Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Population
2.3. Intervention (Exposure)
2.4. Comparison
2.5. Outcome
2.6. Study Design
2.7. Data Sources
- English: physical activity OR exercise OR training OR physical exercise OR fitness OR strength training OR physical intervention OR Pilates OR Yoga OR strengthening OR aerobic OR resistance training OR walking AND pregnancy OR maternal OR antenatal OR pregnant AND health OR wellbeing AND childhood obesity OR child follow-up OR infant adiposity OR paediatric obesity OR paediatric overweight OR macrosomic AND randomized clinical trial OR randomized controlled trial OR RCT.
- Spanish: actividad física OR ejercicio OR entrenamiento OR ejercicio físico OR fitness OR entrenamiento de fuerza OR intervención de actividad física OR Pilates OR Yoga OR fortalecimiento OR aeróbico OR entrenamiento de resistencia OR caminar AND embarazo OR materno OR antenatal OR embarazada AND salud OR bienestar AND obesidad infantil OR seguimiento infantil OR adiposidad infantil OR obesidad pediátrica OR sobrepeso pediátrico OR macrosomía AND ensayo clínico aleatorizado OR ensayo controlado aleatorizado OR ECA.
2.8. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Quality of Evidence and Risk of Bias Assessments
| Author | Year | Country | N | EG | CG | Intervention. Physical Exercise Program | Main Variables Analyzed | Secondary Variables Analyzed | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fq. | Intens. | Dur. of Program | Type of Intervent. | Superv. Class | Dur. of Class | Adh. % | ||||||||
| Bjøntegaard [53] | 2021 | Norway | 281 BMI < 25 | 164 | 117 | 1 | Mod | 12 w | EP: Aerobic, strength, balance exercise | Yes | 60 min | 56.7 | Childhood obesity At birth: birthweight (grams) 7 years: BMI, kg/m2 | Daily activity of children |
| 2 | No | 45 min | ||||||||||||
| Braeken [54] | 2020 | Belgium | 173 BMI ≥ 30 | 96 | 77 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 20 w | Nutrition advice physical activity, | Yes | - | - | Childhood anthropometrics At birth: birthweight 3 to 7 years: weight, BMI, Waist circumference Hip circumference Circumference at umbilicus level Ratios: waist-to-hip/waist-to-height | Neurocognitive development, eating habits and children cardiovascular |
| Chiavaroli [55] | 2018 | New Zealand | 84 BMI 25–30 | 47 | 37 | 5 | 65% VO2max | 16 w | Stationary cycling | No | 40 min | - | Metabolism and body composition in mothers and offspring 1 year: waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, BMI 7 years: Total body fat (%), BMI | Maternal and neonatal outcomes |
| Clark [56] | 2018 | USA | 36 BMI 18.5–35 | 14 | 22 | 3 | Mod | 20 w | EP: Aerobic | Yes | 50 min | - | Neonatal body size At birth: weight, BMI, abdominal circumference, Ponderal Index | Neonatal outcomes |
| Dalrymple [57] | 2020 | UK | 514 BMI ≥ 30 | 250 | 264 | 7 | Light | 8 w | Aerobic, nutrition advice | No | - | - | Childhood adiposity and cardiovascular function At birth: Birthweight, Birthweight > 4 kg, Large for Gestational Age (LGA) > 90th Centile Subscapular skinfold thickness Triceps skinfold thickness 3 years: Weight, Different skinfold thickness, Waist Circumference, Mid upper arm circumference, BMI for age Z-Score | Neonatal and infant outcomes |
| Dodd [58] | 2014a | Australia | 2202 BMI ≥ 25 | 1105 | 1097 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 30 w | Walking, nutrition advice | No | - | - | Infant outcomes At birth: LGA, Birth weight above 4000 g | Maternal outcomes |
| Dodd [59] | 2014b | Australia | 2142 BMI ≥ 25 | 1075 | 1067 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 30 w | Walking, nutrition advice | No | - | - | Infant outcomes At birth: Birth weight, Birth weight (Z-Score), Birth weight ≥ 4.5 kg, Ponderal Index | Maternal outcomes |
