Does Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with oXiris in Septic Shock Have Any Positive Impact? Single-Centre Experience with oXiris Therapy in Septic Shock Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
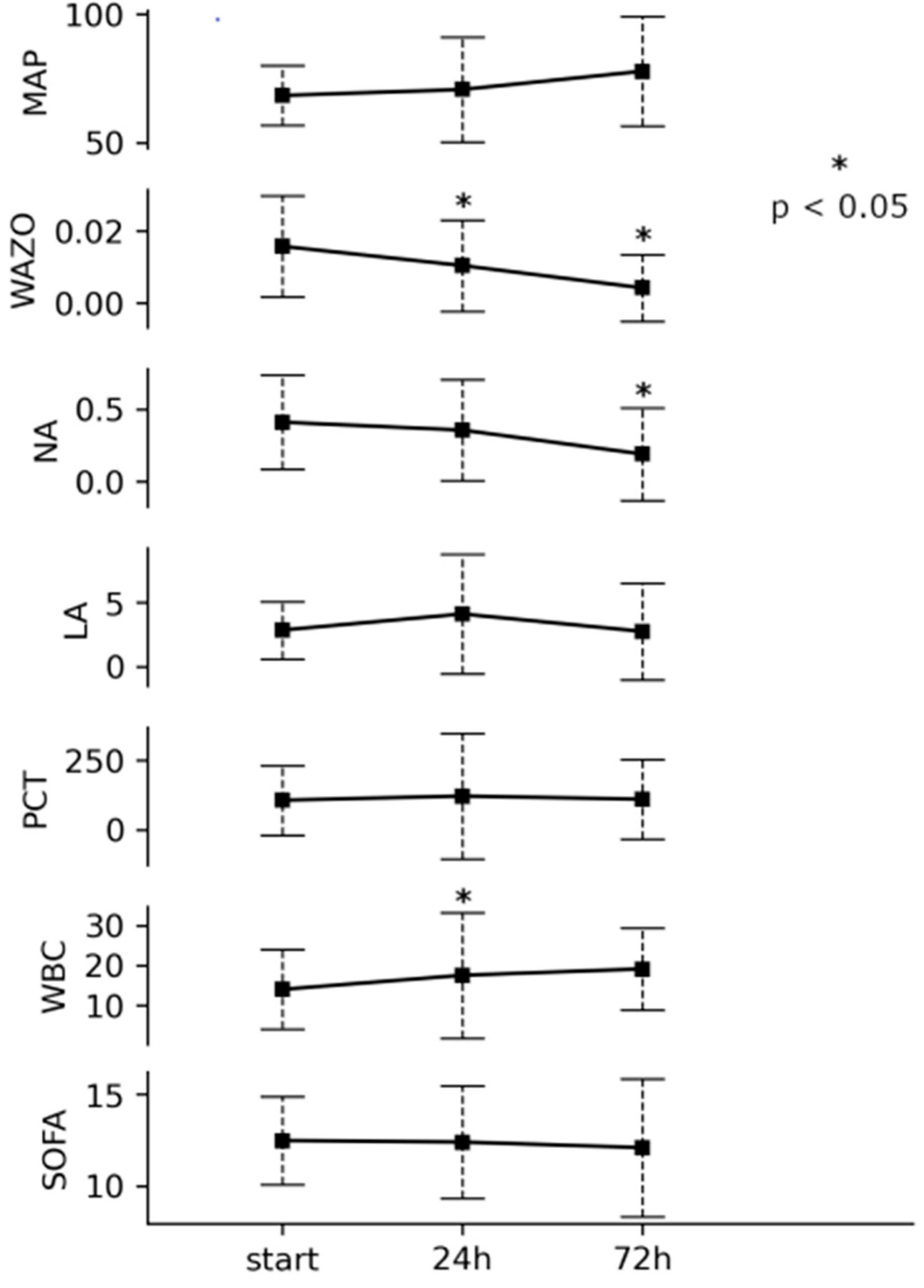
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paoli, C.J.; Reynolds, M.A.; Sinha, M.; Gitlin, M.; Crouser, E. Epidemiology and Costs of Sepsis in the United States—An Analysis Based on Timing of Diagnosis and Severity Level. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel-Garcia, P.D.; Eberle, B.; Kleinert, E.-M.; Hilty, M.P.; Blumenthal, S.; Spanaus, K.; Fodor, P.; Maggiorini, M. Effects of enhanced adsorption haemofiltration versus haemoadsorption in severe, refractory septic shock with high levels of endotoxemia: The ENDoX bicentric, randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intensive Care 2023, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Via, L.; Sangiorgio, G.; Stefani, S.; Marino, A.; Nunnari, G.; Cocuzza, S.; La Mantia, I.; Cacopardo, B.; Stracquadanio, S.; Spampinato, S.; et al. The Global Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019—Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukonen, K.-M.; Bailey, M.; Suzuki, S.; Pilcher, D.; Bellomo, R. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000–2012. JAMA 2014, 311, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venet, F.; Monneret, G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; Wald, R.; Martensson, J.; Maiden, M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Glassford, N.J.; Lankadeva, Y.; Vaara, S.T.; et al. Acute kidney injury in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.N.; Antonelli, M.; Fumagalli, R.; Foltran, F.; Brienza, N.; Donati, A.; Malcangi, V.; Petrini, F.; Volta, G.; Pallavicini, F.M.B.; et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: The EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindenhammer, V.; Girardot, T.; Chaulier, K.; Grégoire, A.; Monard, C.; Huriaux, L.; Illinger, J.; Leray, V.; Uberti, T.; Crozon-Clauzel, J.; et al. oXiris® Use in Septic Shock: Experience of Two French Centres. Blood Purif. 2019, 47 (Suppl. 3), 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, P.; Chang, K.; Yang, M.; Deng, N.; Chen, S.; Su, B. Effect of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with the oXiris Hemofilter on Critically Ill Patients: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Antonelli, M.; Foster, D.M.; Klein, D.J.; Marshall, J.C.; Palevsky, P.M.; Weisberg, L.S.; Schorr, C.A.; Trzeciak, S.; et al. Effect of Targeted Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion on 28-Day Mortality in Patients with Septic Shock and Elevated Endotoxin Level: The EUPHRATES Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schädler, D.; Pausch, C.; Heise, D.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Brederlau, J.; Weiler, N.; Marx, G.; Putensen, C.; Spies, C.; Jörres, A.; et al. The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, B.; Lambert, C.; Kellum, J.A. In vitro comparison of the adsorption of inflammatory mediators by blood purification devices. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turani, F.; Barchetta, R.; Falco, M.; Busatti, S.; Weltert, L. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with the Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Septic Patients: A Case Series. Blood Purif. 2019, 47 (Suppl. S3), 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, M.E.; Hansson, F.; Vincent, J.-L.; Bodelsson, M. Endotoxin and cytokine reducing properties of the oXiris membrane in patients with septic shock: A randomized crossover double-blind study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, Q.; Sun, R.; Wang, N. Application of Different Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Hemofilter in Patients with Septic Shock Complicated with Acute Renal Injury. Iran. J. Public Health 2022, 51, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Ouyang, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhong, D.; Xiang, X.; Li, J. Application of oXiris-continuous hemofiltration adsorption in patients with sepsis and septic shock: A single-centre experience in China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1012998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, S.; Ai, T.