Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Physical Performance in Older Adults with Statin-Associated Asthenia: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
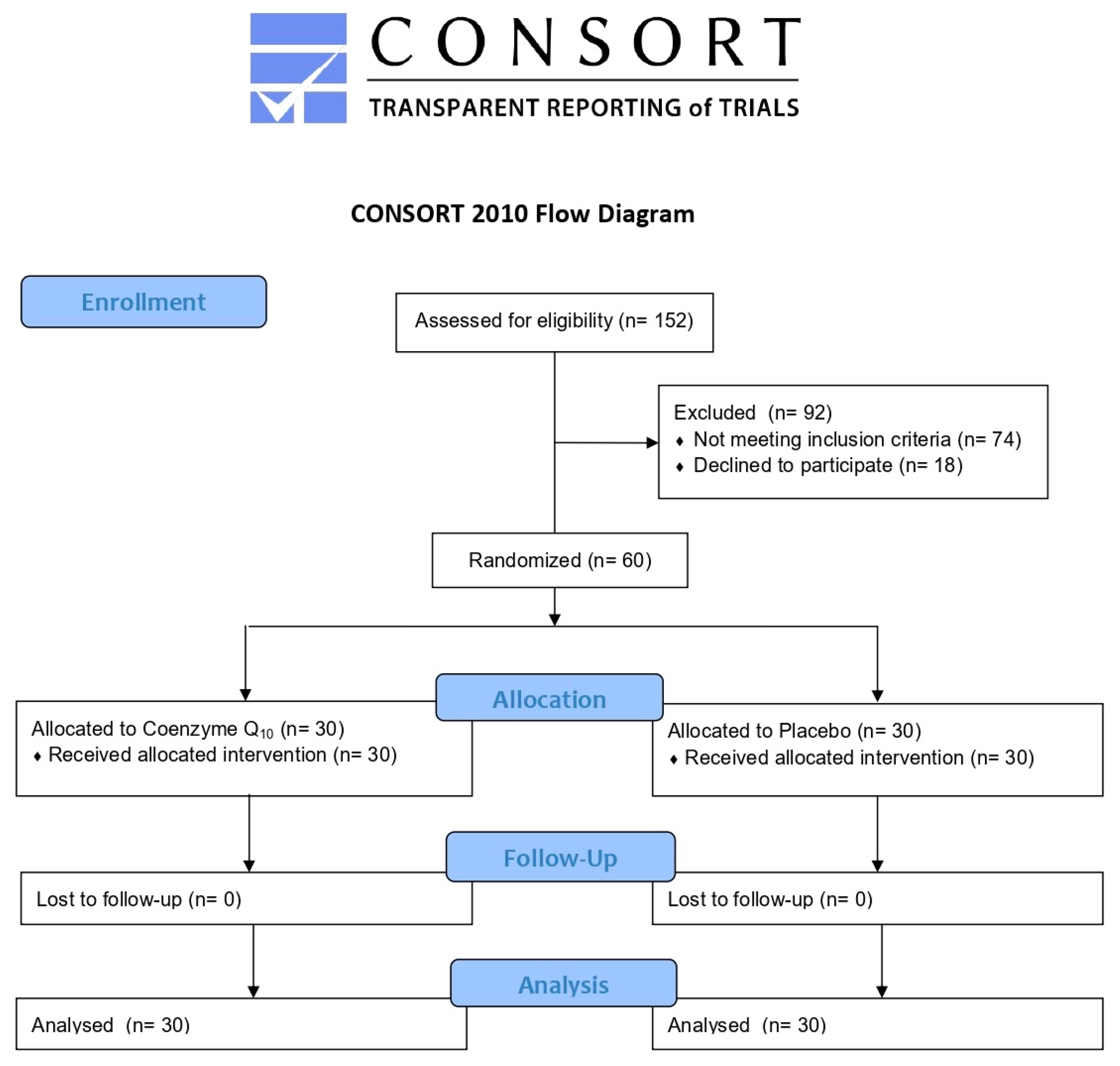
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Assessments
2.3.1. Clinical Data and Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.2. Handgrip Strength Test
2.3.3. Dynamic Physical Performance
2.3.4. Laboratory Analyses
2.3.5. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.3.6. Assessment of Safety and Tolerability
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Yoo, W.; Alesh, I.; Mahajan, N.; Mirowska, K.K.; Mewada, A.; Kahn, J.; Afonso, L.; Williams, K.A., Sr.; Flack, J.M. Effect of long-term exposure to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol beginning early in life on the risk of coronary heart disease: A Mendelian randomization analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strilchuk, L.; Fogacci, F.; Cicero, A.F. Safety and tolerability of injectable lipid-lowering drugs: An update of clinical data. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Effect of statin therapy on muscle symptoms: An individual participant data meta-analysis of large-scale, randomised, double-blind trials. Lancet 2022, 400, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.; Frishman, W.H.; Aronow, W.S. Antihyperlipidemic Treatment Options in Statin Resistance and Intolerance. Cardiol. Rev. 2022; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Contreras, A.; Wenczenovicz, C.; Ruiz-Arellanos, K.; Vesely, E.A.K.; Mogollon, R.; Montori, V.M. Statin intolerance management: A systematic review. Endocrine. 2022; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Warden, B.A.; Guyton, J.R.; Kovacs, A.C.; Durham, J.A.; Jones, L.K.; Dixon, D.L.; Jacobson, T.A.; Duell, P.B. Assessment and management of statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS): A clinical perspective from the National Lipid Association. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2022, 17, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, P.; Panizon, E.; Tosoni, L.M.; Cerrato, C.; Pellicori, F.; Mearelli, F.; Biasinutto, C.; Fiotti, N.; Di Girolamo, F.G.; Biolo, G. Statin-Associated Myopathy: Emphasis on Mechanisms and Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.; Köller, Y.; Surkova, E. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on statin-associated myalgia and adherence to statin therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2020, 299, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizner, A.E.; Quiñones, M.A. Coenzyme Q10 for Patients With Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirilli, I.; Damiani, E.; Dludla, P.V.; Hargreaves, I.; Marcheggiani, F.; Millichap, L.E.; Orlando, P.; Silvestri, S.; Tiano, L. Role of Coenzyme Q10 in Health and Disease: An Update on the Last 10 Years (2010–2020). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Di Micoli, A.; Veronesi, M.; Borghi, C. Noninvasive instrumental evaluation of coenzyme Q10 phytosome on endothelial reactivity in healthy nonsmoking young volunteers: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover clinical trial. Biofactors 2022, 48, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Rodríguez, M.L.; García-Cerdán, M.R.; Calonge-Vallejo, A.R.; Tobella-Andreu, L.; Baena-Díez, J.M.; Schröder, H. Feasibility and results of the short Diet Quality Screener in Primary Care: EMAP study. Enferm. Clin. 2016, 26, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Veronesi, M.; Strocchi, E.; Grandi, E.; Rizzoli, E.; Poli, A.; Marangoni, F.; Borghi, C. A randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Medium-Term Effects of Oat Fibers on Human Health: The Beta-Glucan Effects on Lipid Profile, Glycemia and inTestinal Health (BELT) Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.J.; Spicher, J.M.; Silva-Smith, A.L. Validity and reliability of handgrip dynamometry in older adults: A comparison of two widely used dynamometers. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Martone, A.M.; Salini, S.; Zazzara, M.B.; Candeloro, M.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Tosato, M.; Picca, A.; Marzetti, E. Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a “real world” population: Results from the longevity check-up 7+ project. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, A.; Aiello, M.; Cherubino, F.; Zampogna, E.; Azzola, A.; Chetta, A.; Spanevello, A. The one repetition maximum test and the sit-to-stand test in the assessment of a specific pulmonary rehabilitation program on peripheral muscle strength in COPD patients. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2015, 10, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Crouch, R.H. Two-Minute Step Test of Exercise Capacity: Systematic Review of Procedures, Performance, and Clinimetric Properties. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 42, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Bove, M.; Giovannini, M.; Borghi, C. Impact of a short-term synbiotic supplementation on metabolic syndrome and systemic inflammation in elderly patients: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levi, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoproteins cholesterol in plasma without use of the ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogacci, F.; Rizzoli, E.; Giovannini, M.; Bove, M.; D’Addato, S.; Borghi, C.; Cicero, A.F.G. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Eufortyn® Colesterolo Plus on Serum Lipids, Endothelial Reactivity, Indexes of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Systemic Inflammation in Healthy Subjects with Polygenic Hypercholesterolemia: The ANEMONE Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimi, N.; Sohrabi, Z.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Eskandari, M.H.; Bedeltavana, A.; Famouri, M.; Talezadeh, P. A Novel Fortified Dairy Product and Sarcopenia Measures in Sarcopenic Older Adults: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Berton, L.; Carraro, S.; Bolzetta, F.; De Rui, M.; Perissinotto, E.; Toffanello, E.D.; Bano, G.; Pizzato, S.; Miotto, F.; et al. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on physical performance in healthy elderly women involved in a weekly exercise program: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrangolini, G.; Ronchi, M.; Frattini, E.; De Combarieu, E.; Allegrini, P.; Riva, A. A New Food-grade Coenzyme Q10 Formulation Improves Bioavailability: Single and Repeated Pharmacokinetic Studies in Healthy Volunteers. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzardi, N.; Liparulo, I.; Antonelli, G.; Orsini, F.; Riva, A.; Bergamini, C.; Fato, R. Coenzyme Q10 Phytosome Formulation Improves CoQ10 Bioavailability and Mitochondrial Functionality in Cultured Cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilat-Tsanani, S.; Mor, E.; Schonmann, Y. Statin Use Over 65 Years of Age and All-Cause Mortality: A 10-Year Follow-Up of 19 518 People. J. Am. Ger. Soc. 2019, 67, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, F.; Biffi, A.; Ronco, R.; Franchi, M.; Cammarota, S.; Citarella, A.; Conti, V.; Filippelli, A.; Sellitto, C.; Corrao, G. Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Associated With Discontinuing Statins in Older Patients Receiving Polypharmacy. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2113186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Meng, Y.Y.; Chai, H.; Liang, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Gao, Z.Y.; Shi, D.Z. The effect of statin treatment on circulating coenzyme Q10 concentrations: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2018, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollazadeh, H.; Tavana, E.; Fanni, G.; Bo, S.; Banach, M.; Pirro, M.; von Haehling, S.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of statins on mitochondrial pathways. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrós-Martín, J.A.; Lareu, R.R.; Ramsay, J.P.; Peplies, J.; Reen, F.J.; Headlam, H.A.; Ward, N.C.; Croft, K.D.; Newsholme, P.; Hughes, J.D.; et al. Statin therapy causes gut dysbiosis in mice through a PXR-dependent mechanism. Microbiome 2017, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, H.; Wang, W.T.; Gao, Z.Y.; Shi, D.Z. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on Statin-Induced Myopathy: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banach, M.; Serban, C.; Sahebkar, A.; Ursoniu, S.; Rysz, J.; Muntner, P.; Toth, P.P.; Jones, S.R.; Rizzo, M.; Glasser, S.P.; et al. Effects of coenzyme Q10 on statin-induced myopathy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ochs-Balcom, H.M.; Ma, C.; Isackson, P.J.; Vladutiu, G.D.; Luzum, J.A. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation for the treatment of statin-associated muscle symptoms. Future Cardiol. 2022, 18, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohlmann, T.L.; Kuhlman, A.B.; Morville, T.; Dahl, M.; Asping, M.; Orlando, P.; Silvestri, S.; Tiano, L.; Helge, J.W.; Dela, F.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Statin Treated Patients: A Double-Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobnic, F.; Lizarraga, M.A.; Caballero-García, A.; Cordova, A. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation and Its Impact on Exercise and Sport Performance in Humans: A Recovery or a Performance-Enhancing Molecule? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Wan, S.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Xu, T.; He, J.; Mechanick, J.I.; Wu, W.C.; et al. Micronutrient Supplementation to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2269–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Overall Sample (Mean ± SD; N. 60) | Coenzyme Q10 (Mean ± SD; N. 30) | Placebo (Mean ± SD; N. 30) | p-Value (between Groups) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 74 ± 3 | 74 ± 2 | 73 ± 3 | 0.13 |