| Dodd [60] | 2018 | Australia | 2136 BMI ≥ 25 | 1071 | 1065 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 30 w | Walking, nutrition advice | No | - | - | Children anthropometry 1.5 years: Weight, BMI Z-score > 85th, BMI Z score, mean (SD, Abdomen circumference, BMI Z-Score > 90th, Bio-impedance | Children dietary intake and family food behaviour |
| Dodd [61] | 2020 | Australia | 1418 BMI ≥ 25 | 727 | 691 | - | Counselling | 20 w | Walking, nutrition advice | No | - | 77.2 | Childhood obesity 3 to 5 years: Weight, BMI, BMI Z-Score, BMI Z-Score > 85th percentile, BMI Z-Score > 90th percentile, Weight/height ratio Weight/length ratio Z-Score, Abdomen circumference | Infant outcomes |
| Gallagher [62] | 2018 | USA | 196 BMI ≥ 25 | 97 | 99 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 22 w | Physical activity, nutrition advice | No | - | 34.2 | Infant fat free mass At birth: LGA (>90th percentile), Birth weight, Weight-for-age Z-Score 2 to 4 days after birth: Percentage fat, Total fat mass, Ponderal Index, Sum of skinfolds | Infant outcomes |
| Hopkins [63] | 2010 | New Zealand | 84 BMI ≥ 25 | 47 | 37 | 5 | 65% VO2max | 16 w | Stationary cycling | No | 40 min | - | Maternal insulin sensitivity At birth: Birthweight, BMI, Ponderal Index. 17 days: Body weight, Fat mass. | Neonatal outcomes |
| Huang [64] | 2019 | Australia | 42 BMI ≥ 20 | 23 | 19 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 12 w | Nutrition advice, walking | No | - | 87.2 | Gestational weight gain At birth: Birthweight, Ponderal Index, body fat, Body fat mass. 3 months: Ponderal Index, weight. | Infant outcomes |
| Kolu [65] | 2016 | Finland | 173 BMI ≥ 25 | 85 | 88 | 3 | Lifestyle interv. Mod | 28 w | Nutrition, physical activity advice | No | 30 min | - | Type 2 diabetes mellitus, gestational weight gain At 7 years: BMI | Infant outcomes |
| Kong [66] | 2014 | USA | 34 BMI ≥ 25 | 15 | 19 | 5 | Mod | 20 w | Walking | No | 30 min | - | Post-partum weight retention 1 month: bodyweight weight (Z-Score), weight-for-length (Z-Score), Fat mass 6 months: Bodyweight, Weight (Z-Score), weight-for-length (Z-Score), Fat mass | Children anthropometry |
| Luoto [67] | 2011 | Finland | 399 BMI ≥ 25 | 219 | 180 | 4 times | - | 29 wk | Nutrition, physical activity advice | - | - | - | Gestational diabetes and birthweight At birth: Birthweight, LGA Macrosomia (birthweight > 4500 g) Macrosomia (birthweight > 4000 g) Ponderal Index | Neotanal and child outcomes |
| May [68] | 2023 | USA | 56 BMI 18.5–40 | 31 | 25 | 3 | Mod | 24 wk | EP: Aerobic exercises | Yes | 50 min | 80 | Infant cardiac function and outflow 1 month: Weight, BMI | Infant outcomes |
| McMillan [69] | 2019 | USA | 60 BMI 18.5–35 | 33 | 27 | 3 | Mod | 20 w | EP: Aerobic exercises | Yes | 50 min | - | Infant Neuromotor Development 1 month: BMI, Weight | Infant outcomes |
| Mustila [70] | 2012 | Finland | 72 BMI ≥ 25 | 34 | 38 | 1 | Lifestyle intervention | 28 w | Nutrition, physical activity advice | Yes | - | - | Offspring Weight Gain At birth: Birthweight, Small for Gestational Age (SGA), LGA, Macrosomia. 0–48 months: Weight-for-length/height (Z-Score) 24 to 48 months: BMI (Z-Score) | Infant outcomes |
| Mustila [71] | 2013 | Finland | 185 BMI ≥ 25 | 96 | 89 | 5 | Counselling Light | 22 w | Aerobic and strength exercise, nutrition advice | No | 30 min | - | Childhood obesity at birth: Birthweight, Ponderal Index, SGA, LGA, BMI. 4 months: BMI, Weight-for-length 6 months: BMI, Weight-for-length. 12 months: BMI, Weight-for-length. | Neonatal and infant outcomes |
| Mustila [72] | 2018 | Finland | 147 BMI ≥ 25 | 71 | 76 | - | Counselling | 13 w | Walking and nutrition advice | No | - | - | Offspring’s weight gain at birth: Birthweight, LGA. 6 years: BMI > 25 kg/m2, BMI >30 kg/m2, Weight-for-length ≥ 10% Weight-for-length > 20% | Maternal and neonatal outcomes |
