Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Myopathy, and Thromboembolism: The Additive Value of Echocardiography and Possible New Horizons for Risk Stratification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Atrial Fibrillation: The Size of the Problem
- -
- irregular R-R intervals (when atrioventricular conduction is not impaired);
- -
- absence of distinct repeating P waves;
- -
- irregular atrial activations [1].
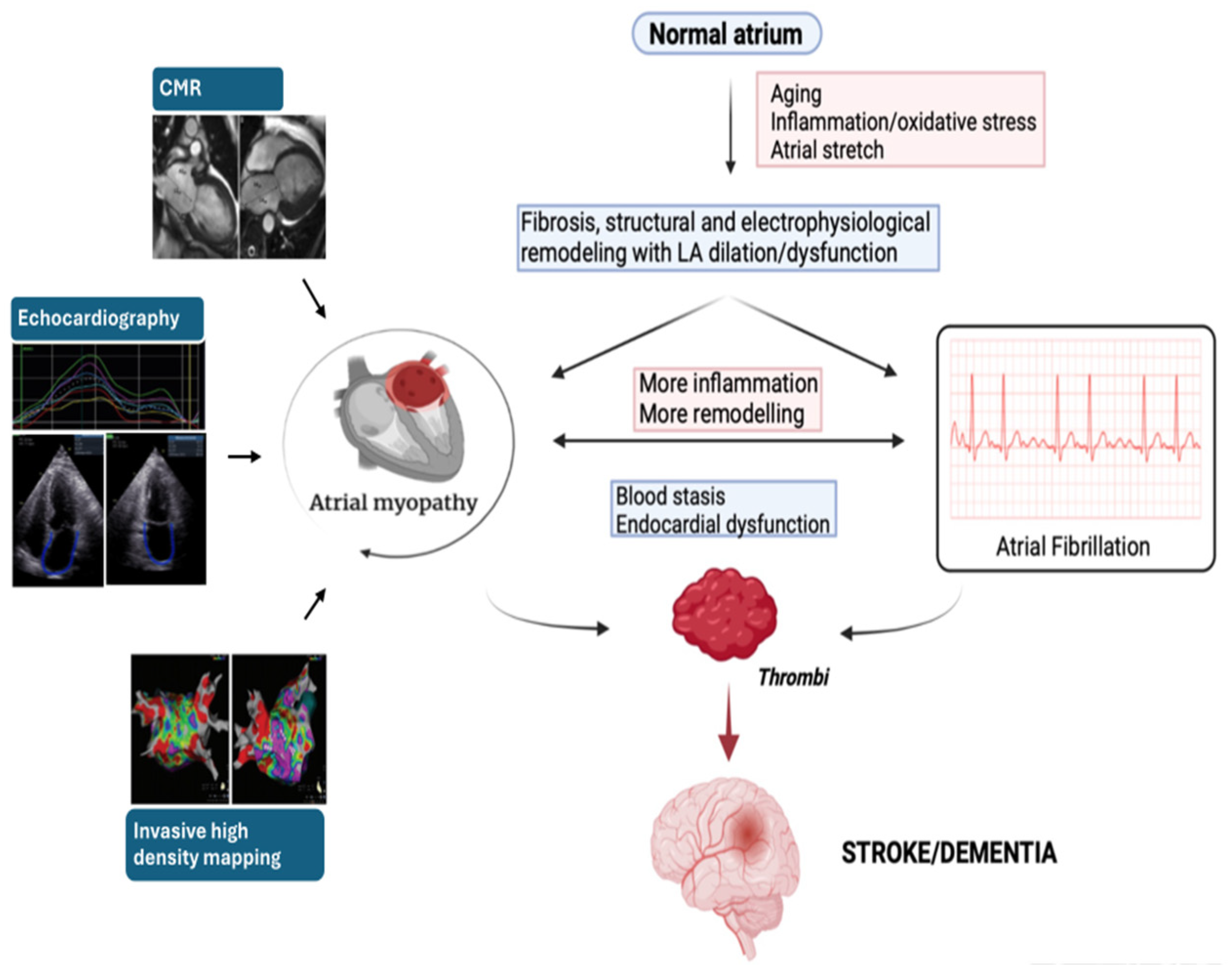
3. Pathophysiological Pathway of Atrial Fibrillation
4. Association between AF, Stroke/TIA, and Dementia—The Emerging Concept of Atrial Myopathy
5. Evaluation of Atrial Cardiomyopathy
6. Potential Applications of AM Study in Clinical Practice
- -
- Stroke Risk: Assessed using the CHA2DS2-VASc score, this domain helps identify patients at high risk for stroke and recommend anticoagulation therapy.
- -
- Symptom Improvement: Evaluated using the EHRA symptom score [152], this domain guides the selection of strategies to improve patient well-being, such as rate control or rhythm control.
- -
- Severity of AF Burden: This domain analyzes the temporal pattern of AF episodes (paroxysmal, persistent, etc.), which influences treatment decisions.
- -
- Substrate of AF: This domain assesses the presence of comorbidities, cardiovascular risk factors, and AM. Understanding these underlying factors is crucial for tailoring treatment strategies.
- Avoiding Stroke with Anticoagulation: This pillar focuses on preventing thromboembolic complications through appropriate anticoagulation therapy.
- Better Symptom Control: This pillar addresses patient symptoms by employing rate control or rhythm control strategies.
- Cardiovascular Risk Modification and concomitant diseases: This pillar aims to manage underlying cardiovascular risk factors, also through lifestyle modifications, to prevent disease progression and improve overall health outcomes.
