Routine Removal of Syndesmotic Screws After Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Fixation Does Not Affect Patient Function and Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postoperative Complications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient and Public Involvement
2.3. Setting
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Surgical Technique
2.6. Study Group
- Group 1: Syndesmosis stabilization was not removed.
- Group 2: Stabilization was routinely removed.
- Group 3: Stabilization removal was performed for specific indications, including infection, stabilization failure, persistent pain exceeding six months postsurgery, and nerve entrapment (reported in one patient).
2.7. Patient Outcomes Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Complications and Hospitalization in the Routinely Reoperated Group—Univariable Analysis
3.3. OMAS Scale and Reoperation
3.4. OMAS Scale and Fracture Type
3.5. OMAS Scale and Fixation Type
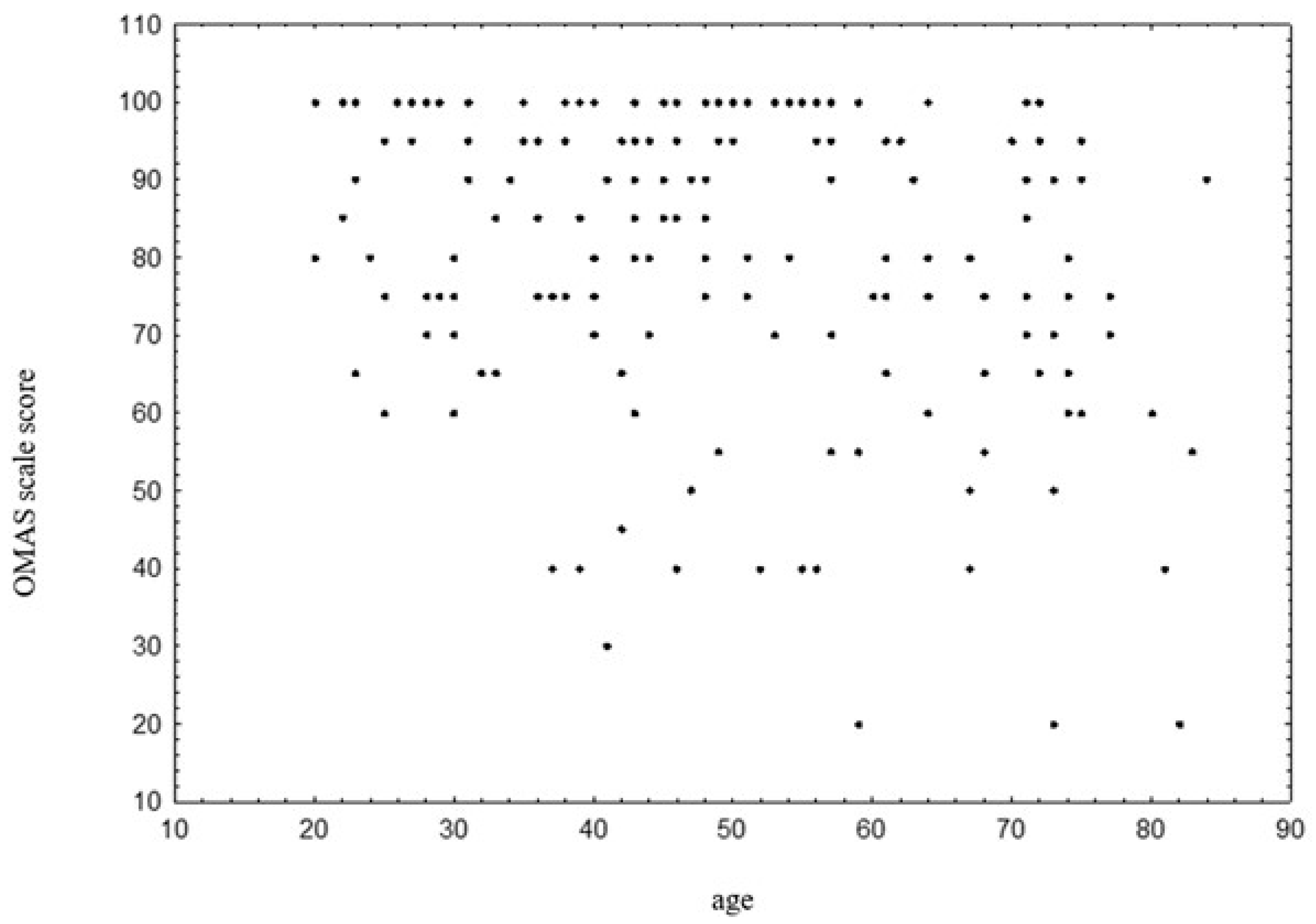
3.6. OMAS Scale and Age
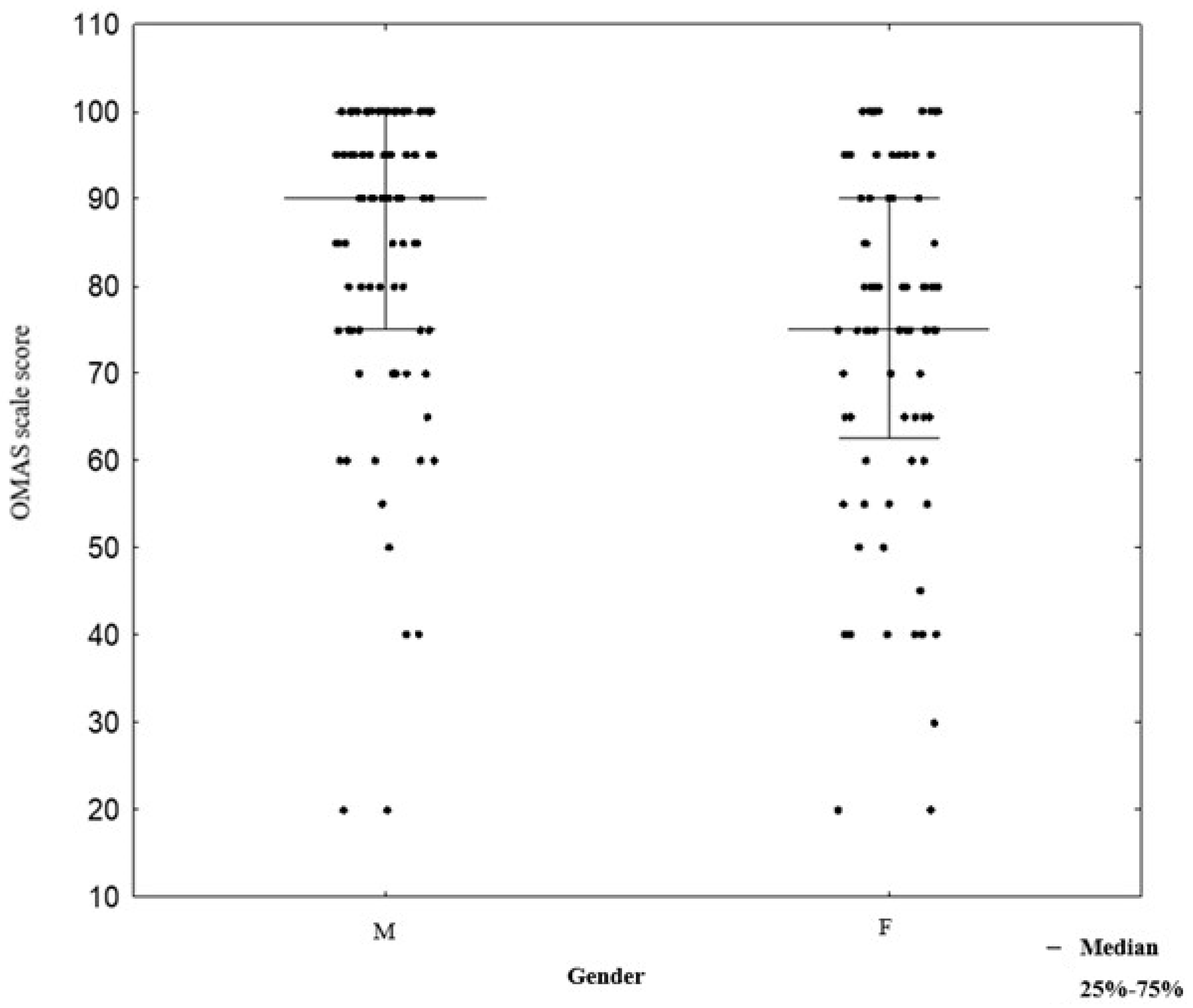
3.7. OMAS Scale and Gender
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AITFL | anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament |
| AOFAS | American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society |
| CT | computed tomography |
| HADS | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale |
| OMAS | Olerud–Molander Ankle Score |
| ORIF | open reduction and internal fixation |
| PITFL | posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament |
| PROMs | patient-reported outcomes |
| RCT | randomized controlled trial |
| SF-36 | SF-36 Health Survey |
| SMFA | Short Musculoskeletal Function Assessment |
| VAS | visual analog scale |
| WHOQOL-BREF | short version of the World Health Organization Quality of Life |
References
- Herzog, M.M.; Kerr, Z.Y.; Marshall, S.W.; Wikstrom, E.A. Epidemiology of ankle sprains and chronic ankle instability. J. Athl. Train. 2019, 54, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doherty, C.; Delahunt, E.; Caulfield, B.; Hertel, J.; Ryan, J.; Bleakley, C. The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salai, M.; Dudkiewicz, I.; Novikov, I.; Amit, Y.; Chechick, A. The epidemic of ankle fractures in the elderly: Is surgical treatment warranted? Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2000, 120, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donken, C.C.; Al-Khateeb, H.; Verhofstad, M.H.; van Laarhoven, C.J. Surgical versus conservative interventions for treating ankle fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 15, CD008470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Court-Brown, C.M.; Caesar, B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury 2006, 37, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.S.; Rees, K.; Cutler, L.; Mangwani, J. Understanding risks and complications in the management of ankle fractures. Indian J. Orthop. 