| Patel [73] | 2017 | UK | 698 BMI ≥ 30 | 342 | 356 | - | Behavioural intervention | 18 w | Nutrition, physical activity advice | - | - | 47.3 | Childhood adiposity At birth: Birthweight, LGA, 6 months: Different skinfold thickness Abdominal circumference (cm) BMI for age (Z-Score) | Maternal dietary and physical activity |
| Perales [74] | 2020 | Spain | BMI 18.5–30 | 688 | 660 | 3 | Mod | 28 w | EP: Aerobic, resistance, pelvic floor training | Yes | 50–55 min | 95 | Maternal cardio-metabolic health at birth: Birthweight, Low birthweight Macrosomia 1 year: BMI, Overweight/obesity 6 years: Overweight/obesity | Maternal/offspring health outcomes |
| Phelan [75] | 2019 | USA | 835 BMI ≥ 25 | 423 | 412 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 20 w | Nutrition, physical activity advice | No | - | 80 | Post-partum weight retention At birth: Weight for length (Z-Score) Different skinfold thickness 1 year: Weight for length (Z-Score) Different skinfold thickness | Children anthropometry |
| Poston [76] | 2015 | UK | 1555 BMI ≥ 30 | 783 | 772 | 1 | Behavioural intervention | 8 w | Nutrition advice | Yes | 60 min | - | Gestacional diabetes and LGA At birth: Birthweight, Birthweight > 4 kg LGA (customised birthweight centiles) ≥90th Population birthweight centiles ≥ 90th | Infant outcomes |
| Rauh [77] | 2015 | Germany | 250 BMI ≥ 18.5 | 167 | 83 | 2 total | Lifestyle intervention | 18 w | Nutrition, physical activity advice | Yes | - | - | Post-partum weight retention 3 days to 12 months: Weight | Infant weight outcomes |
| Ronnberg [78] | 2017 | Sweden | 374 Healthy BMI | 192 | 182 | - | Lifestyle intervention | - | Nutrition advice | - | - | - | Childhood obesity At birth: Birthweight, BMI, BMI (Z-Score) LGA, SGA, Ponderal Index 5 years: BMI, BMI (Z-Score) | Risk estimates for offspring obesity in relation to maternal GWG |
| Sandborg [79] | 2022 | Sweden | 247 Healthy BMI | 122 | 125 | - | Lifestyle intervention | 22 w | APP (nutrition, exercise advice and feedback) | - | - | - | Infant body composition At birth: Birthweight 1 to 2 weeks: Weight, BMI, Body fat, Fat mass index kg/m2 | Infant outcomes |
| Tanvig [80] | 2014 | Denmark | 157 BMI 30–45 | 82 | 75 | 7 | Lifestyle intervention Mod | 22 w | Aerobic exercise | No | 30–60 min | 52 | Offspring anthropometrics and body Composition At birth: Birthweight, Birthweight (Z-Score), Macrosomia, LGA, Abdominal circumference (cm) 2.8 years: BMI, overweight or obese, BMI (Z-Score), Weight, Abdominal circumference, Triceps/Subscapular skinfold (mm) | Neonatal and infant outcomes |
| Tanvig [81] | 2015 | Denmark | 150 BMI 30–45 | 77 | 73 | 7 | Lifestyle intervention Mod | 22 w | Aerobic exercise | No | 30–60 min | 52 | Offspring metabolic risk factor at birth: Birthweight, Abdominal circumference 0 to 12 months: Change in weight 2.8 years: BMI Z-Score, overweight or obese, Abdominal circumference | Infant outcomes |
| Vesco [82] | 2016 | USA | 89 BMI ≥ 30 | 43 | 46 | - | Counselling | 20 w | Nutrition advice | No | - | - | Post-partum weight retention At birth: Birtheight, Weight for age (Z-Score) 2 weeks: Weight, Weight for age (Z-Score) Sum of triceps + subscapular skinfold thicknesses (mm) 1 year: Weight, Weight for age (Z-Score) Weight for length (Z-Score) Sum of triceps + subscapular skinfold thicknesses (mm) | Infant body composition |
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
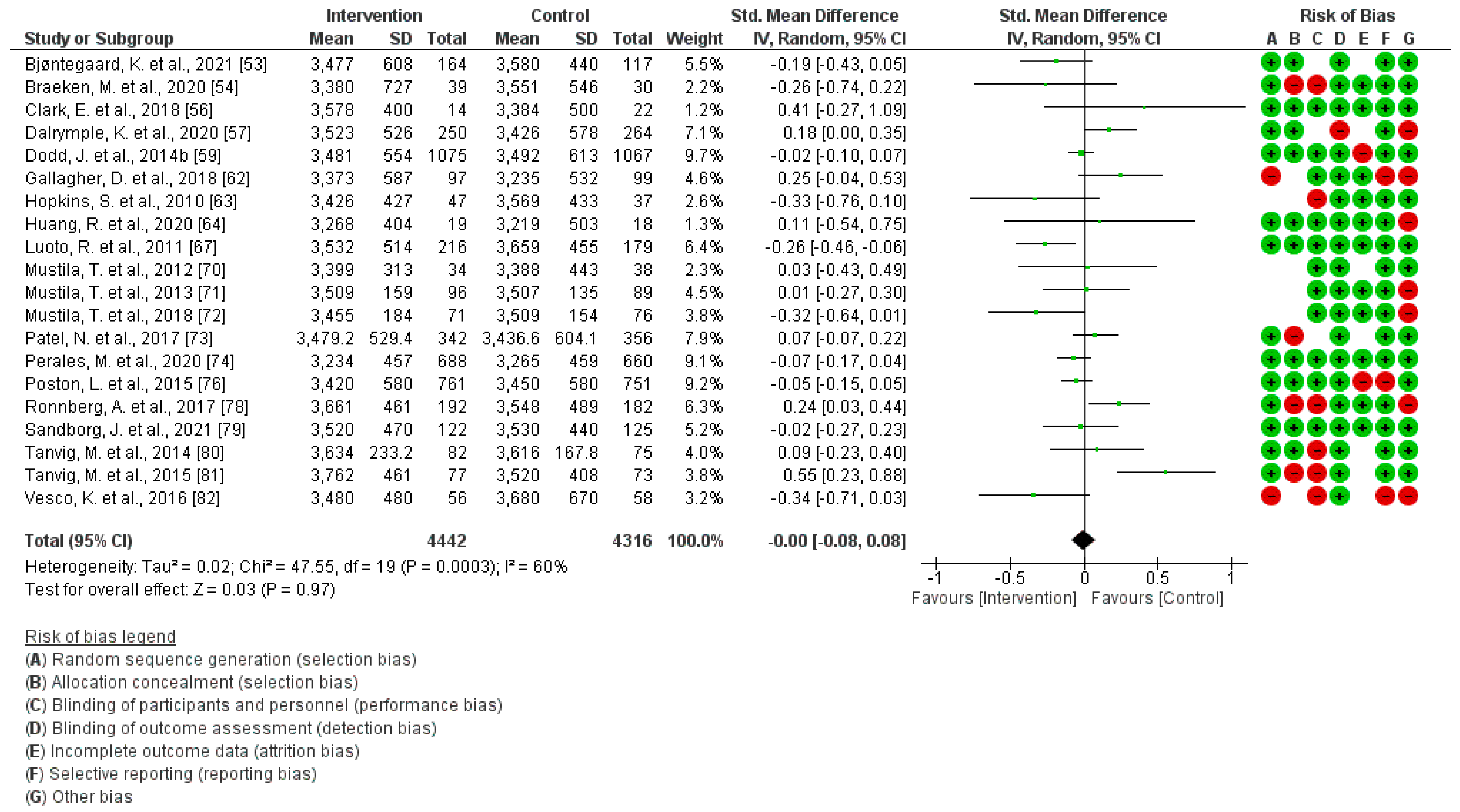
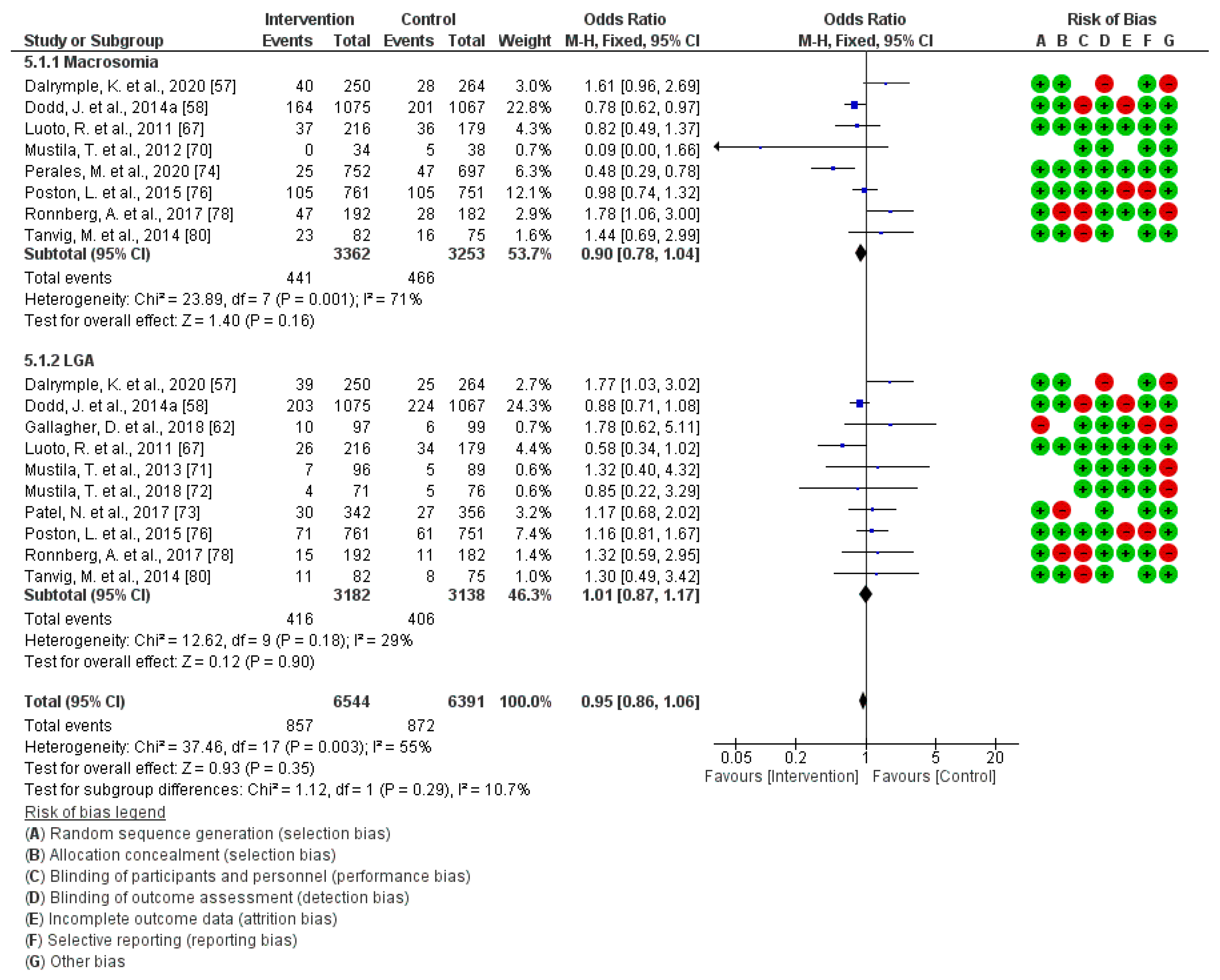
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. PA Effect during Gestation on Birthweight
3.4. PA Effect during Pregnancy on Ponderal Index at Birth
3.5. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Macrosomia and Large for Gestational Age at Birth
3.6. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Children’s BMI (1 Month–7 Years)
