwelling elderly population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Chung, S.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Song, M.Y. Influences of trunk muscles on lumbar lordosis and sacral angle. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijančić, V.; Peharec, S.; Starčević-Klasan, G.; Grubić Kezele, T. Gender Differences in the Relationship between Physical Activity, Postural Characteristics and Non-Specific Low Back Pain in Young Adults. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.Y.; Mok, K.M.; Chan, H.C.K.; Yung, P.S.H.; Chan, K.M. Eccentric hamstring strength deficit and poor hamstring-to-quadriceps ratio are risk factors for hamstring strain injury in football: A prospective study of 146 professional players. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinert, B.L.; Collins, T.; Tehan, C.; Ragan, R.; Kernozek, T.W. Effect of Hamstring-to-quadriceps Ratio on Knee Forces in Females During Landing. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Thompson, A.; Kung, J.T.; Chieh, L.W.; Chou, S.W.; Lin, J.C. Functional isokinetic strength ratios in baseball players with injured elbows. J. Sport Rehabil. 2010, 19, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowicz, A.; Niespodziński, B.; Mieszkowski, J.; Kochanowicz, K.; Sawczyn, S. The effect of gymnastic training on muscle strength and co-activation during isometric elbow and glenohumeral flexion/extension. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 58, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, C.K.; Yeom, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Shin, S.I.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, B.S. Asymmetry of the cross-sectional area of paravertebral and psoas muscle in patients with degenerative scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirase, T.; Lovecchio, F.C.; Allen, M.R.J.; Achebe, C.C.; Mazzucco, M.; Uzzo, R.N.; Kazarian, G.S.; Asada, T.; Nakarai, H.; Subramanian, T.; et al. Preoperative Physical Therapy is Associated with Decreased Length of Stay and Improved Postoperative Mobility in Patients with Sarcopenia Undergoing Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery. Spine 2025, 50, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidar, S.; Salame, K.; Chua, M.; Khashan, M.; Ofir, D.; Grundstein, A.; Hochberg, U.; Lidar, Z.; Regev, G.J. Sarcopenia Is an Independent Risk Factor for Subsequent Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Following Percutaneous Cement Augmentation in Elderly Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava-Bringas, T.I.; Ramírez-Mora, I.; Coronado-Zarco, R.; Macías-Hernández, S.I.; Cruz-Medina, E.; Arellano-Hernández, A.; Hern Ndez-López, M.; León-Hernández, S.R. Association of strength, muscle balance, and atrophy with pain and function in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2014, 27, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, R.E.; Senefeld, J.W.; Pashibin, T.; Neumann, D.A.; Hunter, S.K. Muscle function and fatigability of trunk flexors in males and females. Biol. Sex Differ. 2017, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.S. Back support mechanisms during manual lifting. Phys. Ther. 1989, 69, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturdy, J.T.; Rizeq, H.N.; Silder, A.; Sessoms, P.H.; Silverman, A.K. Concentric and eccentric hip musculotendon work depends on backpack loads and walking slopes. J. Biomech. 