Human Neutrophil Alpha-Defensins Promote NETosis and Liver Injury in Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Potential Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
- (1)
- sex;
- (2)
- the severity of liver failure classified by the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score, Model for End-stage Liver Disease-Sodium (MELD-Na) score, and modified Maddrey Discriminant Function (mDF) score;
- (3)
- ALC decompensation symptoms, such as ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and esophageal varices.
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Females and Males with Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis
3.2. Comparison of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations in the ALC Patients and Individuals in the Control Group
3.3. Comparison of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations in Patients with ALC Based on Age
3.4. Analysis of Correlations of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations with Child-Turcotte-Pugh, MELD-Na, and mDF Scores
3.4.1. Analysis of Correlations of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations with Child-Turcotte-Pugh Scores
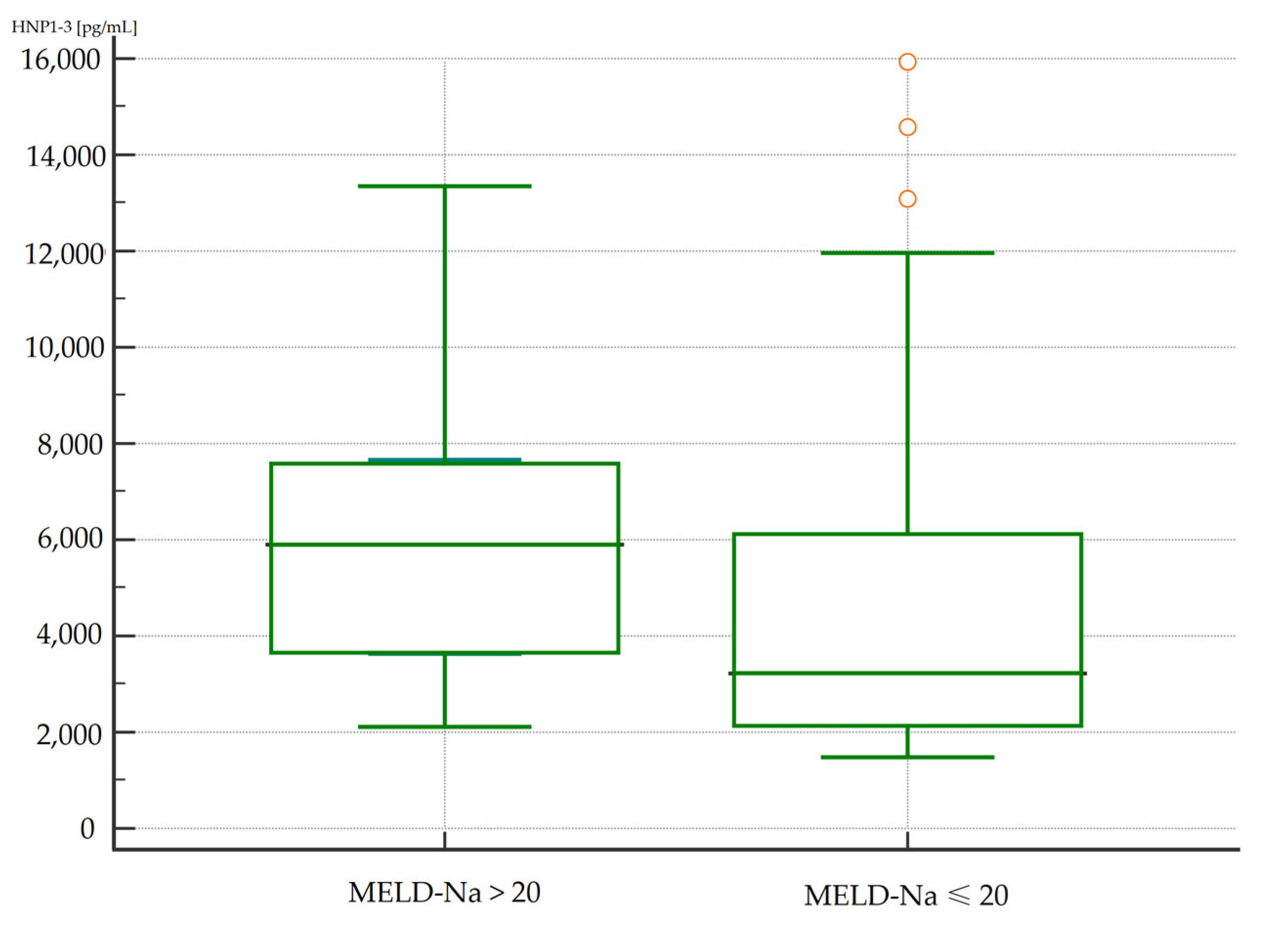
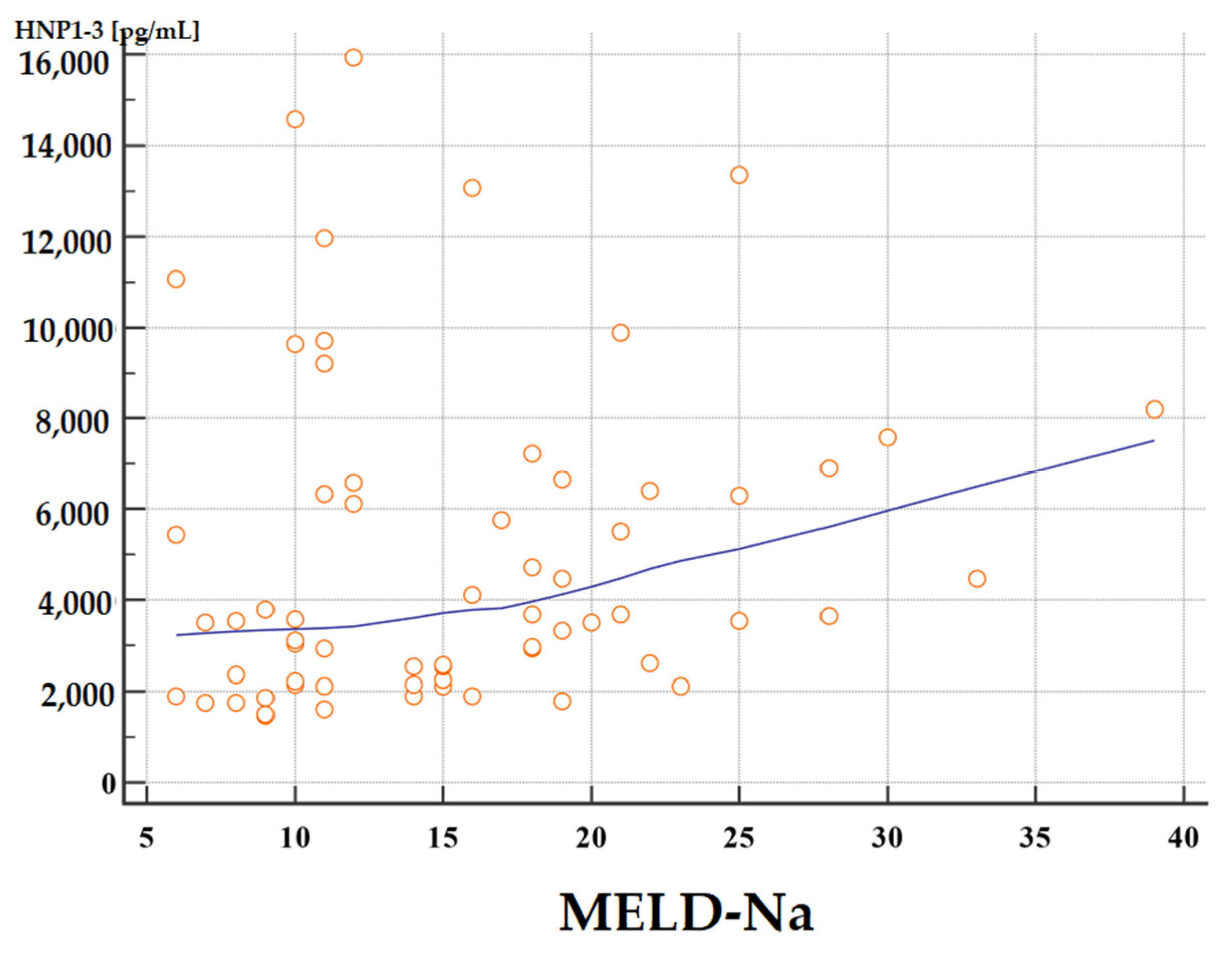
3.4.2. Analysis of Correlations of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations with MELD-Na Scores
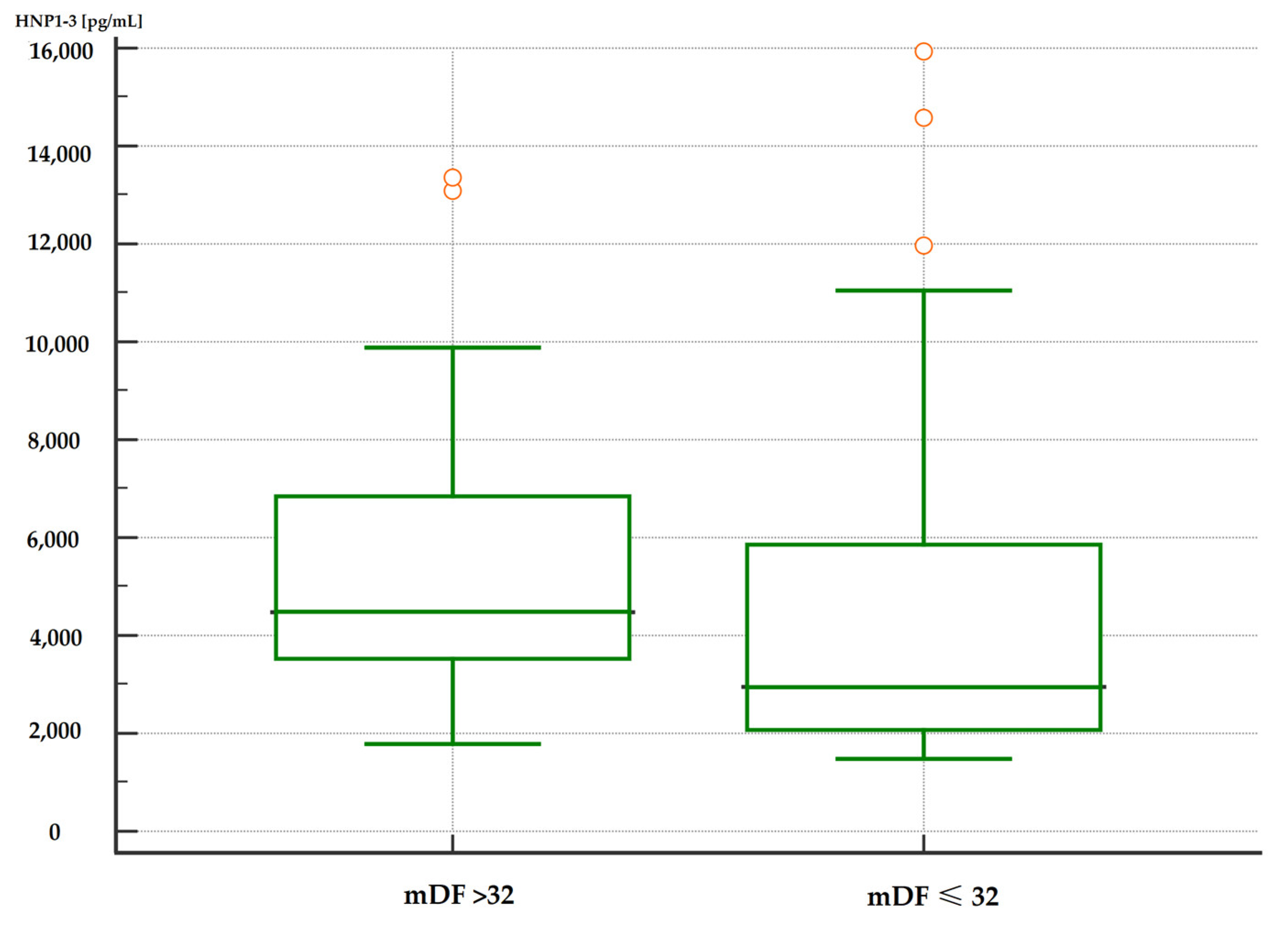
3.4.3. Analysis of Correlations of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations with mDF Scores
3.5. Comparison of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations in Patients with ALC Based on End-Stage Liver Disease Complications
3.5.1. Comparison of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations in Patients with ALC Based on the Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy
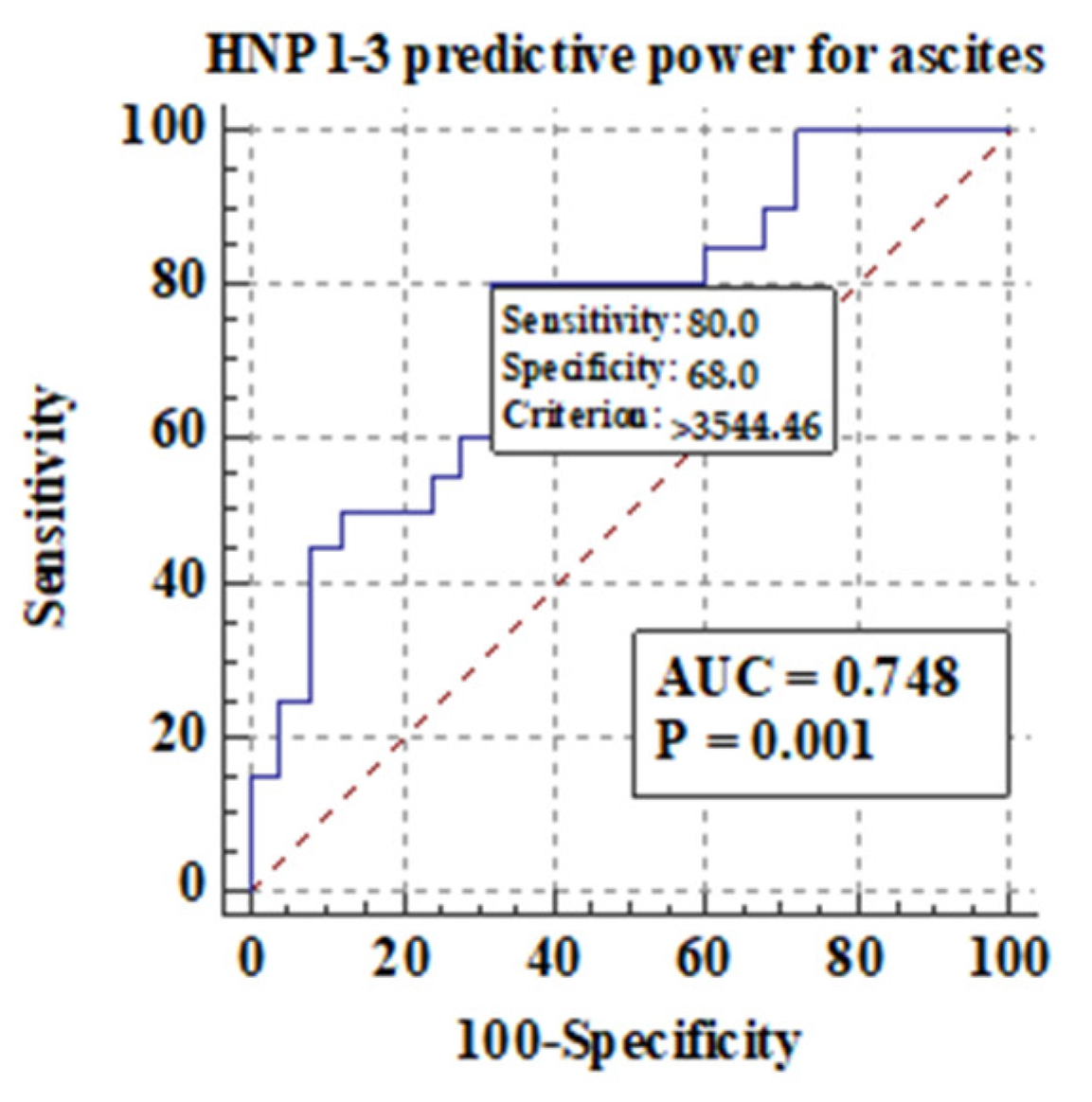
3.5.2. Comparison of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations in Patients with ALC Based on the Development of Ascites and Esophageal Varices
3.5.3. Comparison of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations in Patients with ALC Based on Non-Survival
