Potential Causal Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Selection of the Genetic IVs
2.4. MR Analysis
3. Results
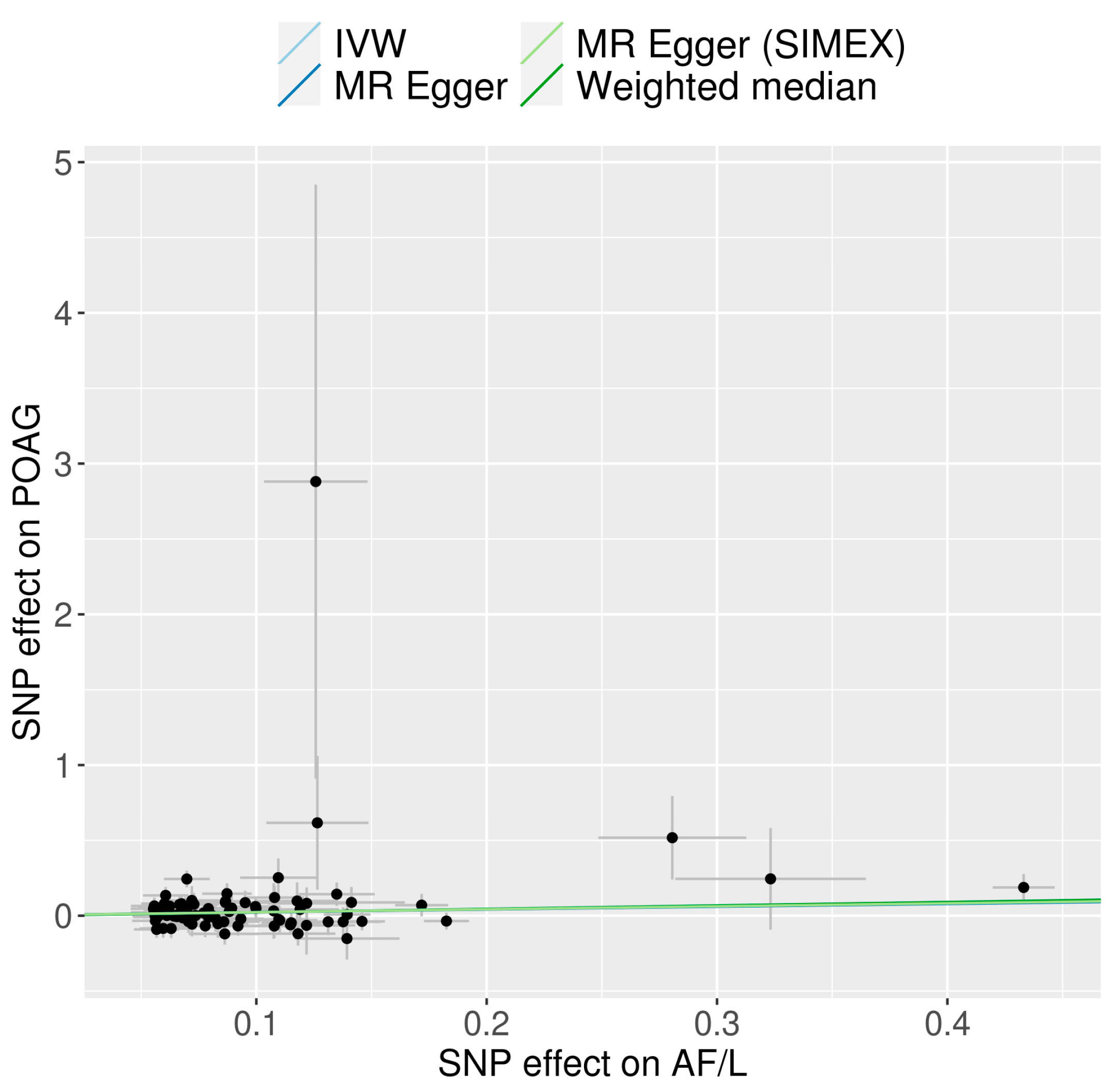
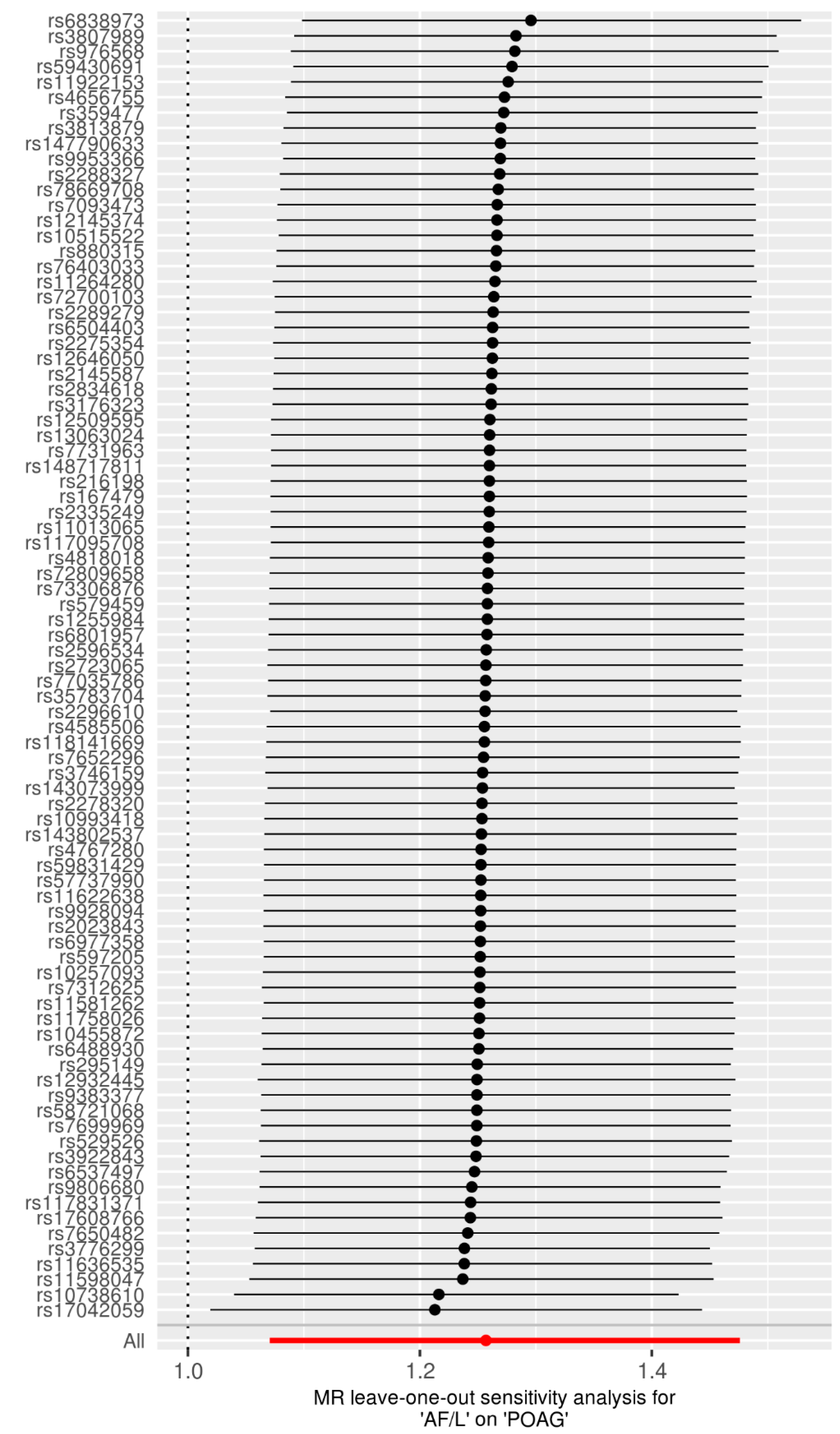
3.1. Genetic IVs in Univariable MR
3.2. Univariable MR for the Causal Effects of AF/L on POAG
3.3. Multivariable MR for the Causal Effects of AF/L on POAG
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Lindsley, K.; Rouse, B.; Hong, H.; Shi, Q.; Friedman, D.S.; Wormald, R.; Dickersin, K. Comparative Effectiveness of First-Line Medications for Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.J.; Nguyen, D.D.; Lai, J.Y. Benzoic acid derivative-modified chitosan-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Methoxylation effects and pharmacological treatments of Glaucoma-related neurodegeneration. J. Control Release 2020, 317, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Aung, T.; Bourne, R.R.; Bron, A.M.; Ritch, R.; Panda-Jonas, S. Glaucoma. Lancet 2017, 390, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.T.; Yoon, B.W.; Seo, J.H. Analysis of risk allele frequencies of single nucleotide polymorphisms related to open-angle glaucoma in different ethnic groups. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Weinreb, R.N. Lamina cribrosa depth in healthy eyes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, M.; Kawasaki, R.; Wang, J.J.; Wong, T.Y.; Crowston, J.; Kiuchi, Y. Vascular risk factors in glaucoma: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2011, 39, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B. Role of cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011, 89, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Weinreb, R.N.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, M. Relationship of intraocular pressure and frequency of spontaneous retinal venous pulsation in primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, J.; Mozaffarieh, M. What is the present pathogenetic concept of glaucomatous optic neuropathy? Surv. Ophthalmol. 2007, 52 (Suppl. S2), S162–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska, J.; Wierzbowski, R.; Stankiewicz, A.; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. Cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with normal tension glaucoma: 24-h heart rate and blood pressure variability analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xia, R.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.; Yao, Y.; Fan, X. Global, regional, and national burdens of atrial fibrillation/flutter from 1990 to 2019: An age-period-cohort analysis using the Global Burden of Disease 2019 study. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 04154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, S.; Hill, A.; Irving, G.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Abdul-Rahim, A.H. Atrial fibrillation and stroke: State-of-the-art and future directions. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareedu, R.K.; Abdalrahman, I.B.; Dharmashankar, K.C.; Granada, J.F.; Chyou, P.H.; Sharma, P.P.; Smith, P.N.; Hayes, J.J.; Greenlee, R.T.; Vidaillet, H. Atrial flutter versus atrial fibrillation in a general population: Differences in comorbidities associated with their respective onset. Clin. Med. Res. 2010, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldo, A.L.; Feld, G.K. Inter-relationships of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikbov, M.M.; Kazakbaeva, G.M.; Rakhimova, E.M.; Panda-Jonas, S.; Fakhretdinova, A.A.; Tuliakova, A.M.; Rusakova, I.A.; Jonas, J.B. Atrial fibrillation and flutter and ocular diseases. The Ural eye and medical study and the Ural very old study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, e1057–e1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, J.; Orgul, S.; Costa, V.P.; Orzalesi, N.; Krieglstein, G.K.; Serra, L.M.; Renard, J.P.; Stefansson, E. The impact of ocular blood flow in glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2002, 21, 359–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleska-Zmijewska, A.; Janiszewski, M.; Wawrzyniak, Z.M.; Kuch, M.; Szaflik, J.; Szaflik, J.P. Is atrial fibrillation a risk factor for normal-tension glaucoma? Medicine 2017, 96, e8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Han, J.C.; Choi, J.A.; Chae, J.E.; Kim, R.B. Association between atrial fibrillation and the risk of glaucoma development: A 12-year Nationwide cohort study. Eye 2023, 37, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Multivariable Mendelian randomization: The use of pleiotropic genetic variants to estimate causal effects. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Lee, Y. Possible Causal Association between Type 2 Diabetes and Glycaemic Traits in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; Yin, H.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Yao, K. Appraising the Effects of Metabolic Traits on the Risk of Glaucoma: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, R.S.; Li, H.; Cheong, A.J.Y.; Fan, Q.; Koh, V.; Raghavan, L.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Cheng, C.Y. Mendelian Randomization Implicates Bidirectional Association between Myopia and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma or Intraocular Pressure. Ophthalmology 2023, 130, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquet, H.; Paylakhi, S.; Kneeland, S.C.; Thai, K.K.; Hoffmann, T.J.; Yin, J.; Kvale, M.N.; Banda, Y.; Tolman, N.G.; Williams, P.A.; et al. A multiethnic genome-wide association study of primary open-angle glaucoma identifies novel risk loci. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipila, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, H.; Yang, J. A generalized linear mixed model association tool for biobank-scale data. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G.; CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Spiller, W.; Bowden, J. Testing and correcting for weak and pleiotropic instruments in two-sample multivariable Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5434–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Davey Smith, G.; Sheehan, N.; Thompson, J. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Seo, J.H. Causal Association of Obesity and Dyslipidemia with Type 2 Diabetes: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes 2022, 13, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; Relton, C.L.