2024, 163, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muellner, M.; Haffer, H.; Chiapparelli, E.; Dodo, Y.; Shue, J.; Tan, E.T.; Zhu, J.; Pumberger, M.; Sama, A.A.; Cammisa, F.P.; et al. Fat infiltration of the posterior paraspinal muscles is inversely associated with the fat infiltration of the psoas muscle: A potential compensatory mechanism in the lumbar spine. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Kim, S.B.; Park, C.K.; Malla, H.P.; Kim, S.M. Cross-Sectional Area of the Lumbar Spine Trunk Muscle and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Rate: A Retrospective Study. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E798–E803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.P.; Huang, Y.; Hu, P.; Lin, W. Lumbar Extensor and Flexor Muscle Structural Changes in Young Female Nurses with Chronic Bilateral Non-Specific Low Back Pain: A Case-Control Study. Discov. Med. 2023, 35, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Murata, H.; Kurokawa, R.; Takaishi, Y.; Asakuno, K.; Kawamoto, T. Myoarchitectonic spinolaminoplasty: Efficacy in reconstituting the cervical musculature and preserving biomechanical function. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2007, 7, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hides, J.A.; Lambrecht, G.; Richardson, C.A.; Stanton, W.R.; Armbrecht, G.; Pruett, C.; Damann, V.; Felsenberg, D.; Belavý, D.L. The effects of rehabilitation on the muscles of the trunk following prolonged bed rest. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmyślna, A.; Żurawski, A.; Rosiński, T.; Pogorzelska, J.; Śliwiński, Z.; Śliwiński, G.; Kiebzak, W. The Relationship Between the Shape of the Spine and the Width of Linea Alba in Children Aged 6-9 Years. Case-Control Study. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 839171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banno, T.; Yamato, Y.; Nojima, O.; Hasegawa, T.; Yoshida, G.; Arima, H.; Oe, S.; Ushirozako, H.; Yamada, T.; Ide, K.; et al. Comparison of the postoperative changes in trunk and lower extremity muscle activities between patients with adult spinal deformity and age-matched controls using surface electromyography. Spine Deform. 2022, 10, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanenburg, J.; Easthope, C.A.; Meinke, A.; Langenfeld, A.; Green, D.A.; Schweinhardt, P. Lunar and mars gravity induce similar changes in spinal motor control as microgravity. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1196929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Moal, B.; Vira, S.; Bronsard, N.; Amabile, C.; Errico, T.; Schwab, F.; Skalli, W.; Dubousset, J.; Lafage, V. Spino-femoral muscles affect sagittal alignment and compensatory recruitment: A new look into soft tissues in adult spinal deformity. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.T.; Serrano, K.C.; Bhatti, P.; Pishgar, F.; Vanderbeek, A.M.; Milani, C.J.; Sneag, D.B. Quantitative MRI Differentiates Electromyography Severity Grades of Denervated Muscle in Neuropathy of the Brachial Plexus. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2022, 56, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable * | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 66.3 ± 9.8 |