3.6. Analysis of Correlation of Serum HNP1-3 Concentrations and Markers of Inflammation in Patients with ALC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global Burden of Liver Disease: 2023 Update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Thiele, M.; Geyer, P.E.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Webel, H.E.; Santos, A.; Gupta, R.; Meier, F.; Strauss, M.; Kjaergaard, M.; et al. Noninvasive Proteomic Biomarkers for Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetto, D.A.; Shah, V.H.; Kamath, P.S. Outpatient Management of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-H.; Han, J.H.; Chwae, Y.-J.; Jung, J.-Y.; Suh, C.-H.; Kwon, J.E.; Kim, H.-A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps May Contribute to the Pathogenesis in Adult-Onset Still Disease. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Herrmann, M.; Zhao, Y.; Muñoz, L.E. Receptor-Mediated NETosis on Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 775267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zong, X.; Jin, M.; Min, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Mechanisms and Regulation of Defensins in Host Defense. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Lu, W. Defensins: A Double-Edged Sword in Host Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Ding, J.; Liao, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, W. Defensins: The Natural Peptide Antibiotic. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adyns, L.; Proost, P.; Struyf, S. Role of Defensins in Tumor Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Dai, J.; Feng, T. Defensins as a Promising Class of Tick Antimicrobial Peptides: A Scoping Review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Fanne, R.; Maraga, E.; Kassem, E.; Groisman, G.; Amsalem, N.; Zeina, A.-R.; Abu Mouch, M.; Taher, R.; Abu-Mouch, S. Human Neutrophil α-Defensins 1–3 Are Upregulated in the Microenvironment of Fibrotic Liver. Medicina 2023, 59, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynkiewicz, R.; Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. Etiology of Viral Induced Acute Liver Failure and Defensins as Potential Therapeutic Agents in