- -
- a guide for anticoagulation strategies within the “A” pillar of the ABC pathway;
- -
- a factor influencing the decision between rhythm/rate control strategies in the “B” pillar, as impaired atrial function may affect treatment efficacy [162];
- -
- an early marker of cardiac disease or progression in patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors within the “C” pillar.
| Most relevant Studies about the Association between Atrial Myopathy and Thromboembolic Risk | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author/Year | Study Design | Study Setting | Number of Patients (n) | References |
| Sade et al. 2022 | Prospective, single-center cohort study | LA strain to predict recurrence of TIA/stroke or new onset of AF in patients with no history of AF enrolled after a cryptogenic stroke event | 186 | [163] |
| Alhakak et al. 2022 | Prospective, multi-center longitudinal study | General low-risk population long-term risk of AF and ischemic stroke based on baseline PALS | 400 | [164] |
| Azemi et al. 2012 | Retrospective, single-center cohort study | Patients with AF, stroke, or TIA with CHA2DS2-VASc scores ≤ 1 before their events | 57 | [165] |
| Saha et al. 2011 | Cross-sectional, single-center cohort study | Association between echocardiographic parameters and CHA2DS2-VASc score in patients with nonvalvular AF | 77 | [166] |
| Obokata et al. 2014 | Prospective, observational, single-center cohort study | LA strain incremental value over CHA2DS2-VASc score in AF patients with or without acute embolism | 286 | [167] |
| Akintoye et al. 2023 | Prospective, single-single center cohort study | LA strain prognostic value to predict incident thrombotic event in patients with AL or ATTR amyloid cardiomyopathy and no history of AF | 448 | [169] |
| Zhang et al. 2023 | Prospective, multi-center study | Association of prevalent and incident AF with stroke and dementia adjusting for LA function and size. | 5458 (stroke analysis) 5461 (dementia analysis) | [172] |
| Kamel et al. 2024 | Randomized, double-blind, double dummy, multi-center study | Apixban 5 mg twice daily vs. aspirin 81 mg once daily in patients ≥ 45 years of age with embolic stroke of undetermined source, evidence of AM and no AF. | 1015 | [173] |
- -
- V1 P-wave terminal force >5000 µV·ms;
- -
- serum N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) >250 pg/mL;
- -
- indexed LA diameter ≥3 cm/m2 on transthoracic echocardiography.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 507; Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 546–547; Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colilla, S.; Crow, A.; Petkun, W.; Singer, D.E.; Simon, T.; Liu, X. Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, J.E.; Gersh, B.J. Atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention in aging patients: What’s good can be even better. Circulation 2014, 130, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Kirkwood, G.; Visweswariah, R.; Fox, D.J. How does Chronic Atrial Fibrillation Influence Mortality in the Modern Treatment Era? Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2015, 11, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrall, G.; Lane, D.; Carroll, D.; Lip, G.Y. Quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 448.e1–448.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 104–132, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotten, U.; Verheule, S.; Kirchhof, P.; Goette, A. Pathophysiological mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: A translational appraisal. Physiological reviews. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 265–325, Erratum in Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boriani, G.; Savelieva, I.; Dan, G.A.; Deharo, J.C.; Ferro, C.; Israel, C.W.; Lane, D.A.; La Manna, G.; Morton, J.; Mitjans, A.M.; et al. Chronic kidney disease in patients with cardiac rhythm disturbances or implantable electrical devices: Clinical significance and implications for decision making-a position paper of the European Heart Rhythm Association endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society and the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society. Europace 2015, 17, 1169–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Feng, T.; Schlesinger, S.; Janszky, I.; Norat, T.; Riboli, E. Diabetes mellitus, blood glucose and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadby, G.; McArdle, N.; Briffa, T.; Hillman, D.R.; Simpson, L.; Knuiman, M.; Hung, J.T. Severity of OSA is an independent predictor of incident atrial fibrillation hospitalization in a large sleep-clinic cohort. Chest 2015, 148, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbelt, A.H.; Siland, J.E.; Geelhoed, B.; Van Der Harst, P.; Hillege, H.L.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M. Clinical, biomarker, and genetic predictors of specific types of atrial fibrillation in a community-based cohort: Data of the PREVEND study. Europace 2017, 19, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalliah, C.J.; Sanders, P.; Kalman, J.M. The Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Atrial Fibrillation. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Coca, A.; Kahan, T.; Boriani, G.; Manolis, A.S.; Olsen, M.H.; Oto, A.; Potpara, T.S.; Steffel, J.; Marín, F.; et al. Hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias: A consensus document from the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and ESC Council on Hypertension, endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS) and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulación Cardíaca y Electrofisiología (SOLEACE). Europace 2017, 19, 891–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, C.; Hendriks, J.M.L.; Elliott, A.D.; Wong, C.X.; Rangnekar, G.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Mahajan, R.; Lau, D.H.; Sanders, P. Alcohol and incident atrial fibrillation—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 246, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, C.; Gervasi, F.; Gaeta, M.; Smuts, C.M.; Schutte, A.E.; Leitzmann, M.F. Physical activity volume in relation to risk of atrial fibrillation. A non-linear meta-regression analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528, Erratum in Circulation 2020, 141, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, V.; Honarbakhsh, S.; Casas, J.P.; Wallace, J.; Hunter, R.; Schilling, R.; Perel, P.; Morley, K.; Banerjee, A.; Hemingway, H. Are cardiovascular risk factors also associated with the incidence of atrial fibrillation? A systematic review and field synopsis of 23 factors in 32 population-based cohorts of 20 million participants. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feghaly, J.; Zakka, P.; London, B.; MacRae, C.A.; Refaat, M.M. Genetics of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesurendra, R.S.; Casadei, B. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart 2019, 105, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, S.A.; Yin, X.; McManus, D.D.; Weng, L.C.; Aparicio, H.J.; Walkey, A.J.; Rafael Romero, J.; Kase, C.S.; Ellinor, P.T.; Wolf, P.; et al. Stroke as the Initial Manifestation of Atrial Fibrillation: The Framingham Heart Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, T.J. Atrial Fibrillation and Dementia. Circulation 2020, 142, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, L.; Rosenqvist, M. Less dementia with oral anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, V.; Woller, S.C.; Stevens, S.; May, H.T.; Bair, T.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Crandall, B.G.; Day, J.D.; Johanning, K.; Long, Y.; et al. Time outside of therapeutic range in atrial fibrillation patients is associated with long-term risk of dementia. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 2206–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, T.J.; Crandall, B.G.; Weiss, J.P.; May, H.T.; Bair, T.L.; Osborn, J.S.; Anderson, J.L.