2014, 48, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bejarano-Pineda, L.; Guss, D.; Waryasz, G.; DiGiovanni, C.W.; Kwon, J.Y. The syndesmosis, Part I: Anatomy, injury mechanism, classi-fication, and diagnosis. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 52, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Janney, C.; Sheu, C.; Jupiter, D.C.; Panchbhavi, V.K. Weight-bearing radiographic analysis of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Spec. 2019, 12, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colò, G.; Bignotti, B.; Costa, G.; Signori, A.; Tagliafico, A.S. Ultrasound or MRI in the evaluation of anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) injuries: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ebraheim, N.A.; Vander Maten, J.W.; Delaney, J.R.; White, E.; Hanna, M.; Liu, J. Cannulated intramedullary screw fixation of distal fibular fractures. Foot Ankle Spec. 2019, 12, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Curnutte, B.; Pan, K.; Liu, J.; Ebraheim, N.A. Biomechanical comparison of suture-button, bioabsorbable screw, and metal screw for ankle syndesmotic repair: A meta-analysis. Foot Ankle Surg. 2021, 27, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebraheim, N.A.; Dailey, M.; Huff, S.; Qu, Y.; White, E.; Liu, J. Minimal invasive fixation can decrease infection rates in diabetic and obese patients with severe ankle fracture and syndesmotic injury. Foot Ankle Spec. 2019, 12, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, T.J.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Open reduction and internal fixation for posterior pilon fracture: Transfibular approach versus posterior approach. Injury 2023, 54, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantigate, D.; Ho, G.; Kirschenbaum, J.; Bäcker, H.; Asherman, B.; Freibott, C.; Greisberg, J.K.; Vosseller, J.T. Timing of open reduction and internal fixation of ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Spec. 2019, 12, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, T. To retain or remove the syndesmotic screw: A review of literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011, 131, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wójtowicz, B.G.; Chawrylak, K.; Lesman, J.; Domżalski, M. Is there any purpose in routine syndesmotic screw removal? Systematic literature review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Dijk, C.N.; Longo, U.G.; Loppini, M.; Florio, P.; Maltese, L.; Ciuffreda, M.; Denaro, V. Classification and diagnosis of acute isolated syndesmotic injuries: ESSKA-AFAS consensus and guidelines. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 1200–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, R.; Parsons, H.; Ellard, D.R.; Kearney, R.S. An evaluation of the measurement properties of the Olerud Molander Ankle Score in adults with an ankle fracture. Physiotherapy 2021, 112, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olerud, C.; Molander, H. A scoring scale for symptom evaluation after ankle fracture. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 1984, 103, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, F.R.K.; Birnie, M.F.; Dingemans, S.A.; van den Bekerom, M.P.J.; Parkkinen, M.; van Veen, R.N.; RODEO collaborator group; Goslings, J.C.; Schepers, T. Functional outcome of routine versus on-demand removal of the syndesmotic screw: A multicentre randomized controlled trial. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ijezie, N.; Fraig, H.; Abolaji, S. Outcomes of the routine removal of the syndesmotic screw. Cureus 2022, 14, e26675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tucker, A.; Street, J.; Kealey, D.; McDonald, S.; Stevenson, M. Functional outcomes following syndesmotic fixation: A comparison of screws retained in situ versus routine removal—Is it really necessary? Injury 2013, 44, 1880–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-Jiménez, H.G.; Garibay-Cervantes, A.; Rosas-Medina, J.A.; Salas-Morales, G.A.; Rodríguez-Reyes, E.J. Prevalencia de las complicaciones relacionadas con el retiro del tornillo de situación [Prevalence of complications related to the removal of the syn-desmotic screw]. Acta Ortop. Mex. 2018, 32, 76–81. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pogliacomi, F.; Artoni, C.; Riccoboni, S.; Calderazzi, F.; Vaienti, E.; Ceccarelli, F. The management of syndesmotic screw in ankle fractures. Acta Biomed. 2018, 90, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanda, I.I.; Hosin, S.; Vermesan, D.; Deleanu, B.; Pop, D.; Crisan, D.; Al-Qatawneh, M.; Mioc, M.; Prejbeanu, R.; Rosca, O. Impact of syndesmotic screw removal on quality of life, mobility, and daily living activities in patients post distal tibiofibular diastasis repair. Medicina 2023, 21, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Desouky, O.; Elseby, A.; Ghalab, A.H. Removal of syndesmotic screw after fixation in ankle fractures: A systematic review. Cureus 2021, 13, e15435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schepers, T.; Van Lieshout, E.M.; de Vries, M.R.; Van der Elst, M. Complications of syndes-motic screw removal. Foot Ankle Int. 2011, 32, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoap, S.C.; Freibott, C.; Baumbach, S.F.; Herterich, V.; Polzer, H.; Vosseller, J.T. A multicenter retrospective study examining complication rates following syndesmotic screw removal. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2020, 5, 2473011420S00442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Dingemans, S.A.; Rammelt, S.; White, T.O.; Goslings, J.C.; Schepers, T. Should syndesmotic screws be removed after surgical fixation of unstable ankle fractures? A systematic review. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walley, K.C.; Hofmann, K.J.; Velasco, B.T.; Kwon, J.Y. Removal of hardware after syndesmotic screw fixation: A systematic literature review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2017, 10, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaftandziev, I.; Spasov, M.; Trpeski, S.; Zafirova-Ivanovska, B.; Bakota, B. Fate of the syndesmotic screw: Search for a prudent solution. Injury 2015, 46, S125–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, A.; Kumar, A.; Katekar, S.; Kapoor, D.; Vishwakarma, G.; Shah, A.; Singh, M.S. Is routine removal of syndesmotic screw justified? A meta-analysis. Foot 2021, 49, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, G.; Jonsson, K.; Ekdahl, C.; Eneroth, M. Outcome and quality of life after surgi-cally treated ankle fractures in patients 65 years or older. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2007, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chong, H.H.; Hau, M.Y.T.; Mishra, P.; Rai, P.; Mangwani, J. Patient outcomes following ankle fracture fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 2021, 42, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikerøy, A.K.; Høiness, P.R.; Andreassen, G.S.; Hellund, J.C.; Madsen, J.E. No difference in functional and radiographic results 8.4 years after quadricortical compared with tri-cortical syndesmosis fixation in ankle fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2010, 24, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.C.; Murphy, B.; O’Loughlin, P. Syndesmotic injury with ankle fracture: A systematic review of screw vs dynamic fixation. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egol, K.A.; Pahk, B.; Walsh, M.; Tejwani, N.C.; Davidovitch, R.I.; Koval, K.J. Outcome after unstable ankle fracture: Effect of syndesmotic stabilization. J. Orthop. Trauma 2010, 24, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Reoperation Due to Indications N = 22 (%) | Routine Screw Removal N = 52 (%) | No Reoperation N = 96 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 14 (63.64%) | 26 (50.00%) | 50 (52.08%) |
| Female | 8 (36.36%) | 26 (50.00%) | 46 (47.92%) | |
| Diabetes | No | 20 (90.91%) | 50 (96.15%) | 87 (90.63%) |
| Yes | 2 (9.09%) | 2 (3.85%) | 9 (9.37%) | |
| Nicotine | No | 14 (63.64%) | 43 (82.69%) | 79 (82.29%) |
