The Role of Thalidomide and Its Analogs in the Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
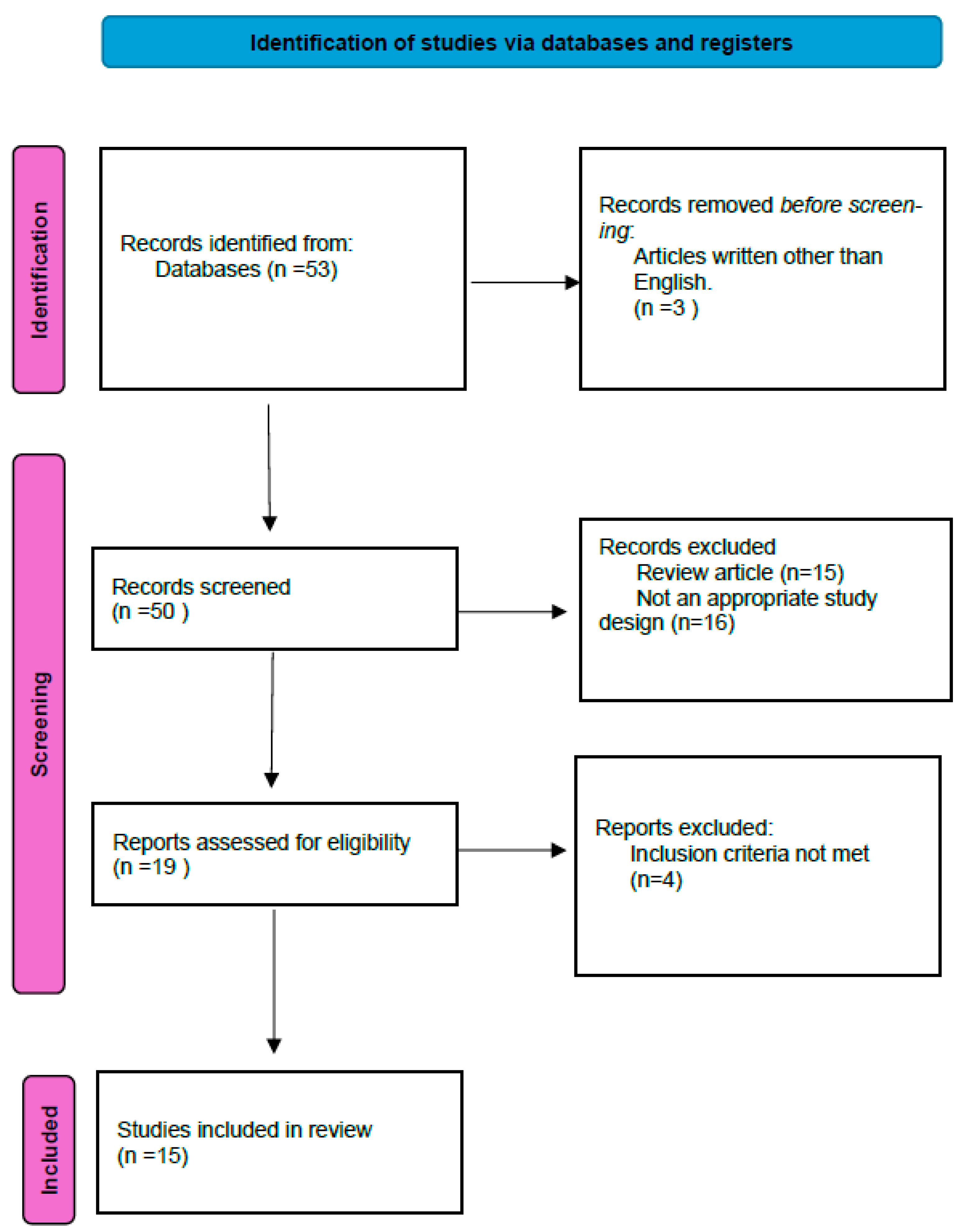
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Evaluation Method
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald, J.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; Pyeritz, R.E. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: An overview of diagnosis, management, and pathogenesis. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteri-Noël, A.; González-García, A.; Patier, J.L.; Fabregate, M.; Bara-Ledesma, N.; López-Rodríguez, M.; del Olmo, V.G.; Manzano, L. Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Genetics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchuk, D.A. Genetic abnormalities in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1998, 5, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasthuri, R.S.; Montifar, M.; Nelson, J.; Kim, H.; Lawton, M.T.; Faughnan, M.E.; Brain Vascular Malformation Consortium HHT Investigator Group. Prevalence and predictors of anemia in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E591–E593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Naik, R.P.; Zakai, N.A. A hematologic support score for longitudinal measurement of blood and iron requirements in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and other chronic bleeding disorders. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisthoff, U.W.; Heckmann, K.; D’Amelio, R.; Grünewald, S.; Knöbber, D.; Falkai, P.; König, J. Health-related quality of life in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 136, 726–733, discussion 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Guttmacher, A.E.; Buscarini, E.; Faughnan, M.E.; Hyland, R.H.; Westermann, C.J.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Plauchu, H. Diagnostic criteria for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome). Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 91, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritharis, A.; Al-Samkari, H.; Kuter, D.J. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Diagnosis and management from the hematologist’s perspective. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroches-Castan, A.; Koca, D.; Liu, H.; Roelants, C.; Resmini, L.; Ricard, N.; Bouvard, C.; Chaumontel, N.; Tharaux, P.-L.; Tillet, E.; et al. BMP9 is a key player in endothelial identity and its loss is sufficient to induce arteriovenous malformations. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, A.; Liso, A.; D’Ovidio, F.; Mestice, A.; Pasculli, G.; Gallitelli, M.; Rizzi, R.; Specchia, G.; Sabbà, C. Vascular endothelial growth factor serum levels are elevated in patients with hereditary hemor rhagic telangiectasia. Acta Haematol. 2003, 110, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, C.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; McDonald, J.; Letarte, M. Potential Second-Hits in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinchi, F.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; da Silva, M.C.; Balla, G.; Balla, J.; Jeney, V. Atherogenesis and iron: From epidemiology to cellular level. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauditz, J.; Lochs, H. Angiogenesis and vascular malformations: Antiangiogenic drugs for treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5979–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalgott, J.; Dos-Santos-Luis, D.; Lebrin, F. Pericytes as targets in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, B.; Ye, H.; Zhang, W.; Guan, J.; Su, K. Thalidomide for Epistaxis in Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Preliminary Study. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 157, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, R.; Quaglia, F.; Klersy, C.; Pagella, F.; Ornati, F.; Chu, F.; Matti, E.; Spinozzi, G.; Plumitallo, S.; Grignani, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of thalidomide for the treatment of severe recurrent epistaxis in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Results of a non-randomised, single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e465–e473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vascern-Hht, O.B.O.; Buscarini, E.; Botella, L.M.; Geisthoff, U.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Mager, H.J.; Pagella, F.; Suppressa, P.; Zarrabeitia, R.; Dupuis-Girod, S.; et al. Safety of thalidomide and bevacizumab in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduini, C.L.; Bellistri, F.; Pagella, F.; Chu, F.; Matti, E.; Spinozzi, G.; Ornati, F.; Canzonieri, C.; Olivieri, C.; Danesino, C.; et al. Efficacy of thalidomide in the treatment of severe recurrent epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): Preliminary results of an ongoing study. Blood 2012, 120, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, M.; Ümit, E.G.; Kırkızlar, H.O.; Özdöver, A.C.; Demir, A.M. Thalidomide for the Management of Bleeding Episodes in Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia, Effects on Epistaxis Severity Score and Quality of Life. Turk. J. Hematol. 2019, 36, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosman, A.; Westermann, C.J.; Snijder, R.; Disch, F.; Mummery, C.L.; Mager, J.J. Follow-up of thalidomide treatment in patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Rhinology 2015, 53, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebrin, F.; Srun, S.; Raymond, K.; Martin, S.; Van Den Brink, S.; Freitas, C.; Bréant, C.; Mathivet, T.; Larrivée, B.; Thomas, J.L.; et al. Thalidomide stimulates vessel maturation and reduces epistaxis in individuals with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Sami, S.; Babu, S. Successful treatment of bleeding gastro-intestinal angiodysplasia in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia with thalidomide. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr0820114585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzada, A.; Töppler, G.-J.; Cameron, S.; Schwörer, H.; Ramadori, G. A case report of a patient with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia treated successively with thalidomide and bevacizumab. Case Rep. Oncol. 2010, 3, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Hsu, H.; Hu, R.; Lee, P.; Ho, C. Long-term therapy with thalidomide in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Case report and literature review. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ogo, T.; Tahara, N.; Fukui, S.; Tsuji, A.; Ueda, J.; Fukumoto, Y.; Nakanishi, N.; Ogawa, H.; Yasuda, S. Thalidomide for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 1205–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, Q. Successful treatment of thalidomide for recurrent bleeding due to gastric angiodysplasia in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Samour, M.M.; Saygin, C.; Abdallah, R.; Kundu, S.; McCrae, K.R. Pomalidomide in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Interim results of a phase I study. Blood 2016, 128, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Iyer, V.; Pishko, A.M.; E Decker, J.; Whitehead, K.J.; Conrad, M.B.; Weiss, C.; Parambil, J.; Zumberg, M.S.; et al. PATH-HHT, a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Demonstrates That Pomalidomide Reduces Epistaxis and Improves Quality of Life. Blood 2023, 142, LBA-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowcock, S.J.; Patrick, H.E. Lenalidomide to control gastrointestinal bleeding in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Potential implications for angiodysplasias? Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, T.D.; Bunde, C.J.; Fillmore, B.J. Mechanism of action in thalidomide teratogenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.-L.; Yi, Y.-F.; Zhou, S.-K.; Xie, S.-S.; Zhang, G.-S. Thalidomide Effects in Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia During Therapeutic Treatment and in Fli-EGFP Transgenic Zebrafish Model. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 3050–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halderman, A.A.; Ryan, M.W.; Clark, C.; Sindwani, R.; Reh, D.D.; Poetker, D.M.; Invernizzi, R.; Marple, B.F. Medical treatment of epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: An evidence-based review. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarbandhan, S.; Van Der Veer, W.M.; Mulder, C.J.J. Double-balloon endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of hemorrhage from retrovalvular angiodysplasias. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2008, 17, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khatri, N.V.; Patel, B.; Kohli, D.R.; Solomon, S.S.; Bull-Henry, K.; Kessler, C.M. Lenalidomide as a novel therapy for gastrointestinal angiodysplasia in von Willebrand disease. Haemophilia 2018, 24, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Livesey, J.; A Manning, R.; Meek, J.H.; E Jackson, J.; Kulinskaya, E.; A Laffan, M.; Shovlin, C.L. Low serum iron levels are associated with elevated plasma levels of coagulation factor VIII and pulmonary emboli/deep venous thromboses in replicate cohorts of patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Thorax 2012, 67, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, T.W. Thrombin generation by thalidomide. Hemost. Lab. 2010, 3, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Grobost, V.; Hammi, S.; Pereira, B.; Guilhem, A.; Duffau, P.; Seguier, J.; Parrot, A.; Gautier, G.; Alric, L.; Kerjouan, M.; et al. Antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: A large French cohort study (RETROPLACOTEL). Thromb. Res. 2023, 229, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droege, F.; Pylaeva, E.; Siakaeva, E.; Bordbari, S.; Spyra, I.; Thangavelu, K.; Lueb, C.; Domnich, M.; Lang, S.; Geisthoff, U.; et al. Impaired Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Anemia-Associated T Cell Deficiency in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Systemic therapies, guidelines, and an evolving standard of care. Blood 2021, 137, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis-Girod, S.; Shovlin, C.L.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Mager, H.J.; Sabba, C.; Droege, F.; Fargeton, A.E.; Fialla, A.D.; Gandolfi, S.; Hermann, R.; et al. European Reference Network for Rare Vascular Diseases (VASCERN): When and how to use intravenous bevacizumab in Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)? Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faughnan, M.E.; Mager, J.J.; Hetts, S.W.; Palda, V.A.; Ratjen, F. Second International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1035–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choe, S.W.; Sprecher, D.; Lee, Y.; POh, S. Selective effects of oral antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors on an animal model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, S.; Chandakkar, P.; Zhao, H.; Papoin, J.; Chatterjee, P.K.; Christen, E.; Metz, C.N.; Blanc, L.; Campagne, F.; Marambaud, P. Tacrolimus rescues the signaling and gene expression signature of endothelial ALK1 loss-of-function and improves HHT vascular pathology. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 4786–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Moore, J.C.; Morgan, D.G. Gastrointestinal Angiodysplasia and Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 858–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Liang, R.; Press, K.; Schmidt, A.; Shabani, Z.; Leng, K.; Wang, C.; Sekhar, A.; Shi, J.; Devlin, G.W.; et al. Evaluation of AAV Capsids and Delivery Approaches for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Gene Therapy. Transl. Stroke Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalid, Y.; Darji, Z.; Shenkar, R.; Clancy, M.; Dyamenahalli, U.; Awad, I.A.; The Multidisciplinary Faculty of the HHT Center of Excellence at University of Chicago Medicine. Multidisciplinary coordinated care of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease). Vasc. Med. 2023, 28, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | No. of Patients | Age, y | Thalidomide Dose, mg/d | Duration of Treatment (m) | Treatment Effect Evaluation | Side Effects | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Incidence Rate (%) | Stopped Treatment Because of Side Effects | |||||
| Fang et al. [16] | 7 | 49.1 | 50–100 | 12.8 | ESS: 5 | ESS: 0.9 | 57 | 1 |
| Invernizzi et al. [17] | 31 | 62.6 | 50–150 | 15.9 | Total erythrocytes transfusion: 23 | Total erythrocytes transfusion: 3 | 58 | 0 |
| Buscarini et al. [18] | 67 | 66.4 | 100–200 | 13.4 | Reducing Transfusion dependency, GI bleeding, and epistaxis. No effect in AVM. | 55 | 3 fatal AE | |
| Balduini et al. [19] | 11 | 67 | 50–200 | 11.0 | Reducing transfusion dependency and epistaxis; increasing hemoglobin level | Nonserious constipation and drowsiness | ||
| Baysal et al. [20] | 6 | 60.5 | 50–100 | 8 | ESS: 7.4 | ESS: 3.1 | 33 | 0 |
| Hg: 8.8 g/dL | Hg: 11.5 g/dL | |||||||
| Erythrocytes transfusion: 5/month | Erythrocytes transfusion: 0.8/month | |||||||
| Hosman et al. [21] | 12 | 69.5 | 50–100 | 7 | Number of epistaxis: 40.8/week | Number of epistaxis: 5.6/week | 66 | 7 |
| Total erythrocytes transfusion: 3.7 | Total erythrocytes transfusion: 0.5 | |||||||
| Lebrin et al. [22] | 7 | Range: 48–75 | 100 | * 6–60 | Hg: 6.0 g/dL | Hg: 7.4 g/dL | 85 | 3 |
| Alam et al. [23] | 1 | 77 | 100 | 16 | Hg: 5.8 g/dL | Hg: 13.0 g/dL | 0 | 0 |
| Total erythrocytes transfusion: 43 | Total erythrocytes transfusion: 1 | |||||||
| Amanzada et al. [24] | 1 | 59 | 200 | 29 | Reducing transfusion dependency | 100 | 1 | |
| Chen et al. [25] | 1 | 38 | 50 | 6 | Erythrocytes transfusion frequency: 3 times a week | Erythrocytes transfusion frequency: once a month | 0 | 0 |
| Nakamura et al. [26] | 1 | 37 | 50 | 12 | Reducing transfusion dependency | 100 | 1 | |
| Wang et al. [27] | 1 | 77 | 100 | 12 | Reducing epistaxis | 0 | 0 | |
| Study | No. of Patients | Age, y | Pomalidomide Dose, mg/d | Duration of Treatment (m) | Treatment Effect Evaluation | Side Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence Rate (%) | Stopped Treatment Because of Side Effects (%) | ||||||
| Samour M et al. [28] | 6 | min: 48–max: 70 | min: 1–max: 5 | 6 | Increasing in hemoglobin of more than 1 g/dL decreasing of more than 50% in ESS | 66 | 50 |
| Al-Samkari H et al. [29] | 95 | 58.8 | 4 | 24 | Decreasing in ESS compared to placebo (p = 0.003) | 60 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ugur, M.C.; Baysal, M.; Umit, E.G. The Role of Thalidomide and Its Analogs in the Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185404
Ugur MC, Baysal M, Umit EG. The Role of Thalidomide and Its Analogs in the Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(18):5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185404
Chicago/Turabian StyleUgur, Mehmet Can, Mehmet Baysal, and Elif Gulsum Umit. 2024. "The Role of Thalidomide and Its Analogs in the Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 18: 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185404
APA StyleUgur, M. C., Baysal, M., & Umit, E. G. (2024). The Role of Thalidomide and Its Analogs in the Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(18), 5404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185404