| Weight (kg) | 72 ± 5 | 71 ± 4 | 73 ± 5 | 0.09 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 92 ± 6 | 91 ± 5 | 93 ± 6 | 0.17 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 25 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | 0.09 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 136 ± 6 | 136 ± 5 | 135 ± 6 | 0.49 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 88 ± 3 | 87 ± 2 | 88 ± 3 | 0.13 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 201 ± 12 | 203 ± 11 | 199 ± 9 | 0.13 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 46 ± 3 | 45 ± 3 | 47 ± 3 | 0.06 |
| Non HDL-C (mg/dL) | 158 ± 9 | 159 ± 9 | 157 ± 8 | 0.37 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 115 ± 7 | 116 ± 6 | 113 ± 7 | 0.08 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 213 ± 17 | 216 ± 16 | 210 ± 14 | 0.13 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 89 ± 4 | 88 ± 3 | 89 ± 4 | 0.28 |
| AST (U/L) | 24 ± 2 | 24 ± 3 | 23 ± 2 | 0.13 |
| ALT (U/L) | 25 ± 3 | 24 ± 2 | 25 ± 3 | 0.13 |
| Gamma-GT (mg/dL) | 36 ± 5 | 35 ± 3 | 36 ± 5 | 0.36 |
| CPK (U/L) | 164 ± 22 | 164 ± 19 | 163 ± 21 | 0.85 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 73 ± 6 | 73 ± 5 | 72 ± 6 | 0.49 |
| Parameters | Coenzyme Q10 (N. 30) | Placebo (N. 30) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 4-Week Follow-Up | 8-Week Follow-Up | Baseline | 4-Week Follow-Up | 8-Week Follow-Up | |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 136 ± 5 | 134 ± 6 | 132 ± 5 * | 135 ± 6 | 134 ± 5 | 133 ± 6 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 87 ± 2 | 86 ± 2 | 85 ± 3 | 88 ± 3 | 86 ± 2 | 86 ± 1 |
| HGs (kg) | 15.1 ± 0.8 | 16.5 ± 0.6 | 19.6 ± 0.5 *°§ | 15.2 ± 0.6 | 14.7 ± 0.7 | 15.0 ± 0.6 |
| 1-min STS repetitions | 18.7 ± 2.9 | 21.5 ± 2.8 | 25.5 ± 2.7 *°§ | 18.4 ± 2.7 | 19.1 ± 2.8 | 18.5 ± 2.57 |
| 2MST (steps) | 100.3 ± 5.9 | 105.5 ± 6.6 | 111.5 ± 5.5 *§ | 101.3 ± 6.4 | 100.8 ± 5.5 | 102.6 ± 5.8 |
| VAS for asthenia | 6 (3–8) | 4 (2–6) *° | 3 (2–5) *°§ | 5 (3–8) | 4 (3–7) * | 6 (3–8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fogacci, F.; Giovannini, M.; Tocci, G.; Imbalzano, E.; Borghi, C.; Cicero, A.F.G. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Physical Performance in Older Adults with Statin-Associated Asthenia: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133741
Fogacci F, Giovannini M, Tocci G, Imbalzano E, Borghi C, Cicero AFG. Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Physical Performance in Older Adults with Statin-Associated Asthenia: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133741
Chicago/Turabian StyleFogacci, Federica, Marina Giovannini, Giuliano Tocci, Egidio Imbalzano, Claudio Borghi, and Arrigo F. G. Cicero. 2024. "Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Physical Performance in Older Adults with Statin-Associated Asthenia: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133741
APA StyleFogacci, F., Giovannini, M., Tocci, G., Imbalzano, E., Borghi, C., & Cicero, A. F. G. (2024). Effect of Coenzyme Q10 on Physical Performance in Older Adults with Statin-Associated Asthenia: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133741