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Horne, B.D.; Lappe, D.L.; et al. Patients treated with catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation have long-term rates of death, stroke, and dementia similar to patients without atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 22, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.N.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, K.W.; Yu, H.T.; Uhm, J.S.; Joung, B.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, E.; Pak, H.N. Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation Improves 1-Year Follow-Up Cognitive Function, Especially in Patients with Impaired Cognitive Function. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.Y.; Gupta, D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial fibrillation and the prothrombotic state: Revisiting Virchow’s triad in 2020. Heart 2020, 106, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.; Shantsila, E.; Lip, G.Y. Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: Virchow’s triad revisited. Lancet 2009, 373, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goette, A.; Kalman, J.M.; Aguinaga, L.; Akar, J.; Cabrera, J.A.; Chen, S.A.; Chugh, S.S.; Corradi, D.; D’Avila, A.; Dobrev, D.; et al. EHRA/HRS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus on atrial cardiomyopathies: Definition, characterization, and clinical implication. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, e3–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, H.; Bartz, T.M.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Okin, P.M.; Thacker, E.L.; Patton, K.K.; Stein, P.K.; deFilippi, C.R.; Gottesman, R.F.; Heckbert, S.R.; et al. Atrial Cardiopathy and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study). Stroke 2018, 49, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambatti, M.; Connolly, S.J.; Gold, M.R.; Morillo, C.A.; Capucci, A.; Muto, C.; Lau, C.P.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Carlson, M.; et al. Temporal relationship between subclinical atrial fibrillation and embolic events. Circulation 2014, 129, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triposkiadis, F.; Pieske, B.; Butler, J.; Parissis, J.; Giamouzis, G.; Skoularigis, J.; Brutsaert, D.; Boudoulas, H. Global left atrial failure in heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.D.; Aronis, K.N.; Chrispin, J.; Patil, K.D.; Marine, J.E.; Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Calkins, H. Obesity, Exercise, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, and Modifiable Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2899–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binici, Z.; Intzilakis, T.; Nielsen, O.W.; Køber, L.; Sajadieh, A. Excessive supraventricular ectopic activity and increased risk of atrial fibrillation and stroke. Circulation 2010, 121, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.S.; Kumarathurai, P.; Falkenberg, J.; Nielsen, O.W.; Sajadieh, A. Excessive Atrial Ectopy and Short Atrial Runs Increase the Risk of Stroke Beyond Incident Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppahally, S.S.; Akoum, N.; Burgon, N.S.; Badger, T.J.; Kholmovski, E.G.; Vijayakumar, S.; Rao, S.N.; Blauer, J.; Fish, E.N.; Dibella, E.; et al. Left atrial strain and strain rate in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation: Relationship to left atrial structural remodeling detected by delayed-enhancement, M.R.I. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigh, G.; Shah, S.J.; Patel, R.B. Left Atrial Myopathy in Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: Clinical Implications, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2021, 18, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, C.P.; Galloway, J.M.; Gonzalez, M.S.; Gaballa, M.; Basnight, M.A. Estimation of left ventricular filling pressures using two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography in adult patients with cardiac disease. Additional value of analyzing left atrial size, left atrial ejection fraction and the difference in duration of pulmonary venous and mitral flow velocity at atrial contraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geske, J.B.; Sorajja, P.; Nishimura, R.A.; Ommen, S.R. The relationship of left atrial volume and left atrial pressure in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: An echocardiographic and cardiac catheterization study. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guron, C.W.; Hartford, M.; Rosengren, A.; Thelle, D.; Wallentin, I.; Caidahl, K. Usefulness of atrial size inequality as an indicator of abnormal left ventricular filling. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 1448–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simek, C.L.; Feldman, M.D.; Haber, H.L.; Wu, C.C.; Jayaweera, A.R.; Kaul, S. Relationship between left ventricular wall thickness and left atrial size: Comparison with other measures of diastolic function. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 1995, 8, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersbøll, M.; Andersen, M.J.; Valeur, N.; Mogensen, U.M.; Waziri, H.; Møller, J.E.; Hassager, C.; Søgaard, P.; Køber, L. The prognostic value of left atrial peak reservoir strain in acute myocardial infarction is dependent on left ventricular longitudinal function and left atrial size. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lønborg, J.T.; Engstrøm, T.; Møller, J.E.; Ahtarovski, K.A.; Kelbæk, H.; Holmvang, L.; Jørgensen, E.; Helqvist, S.; Saunamäki, K.; Søholm, H.; et al. Left atrial volume and function in patients following ST elevation myocardial infarction and the association with clinical outcome: A cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.E.; Miyasaka, Y.; Seward, J.B.; Gersh, B.J.; Rosales, A.G.; Bailey, K.R.; Petty, G.W.; Wiebers, D.O.; Tsang, T.S. Left atrial volume in the prediction of first ischemic stroke in an elderly cohort without atrial fibrillation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Wolf, P.A.; Levy, D.J. Left atrial size and the risk of stroke and death. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1995, 92, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolca, O.; Akdemir, O.; Eren, M.; Dagdeviren, B.; Yildirim, A.; Tezel, T. Left atrial maximum volume is a recurrence predictor in lone atrial fibrillation: An acoustic quantification study. Jpn. Heart J. 2002, 43, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tullio, M.R.; Sacco, R.L.; Sciacca, R.R.; Homma, S. Left atrial size and the risk of ischemic stroke in an ethnically mixed population. Stroke 1999, 30, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaker, G.C.; Fletcher, K.A.; Rothbart, R.M.; Halperin, J.L.; Hart, R.G. Clinical and echocardiographic features of intermittent atrial fibrillation that predict recurrent atrial fibrillation. Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation (SPAF) Investigators. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 76, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottkamp, H. Fibrotic atrial cardiomyopathy: A specific disease/syndrome supplying substrates for atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia, sinus node disease, AV node disease, and thromboembolic complications. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.S.; Barnes, M.E.; Bailey, K.R.; Leibson, C.L.; Montgomery, S.C.; Takemoto, Y.; Diamond, P.M.; Marra, M.A.; Gersh, B.J.; Wiebers, D.O.; et al. Left atrial volume: Important risk marker of incident atrial fibrillation in 1655 older men and women. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, S.M.; Larson, M.G.; Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D. Echocardiographic predictors of nonrheumatic atrial fibrillation. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1994, 89, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.S.; Barnes, M.E.; Gersh, B.