Adapted Taekwondo Improves Postural Balance and Health-Related Quality of Life Concerning Multicomponent Training and Walking Exercise in Older Females: A Randomized Controlled Trial (TKD and Aging Project)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
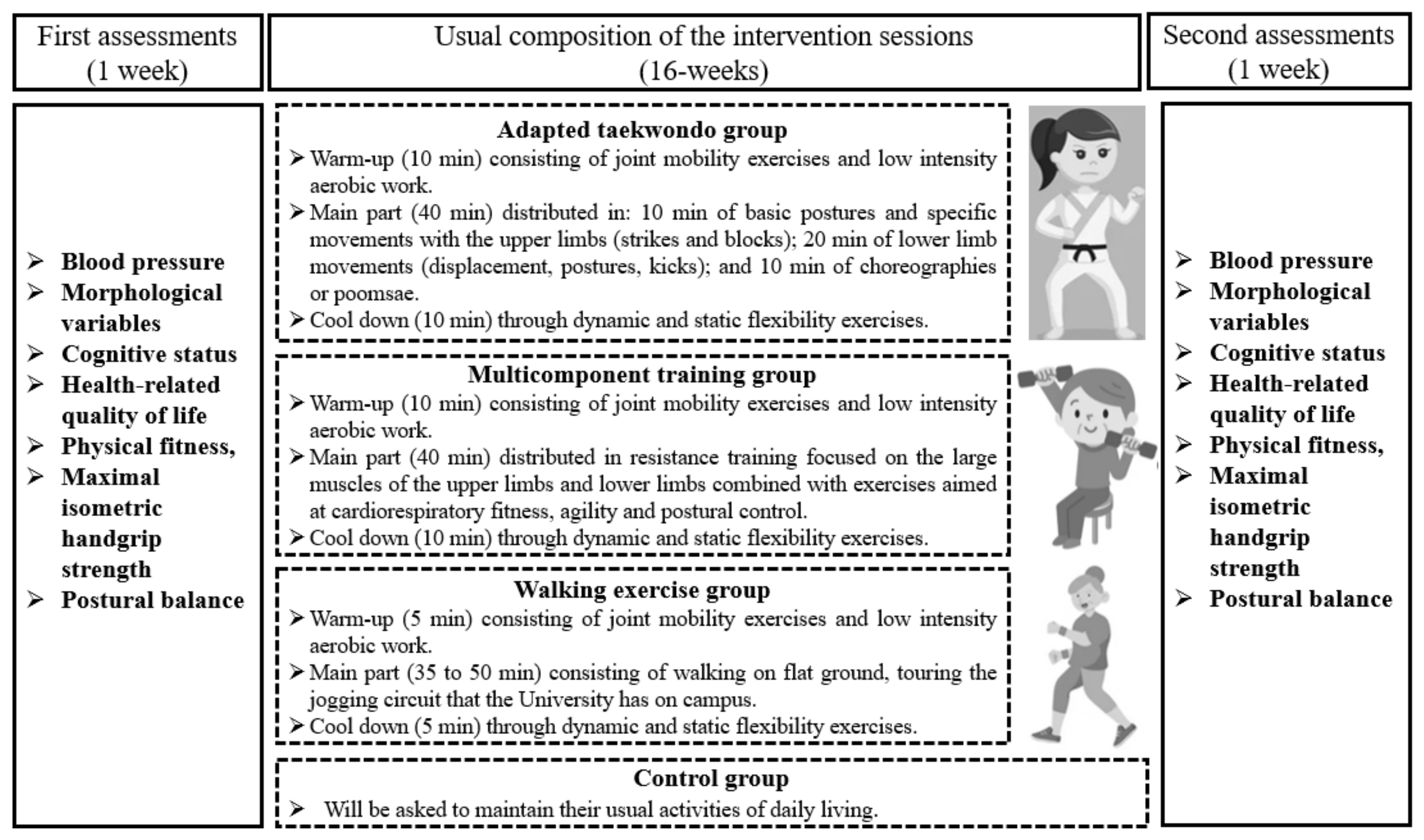
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Primary Outcomes
2.3.1. Blood Pressure
2.3.2. Morphological Variables
2.3.3. Frequency of Food Consumption
2.3.4. Cognitive Status
2.3.5. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL)
2.3.6. Physical Fitness
2.3.7. Maximal Isometric Handgrip Strength (MIHS)
2.3.8. Postural Balance
2.4. Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Intervention
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Pressure, Morphological Variables, and Frequency of Food Consumption
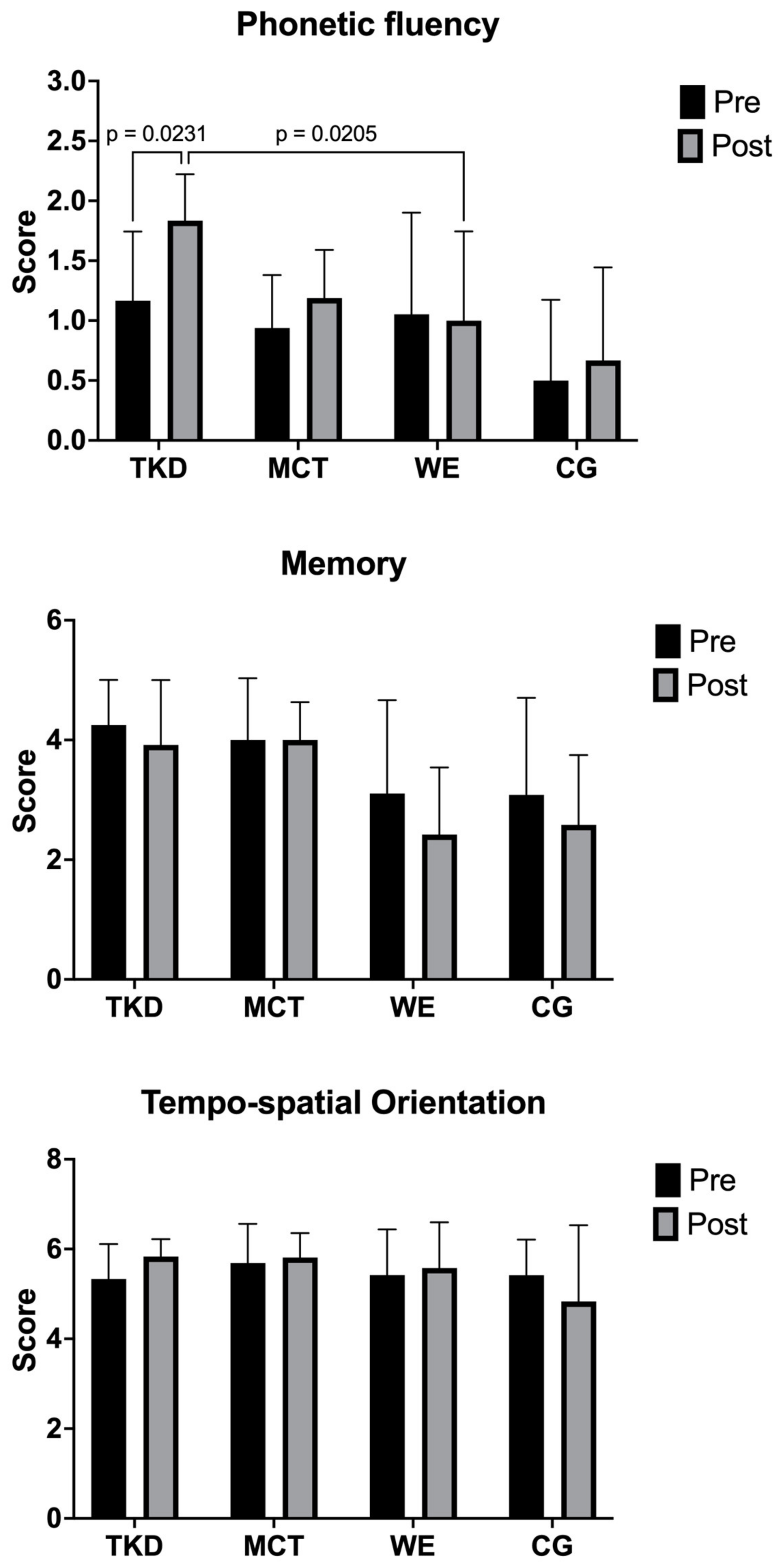
3.2. Cognitive Status
3.3. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL)
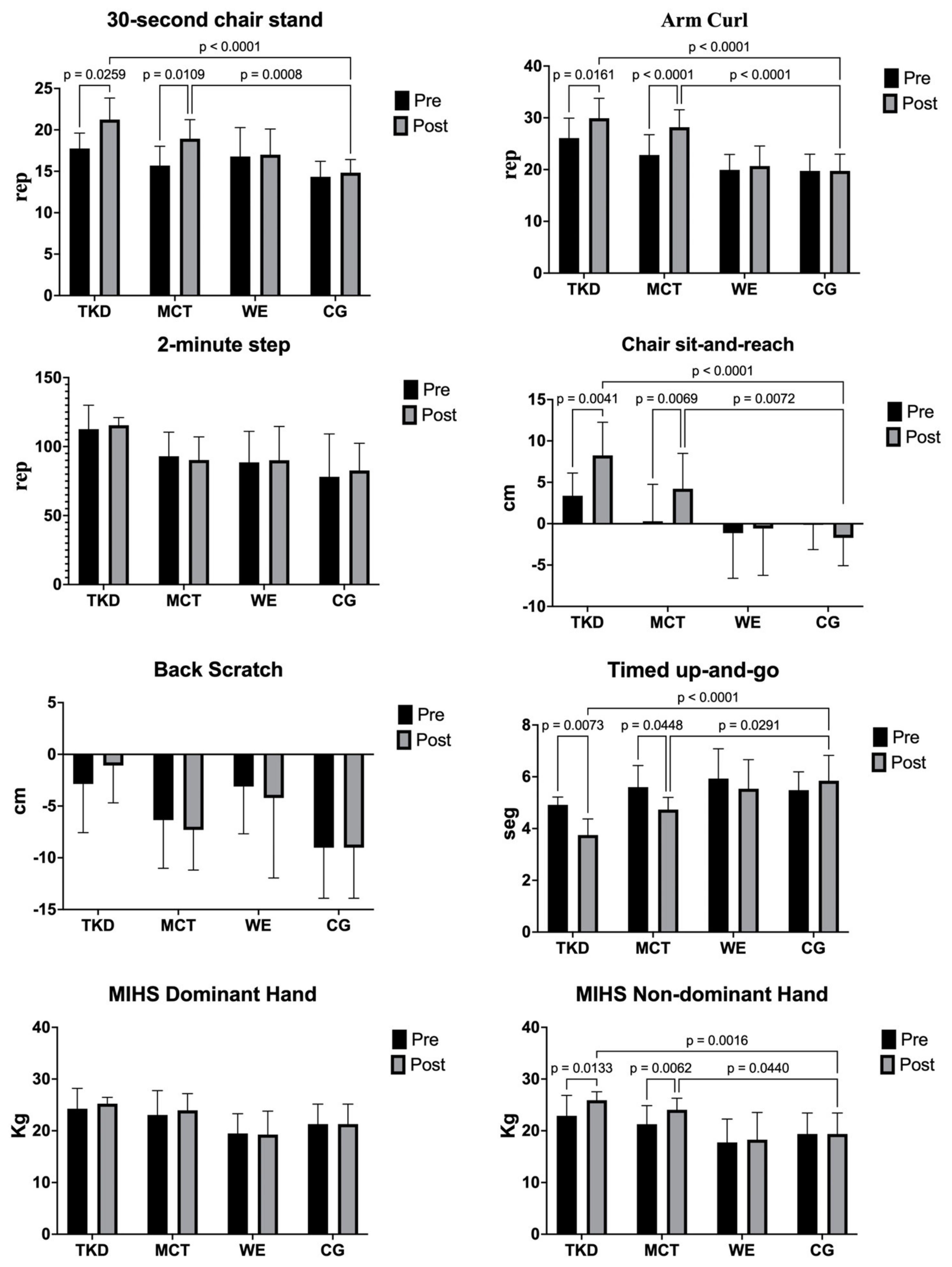
3.4. Physical Fitness and Maximal Isometric Handgrip Strength (MIHS)
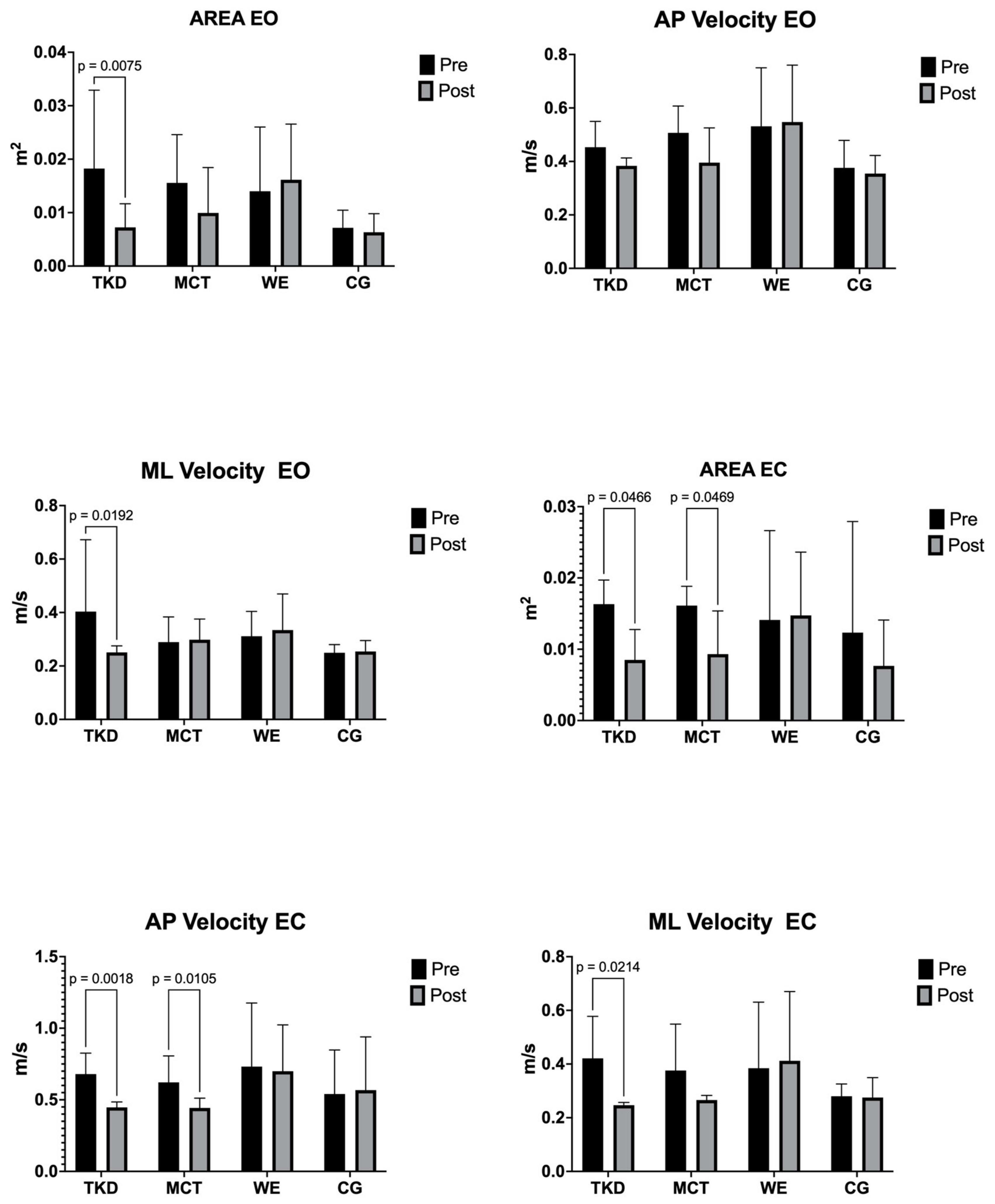
3.5. Postural Balance
4. Discussion
4.1. Blood Pressure, Morphological Variables, and Frequency of Food Consumption
4.2. Cognitive Status
4.3. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL)
4.4. Maximal Isometric Handgrip Strength (MIHS)
4.5. Arm Curl Test
4.6. 30 s Chair Stand Test
4.7. Flexibility
4.8. Postural Balance
4.9. Timed Up-And-Go (TUG)
4.10. 2-min Step Test
4.11. Limitations and Strengths
4.12. Practical Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Branco, B.H.M.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Mendez-Rebolledo, G.; Concha-Cisternas, Y.; Hernandez-Martínez, J. Effectiveness of Olympic Combat Sports on Balance, Fall Risk or Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Biology 2022, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Vásquez, C.; Hernandez-Martinez, J.; Ramos-Espinoza, F.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Magnani Branco, B.H.; Guzman-Munoz, E.; Floriano Landim, S.; Mondaca-Urrutia, J.; Valdés-Badilla, P. Effects of olympic combat sports on cardiorespiratory fitness in non-athlete population: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Espinoza, F.; Muñoz-Vasquez, C.; Hernandez-Martinez, J.; Lucero, B.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; BH, M.B.; Vásquez-Carrasco, E.; Cancino, M.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Fitness, P. Effects of combat sports on cognitive function in older people: A systematic review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2024, 64, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Delgado-Floody, P.; Núñez-Espinosa, C.; Monsalves-Álvarez, M.; Andrade, D. Effects of Olympic Combat Sports on Health-Related Quality of Life in Middle-Aged and Older People: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 797537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Roh, H.-T. Taekwondo Enhances Cognitive Function as a Result of Increased Neurotrophic Growth Factors in Elderly Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-H.; Hong, G.