| Sex (M/F) (no.) | 33:79 |
| BMI (kg/m2) & | 27.7 ± 6.0 |
| Smoker (current or former), n(%) | 28(25.0%) |
| Diabetes, n(%) | 5(4.5%) |
| Tumor, n(%) | 13(11.6%) |
| Hypertension, n(%) | 45(40.1%) |
| Osteoporosis, n(%) | 20(17.9%) |
| Dyslipidemia, n(%) | 32(28.6%) |
| Coronary artery disease, n(%) | 11(9.8%) |
| Peripheral neuropathy, n(%) | 1(0.9%) |
| Autoimmune, n(%) | 4(3.6%) |
| Anxiety, n(%) | 7(6.3%) |
| Spinal alignment parameters | |
| Max Cobb (°) | 38.7 ± 19.9 |
| TK (T4–T12) (°) | 25.6 ± 13.9 |
| LL (L1–S1) (°) | 25.1 ± 18.5 |
| SS (°) | 25.1 ± 11.1 |
| PI (°) | 55.6 ± 11.6 |
| PI–LL (°) | 30.5 ± 15.1 |
| PT (°) | 30.5 ± 7.2 |
| SVA (mm) | 87.7 ± 69.8 |
| L1PA (°) | 15.1 ± 8.5 |
| L1PA offset (°) | 8.3 ± 7.3 |
| T4PA (°) | 26.8 ± 9.6 |
| T4–L1PA mismatch (°) | 11.6 ± 7.7 |
| Trunk muscle assessment # | |
| CSAP | 3707.9 ± 1074.5 |
| CSAA | 2148.7 ± 718.4 |
| CSAP/A | 1.83 ± 0.59 |
| Assessment | Max Cobb | TK | LL | SS | PI | PI–LL | PT | SVA | L1PA | L1PA Offset | T4PA | T4–L1PA Mismatch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSAP | r2 = 0.100 | r2 = 0.009 | r2 = 0.021 | r2 = 0.057 | r2 = 0.011 | r2 = 0.009 | r2 = 0.043 | r2 = 0.005 | r2 = 0.000 | r2 = 0.010 | r2 = 0.032 | r2 = 0.044 |
| p = 0.001 | p = 0.329 | p = 0.124 | p = 0.011 | p = 0.266 | p = 0.308 | p = 0.028 | p = 0.464 | p = 0.901 | p = 0.301 | p = 0.057 | p = 0.027 | |
| CSAA | r2 = 0.210 | r2 = 0.024 | r2 = 0.000 | r2 = 0.004 | r2 = 0.002 | r2 = 0.003 | r2 = 0.001 | r2 = 0.011 | r2 = 0.000 | r2 = 0.001 | r2 = 0.007 | r2 = 0.011 |
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.101 | p = 0.877 | p = 0.502 | p = 0.646 | p = 0.590 | p = 0.713 | p = 0.268 | p = 0.981 | p = 0.735 | p = 0.383 | p = 0.270 | |
| CSAP/A | r2 = 0.029 | r2 = 0.015 | r2 = 0.042 | r2 = 0.057 | r2 = 0.016 | r2 = 0.023 | r2 = 0.029 | r2 = 0.000 | r2 = 0.001 | r2 = 0.003 | r2 = 0.010 | r2 = 0.028 |
| p = 0.073 | p = 0.196 | p = 0.031 | p = 0.011 | p = 0.187 | p = 0.108 | p = 0.074 | p = 0.859 | p = 0.687 | p = 0.563 | p = 0.292 | p = 0.080 |
| Assessment | Max Cobb | TK | LL | SS | PI | PI–LL | PT | SVA | L1PA | L1PA Offset | T4PA | T4–L1PA Mismatch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSAP | r2 = 0.100 | r2 = 0.009 | r2 = 0.024 | r2 = 0.058 | r2 = 0.012 | r2 = 0.016 | r2 = 0.043 | r2 = 0.042 | r2 = 0.029 | r2 = 0.042 | r2 = 0.048 | r2 = 0.045 |
| p = 0.003 | p = 0.608 | p = 0.261 | p = 0.038 | p = 0.525 | p = 0.404 | p = 0.089 | p = 0.096 | p = 0.202 | p = 0.096 | p = 0.068 | p = 0.083 | |
| CSAA | r2 = 0.212 | r2 = 0.024 | r2 = 0.000 | r2 = 0.005 | r2 = 0.003 | r2 = 0.005 | r2 = 0.001 | r2 = 0.013 | r2 = 0.009 | r2 = 0.007 | r2 = 0.008 | r2 = 0.016 |
| p = 0.000 | p = 0.259 | p = 0.974 | p = 0.762 | p = 0.841 | p = 0.768 | p = 0.931 | p = 0.481 | p = 0.623 | p = 0.664 | p = 0.658 | p = 0.423 | |
| CSAP/A | r2 = 0.050 | r2 = 0.048 | r2 = 0.056 | r2 = 0.134 | r2 = 0.096 | r2 = 0.028 | r2 = 0.029 | r2 = 0.001 | r2 = 0.114 | r2 = 0.031 | r2 = 0.018 | r2 = 0.094 |
| p = 0.060 | p = 0.070 | p = 0.044 | p = 0.000 | p = 0.004 | p = 0.209 | p = 0.196 | p = 0.945 | p = 0.001 | p = 0.184 | p = 0.376 | p = 0.005 |