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Seward, J.B. Risks for atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure in patients >/=65 years of age with abnormal left ventricular diastolic relaxation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, T.S.; Gersh, B.J.; Appleton, C.P.; Tajik, A.J.; Barnes, M.E.; Bailey, K.R.; Oh, J.K.; Leibson, C.; Montgomery, S.C.; Seward, J.B. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction as a predictor of the first diagnosed nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in 840 elderly men and women. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinart, R.; Boyko, V.; Schwammenthal, E.; Kuperstein, R.; Sagie, A.; Hod, H.; Matetzky, S.; Behar, S.; Eldar, M.; Feinberg, M.S. Long-term prognostic significance of left atrial volume in acute myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, J.E.; Hillis, G.S.; Oh, J.K.; Seward, J.B.; Reeder, G.S.; Wright, R.S.; Park, S.W.; Bailey, K.R.; Pellikka, P.A. Left atrial volume: A powerful predictor of survival after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2003, 107, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini, F.L.; Cortigiani, L.; Baldini, U.; Boni, A.; Nuti, R.; Barsotti, L.; Micheli, G. Prognostic value of left atrial enlargement in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, Y.K.; Jun, D.H.; Nam, C.W.; Han, S.W.; Hur, S.H.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, K.B. Prognostic implications of the NT-ProBNP level and left atrial size in non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modena, M.G.; Muia, N.; Sgura, F.A.; Molinari, R.; Castella, A.; Rossi, R. Left atrial size is the major predictor of cardiac death and overall clinical outcome in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: A long-term follow-up study. Clin. Cardiol. 1997, 20, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabharwal, N.; Cemin, R.; Rajan, K.; Hickman, M.; Lahiri, A.; Senior, R. Usefulness of left atrial volume as a predictor of mortality in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddukuri, P.V.; Vieira, M.L.; DeCastro, S.; Maron, M.S.; Kuvin, J.T.; Patel, A.R.; Pandian, N.G. What is the best approach for the assessment of left atrial size? Comparison of various unidimensional and two-dimensional parameters with three-dimensional echocardiographically determined left atrial volume. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2006, 19, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gutman, J.M.; Heilbron, D.; Wahr, D.; Schiller, N.B. Atrial volume in a normal adult population by two-dimensional echocardiography. Chest 1984, 86, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, M.; Garg, A.; Gelow, J.; Jacobson, T.; Broberg, C. Comparison of left and right atrial volume by echocardiography versus cardiac magnetic resonance imaging using the area-length method. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, E.; Baekkevar, M.; Roislien, J.; Rodevand, O.; Otterstad, J.E. Normal reference ranges for left and right atrial volume indexes and ejection fractions obtained with real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2009, 10, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, D.; Badano, L.P.; Muraru, D.; Dal Bianco, L.; Cucchini, U.; Kocabay, G.; Kovàcs, A.; Casablanca, S.; Iliceto, S. Right atrial size and function assessed with three-dimensional and speckle-tracking echocardiography in 200 healthy volunteers. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.K.; Dahl, J.S.; Henriksen, J.E.; Hey, T.M.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Møller, J.E. Left atrial volume index: Relation to long-term clinical outcome in type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 2416–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Kawasaki, M.; Tanaka, R.; Ono, K.; Hirose, T.; Iwama, M.; Watanabe, T.; Noda, T.; Watanabe, S.; Takemura, G.; et al. Left atrial global and regional function in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation has already been impaired before enlargement of left atrium: Velocity vector imaging echocardiography study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 13, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Shah, A.M.; Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Antman, E.M.; Grip, L.T.; Deenadayalu, N.; Hoffman, E.; Patel, I.; Shi, M.; et al. Left atrial structure and function in atrial fibrillation: ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olshansky, B.; Heller, E.N.; Mitchell, L.B.; Chandler, M.; Slater, W.; Green, M.; Brodsky, M.; Barrell, P.; Greene, H.L. Are transthoracic echocardiographic parameters associated with atrial fibrillation recurrence or stroke? Results from the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinaru, D.; Tribouilloy, C.; Grigioni, F.; Avierinos, J.F.; Suri, R.M.; Barbieri, A.; Szymanski, C.; Ferlito, M.; Michelena, H.; Tafanelli, L.; et al. Left atrial size is a potent predictor of mortality in mitral regurgitation due to flail leaflets: Results from a large international multicenter study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2011, 4, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, M.R.; Chandraratna, P.A.; Reid, C.L.; Lin, S.L.; Rahimtoola, S.H. Accuracy of nondirected and directed M-mode echocardiography as an estimate of left atrial size. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 60, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.J.; Ryan, E.W.; Schiller, N.B.; Foster, E. Best method in clinical practice and in research studies to determine left atrial size. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 84, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loperfido, F.; Pennestri, F.; Digaetano, A.; Scabbia, E.; Santarelli, P.; Mongiardo, R.; Schiavoni, G.; Coppola, E.; Manzoli, U. Assessment of left atrial dimensions by cross sectional echocardiography in patients with mitral valve disease. Br. Heart J. 1983, 50, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, H.; Jackson, K.; Chenzbraun, A. Switching to volumetric left atrial measurements: Impact on routine echocardiographic practice. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2011, 12, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottdiener, J.S.; Kitzman, D.W.; Aurigemma, G.P.; Arnold, A.M.; Manolio, T.A. Left atrial volume, geometry, and function in systolic and diastolic heart failure of persons > or =65 years of age (the cardiovascular health study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Cicoira, M.; Zanolla, L.; Sandrini, R.; Golia, G.; Zardini, P.; Enriquez-Sarano, M. Determinants and prognostic value of left atrial volume in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, Y.; Barnes, M.E.; Seward, J.B.; Lester, S.J.; Appleton, C.A.; Gersh, B.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Tsang, T.S. Usefulness of left atrial volume in predicting first congestive heart failure in patients > or = 65 years of age with well-preserved left ventricular systolic function. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, T.; Tanabe, K.; Ono, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Okada, M.; Sumida, T.; Konda, T.; Fujii, Y.; Kawai, J.; Yagi, T.; et al. Left atrial volume and the risk of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2004, 17, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, T.S.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Barnes, M.E.; Miyasaka, Y.; Gersh, B.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Cha, S.S.; Seward, J.B. Prediction of cardiovascular outcomes with left atrial size: Is volume superior to area or diameter? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, A.M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Mahoney, D.W.