-R.; Min, D.-K.; Kim, E.-H.; Park, S.-K. Effects of functional fitness enhancement through taekwondo training on physical characteristics and risk factors of dementia in elderly women with depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Scott, S.D.; Pekas, E.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y. Taekwondo training reduces blood catecholamine levels and arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women with stage-2 hypertension: Randomized clinical trial. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2019, 41, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Branco, B.H.M.; Hernandez-Martinez, J.; Nobari, H. Impact of adapted taekwondo vs. multicomponent training on health status in independent older women: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1236402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Falls. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/falls (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Cadore, E.L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sinclair, A.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of different exercise interventions on risk of falls, gait ability, and balance in physically frail older adults: A systematic review. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.N.; Ferreira, L.H.B.; Bento, P.C.B. Effects of Home-Based Exercise Programs on Mobility, Muscle Strength, Balance, and Gait in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2023, 31, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.P. Randomised and non-randomised studies to estimate the effect of community-level public health interventions: Definitions and methodological considerations. Emerg. Themes Epidemiol. 2017, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juszczak, E.; Altman, D.G.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K. Reporting of Multi-Arm Parallel-Group Randomized Trials: Extension of the CONSORT 2010 Statement. JAMA 2019, 321, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busani, S.; Tosi, M.; Mighali, P.; Vandelli, P.; D’Amico, R.; Marietta, M.; Forfori, F.; Donati, A.; Cinnella, G.; De Monte, A.; et al. Multi-centre, three arm, randomized controlled trial on the use of methylprednisolone and unfractionated heparin in critically ill ventilated patients with pneumonia from SARS-CoV-2 infection: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, L.; Shamseer, L.; Altman, D.G.; Weeks, L.; Peters, J.; Kober, T.; Dias, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Plint, A.C.; Moher, D. Consolidated standards of reporting trials (CONSORT) and the completeness of reporting of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) published in medical journals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, MR000030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Branco, B.H.M.; Zapata-Bastias, J.; Lucero, B.; Castillo-Retamal, F. Effectiveness of Adapted Taekwondo, Multi-Component Training and Walking Exercise on Health Status in Independent Older Women: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial (TKD & Aging Project). Biology 2022, 11, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Godoy-Cumillaf, A.; Concha-Cisternas, Y.; Ortega-Spuler, J.