ALF Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1153528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Shao, T.; Deng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, M.; et al. Recent Insights into the Role of Defensins in Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, A.; Marin, M.; Honnen, W.; Ramasamy, S.; Porter, E.; Subbian, S.; Pinter, A.; Melikyan, G.B.; Lu, W.; et al. Human Defensins Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Blocking Viral Entry. Viruses 2021, 13, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, S.; Nagaraj, R.; Idris, M.M. Defensins: Therapeutic Molecules with Potential to Treat SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Indian J. Med. Res. 2022, 155, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.L.T.; Trujillo-Paez, J.V.; Umehara, Y.; Yue, H.; Peng, G.; Kiatsurayanon, C.; Chieosilapatham, P.; Song, P.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Role of Antimicrobial Peptides in Skin Barrier Repair in Individuals with Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The WHO Regional Office for Europe. Food-Based Dietary Guidelines in the WHO European Region. 2020. Available online: https://knowledge4policy.ec.europa.eu/health-promotion-knowledge-gateway/food-based-dietary-guidelines-europe-table-17_en (accessed on 19 February 2024).
- Kasztelan-Szczerbinska, B.; Adamczyk, K.; Surdacka, A.; Rolinski, J.; Michalak, A.; Bojarska-Junak, A.; Szczerbinski, M.; Cichoz-Lach, H. Gender-Related Disparities in the Frequencies of PD-1 and PD-L1 Positive Peripheral Blood T and B Lymphocytes in Patients with Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: A Single Center Pilot Study. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasztelan-Szczerbinska, B.; Surdacka, A.; Slomka, M.; Rolinski, J.; Celinski, K.; Cichoz-Lach, H.; Madro, A.; Szczerbinski, M. Angiogenesis-Related Biomarkers in Patients with Alcoholic Liver Disease: Their Association with Liver Disease Complications and Outcome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 673032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasztelan-Szczerbińska, B.; Surdacka, A.; Celiński, K.; Roliński, J.; Zwolak, A.; Miącz, S.; Szczerbiński, M. Prognostic Significance of the Systemic Inflammatory and Immune Balance in Alcoholic Liver Disease with a Focus on Gender-Related Differences. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursz, M.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Moreno, C.; Spahr, L.; Sterneck, M.; Cortez-Pinto, H. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 154–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K.; Kivlahan, D.R.; McDonell, M.B.; Fihn, S.D.; Bradley, K.A. The AUDIT Alcohol Consumption Questions (AUDIT-C): An Effective Brief Screening Test for Problem Drinking. Ambulatory Care Quality Improvement Project (ACQUIP). Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Källmén, H.; Elgán, T.H.; Wennberg, P.; Berman, A.H. Concurrent Validity of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) in Relation to Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) Severity Levels According to the Brief DSM-5 AUD Diagnostic Assessment Screener. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2019, 73, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadjesari, Z.; White, I.R.; McCambridge, J.; Marston, L.; Wallace, P.; Godfrey, C.; Murray, E. Validation of the AUDIT-C in Adults Seeking Help with Their Drinking Online. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2017, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, M.; Córdoba, J.; Doval, E.; Jacas, C.; Pujadas, F.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J. Development of a Clinical Hepatic Encephalopathy Staging Scale. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickel, F.; Datz, C.; Hampe, J.; Bataller, R. Pathophysiology and Management of Alcoholic Liver Disease: Update 2016. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, J. New Assessment of Hepatic Encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinger, J.L. High 10-Year Mortality in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Where Do We Go from Here? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 961–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraglund, F.; Deleuran, T.; Askgaard, G.; Fleming, K.M.; Jepsen, P. Decreasing Incidence of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease in Denmark: A 25-Year Nationwide Study. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhala, N.; Mellinger, J.; Asrani, S.K.; Shah, V.H. Tackling the Burden of Preventable Liver Disease in the USA. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhala, N.; Subhani, M.; Aithal, G.P. Liver Disease Admissions in the UK Are Increasing, Urgently Needing Local and National Solutions. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.M.; Ratnasekera, I.; Powell, E.E.; Hume, D.A. Causes and Consequences of Innate Immune Dysfunction in Cirrhosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Kuebler, W.M. Significance of Mast Cell Formed Extracellular Traps in Microbial Defense. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 62, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Chandra, A.; R, R.; Nigam, J.; Rajan, P.; Parmar, D.; Srivastava, R.N.; Gupta, V. Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides and Cytokines in Human Omentum Following Abdominal Surgery. Cureus 2021, 13, e17477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhai, Z.; Long, H.; Yang, G.; Deng, B.; Deng, J. Inducible Expression of Defensins and Cathelicidins by Nutrients and Associated Regulatory Mechanisms. Peptides 2020, 123, 170177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.-H.; Min, S.-Y.; Yu, H.-W.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J. Effects of Apigenin on RBL-2H3, RAW264.7, and HaCaT Cells: Anti-Allergic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Skin-Protective Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Hou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Su, H.; Koci, M.D.; Yin, H.; Zhang, C. NF-κB Activation Enhances STING Signaling by Altering Microtubule-Mediated STING Trafficking. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M. Self-Regulation of the Inflammatory Response by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruitwala, S.; El-Naccache, D.W.; Chang, T.L. Multifaceted Immune Functions of Human Defensins and Underlying Mechanisms. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 88, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Tanaka, N. PPARs as Metabolic Regulators in the Liver: Lessons from Liver-Specific PPAR-Null Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.