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Redfield, M.M. Left atrial volume as an index of left atrial size: A population-based study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.; Bricknell, K.; Marwick, T.H. Use of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography to measure left atrial volume: Comparison with other echocardiographic techniques. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2005, 18, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Levett, K.; Boyd, A.; Leung, D.Y.; Schiller, N.B.; Ross, D.L. Compensatory changes in atrial volumes with normal aging: Is atrial enlargement inevitable? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Tani, T.; Yagi, T.; Fujii, Y.; Konda, T.; Kawai, J.; Sumida, T.; Morioka, S.; Kihara, Y. Left atrial volume in normal Japanese adults. Circ. J. 2006, 70, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceira, A.M.; Cosín-Sales, J.; Roughton, M.; Prasad, S.K.; Pennell, D.J. Reference left atrial dimensions and volumes by steady state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2010, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodevan, O.; Bjornerheim, R.; Ljosland, M.; Maehle, J.; Smith, H.J.; Ihlen, H. Left atrial volumes assessed by three- and two-dimensional echocardiography compared to MRI estimates. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 1999, 15, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovska, J.; Cronin, P.; Patel, S.; Gross, B.H.; Oral, H.; Chughtai, K.; Kazerooni, E.A. Reference normal absolute and indexed values from ECG-gated MDCT: Left atrial volume, function, and diameter. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujino, K.; Barnes, M.E.; Cha, S.S.; Langins, A.P.; Bailey, K.R.; Seward, J.B.; Tsang, T.S. Two-dimensional echocardiographic methods for assessment of left atrial volume. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurigemma, G.P.; Gottdiener, J.S.; Arnold, A.M.; Chinali, M.; Hill, J.C.; Kitzman, D. Left atrial volume and geometry in healthy aging: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaka, Y.; Tsujimoto, S.; Maeba, H.; Yuasa, F.; Takehana, K.; Dote, K.; Iwasaka, T. Left atrial volume by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography: Validation by 64-slice multidetector computed tomography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2011, 24, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, A.; Brinkert, M.; Kawel, N.; Buechel, R.R.; Leibundgut, G.; Grize, L.; Kühne, M.; Bremerich, J.; Kaufmann, B.A.; Zellweger, M.; et al. Functional assessment of the left atrium by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography using a novel dedicated analysis tool: Initial validation studies in comparison with computed tomography. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2011, 12, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artang, R.; Migrino, R.Q.; Harmann, L.; Bowers, M.; Woods, T.D. Left atrial volume measurement with automated border detection by 3-dimensional echocardiography: Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2009, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor-Avi, V.; Yodwut, C.; Jenkins, C.; Kühl, H.; Nesser, H.J.; Marwick, T.H.; Franke, A.; Weinert, L.; Niel, J.; Steringer-Mascherbauer, R.; et al. Real-time 3D echocardiographic quantification of left atrial volume: Multicenter study for validation with CMR. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, S.; Canali, E.; Foschi, M.L.; Santini, D.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Pandian, N.G.; De Castro, S. Long-term prognostic significance of three-dimensional echocardiographic parameters of the left ventricle and left atrium. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, I.W.; Song, J.M.; Lee, E.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.J.; Kang, D.H.; Song, J.K. Left atrial volume measured by real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography predicts clinical outcomes in patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction and in sinus rhythm. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2008, 21, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Ribeiro, A.L.P.; Platonov, P.G.; Cygankiewicz, I.; Soliman, E.Z.; Gorenek, B.; Ikeda, T.; Vassilikos, V.P.; Steinberg, J.S.; Varma, N.; et al. P Wave Parameters and Indices: A Critical Appraisal of Clinical Utility, Challenges, and Future Research-A Consensus Document Endorsed by the International Society of Electrocardiology and the International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrocardiology. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e010435. [Google Scholar]
- Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Galderisi, M.; Wolf, P.A.; Benjamin, E.J.; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institutes of Health. Doppler transmitral flow indexes and risk of atrial fibrillation (the Framingham Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, A.V.; Tarabini Castellani, E.; Molinari, R.; Mattioli, G. Restoration of atrial function after atrial fibrillation of different etiological origins. Cardiology 1996, 87, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuda, S.; Nakatani, S.; Isobe, F.; Kosakai, Y.; Miyatake, K. Comparative efficacy of the maze procedure for restoration of atrial contraction in patients with and without giant left atrium associated with mitral valve disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizukuda, Y.; Bolan, C.D.; Tripodi, D.J.; Yau, Y.Y.; Nguyen, T.T.; Botello, G.; Sachdev, V.; Sidenko, S.; Ernst, I.; Waclawiw, M.A.; et al. Significance of left atrial contractile function in asymptomatic subjects with hereditary hemochromatosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, W.J.; Leeman, D.E.; Gotch, P.J.; Come, P.C. Pulsed Doppler evaluation of atrial mechanical function after electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1989, 13, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Fukuda, N.; Iuchi, A.; Tabata, T.; Tanimoto, M.; Manabe, K.; Kageji, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Yamada, H.; Ito, S. Left Atrial Systolic Performance in the Presence of Elevated Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure: Evaluation by Transesophageal Pulsed Doppler Echocardiography of Left Ventricular Inflow and Pulmonary Venous Flow Velocities. Echocardiography 1997, 14, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Iuchi, A.; Tabata, T.; Yamada, H.; Manabe, K.; Kageji, Y.; Abe, M.; Fukuda, N.; Ito, S. Transesophageal pulsed Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of left atrial systolic performance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Combined analysis of transmitral and pulmonary venous flow velocities. Clin. Cardiol. 1997, 20, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, H.; Kunichika, H.; Murata, K.; Seki, K.; Katayama, K.; Hiro, T.; Miura, T.; Matsuzaki, M. Improvement of afterload mismatch of left atrial booster pump function with positive inotropic agent. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuchi, A.; Oki, T.; Tabata, T.; Manabe, K.; Kageji, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Hama, M.; Yamada, H.; Fukuda, N. Changes in pulmonary venous and transmitral flow velocity patterns after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiol. 1995, 25, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ari, H.; Ari, S.; Akkaya, M.; Aydin, C.; Emlek, N.; Sarigül, O.Y.; Çetinkaya, S.; Bozat, T.; Şentürk, M.; Karaağaç, K. Predictive value of atrial electromechanical delay for atrial fibrillation recurrence. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, Y.; Nozawa, Y.; Ogasawara, M.; Yuda, S.; Sato, S.; Sakasai, T.; Oka, M.; Katayama, H.; Sato, M.; Kouzu, H.; et al. Atrial electromechanical interval may predict cardioembolic stroke in apparently low risk elderly patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography 2014, 31, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, G.; Akcay, A.; Sokmen, A.; Ozkaya, M.; Guler, E.; Sokmen, G.; Kaya, H.; Nacar, A.B.; Tuncer, C. Assessment of atrial electromechanical delay, diastolic functions, and left atrial mechanical functions in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nar, G.; Ergul, B.; Aksan, G.; Inci, S. Assessment of Atrial Electromechanical Delay and Left Atrial Mechanical Functions in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksan, G.; Nar, G.; Soylu, K.; İnci, S.; Yuksel, S.; Ocal, H.S.; Yuksel, E.P.; Gulel, O. Assessment of atrial electromechanical delay and left atrial mechanical functions in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Echocardiography 2015, 32, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilter, A.; Kırış, A.; Kaplan, Ş.; Kutlu, M.; Şahin, M.; Erem, C.; Civan, N.; Kangül, F. Atrial conduction times and left atrium mechanical functions in patients with active acromegaly. Endocrine 2015, 48, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akıl, M.A.; Akıl, E.; Bilik, M.Z.; Oylumlu, M.; Acet, H.; Yıldız, A.; Akyüz, A.; Ertaş, F.; Toprak, N. The relationship between atrial electromechanical delay and left atrial mechanical function in stroke patients. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozios, I.; Vouliotis, A.I.; Dilaveris, P.; Tsioufis, C. Electro-Mechanical Alterations in Atrial Fibrillation: Structural, Electrical, and Functional Correlates. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, P.; Weijs, B.; Bemelmans, N.M.A.A.; Mügge, A.; Eckardt, L.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Bax, J.J.; Linz, D.; den Uijl, D.W. Echocardiography-derived total atrial conduction time (PA-TDI duration): Risk stratification and guidance in atrial fibrillation management. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, K.; Ito, T.; Miyamura, M.; Kanzaki, Y.; Sohmiya, K.; Hoshiga, M. Usefulness of tissue Doppler-derived atrial electromechanical delay for identifying patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2020, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, P.; Hars, C.; Schiedat, F.; Bösche, L.I.; Gotzmann, M.; Strauch, J.; Dietrich, J.W.; Vogt, M.; Tannapfel, A.; Deneke, T.; et al. Correlation between total atrial conduction time estimated via tissue Doppler imaging (PA-TDI Interval), structural atrial remodeling and new-onset of atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, F.H.; Erdem, A.; Özlü, F.; Ozturk, S.; Ayhan, S.S.; Çağlar, S.O.; Yazici, M. Electrophysiological validation of total atrial conduction time measurement by tissue doppler echocardiography according to age and sex in healthy adults. J. Arrhythm. 2016, 32, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou, R.; Leung, M.; Tonsbeek, A.M.; Podlesnikar, T.; Maan, A.C.; Schalij, M.J.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; Delgado, V.; Bax, J.J. Effect of Aging on Left Atrial Compliance and Electromechanical Properties in Subjects without Structural Heart Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özlü, M.F.; Erdem, K.; Kırış, G.; Parlar, A.İ.; Demirhan, A.; Ayhan, S.S.; Erdem, A.; Öztürk, S.; Tekelioğlu, Ü.Y.; Yazıcı, M. Predictive value of total atrial conduction time measured with tissue Doppler imaging for postoperative atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2013, 37, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, P.; Schiedat, F.; Dietrich, J.W.; Shin, D.I.; Kara, K.; Mügge, A.; Deneke, T. Reverse atrial remodeling in patients who maintain sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion: Evidence derived from the measurement of total atrial conduction time assessed by PA-TDI interval. J. Echocardiogr. 2014, 12, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Uijl, D.W.; Delgado, V.; Bertini, M.; Tops, L.F.; Trines, S.A.; van de Veire, N.R.; Zeppenfeld, K.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J. Impact of left atrial fibrosis and left atrial size on the outcome of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart 2011, 97, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Tsao, H.M.; Chang, S.L.; Lo, L.W.; Hu, Y.F.; Tuan, T.C.; Li, C.H.; Chang, H.Y.; Wu, T.J.; et al. Prolonged atrium electromechanical interval is associated with stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Yuda, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Hashimoto, A.; Uno, K.; Nakata, T.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Miura, T.; Ura, N.; Shimamoto, K. Strain rate imaging for noninvasive functional quantification of the left atrium: Comparative studies in controls and patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2005, 18, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianna-Pinton, R.; Moreno, C.A.; Baxter, C.M.; Lee, K.S.; Tsang, T.S.; Appleton, C.P. Two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left atrium: Feasibility and regional contraction and relaxation differences in normal subjects. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Yoon, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, K.T.; Park, S.C.; et al. Feasibility of two-dimensional global longitudinal strain and strain rate imaging for the assessment of left atrial function: A study in subjects with a low probability of cardiovascular disease and normal exercise capacity. Echocardiography 2009, 26, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Caputo, M.; Mondillo, S.; Ballo, P.; Palmerini, E.; Lisi, M.; Marino, E.; Galderisi, M. Feasibility and reference values of left atrial longitudinal strain imaging by two-dimensional speckle tracking. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2009, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciulli, T.F.; Saccheri, M.C.; Lax, J.A.; Bermann, A.M.; Ferreiro, D.E. Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography for the assessment of atrial function. World J. Cardiol. 2010, 2, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Lisi, M.; Focardi, M.; Reccia, R.; Natali, B.M.; Sparla, S.; Mondillo, S. Left atrial deformation analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography for prediction of cardiovascular outcomes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.; McKay, T.; Byth, K.; Marwick, T.H. Abnormalities of left atrial function after cardioversion: An atrial strain rate study. Heart 2007, 93, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Fung, J.W.; Yip, G.W.; Zhang, Y.; Ho, P.P.; Tse, D.M.; Yu, C.M.; Sanderson, J.E. Atrial strain rate echocardiography can predict success or failure of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation: A combined transthoracic tissue Doppler and transoesophageal imaging study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 114, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Malisius, R.; Krause, K.; Lampe, F.; Bahlmann, E.; Boczor, S.; Antz, M.; Ernst, S.; Kuck, K.H. Strain rate imaging for functional quantification of the left atrium: Atrial deformation predicts the maintenance of sinus rhythm after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Caracciolo, G.; Khan, U.; Mori, N.; Saha, S.K.; Srivathsan, K.; Altemose, G.; Scott, L.; Sengupta, P.; Jahangir, A. Left atrial reservoir function predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A two-dimensional speckle strain study. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2011, 31, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, K.; Magne, J.; Rosca, M.; Piérard, L.A.; Lancellotti, P. Left atrial function and remodelling in aortic stenosis. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2011, 12, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, K.; Magne, J.; Rosca, M.; Piérard, L.A.; Lancellotti, P. Impact of aortic valve stenosis on left atrial phasic function. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, M.C.; Choudhuri, I.; Belohlavek, M.; Jahangir, A.; Carerj, S.; Oreto, L.; Khandheria, B.K. New echocardiographic techniques for evaluation of left atrial mechanics. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 13, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, N.P.; Witte, K.K.; Thackray, S.D.; Goodge, L.J.; Clark, A.L.; Cleland, J.G. Effect of age and sex on left atrial morphology and function. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2003, 4, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, Y.W.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, W.T.; Chen, J.Y.; Lin, L.J. Association of left atrial strain and strain rate assessed by speckle tracking echocardiography with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Echocardiography 2009, 26, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, H.; Zhong, M.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Strain rate imaging for noninvasive functional quantification of the left atrium in hypertensive patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Cardiology 2008, 109, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modesto, K.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Cauduro, S.A.; Lacy, M.; Khandheria, B.K.; Pellikka, P.A.; Belohlavek, M.; Seward, J.B.; Kyle, R.; Tajik, A.J.; et al. Left atrial myopathy in cardiac amyloidosis: Implications of novel echocardiographic techniques. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Salvo, G.; Caso, P.; Lo Piccolo, R.; Fusco, A.; Martiniello, A.R.; Russo, M.G.; D’Onofrio, A.; Severino, S.; Calabró, P.; Pacileo, G.; et al. Atrial myocardial deformation properties predict maintenance of sinus rhythm after external cardioversion of recent-onset lone atrial fibrillation: A color Doppler myocardial imaging and transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic study. Circulation 2005, 112, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Caso, P.; Romano, S.; Scarafile, R.; Cuomo, S.; Salerno, G.; Riegler, L.; Limongelli, G.; Di Salvo, G.; Romano, M.; et al. Association between left atrial myocardial function and exercise capacity in patients with either idiopathic or ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: A two-dimensional speckle strain study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 132, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Caso, P.; Romano, S.; Scarafile, R.; Riegler, L.; Salerno, G.; Limongelli, G.; Di Salvo, G.; Calabrò, P.; Del Viscovo, L.; et al. Different effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on left atrial function in patients with either idiopathic or ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy: A two-dimensional speckle strain study. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2738–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, M.; Mandoli, G.E.; Loiacono, F.; Sparla, S.; Iardino, E.; Mondillo, S. Left atrial strain: A useful index in atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 220, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.A.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, G.Y. Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2012, 20, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, T.; Robinet, S.; Dulgheru, R.; Bernard, A.; Ilardi, F.; Contu, L.; Addetia, K.; Caballero, L.; Kacharava, G.; Athanassopoulos, G.D.; et al. Echocardiographic reference ranges for normal left atrial function parameters: Results from the EACVI NORRE study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, F.; D’Elia, N.; Nolan, M.T.; Marwick, T.H.; Negishi, K. Normal Ranges of Left Atrial Strain by Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Miglioranza, M.H.; Magne, J.; Mandoli, G.E.; Benfari, G.; Ancona, R.; Sibilio, G.; Reskovic Luksic, V.; Dejan, D.; Griseli, L.; et al. Multicentric Atrial Strain COmparison between Two Different Modalities: MASCOT HIT Study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Cai, Y.; Meng, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, M.; Ding, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Left atrial reservoir strain measurements derived from intracardiac echocardiography in patients with atrial fibrillation: Comparison with transthoracic echocardiography. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2023, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Mandoli, G.E.; Lisi, E.; Ibrahim, A.; Incampo, E.; Buccoliero, G.; Rizzo, C.; Devito, F.; Ciccone, M.M.; Mondillo, S. Left atrial, ventricular and atrio-ventricular strain in patients with subclinical heart dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laish-Farkash, A.; Perelshtein Brezinov, O.; Valdman, A.; Tam, D.; Rahkovich, M.; Kogan, Y.; Marincheva, G. Evaluation of left atrial remodeling by 2D-speckle-tracking echocardiography versus by high-density voltage mapping in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisi, M.; Mandoli, G.E.; Cameli, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Righini, F.M.; Benfari, G.; Rubboli, A.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Focardi, M.; Tsioulpas, C.; et al. Left atrial strain by speckle tracking predicts atrial fibrosis in patients undergoing heart transplantation. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, M.; Cameli, M.; Mandoli, G.E.; Pastore, M.C.; Righini, F.M.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Focardi, M.; Rubboli, A.; Mondillo, S.; Henein, M.Y. Detection of myocardial fibrosis by speckle-tracking echocardiography: From prediction to clinical applications. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potpara, T.S.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hindricks, G.; Camm, A.J. The 4S-AF Scheme (Stroke Risk; Symptoms; Severity of Burden; Substrate): A Novel Approach to In-Depth Characterization (Rather than Classification) of Atrial Fibrillation. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Auricchio, A.; Bax, J.; Crijns, H.; Camm, J.; Diener, H.C.; Goette, A.; Hindricks, G.; Hohnloser, S.; Kappenberger, L.; et al. Outcome parameters for trials in atrial fibrillation: Recommendations from a consensus conference organized by the German Atrial Fibrillation Competence NETwork and the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace 2007, 9, 1006–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, M.V.; Pierucci, N.; Trivigno, S.; Cipollone, P.; Piro, A.; Chimenti, C.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Miraldi, F.; Vizza, C.D.; Lavalle, C. Probability Score to Predict Spontaneous Conversion to Sinus Rhythm in Patients with Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation When Less Could Be More? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, S.; Borof, K.; Brandes, A.; Breithardt, G.; Camm, A.J.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Eckardt, L.; Gessler, N.; Goette, A.; Haegeli, L.M.; et al. Systematic, early rhythm control strategy for atrial fibrillation in patients with or without symptoms: The EAST-AFNET 4 trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, L.; Sehner, S.; Suling, A.; Borof, K.; Breithardt, G.; Crijns, H.; Goette, A.; Wegscheider, K.; Zapf, A.; Camm, J.; et al. Attaining sinus rhythm mediates improved outcome with early rhythm control therapy of atrial fibrillation: The EAST-AFNET 4 trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4127–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickow, J.; Kirchhof, P.; Van Houten, H.K.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Dinshaw, L.H.W.; Friedman, P.A.; Packer, D.L.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Yao, X. Generalizability of the EAST-AFNET 4 Trial: Assessing Outcomes of Early Rhythm-Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e024214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, A.; Maj, J.B.; Marafi, M.; Donato, F.; Vescovo, G.; Russo, V.; Proietti, R. The role of cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities in the link between atrial fibrillation and cognitive impairment: An appraisal of current scientific evidence. Medicina 2019, 55, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp, M.E.; Ariyaratnam, J.; Lau, D.; Sanders, P. Lifestyle modifications for treatment of atrial fibrillation. Heart 2020, 106, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, S.