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Durán-Agüero, S.; Vargas-Vitoria, R.; Magnani-Branco, B. Changes in anthropometric parameters and physical fitness in older adults after participating in a 16-weeks physical activity program. Rev. Fac. Med. Univ. Nac. Colomb. 2020, 68, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Salud. Manual de Aplicación del Examen de Medicina Preventiva del Adulto Mayor. 2013. Available online: http://web.minsal.cl/portal/url/item/ab1f81f43ef0c2a6e04001011e011907.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Reddy, A.K.; Jogendra, M.R.; Rosendorff, C. Blood pressure measurement in the geriatric population. Blood Press. Monit. 2014, 19, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfell-Jones, M.J.; Stewart, A.; de Ridder, J. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11072/1510 (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Valdés Badilla, P.; Godoy Cumillaf, A.; Ortega Spuler, J.; Díaz Aravena, D.; Castro Garrido, N.; Sandoval Muñoz, L.; Herrera Valenzuela, T.; López Fuenzalida, A.; Vargas Vitoria, R.; Durán Agüero, S. Relación entre índices antropométricos de salud con el consumo de alimentos en adultos mayores físicamente activos. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derio, C.D.; Bonnet, S.G.; Ponce, M.T.; Yanez, A.A.; Chonchol, A.S.; Pellegrino, M.B. Memoria, fluidez y orientación: Prueba de cribado de deterioro cognitivo en 5 minutos. Neurología 2013, 28, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilagut, G.; Ferrer, M.; Rajmil, L.; Rebollo, P.; Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Quintana, J.M.; Santed, R.; Valderas, J.M.; Ribera, A.; Domingo-Salvany, A. El cuestionario de salud SF-36 español: Una década de experiencia y nuevos desarrollos. Gac. Sanit. 2005, 19, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikli, R.; Jones, J. Development and Validation of Criterion-Referenced Clinically Relevant Fitness Standards for Maintaining Physical Independence in Later Years. Gerontologist 2013, 53, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fess, E. Grip Strength, 2nd ed.; American Society of Hand Therapists: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, M.; Freitas, S.M. Revision of posturography based on force plate for balance evaluation. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2010, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colado, J.C.; Pedrosa, F.M.; Juesas, A.; Gargallo, P.; Carrasco, J.J.; Flandez, J.; Chupel, M.U.; Teixeira, A.M.; Naclerio, F. Concurrent validation of the OMNI-Resistance Exercise Scale of perceived exertion with elastic bands in the elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 103, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallant, J. A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS; Education, M.G.-H., Ed.; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2011; 358p. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, A.M.; Marzetti, E.; Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Tosato, M.; Santoro, L.; Di Giorgio, A.; Nesci, A.; Sisto, A.; Santoliquido, A.; et al. Exercise and Protein Intake: A Synergistic Approach against Sarcopenia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2672435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, N.E.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznariç, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.S.; Sousa, L.C.M.; de Oliveira Silva, D.F.; Pimentel, J.B.; Evangelista, K.; Lyra, C.O.; Lopes, M.; Lima, S. A Systematic Review on Processed/Ultra-Processed Foods and Arterial Hypertension in Adults and Older People. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, S.T.; Loehr, L.R.; Butler, K.R.; Chakladar, S.; Chang, P.P.; Folsom, A.R.; Heiss, G.; MacLehose, R.F.; Matsushita, K.; Avery, C.L. Reducing the Blood Pressure-Related Burden of Cardiovascular Disease: Impact of Achievable Improvements in Blood Pressure Prevention and Control. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welford, P.; Östh, J.; Hoy, S.; Rossell, S.L.; Pascoe, M.; Diwan, V.; Hallgren, M. Effects of Yoga and Aerobic Exercise on Verbal Fluency in Physically Inactive Older Adults: Randomized Controlled Trial (FitForAge). Clin. Interv. Aging 2023, 18, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, P.; Dahmen-Zimmer, K.; Kudielka, B.M.; Schulz, A. Effects of Karate Training Versus Mindfulness Training on Emotional Well-Being and Cognitive Performance in Later Life. Res. Aging 2017, 39, 1118–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delezie, J.; Handschin, C. Endocrine Crosstalk Between Skeletal Muscle and the Brain. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belviranli, M.; Okudan, N.; Kabak, B.; Erdoğan, M.; Karanfilci, M. The relationship between brain-derived neurotrophic factor, irisin and cognitive skills of endurance athletes. Physician Sportsmed. 2016, 44, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damirchi, A.; Hosseini, F.; Babaei, P. Mental Training Enhances Cognitive Function and BDNF More Than Either Physical or Combined Training in Elderly Women With MCI: A Small-Scale Study. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2018, 33, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oztasyonar, Y. Interaction between different sports branches such as taekwondo, box, athletes and serum brain derived neurotrophic factor levels. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta Mello Portugal, E.; Cevada, T.; Sobral Monteiro-Junior, R.; Teixeira Guimarães, T.; da Cruz Rubini, E.; Lattari, E.; Blois, C.; Camaz Deslandes, A. Neuroscience of exercise: From neurobiology mechanisms to mental health. Neuropsychobiology 2013, 68, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.; Climstein, M.; Moore, B.; Del Vecchio, L. Older Persons Participation in Hard Martial Arts: Opportunities to Improve Psychological Well-Being? A Scoping Review. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2024, 17, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Klompstra, L.; Ekdahl, A.W.; Krevers, B.; Milberg, A.; Eckerblad, J. Factors related to health-related quality of life in older people with multimorbidity and high health care consumption over a two-year period. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Alarcón-Rivera, M.; Hernandez-Martinez, J.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Branco, B.; Núñez-Espinosa, C.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E. Factors Associated with Poor Health-Related Quality of Life in Physically Active Older People. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enssle, F.; Kabisch, N. Urban green spaces for the social interaction, health and well-being of older people—An integrated view of urban ecosystem services and socio-environmental justice. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 109, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, M.K.; Park, H.; Park, S.K. Effects of Regular Taekwondo Intervention on Health-Related Physical Fitness, Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Elderly Women with Hypertension. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.; Jacinto, M.; Antunes, R.; Monteiro, D.; Mendes, D.; Matos, R.; Amaro, N. Comparing the Effects of Multicomponent and Concurrent Exercise Protocols on Muscle Strength in Older Adults. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musalek, C.; Kirchengast, S. Grip Strength as an Indicator of Health-Related Quality of Life in Old Age-A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, R.P.; Kraemer, W.J.; Snih, S.A.; Peterson, M.D. Handgrip Strength and Health in Aging Adults. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, J.L.; Sales, M.M.; Sousa, C.V.; da Silva Aguiar, S.; Asano, R.Y.; de Moraes, J.F.V.N.; Soares, B.R.A.; Neves, R.V.P.; de Moraes, M.R.; Simões, H.G. 12 weeks of Brazilian jiu-jitsu training improves functional fitness in elderly men. Sport Sci. Health 2016, 12, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Junior, R.; Franchini, E. Developing strength-endurance for combat sports athletes. Rev. Artes Marciales Asiát. 2021, 16, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, D.; Climstein, M.; Whitting, J.; Del Vecchio, L. Impact Force and Velocities for Kicking Strikes in Combat Sports: A Literature Review. Sports 2024, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofré-Saldía, E.; Villalobos-Gorigoitía, Á.; Cofré-Bolados, C.; Ferrari, G.; Gea-García, G.M. Multicomponent Training in Progressive Phases Improves Functional Capacity, Physical Capacity, Quality of Life, and Exercise Motivation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailapalli, D.R.; Benton, J.; Woodward, T.W. Biomechanics of the taekwondo axe kick: A review. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2015, 10, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasik, J.; Shan, G. Factors influencing the effectiveness of axe kick in taekwon-do. Arch. Budo 2014, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jofré-Saldía, E.; Villalobos-Gorigoitía, Á.; Gea-García, G. Methodological Proposal for Strength and Power Training in Older Athletes: A Narrative Review. Curr. Aging Sci. 2022, 15, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria da Silva, N.; Silva de França, M.; Freitas Holanda de Almeida, D.K.; Guedes de Lima, E.S.; Brito Dos Santos, V.H.; Victor de Araújo Souza, J.; Larrad, A.R.; de Almeida Aloise, D.; Freire Vieira Lima, N.M. Effects of a Multicomponent Exercise Program on Groups of Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Low Schooling: A Pilot Study. J. Aging Res. 2021, 2021, 8829332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.K.; Cavalcante, B.; Santos, P.R.; Da Silva, D.T.; Araujo, F.; Carvalho, R.G.; Souza, M. 12 Weeks of progressive resistance training on postural balance and concerns about falling in older adults: Randomized controlled trial. Motricidade 2021, 17, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Pons van Dijk, G.; Lenssen, A.F.; Leffers, P.; Kingma, H.; Lodder, J. Taekwondo training improves balance in volunteers over 40. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, S.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Berlanga, L.A.; Martos-Duarte, M.; Perea-Unceta, L.; Romero-Morales, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Functional mobility and physical fitness are improved through a multicomponent training program in institutionalized older adults. Geroscience 2024, 46, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Josephson, K.R. The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2002, 18, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, T.F.F.; Doleman, B.; Hatt, J.; Paul, M.; Toft, S.; Lund, J.N.; Phillips, B.E. The role of resistance exercise training for improving cardiorespiratory fitness in healthy older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Before | After | Time × Group p Value | Time × Group F Value | ηp2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Physical functioning (%) | TKD | 84.6 | 14.2 | 91.7 | 13.2 | 0.159 | 1.75 | 0.081 |
| MCT | 80.0 | 12.1 | 91.6 | 16.5 | ||||
| WE | 85.3 | 15.6 | 77.1 | 21.7 | ||||
| CG | 60.8 | 24.6 | 64.2 | 28.7 | ||||
| Body pain (%) | TKD | 44.2 | 19.0 | 77.3 | 25.9 | 0.041 | 3.31 | 0.122 |
| MCT | 52.2 | 19.6 | 81.4 | 22.8 | ||||
| WE | 56.6 | 14.3 | 63.8 | 25.2 | ||||
| CG | 45.0 | 14.8 | 63.3 | 18.3 | ||||
| Role limitation-physical (%) | TKD | 91.7 | 19.5 | 95.8 | 14.4 | 0.924 | 0.15 | 0.007 |
| MCT | 93.8 | 14.4 | 93.8 | 19.4 | ||||
| WE | 97.4 | 11.5 | 97.4 | 11.5 | ||||
| CG | 91.7 | 19.5 | 94.4 | 19.2 | ||||
| Role limitation-emotional (%) | TKD | 95.8 | 14.4 | 95.8 | 14.4 | 0.542 | 0.73 | 0.033 |
| MCT | 93.8 | 17.1 | 96.9 | 12.5 | ||||
| WE | 90.4 | 25.6 | 91.2 | 24.4 | ||||
| CG | 86.1 | 25.5 | 75.2 | 22.7 | ||||
| Mental health (%) | TKD | 66.3 | 18.6 | 66.0 | 16.0 | 0.109 | 0.42 | 0.089 |
| MCT | 61.0 | 17.0 | 67.0 | 11.5 | ||||
| WE | 63.6 | 11.8 | 60.4 | 13.5 | ||||
| CG | 56.3 | 12.7 | 70.8 | 14.4 | ||||
| Social functioning (%) | TKD | 65.6 | 23.3 | 70.8 | 24.0 | 0.945 | 0.12 | 0.006 |