-D. The Role of PPARs in Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Chronic Liver Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 180–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraga, E.; Safadi, R.; Amer, J.; Higazi, A.A.; Fanne, R.A. Alleviation of Hepatic Steatosis by Alpha-Defensin Is Associated with Enhanced Lipolysis. Medicina 2023, 59, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, M.N.; Musto, J.; Lucey, M.R. Novel Treatments for Alcoholic Hepatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 37, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badal, B.D.; Bajaj, J.S. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2023, 27, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lou, C.; Zheng, X.; Pang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhu, M.; Dai, X.; Wang, J.; Tu, M.; Xu, W.; et al. Plasma Human Neutrophil Peptides as Biomarkers of Disease Severity and Mortality in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Fanne, R.; Arbel, Y.; Chorin, E.; Maraga, E.; Groisman, G.M.; Higazi, A.A.; Banai, S. Association between Tissue Human Neutrophil Peptide 1-3 Levels and Cardiovascular Phenotype: A Prospective, Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221127099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Shu, Q.; Fang, X. Human Neutrophil Defensins Disrupt Liver Interendothelial Junctions and Aggravate Sepsis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 7659282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Males ALC n = 51 | Females ALC n = 11 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | ||
| Age, years a | 47.00 | 33.00–64.00 | 56.00 | 26.00–61.00 | 0.28 |
| ALT, U/L a | 42.00 | 17.50–228.25 | 38.00 | 22.00–480.00 | 0.93 |
| AST, U/L a | 101.00 | 34.40–360.40 | 112.00 | 43.00–550.00 | 0.74 |
| ALP, U/L a | 153.00 | 56.50–405.15 | 121.00 | 73.00–411.00 | 0.76 |
| GGT, U/L a | 378.00 | 43.20–2558.20 | 444.00 | 155.00–2193.00 | 0.16 |
| Bilirubin, mg/dL a | 2.90 | 0.60–16.57 | 1.70 | 0.60–34.10 | 0.82 |
| Albumin, g/dL a | 3.08 | 2.00–4.13 | 2.94 | 2.43–4.62 | 0.73 |