-R.; Choi, E.-K.; Lee, H.; Chung, J.; Choi, J.; Han, M.; Ahn, H.-J.; Kwon, S.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. Low risk of dementia in patients with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation and a clustering of healthy lifestyle behaviors: A nationwide population-based cohort study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e023739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-R.; Choi, E.-K.; Park, S.-H.; Chung, J.-W.; Choi, J.-M.; Han, M.-J.; Jung, J.-H.; Han, K.-D.; Oh, S.; et al. Risk of dementia after smoking cessation in patients with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2217132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Lee, S.-R.; Choi, E.-K.; Han, K.-D.; Jung, J.-H.; Ahn, H.-J.; Yun, J.P.; Kwon, S.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Exercise and the risk of dementia in patients with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population-based study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.R.; Yakupoglu, H.Y.; Kralj-Hans, I.; Haldar, S.; Bahrami, T.; Clague, J.; De Souza, A.; Hussain, W.; Jarman, J.; Jones, D.G.; et al. Left Atrial Function Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Ablation of Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, e015352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, L.E.; Keskin, S.; Can, U.; Çolak, A.; Yüce, D.; Çiftçi, O.; Özin, B.; Müderrisoğlu, H. Left atrial mechanics for secondary prevention from embolic stroke of undetermined source. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhakak, A.S.; Biering-Sørensen, S.R.; Møgelvang, R.; Modin, D.; Jensen, G.B.; Schnohr, P.; Iversen, A.Z.; Svendsen, J.H.; Jespersen, T.; Gislason, G.; et al. Usefulness of left atrial strain for predicting incident atrial fibrillation and ischaemic stroke in the general population. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azemi, T.; Rabdiya, V.M.; Ayirala, S.R.; McCullough, L.D.; Silverman, D.I. Left atrial strain is reduced in patients with atrial fibrillation, stroke or TIA, and low risk CHADS(2) scores. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2012, 25, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Anderson, P.L.; Caracciolo, G.; Kiotsekoglou, A.; Wilansky, S.; Govind, S.; Mori, N.; Sengupta, P.P. Global left atrial strain correlates with CHADS2 risk score in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2011, 24, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obokata, M.; Negishi, K.; Kurosawa, K.; Tateno, R.; Tange, S.; Arai, M.; Amano, M.; Kurabayashi, M. Left atrial strain provides incremental value for embolism risk stratification over CHA2DS2-VASc score and indicates prognostic impact in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2014, 27, 709–716.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, I.C.; Park, J.B.; Cho, G.Y.; Marwick, T.H. Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Heart Failure. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintoye, E.; Majid, M.; Klein, A.L.; Hanna, M. Prognostic Utility of Left Atrial Strain to Predict Thrombotic Events and Mortality in Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, M.; Lisi, M.; Reccia, R.; Bennati, E.; Malandrino, A.; Solari, M.; Bigio, E.; Biagioli, B.; Righini, F.M.; Maccherini, M.; et al. Pre-operative left atrial strain predicts post-operative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 30, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.C.; Degiovanni, A.; Grisafi, L.; Renda, G.; Sozzani, M.; Giordano, A.; Salvatici, C.; Lorenz, V.; Pierfelice, F.; Cappelli, C.; et al. Left Atrial Strain to Predict Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 17, e015969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Ji, Y.; Wang, W.; Norby, F.L.; Parikh, R.; Eaton, A.A.; Inciardi, R.M.; Alonso, A.; Soliman, E.Z.; Mosley, T.H.; et al. Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Stroke and Dementia Accounting for Left Atrial Function and Size. JACC Adv. 2023, 2, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, H.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Tirschwell, D.L.; Kronmal, R.A.; Marshall, R.S.; Broderick, J.P.; Aragón García, R.; Plummer, P.; Sabagha, N.; Pauls, Q.; et al. Apixaban to Prevent Recurrence After Cryptogenic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Cardiopathy: The ARCADIA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiseth, O.A.; Morris, D.A.; Cardim, N.; Cikes, M.; Delgado, V.; Donal, E.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Galderisi, M.; Gerber, B.L.; Gimelli, A.; et al. Multimodality imaging in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: An expert consensus document of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, e34–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Atrial Myopathy: EHRAS Classification | |
|---|---|
| EHRAS class | Histological features |
| I | Morphological/molecular changes affecting the cardiomyocytes (hypertrophy and myocytolysis). Absence of significant tissue fibrosis or interstitial changes |
| II | Predominance of fibrotic changes. Normal appearance of cardiomyocytes |
| III | Combination of changes in the cardiomyocyte and tissue fibrosis |
| IV | Non-fibrotic alteration of interstitial matrix |
| a | Amyloid accumulation |
| f | Fatty infiltration |
| i | Inflammatory cells |
| o | Other interstitial alterations |
| Most Relevant Studies Regarding LA Strain Values in Healthy Subjects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Name/Author, Year | Study Design | Number of Patients (n) | Normal Pals Values (mean ± sd or Medial IQR) | References |
| Cameli et al., 2009 | Obstervational, monocentric study | 60 | 42.2% ± 6.1% | [124] |
| Pathan et al., 2016 | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 2542 | 39.4% (38.0–40.8%) | [144] |
| EACVI NORRE study, 2018 | Observational, multicenter study | 371 | 42.5% (36.1–48.0%) | [143] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campora, A.; Lisi, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Mandoli, G.E.; Ferrari Chen, Y.F.; Pasquini, A.; Rubboli, A.; Henein, M.Y.; Cameli, M. Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Myopathy, and Thromboembolism: The Additive Value of Echocardiography and Possible New Horizons for Risk Stratification. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133921
Campora A, Lisi M, Pastore MC, Mandoli GE, Ferrari Chen YF, Pasquini A, Rubboli A, Henein MY, Cameli M. Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Myopathy, and Thromboembolism: The Additive Value of Echocardiography and Possible New Horizons for Risk Stratification. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133921
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampora, Alessandro, Matteo Lisi, Maria Concetta Pastore, Giulia Elena Mandoli, Yu Fu Ferrari Chen, Annalisa Pasquini, Andrea Rubboli, Michael Y. Henein, and Matteo Cameli. 2024. "Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Myopathy, and Thromboembolism: The Additive Value of Echocardiography and Possible New Horizons for Risk Stratification" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133921
APA StyleCampora, A., Lisi, M., Pastore, M. C., Mandoli, G. E., Ferrari Chen, Y. F., Pasquini, A., Rubboli, A., Henein, M. Y., & Cameli, M. (2024). Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Myopathy, and Thromboembolism: The Additive Value of Echocardiography and Possible New Horizons for Risk Stratification. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133921