| MCT | 62.5 | 25.4 | 62.5 | 18.3 | ||||
| WE | 69.1 | 15.8 | 69.7 | 24.0 | ||||
| CG | 47.9 | 14.9 | 52.5 | 13.4 | ||||
| Vitality (%) | TKD | 65.8 | 12.4 | 69.2 | 19.5 | 0.547 | 0.72 | 0.038 |
| MCT | 66.9 | 14.2 | 58.1 | 12.9 | ||||
| WE | 64.7 | 9.9 | 59.2 | 17.1 | ||||
| CG | 48.3 | 14.2 | 45.8 | 24.8 | ||||
| General health (%) | TKD | 54.2 | 21.4 | 78.8 | 20.1 | 0.007 | 2.27 | 0.084 |
| MCT | 58.4 | 13.9 | 73.1 | 22.6 | ||||
| WE | 56.8 | 17.6 | 60.5 | 18.2 | ||||
| CG | 49.1 | 16.5 | 54.1 | 24.3 | ||||
| Group | Before | After | Time × Group p Value | Time × Group F Value | ηp2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| 30 s chair stand (rep) | TKD | 17.8 | 1.9 | 21.3 | 2.6 | 0.017 | 4.25 | 0.179 |
| MCT | 15.7 | 2.3 | 18.9 | 2.3 | ||||
| WE | 16.8 | 3.5 | 17.0 | 3.1 | ||||
| CG | 14.3 | 1.9 | 14.8 | 1.6 | ||||
| Arm curl(rep) | TKD | 26.1 | 3.8 | 29.9 | 3.8 | <0.001 | 8.52 | 0.299 |
| MCT | 22.8 | 3.9 | 28.2 | 3.4 | ||||
| WE | 19.9 | 3.0 | 20.7 | 3.9 | ||||
| CG | 19.8 | 3.2 | 19.8 | 3.2 | ||||
| 2-min step (rep) | TKD | 112.7 | 17.3 | 115.5 | 5.5 | 0.737 | 0.42 | 0.022 |
| MCT | 93.0 | 17.5 | 90.3 | 16.8 | ||||
| WE | 88.5 | 22.5 | 90.1 | 24.6 | ||||
| CG | 78.1 | 31.1 | 82.7 | 19.7 | ||||
| Chair sit-and-reach (cm) | TKD | 3.4 | 2.7 | 8.3 | 4.0 | <0.001 | 8.56 | 0.297 |
| MCT | 0.3 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4.3 | ||||
| WE | −1.1 | 5.5 | −0.6 | 5.7 | ||||
| CG | −0.1 | 3.0 | −1.7 | 3.4 | ||||
| Back scratch (cm) | TKD | −2.9 | 4.7 | −1.1 | 3.6 | 0.625 | 0.59 | 0.028 |
| MCT | −6.4 | 4.7 | −7.3 | 3.9 | ||||
| WE | −3.1 | 4.6 | −4.2 | 7.7 | ||||
| CG | −9.0 | 4.9 | −9.0 | 4.9 | ||||
| Timed up-and-go (s) | TKD | 4.9 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 0.004 | 5.88 | 0.220 |
| MCT | 5.6 | 0.8 | 4.7 | 0.5 | ||||
| WE | 5.9 | 1.2 | 5.5 | 1.1 | ||||
| CG | 5.5 | 0.7 | 5.8 | 1.0 | ||||
| MIHS dominant hand (kg) | TKD | 24.3 | 3.9 | 25.3 | 1.2 | 0.480 | 0.85 | 0.044 |
| MCT | 23.1 | 4.7 | 24.0 | 3.2 | ||||
| WE | 19.5 | 3.8 | 19.3 | 4.5 | ||||
| CG | 21.3 | 3.9 | 21.3 | 3.9 | ||||
| MIHS non-dominant hand (kg) | TKD | 22.9 | 4.0 | 25.9 | 1.6 | 0.013 | 4.53 | 0.194 |
| MCT | 21.3 | 3.6 | 24.1 | 2.2 | ||||
| WE | 17.8 | 4.5 | 18.3 | 5.3 | ||||
| CG | 19.4 | 4.1 | 19.4 | 4.1 | ||||
| Group | Before | After | Time × Group p Value | Time × Group F Value | ηp2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Area EO (m2) | TKD | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 5.32 | 0.222 |
| MCT | 0.016 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.008 | ||||
| WE | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.010 | ||||
| CG | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.003 | ||||
| AP velocity EO (m/s) | TKD | 0.453 | 0.097 | 0.384 | 0.029 | 0.073 | 2.70 | 0.128 |
| MCT | 0.507 | 0.100 | 0.396 | 0.130 | ||||
| WE | 0.531 | 0.219 | 0.548 | 0.213 | ||||
| CG | 0.376 | 0.103 | 0.355 | 0.068 | ||||
| ML velocity EO (m/s) | TKD | 0.403 | 0.269 | 0.251 | 0.024 | 0.016 | 4.34 | 0.191 |
| MCT | 0.289 | 0.094 | 0.298 | 0.077 | ||||
| WE | 0.311 | 0.093 | 0.334 | 0.135 | ||||