| Yes | 8 (36.36%) | 9 (17.31%) | 17 (17.71%) | |
| Fracture type | Weber B | 19 (86.36%) | 43 (82.69%) | 64 (66.67%) |
| Weber C | 3 (13.64%) | 8 (15.38%) | 26 (27.08%) | |
| Synostosis | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (1.92%) | 6 (6.25%) | |
| Synthesis type | 1 three-cortical screw | 12 (54.55%) | 38 (73.08%) | 48 (50.00%) |
| 1 four-cortical screw | 3 (13.64%) | 11 (21.15%) | 19 (19.79%) | |
| 2 screws | 6 (27.27%) | 3 (5.77%) | 16 (16.67%) | |
| Endobutton | 1 (4.55%) | 0 (0.00%) | 13 (13.54%) | |
| Variable | Reoperation Due to Indications Median (25–75%) | Routine Screw Removal Median (25–75%) | No Reoperation Median (25–75%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 52 (42–57) | 48 (39–69.5) | 44 (34.5–61) |
| OMAS | 80 (65 -100) | 80 (70–95) | 85 (72.5–95) |
| Follow-up time (months) | 10 (8–17) | 12 (6–19) | 5 (3–8) |
| Reoperation | No Reoperation | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Complications | 67 (90.54%) | 94 (97.92%) | 0.042 |
| Complications | 7 (9.46%) | 2 (2.08%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wójtowicz, B.G.; Chawrylak, K.; Lesman, J.; Makowski, H.; Kuczyński, K.; Maciejowski, M.; Raciborski-Król, A.; Domżalski, M. Routine Removal of Syndesmotic Screws After Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Fixation Does Not Affect Patient Function and Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postoperative Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103276
Wójtowicz BG, Chawrylak K, Lesman J, Makowski H, Kuczyński K, Maciejowski M, Raciborski-Król A, Domżalski M. Routine Removal of Syndesmotic Screws After Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Fixation Does Not Affect Patient Function and Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postoperative Complications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103276
Chicago/Turabian StyleWójtowicz, Błażej Grzegorz, Katarzyna Chawrylak, Jędrzej Lesman, Hubert Makowski, Kacper Kuczyński, Michał Maciejowski, Antoni Raciborski-Król, and Marcin Domżalski. 2025. "Routine Removal of Syndesmotic Screws After Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Fixation Does Not Affect Patient Function and Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postoperative Complications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103276
APA StyleWójtowicz, B. G., Chawrylak, K., Lesman, J., Makowski, H., Kuczyński, K., Maciejowski, M., Raciborski-Król, A., & Domżalski, M. (2025). Routine Removal of Syndesmotic Screws After Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Fixation Does Not Affect Patient Function and Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postoperative Complications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103276