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, M. Effect of CRRT with oXiris filter on hemodynamic instability in surgical septic shock with AKI: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2022, 45, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, H.; Chan, K.; Kwan, M.; Yan, W. Application of endotoxin and cytokine adsorption haemofilter in septic acute kidney injury due to Gram-negative bacterial infection. Hong Kong Med. J. 2013, 19, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guan, M.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Fu, P. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Acute Kidney Injury with Septic Shock: A Retrospective Observational Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 789623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Xiao, W.; Lin, J. Effect of oXiris-CVVH on the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Septic Shock: An Inverse Probability of Treatment-Weighted Analysis. Blood Purif. 2022, 51, 972–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siew, L.Y.; Lee, Z.-Y.; Yunos, N.M.; Atan, R.; Cove, M.E.; Lumlertgul, N.; Srisawat, N.; Hasan, M.S. Outcomes of extracorporeal blood purification with oXiris® membrane in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2024, 83, 154844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Deng, K.; et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy with the adsorptive oXiris filter may be associated with the lower 28-day mortality in sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shaw, A.R.; Chaijamorn, W.; Mueller, B.A. We Underdose Antibiotics in Patients on CRRT. Semin. Dial. 2016, 29, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.K.; Kaushik, M.; Tan, C.W.; Liew, Z.H.; Teo, S.H.; Loo, C.M.; Ng, L.C.; Choong, L.H.L.; Foo, M.W.Y. Augmented Adsorptive Blood Purification during Continuous Veno-Venous Haemodiafiltration in a Severe Septic, Acute Kidney Injury Patient: Use of oXiris®: A Single Centre Case Report. Blood Purif. 2019, 47 (Suppl. S3), 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of patients | 32 |
| Age (years, SD) | 37–84 (69) |
| Sex (M:F) | 14:18 |
| Charlson score (SD) | 0–18 (16) |
| SAPS III (upon admission/mortality risk) | 46–93 (70)/16–93% (69%) |
| SOFA (upon admission) | 7–16 (10) |
| Site of Infection | |
|---|---|
| Abdominal | 23 (71.9%) |
| laparotomy | 20 (87%) |
| Intestinal perforation | 11 |
| Ischemia | 3 |
| Mechanical ileus | 3 |
| Cholecystitis | 3 |
| Pancreatitis | 1 |
| Pneumonia | 7 (9.4%) |
| Urosepsis | 2 (6.3%) |
| Etiology | |
| Identified pathogen | 28 (87.5%) |
| Gram-negative bacilli | 20 |
| Enterococci | 6 |
| Positive blood cultures | 16 (50%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mielnicki, W.; Dyla, A.; Zając, M.; Rokicka-Demitraszek, N.; Smereka, J. Does Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with oXiris in Septic Shock Have Any Positive Impact? Single-Centre Experience with oXiris Therapy in Septic Shock Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247527
Mielnicki W, Dyla A, Zając M, Rokicka-Demitraszek N, Smereka J. Does Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with oXiris in Septic Shock Have Any Positive Impact? Single-Centre Experience with oXiris Therapy in Septic Shock Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(24):7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247527
Chicago/Turabian StyleMielnicki, Wojciech, Agnieszka Dyla, Marta Zając, Natalia Rokicka-Demitraszek, and Jacek Smereka. 2024. "Does Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with oXiris in Septic Shock Have Any Positive Impact? Single-Centre Experience with oXiris Therapy in Septic Shock Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 24: 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247527
APA StyleMielnicki, W., Dyla, A., Zając, M., Rokicka-Demitraszek, N., & Smereka, J. (2024). Does Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy with oXiris in Septic Shock Have Any Positive Impact? Single-Centre Experience with oXiris Therapy in Septic Shock Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(24), 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247527