| Regression Model | Muscle Parameter | Max Cobb | TK | LL | SS | PI | PI–LL | PT | SVA | L1PA | L1PA Offset | T4PA | T4–L1PA Mismatch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | CSAP | 867.4 | 798.0 | 859.5 | 742.3 | 756.2 | 816.5 | 646.3 | 1159.3 | 687.2 | 651.6 | 711.0 | 662.4 |
| Quadratic | CSAP/A | 875.4 | 795.5 | 857.5 | 734.8 | 748.1 | 816.3 | 649.9 | 1161.7 | 675.6 | 651.2 | 714.7 | 658.4 |
| Decreased AIC value from linear to quadratic model | −8.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 7.4 | 8.0 | 0.2 | −3.6 | −2.4 | 11.6 | 0.4 | −3.7 | 4.1 | |
| Parameters | CSAP/A | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Group (n = 38) | Middle Group (n = 52) | High Group (n = 22) | Total | L Versus M | L Versus H | M Versus H | |
| Max Cobb (°) | 36.3 (17.2, 49.3) | 36.5 (25.3, 52.5) | 47.5 (34.2, 55.0) | 0.207 $ | NS | NS | NS |
| TK (°) # | 30.8 ± 15.9 | 27.8 ± 12.7 | 26.6 ± 13.2 | 0.459 * | NS | NS | NS |
| LL (°) | 22.5 ± 21.1 | 23.4 ± 15.9 | 33.5 ± 17.5 | 0.056 * | NS | 0.026 | 0.031 |
| SS (°) | 24.0 ± 12.0 | 23.6 ± 9.2 | 30.7 ± 12.6 | 0.030 * | NS | 0.023 | 0.012 |
| PI (°) | 57.1 ± 12.6 | 52.7 ± 10.0 | 59.9 ± 12.0 | 0.031 * | NS | NS | 0.015 |
| PI–LL (°) | 30.7 (21.5, 41.9) | 29.4 (19.9, 37.8) | 21.4 (17.6, 34.3) | 0.226 $ | NS | NS | NS |
| PT (°) # | 31.0 (26.1, 38.6) | 27.7 (24.9, 34.0) | 29.0 (25.2, 32.9) | 0.056 $ | NS | NS | NS |
| SVA (mm) # | 85.5 (48.9, 136.7) | 70.4 (36.7, 112.6) | 66.2 (34.1, 137.1) | 0.790 $ | NS | NS | NS |
| L1PA (°) | 17.5 ± 8.4 | 12.5 ± 7.1 | 17.5 ± 9.9 | 0.007 * | 0.005 | NS | 0.018 |
| L1PA offset (°) # | 9.6 (3.9, 16.0) | 6.5 (3.0, 11.8) | 6.4 (3.2, 10.5) | 0.195 $ | NS | NS | NS |
| T4PA (°) # | 28.9 (22.0, 36.3) | 24.1 (18.9, 31.3) | 23.3 (18.6, 30.6) | 0.147 $ | NS | NS | NS |
| T4–L1PA mismatch (°) # | 10.0 (6.0, 17.0) | 12.6 (9.3, 17.5) | 8.9 (2.9, 11.7) | 0.041 $ | NS | NS | 0.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Dekhne, M.; Durbas, A.; Subramanian, T.; Dykhouse, G.; Uzzo, R.N.; Colón, L.F.; Owusu-Sarpong, S.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Balance or Strength? Reconsidering Muscle Metrics in Sagittal Malalignment in Adult Sagittal Deformity Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103293
Huang D, Wang Z, Dekhne M, Durbas A, Subramanian T, Dykhouse G, Uzzo RN, Colón LF, Owusu-Sarpong S, Kim HJ, et al. Balance or Strength? Reconsidering Muscle Metrics in Sagittal Malalignment in Adult Sagittal Deformity Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103293
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Donghua, Zhan Wang, Mihir Dekhne, Atahan Durbas, Tejas Subramanian, Gabrielle Dykhouse, Robert N. Uzzo, Luis Felipe Colón, Stephane Owusu-Sarpong, Han Jo Kim, and et al. 2025. "Balance or Strength? Reconsidering Muscle Metrics in Sagittal Malalignment in Adult Sagittal Deformity Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103293
APA StyleHuang, D., Wang, Z., Dekhne, M., Durbas, A., Subramanian, T., Dykhouse, G., Uzzo, R. N., Colón, L. F., Owusu-Sarpong, S., Kim, H. J., & Lovecchio, F. (2025). Balance or Strength? Reconsidering Muscle Metrics in Sagittal Malalignment in Adult Sagittal Deformity Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103293