| INR a | 1.29 | 0.93–2.23 | 1.33 | 0.60–2.54 | 0.87 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL a | 0.80 | 0.42–1.57 | 0.60 | 0.40–2.90 | 0.14 |
| CRP, mg/L a | 20.23 | 1.69–144.82 | 23.90 | 0.53–109.70 | 0.74 |
| WBC, ×109/L a | 7.00 | 3.24–15.94 | 5.79 | 4.07–13.55 | 0.94 |
| NEU, ×109/L a | 4.52 | 1.51–13.85 | 3.57 | 2.74–12.52 | 0.86 |
| LYM, ×109/L a | 1.06 | 0.44–2.37 | 0.92 | 0.46–1.55 | 0.39 |
| NLR a | 3.98 | 1.47–14.81 | 4.03 | 2.06–27.22 | 0.68 |
| CTP, points a | 8.00 | 5.00–13.00 | 8.00 | 5.00–13.00 | 0.78 |
| MELD-Na, points a | 15.00 | 6.25–25.00 | 11.00 | 7.00–39.00 | 0.89 |
| mDF, points a | 24.40 | 2.21–75.39 | 15.40 | 1.06–102.44 | 0.88 |
| Ascites, % of patients b | 26 (50.98) | 5 (45.45) | 0.65 | ||
| Encephalopathy, % of patients b | 16 (31.37) | 2 (18.18) | 0.67 | ||
| Esophageal varices, % of patients b | 24 (47.05) | 4 (36.36) | 1.00 | ||
| Non-survival, % of patients b | 2 (3.92) | 1 (9.09) | 0.33 | ||
| Variable, ng/mL | ALC Men n = 51 | ALC Women n = 11 | p a | ALC Patients n = 62 | Controls n = 24 | p a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | |||
| HNP1-3 | 3.55 | 1.63–12.80 | 3.65 | 2.35–14.58 | 0.25 | 3.57 | 1.76–12.86 | 2.07 | 1.20–7.30 | 0.0009 |
| Variable, ng/mL | ALC Males n = 51 | Controls Males n = 15 | p a | ALC Females n = 11 | Controls Females n = 9 | p a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | |||
| HNP1-3 | 3.55 | 1.63–12.80. | 2.16 | 1.12–8.89 | 0.044 | 3.65 | 2.35–14.58 | 2.02 | 1.18–4.25 | 0.003 |
| Variable, ng/mL | Age > 40 Years n = 28 | Age < 40 Years n = 32 | p a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | ||
| HNP1-3 | 3.56 | 1.67–13.23 | 3.63 | 1.94–11.50 | 0.66 |
| Variable (ng/mL) | ALC | p a | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTP Class A n = 17 | CTP Class B n = 25 | CTP Class C n = 20 | |||||||||||
| Median | Minimum | 25–75 Percentile | Maximum | Median | Minimum | 25–75 Percentile | Maximum | Median | Minimum | 25–75 Percentile | Maximum | ||
| HNP1-3 | 3.09 | 1.48 | 1.91–5.44 | 11.96 | 3.52 | 1.50 | 2.32–6.46 | 15.94 | 4.49 | 1.60 | 3.03–6.99 | 13.35 | 0.30 |
| Variable (ng/mL) | MELD-Na > 20 (Points) n = 13 | MELD-Na ≤ 20 (Points) n = 49 | p a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | ||