| CG | 0.249 | 0.031 | 0.254 | 0.041 | ||||
| Area EC (m2) | TKD | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.021 | 4.07 | 0.167 |
| MCT | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.006 | ||||
| WE | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.009 | ||||
| CG | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.006 | ||||
| AP velocity EC (m/s) | TKD | 0.679 | 0.147 | 0.447 | 0.038 | 0.003 | 6.50 | 0.241 |
| MCT | 0.622 | 0.185 | 0.443 | 0.069 | ||||
| WE | 0.732 | 0.445 | 0.700 | 0.324 | ||||
| CG | 0.540 | 0.307 | 0.568 | 0.372 | ||||
| ML velocity EC (m/s) | TKD | 0.421 | 0.156 | 0.247 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 6.43 | 0.213 |
| MCT | 0.376 | 0.173 | 0.266 | 0.017 | ||||
| WE | 0.385 | 0.246 | 0.412 | 0.258 | ||||
| CG | 0.280 | 0.046 | 0.275 | 0.074 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdés-Badilla, P.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Hernandez-Martinez, J.; Cid-Calfucura, I.; Vásquez-Carrasco, E.; Aristegui-Mondaca, J.; Aravena-Sagardia, P.; Mota, J.; Zapata-Bastias, J.; et al. Adapted Taekwondo Improves Postural Balance and Health-Related Quality of Life Concerning Multicomponent Training and Walking Exercise in Older Females: A Randomized Controlled Trial (TKD and Aging Project). J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237250
Valdés-Badilla P, Herrera-Valenzuela T, Guzmán-Muñoz E, Hernandez-Martinez J, Cid-Calfucura I, Vásquez-Carrasco E, Aristegui-Mondaca J, Aravena-Sagardia P, Mota J, Zapata-Bastias J, et al. Adapted Taekwondo Improves Postural Balance and Health-Related Quality of Life Concerning Multicomponent Training and Walking Exercise in Older Females: A Randomized Controlled Trial (TKD and Aging Project). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(23):7250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237250
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdés-Badilla, Pablo, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Eduardo Guzmán-Muñoz, Jordan Hernandez-Martinez, Izham Cid-Calfucura, Edgar Vásquez-Carrasco, Juan Aristegui-Mondaca, Pablo Aravena-Sagardia, Jorge Mota, José Zapata-Bastias, and et al. 2024. "Adapted Taekwondo Improves Postural Balance and Health-Related Quality of Life Concerning Multicomponent Training and Walking Exercise in Older Females: A Randomized Controlled Trial (TKD and Aging Project)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 23: 7250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237250
APA StyleValdés-Badilla, P., Herrera-Valenzuela, T., Guzmán-Muñoz, E., Hernandez-Martinez, J., Cid-Calfucura, I., Vásquez-Carrasco, E., Aristegui-Mondaca, J., Aravena-Sagardia, P., Mota, J., Zapata-Bastias, J., Luarte-Rocha, C., & Branco, B. H. M. (2024). Adapted Taekwondo Improves Postural Balance and Health-Related Quality of Life Concerning Multicomponent Training and Walking Exercise in Older Females: A Randomized Controlled Trial (TKD and Aging Project). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(23), 7250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237250