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Davey Smith, G.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: The role of the I2 statistic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Publisher Correction: Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.M.B.; Wood, A.M.; Burgess, S. Extending the MR-Egger method for multivariable Mendelian randomization to correct for both measured and unmeasured pleiotropy. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 4705–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.K.; Loh, P.R.; Finucane, H.K.; Ripke, S.; Yang, J.; Patterson, N.; Daly, M.J.; Price, A.L.; Neale, B.M.; Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Anttila, V.; Gusev, A.; Day, F.R.; Loh, P.R.; ReproGen, C.; Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Duncan, L.; Genetic Consortium for Anorexia Nervosa of the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Richardson, T.G.; Millard, L.A.C.; Hemani, G.; Elsworth, B.L.; Raistrick, C.A.; Vilhjalmsson, B.; Neale, B.M.; Haycock, P.C.; Smith, G.D.; et al. PhenoSpD: An integrated toolkit for phenotypic correlation estimation and multiple testing correction using GWAS summary statistics. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lee, S.; Won, S. Causal Evaluation of Laboratory Markers in Type 2 Diabetes on Cancer and Vascular Diseases Using Various Mendelian Randomization Tools. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 597420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadway, D.C.; Drance, S.M. Glaucoma and vasospasm. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 82, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdady, I.; Russman, A.; Buletko, A.B. Atrial Fibrillation and Ischemic Stroke: A Clinical Review. Semin. Neurol. 2021, 41, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, N.; Kulic, M.; Dilic, M.; Dzubur, A.; Durak, A.; Pepic, E.; Smajic, E.; Kusljugic, Z. The Cumulative Incidence of Stroke, Myocardial infarction, Heart Failure and Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Med. Arch. 2017, 71, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Proietti, M.; Potpara, T.; Mansour, M.; Savelieva, I.; Tse, H.F.; Goette, A.; Camm, A.J.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Gupta, D.; et al. Atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention: 25 years of research at EP Europace journal. Europace 2023, 25, euad226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayreh, S.S.; Podhajsky, P.A.; Zimmerman, M.B. Retinal artery occlusion: Associated systemic and ophthalmic abnormalities. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.C.; Lin, H.L.; Hsu, C.A.; Li, Y.C.; Hsu, M.H. Atrial Fibrillation and Coronary Artery Disease as Risk Factors of Retinal Artery Occlusion: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 374616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, J.; Konieczka, K.; Flammer, A.J. The primary vascular dysregulation syndrome: Implications for eye diseases. EPMA J. 2013, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perasalo, R.; Perasalo, J.; Raitta, C. Electrocardiographic changes in institutionalized geriatric glaucoma patients. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1992, 230, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitale, P.M.; Shen, G.; Sigireddi, R.R.; Polo-Prieto, M.; Park, Y.H.; Gibson, S.E.; Westenskow, P.D.; Channa, R.; Frankfort, B.J. Selective vulnerability of the intermediate retinal capillary plexus precedes retinal ganglion cell loss in ocular hypertension. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1073786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, A.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Ye, C.; Lu, F. Structure-function correlation of localized visual field defects and macular microvascular damage in primary open-angle glaucoma. Microvasc. Res. 2020, 130, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, S. Hypertension as a Risk Factor for Primary Open-angle Glaucoma: A Meta-analysis. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2023, 33, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Bae, H.W.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, C.Y. Increased Risks of Open-Angle Glaucoma in Untreated Hypertension. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 252, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallistratos, M.S.; Poulimenos, L.E.; Manolis, A.J. Atrial fibrillation and arterial hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellervik, C.; Roselli, C.; Christophersen, I.E.; Alonso, A.; Pietzner, M.; Sitlani, C.M.; Trompet, S.; Arking, D.E.; Geelhoed, B.; Guo, X.; et al. Assessment of the Relationship Between Genetic Determinants of Thyroid Function and Atrial Fibrillation: A Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavar, A.; Saseendrakumar, B.R.; Lee, T.C. Associations Between Thyroid Eye Disease and Glaucoma Among Those Enrolled in the National Institutes of Health All of Us Research Program: Corrigendum. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 39, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggewie, B.; Gouveris, H.; Bahr, K. A Narrative Review of the Association between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Glaucoma in Adults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Nattel, S.; Kalman, J.M.; Sanders, P. Sleep Apnea and Atrial Fibrillation. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 13, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.K.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Ahmed, H.M.; Gopinathannair, R.; Joglar, J.A.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Pack, Q.R.; Sanders, P.; Trulock, K.M.; et al. Lifestyle and Risk Factor Modification for Reduction of Atrial Fibrillation: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e750–e772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voskoboinik, A.; Marcus, G.M. The Impact of Alcohol Intake on Atrial Fibrillation. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, K.V.; Madjedi, K.; Luben, R.N.; Chua, S.Y.L.; Warwick, A.N.; Chia, M.; Pasquale, L.R.; Wiggs, J.L.; Kang, J.H.; Hysi, P.G.; et al. Alcohol, Intraocular Pressure, and Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Nielsen, J.