| HNP1-3 | 5.90 | 3.64–7.65 | 3.23 | 2.54–3.92 | 0.02 |
| Variable (ng/mL) | mDF > 32 (Points) n = 26 | mDF ≤ 32 (Points) n = 36 | p a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | ||
| HNP1-3 | 4.49 | 3.65–6.60 | 2.94 | 2.23–3.59 | 0.01 |
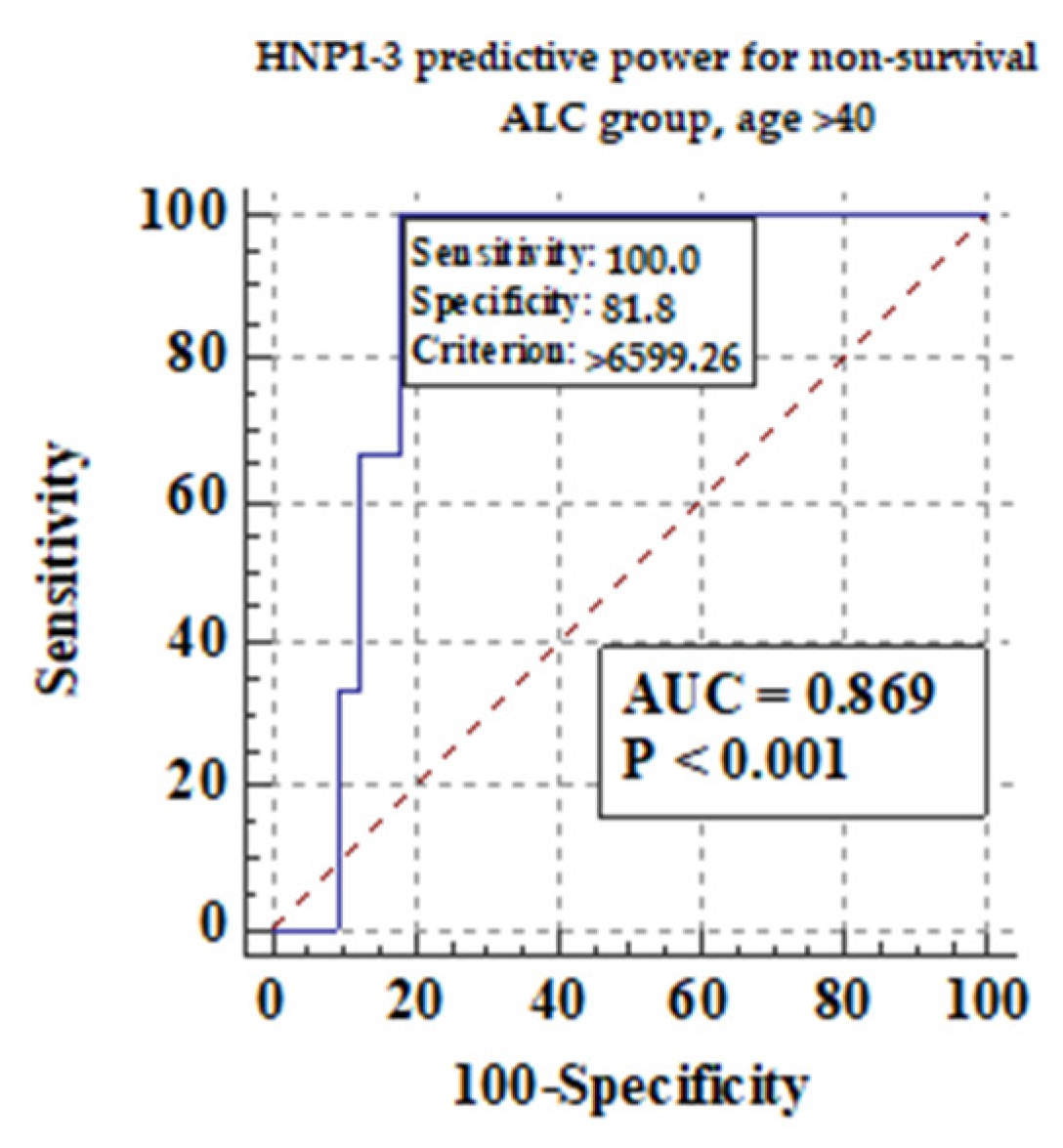
| Variable (ng/mL) | Non-Survival n = 3 | Survival n = 59 | p a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 5–95 Percentile | Median | 5–95 Percentile | ||
| HNP1-3 | 8.21 | 2.41–9.71 | 3.55 | 1.76–13.08 | 0.54 |
| Markers of Inflammation | HNP1-3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Rho | p a | |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.14 | 0.41 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 0.20 | 0.23 |
| NEU (×109/L) | 0.17 | 0.28 |
| NLR | 0.26 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rycyk-Bojarzyńska, A.; Kasztelan-Szczerbińska, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Surdacka, A.; Roliński, J. Human Neutrophil Alpha-Defensins Promote NETosis and Liver Injury in Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Potential Therapeutic Agents. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051237
Rycyk-Bojarzyńska A, Kasztelan-Szczerbińska B, Cichoż-Lach H, Surdacka A, Roliński J. Human Neutrophil Alpha-Defensins Promote NETosis and Liver Injury in Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Potential Therapeutic Agents. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051237
Chicago/Turabian StyleRycyk-Bojarzyńska, Anna, Beata Kasztelan-Szczerbińska, Halina Cichoż-Lach, Agata Surdacka, and Jacek Roliński. 2024. "Human Neutrophil Alpha-Defensins Promote NETosis and Liver Injury in Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Potential Therapeutic Agents" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051237
APA StyleRycyk-Bojarzyńska, A., Kasztelan-Szczerbińska, B., Cichoż-Lach, H., Surdacka, A., & Roliński, J. (2024). Human Neutrophil Alpha-Defensins Promote NETosis and Liver Injury in Alcohol-Related Liver Cirrhosis: Potential Therapeutic Agents. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051237