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Dey, R.; Gabrielsen, M.E.; Wolford, B.N.; LeFaive, J.; VandeHaar, P.; Gagliano, S.A.; Gifford, A.; et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Burgess, S. Use of Mendelian randomization to assess the causal status of modifiable exposures for rheumatic diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 38, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Firth logistic regression for rare variant association tests. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Traits | Data Source | No. of Participants | Population | No. of Variants | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | FinnGen | 237,690 (45,766 cases + 191,924 controls) | European (Finland) | 20,164,886 | [27] |
| Hypertension | FinnGen | 377,209 (111,581 cases + 265,626 controls) | European (Finland) | 20,170,234 | |
| Autoimmune hyperthyroidism | FinnGen | 281,683 (1828 cases + 279,855 controls) | European (Finland) | 20,167,370 | |
| Sleep apnoea | FinnGen | 375,657 (38,998 cases + 336,659 controls) | European (Finland) | 20,170,208 | |
| Alcohol use disorder, ICD-based | FinnGen | 377,277 (15,715 cases + 361,562 controls) | European (Finland) | 20,170,236 | |
| Primary open-angle glaucoma | UKB | 456,351 (654 cases + 455,697 controls) | European (UK) | 11,831,932 | [28] |
| Exposure | Heterogeneity | Horizontal Pleiotropy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR-Egger | MR-Egger (SIMEX) | |||||||||
| N | F | I2 (%) | p-Value * | p-Value # | p-Value † | Intercept, β (SE) | p-Value | Intercept, β (SE) | p-Value | |
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 85 | 114.53 | 97.93 | 0.338 | 0.312 | 0.338 | 0.004 (0.017) | 0.797 | 0.004 (0.018) | 0.848 |
| IVW | MR-Egger | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposures | Conditional F | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Model 1 | |||||
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 22.48 | 1.24 (1.02, 1.51) | 0.034 | 1.24 (1.02, 1.51) | 0.034 |
| Hypertension | 14.16 | 1.00 (0.74, 1.34) | 0.984 | 1.00 (0.74, 1.34) | 0.983 |
| Autoimmune hyperthyroidism | 4.08 | 1.03 (0.91, 1.17) | 0.617 | 1.04 (0.90, 1.20) | 0.607 |
| Sleep apnoea | 3.19 | 0.60 (0.33, 1.09) | 0.092 | 0.60 (0.33, 1.09) | 0.094 |
| Alcohol use disorder, ICD-based | 3.21 | 1.09 (0.80, 1.48) | 0.596 | 1.09 (0.80, 1.48) | 0.595 |
| Model 2 | |||||
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 20.75 | 1.24 (1.02, 1.52) | 0.032 | 1.28 (1.04, 1.57) | 0.019 |
| Hypertension | 25.84 | 0.90 (0.69, 1.18) | 0.449 | 1.12 (0.69, 1.83) | 0.637 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Seo, J.H. Potential Causal Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247670
Lee Y, Seo JH. Potential Causal Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(24):7670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247670
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young, and Je Hyun Seo. 2024. "Potential Causal Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 24: 7670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247670
APA StyleLee, Y., & Seo, J. H. (2024). Potential Causal Association Between Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(24), 7670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247670