3.7. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Children´s Weight (1 Month–7 Years)
3.8. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Children´s Skinfold Thicknesses (Abdominal/Triceps/Subescapularis)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Overweight and Obesity. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Daniels, S.R. The consequences of childhood overweight and obesity. Future Child. 2006, 16, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, J.J.; Methven, E.; McDowell, Z.C.; Hacking, B.; Alexander, D.; Stewart, L. Health consequences of obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorof, J.; Daniels, S. Obesity hypertension in children: A problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension 2002, 40, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, H.; Shoseyov, D.; Feigenbaum, D.; Genis, M.; Friger, M.; Peled, R.; Sharff, S. The relationship between asthma and obesity in children: Is it real or a case of over diagnosis? J. Asthma 2004, 41, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, G.B., Jr.; Fiser, D.H.; Jackson, R. Sleep-associated breathing disorders in morbidly obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. 1989, 115, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovitz, S.D.; Pereira, M.A.; Vazquez, G.; Lytle, L.A.; Himes, J.H. The interaction of childhood height and childhood BMI in the prediction of young adult BMI. Obesity 2008, 16, 2336–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, L.S.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Maturational timing and overweight prevalence in US adolescent girls. Am. J. Public Health 2001, 91, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavine, J.E.; Schwimmer, J.B. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the pediatric population. Clin. Liver Dis. 2004, 8, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.R.; Arnett, D.K.; Eckel, R.H.; Gidding, S.S.; Hayman, L.L.; Kumanyika, S.; Robinson, T.N.; Scott, B.J.; St Jeor, S.; Williams, C.L. Overweight in children and adolescents. Pathophysiology, consequences, prevention, and treatment. Circulation 2005, 111, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortmaker, S.L.; Must, A.; Perrin, J.M.; Sobol, A.M.; Dietz, W.H. Social and economic consequences of overweight in adolescence and young adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplan, J.P.; Liverman, C.T.; Kraak, V.I. Preventing childhood obesity: Health in the balance: Executive summary. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.D.; Carey, N. The Epigenetics of Normal Pregnancy. Obstet. Med. 2013, 6, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichetzeder, C. Overweight and obesity in pregnancy: Their impact on epigenetics. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faienza, M.F.; Chiarito, M.; Molina-Molina, E.; Shanmugam, H.; Lammert, F.; Krawczyk, M.; D’Amato, G.; Portincasa, P. Childhood obesity, cardiovascular and liver health: A growing epidemic with age. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.; Rautava, S. Early Microbe Contact and Obesity Risk: Evidence Of Causality? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63 (Suppl. S1), S3–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Y. Association of the Severity of Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy with Birthweight, Childhood Obesity, and Blood Pressure at Age 7. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Cianflone, K.; Biron, S.; Hould, F.S.; Lebel, S.; Marceau, S.; Lescelleur, O.; Biertho, L.; Simard, S.; Kral, J.G.; et al. Effects of maternal surgical weight loss in mothers on intergenerational transmission of obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4275–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, J.G.; Biron, S.; Simard, S.; Hould, F.S.; Lebel, S.; Marceau, S.; Marceau, P. Large maternal weight loss from obesity surgery prevents transmission of obesity to children who were followed for 2 to 18 years. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e1644–e1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B. Childhood Obesity: Current Situation and Future Opportunities. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63 (Suppl. S1), S18–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L.L.; Ventura, A.K. Preventing childhood obesity: What works? Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornoy, A. Prenatal origin of obesity and their complications: Gestational diabetes, maternal overweight and paradoxical effects of fetal growth restriction and macrosomia. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 32, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Sheppard, A.; Gluckman, P.D.; Lillycrop, K.A.; Burdge, G.C.; McLean, C.; Rodford, J.; Slater-Jefferies, J.L.; Garratt, E.; Crozier, S.R.; et al. Epigenetic gene promoter methylation at birth is associated with child’s later adiposity. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain with Maternal and Infant Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro Golab, B.; Santos, S.; Voerman, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Gaillard, R. MOCO Study Group Authors. Influence of maternal obesity on the association between common pregnancy complications and risk of childhood obesity: An individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillman, M.W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.; Berkey, S.; Field, A.E.; Colditz, G.A. Maternal gestational diabetes, birthweigt, and adolescent obesity. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Taveras, E.M.; Kleinman, K.P.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Gillman, M.W. Gestational weight gain and child adiposity at age 3 years. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 196, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, A.; Tilling, K.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Sattar, N.; Brion, M.J.; Benfield, L.; Ness, A.; Deanfield, J.; Hingorani, A.; Nelson, S.M.; et al. Association of maternal weight gain in pregnancy with offspring obesity and metabolic and vascular traits in childhood. Circulation 2010, 121, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athukorala, C.; Rumbold, A.R.; Willson, K.J.; Crowther, C.A. The risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women who are overweight or obese. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2010, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poston, L.; Harthoorn, L.F.; Van Der Beek, E.M. Obesity in pregnancy: Implications for the mother and lifelong health of the child. A consensus statement. Pediatr. Research. 2011, 69, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, L.K.; Prins, J.B.; Chang, A.M.; McIntyre, H.D. The prevalence and impact of overweight and obesity in an Australian obstetric population. Med. J. Aust. 2006, 184, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.M.; Grivell, R.M.; Nguyen, A.-M.; Chan, A.; Robinson, J.S. Maternal and perinatal health outcomes by body mass index category. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 51, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.Y.; Callaghan, W.M.; Bish, C.L.; D’Angelo, D. Gestational weight gain by body mass index among US women delivering live births, 2004-2005: Fueling future obesity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 200, 271.e1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, A.; Zhang, J.; Dagvadorj, A.; Hirayama, F.; Shibuya, K.; Souza, J.P.; Gülmezoglu, A.M. Macrosomia in 23 developing countries: An analysis of a multicountry, facility-based, cross-sectional survey. Lancet 2013, 381, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, T. The macrosomic fetus: A challenge in current obstetrics. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2008, 87, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenhaim, H.A.; Kinch, R.A.; Morin, L.; Benjamin, A.; Usher, R. Effect of prepregnancy body mass index categories on obstetrical and neonatal outcomes. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007, 275, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, D.A.; Magann, E.F.; Francis, J.; Morrison, J.C.; Newnham, J.P. Prepregnancy body mass index and pregnancy outcomes. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2006, 95, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergren, M.I. Maternal morbid obesity and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcome. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 103, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, C.A.; Hiller, J.E.; Moss, J.R.; McPhee, A.J.; Jeffries, W.S.; Robinson, J.S.; Group ftACISiPWAT. Effect of treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus on pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohr, E.A.; Bech, B.H.; Davies, M.J.; Frydenberg, M.; Henriksen, T.B.; Olsen, J. Prepregnancy obesity and fetal death: A study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 106, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.O.; Sterling, B.S.; Timmerman, G.M. Retention of pregnancy-related weight in the early postpartum period: Implications for women’s health services. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2005, 34, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.M.; Presley, L.; Minium, J.; Hauguel-de Mouzon, S. Fetuses of obese mothers develop insulin resistance in utero. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Pettus, M.C.; Malkani, S. Epigenetics and childhood obesity. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottola, M.F.; Davenport, M.H.; Ruchat, S.M.; Davies, G.A.; Poitras, V.J.; Gray, C.E. 2019 Canadian guideline for physical activity throughout pregnancy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on PA and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Jose, C.; Sánchez-Polán, M.; Barakat, R.; Gil-Ares, J.; Refoyo, I. Level of Physical Activity in Pregnant Populations from Different Geographic Regions: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, L.V.; Tipton, E.; Johnson, M.C. Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granholm, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M. Use of the GRADE approach in systematic reviews and guidelines. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2018, 74, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjøntegaard, K.A.; Stafne, S.N.; Mørkved, S.; Salvesen, K.Å.; Evensen, K.A.I. Body mass index and physical activity in seven-year-old children whose mothers exercised during pregnancy: Follow-up of a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeken, M.A.K.A.; Bogaerts, A. Effect of Lifestyle Interventions in Obese Pregnant Women on the Neurocognitive Development and Anthropometrics of Preschool Children. Obes. Facts. 2020, 13, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavaroli, V.; Hopkins, S.A.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Biggs, J.B.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Brennan, C.H.; Seneviratne, S.N.; Higgins, C.; Baldi, J.C.; McCowan, L.M.E.; et al. Exercise in pregnancy: 1-year and 7-year follow-ups of mothers and offspring after a randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, E.; Isler, C.; Strickland, D.; McMillan, A.G.; Fang, X.; Kuehn, D.; Ravisankar, S.; Strom, C.; May, L.E. Influence of aerobic exercise on maternal lipid levels and offspring morphometrics. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalrymple, K.V.; Tydeman, F.A.S.; Taylor, P.D.; Flynn, A.C.; O’Keeffe, M.; Briley, A.L.; Santosh, P.; Hayes, L.; Robson, S.C.; Nelson, S.M.; et al. Adiposity and cardiovascular outcomes in three-year-old children of participants in UPBEAT, an RCT of a complex intervention in pregnant women with obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, J.M.; Turnbull, D.; McPhee, A.J.; Deussen, A.R.; Grivell, R.M.; Yelland, L.N.; Crowther, C.A.; Wittert, G.; Owens, J.A.; Robinson, J.S.; et al. Antenatal lifestyle advice for women who are overweight or obese: LIMIT randomised trial. BMJ 2014, 348, g1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, J.M.; McPhee, A.J.; Turnbull, D.; Yelland, L.N.; Deussen, A.R.; Grivell, R.M.; Crowther, C.A.; Wittert, G.; Owens, J.A.; Robinson, J.S.; et al. The effects of antenatal dietary and lifestyle advice for women who are overweight or obese on neonatal health outcomes: The LIMIT randomised trial. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.M.; Louise, J.; Deussen, A.R.; McPhee, A.J.; Owens, J.A.; Robinson, J.S. Prenatal Diet and Child Growth at 18 Months. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20180035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.M.; Deussen, A.R.; Louise, J. Effects of an antenatal dietary intervention in women with obesity or overweight on child outcomes at 3-5 years of age: LIMIT randomised trial follow-up. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Rosenn, B.; Toro-Ramos, T.; Paley, C.; Gidwani, S.; Horowitz, M.; Crane, J.; Lin, S.; Thornton, J.C.; Pi-Sunyer, X. Greater Neonatal Fat-Free Mass and Similar Fat Mass Following a Randomized Trial to Control Excess Gestational Weight Gain. Obesity 2018, 26, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, S.A.; Baldi, J.C.; Cutfield, W.S.; McCowan, L.; Hofman, P.L. Exercise training in pregnancy reduces offspring size without changes in maternal insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2080–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.C.; Silva, D.; Beilin, L.; Neppe, C.; Mackie, K.E.; Roffey, E.; Gibson, L.Y.; D’Vaz, N.; Christian, H.; Reid, C.M.; et al. Feasibility of conducting an early pregnancy diet and lifestyle e-health intervention: The Pregnancy Lifestyle Activity Nutrition (PLAN) project. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2020, 11, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolu, P.; Raitanen, J.; Puhkala, J.; Tuominen, P.; Husu, P.; Luoto, R. Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of a Cluster-Randomized Prenatal Lifestyle Counseling Trial: A Seven-Year Follow-Up. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.L.; Campbell, C.; Wagner, K.; Peterson, A.; Lanningham-Foster, L. Impact of a walking intervention during pregnancy on post-partum weight retention and infant anthropometric outcomes. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2014, 5, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoto, R.; Kinnunen, T.I.; Aittasalo, M.; Kolu, P.; Raitanen, J.; Ojala, K.; Mansikkamäki, K.; Lamberg, S.; Vasankari, T.; Komulainen, T.; et al. Primary prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus and large-for-gestational-age newborns by lifestyle counseling: A cluster-randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, L.E.; McDonald, S.; Stewart, C.; Newton, E.; Isler, C.; Steed, D.; Sarno, L.A.; Kelley, G.A.; Chasan-Taber, L.; Kuehn, D.; et al. Influence of Supervised Maternal Aerobic Exercise during Pregnancy on 1-Month-Old Neonatal Cardiac Function and Outflow: A Pilot Study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2023, 55, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, A.G.; May, L.E.; Gaines, G.G.; Isler, C.; Kuehn, D. Effects of Aerobic Exercise during Pregnancy on 1-Month Infant Neuromotor Skills. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustila, T.; Raitanen, J.; Keskinen, P.; Saari, A.; Luoto, R. Lifestyle counseling during pregnancy and offspring weight development until four years of age: Follow-up study of a controlled trial. J. Negat. Results Biomed. 2012, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustila, T.; Raitanen, J.; Keskinen, P.; Saari, A.; Luoto, R. Pragmatic controlled trial to prevent childhood obesity in maternity and child health care clinics: Pregnancy and infant weight outcomes (the VACOPP Study). BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustila, T.; Raitanen, J.; Keskinen, P.; Luoto, R. A pragmatic controlled trial to prevent childhood obesity within a risk group at maternity and child health-care clinics: Results up to six years of age (the VACOPP study). BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Godfrey, K.M.; Pasupathy, D.; Levin, J.; Flynn, A.C.; Hayes, L.; Briley, A.L.; Bell, R.; Lawlor, D.A.; Oteng-Ntim, E.; et al. Infant adiposity following a randomised controlled trial of a behavioural intervention in obese pregnancy. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perales, M.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Barakat, R.; Cordero, Y.; Peláez, M.; López, C.; Ruilope, L.M.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Lucia, A. Gestational Exercise and Maternal and Child Health: Effects until Delivery and at Post-Natal Follow-up. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, S.; Clifton, R.G.; Haire-Joshu, D.; Redman, L.M.; Van Horn, L.; Evans, M.; Joshipura, K.; Couch, K.A.; Arteaga, S.S.; Cahill, A.G.; et al. One-year postpartum anthropometric outcomes in mothers and children in the LIFE-Moms lifestyle intervention clinical trials. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poston, L.; Bell, R.; Croker, H.; Flynn, A.C.; Godfrey, K.M.; Goff, L.; Hayes, L.; Khazaezadeh, N.; Nelson, S.M.; Oteng-Ntim, E.; et al. Effect of a behavioural intervention in obese pregnant women (the UPBEAT study): A multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauh, K.; Günther, J.; Kunath, J.; Stecher, L.; Hauner, H. Lifestyle intervention to prevent excessive maternal weight gain: Mother and infant follow-up at 12 months postpartum. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronnberg, A.K.; Hanson, U.; Nilsson, K. Effects of an antenatal lifestyle intervention on offspring obesity—a 5-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborg, J.; Henriksson, P.; Söderström, E.; Migueles, J.H.; Bendtsen, M.; Blomberg, M.; Löf, M. The effects of a lifestyle intervention (the HealthyMoms app) during pregnancy on infant body composition: Secondary outcome analysis from a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvig, M.; Vinter, C.A.; Jørgensen, J.S.; Wehberg, S.; Ovesen, P.G.; Lamont, R.F.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Christesen, H.T.; Jensen, D.M. Anthropometrics and body composition by dual energy X-ray in children of obese women: A follow-up of a randomized controlled trial (the Lifestyle in Pregnancy and Offspring [LiPO] study). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tanvig, M.; Vinter, C.A.; Jørgensen, J.S.; Wehberg, S.; Ovesen, P.G.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Christesen, H.T.; Jensen, D.M. Effects of lifestyle intervention in pregnancy and anthropometrics at birth on offspring metabolic profile at 2.8 years: Results from the Lifestyle in Pregnancy and Offspring (LiPO) study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesco, K.K.; Leo, M.C.; Karanja, N.; Gillman, M.W.; McEvoy, C.T.; King, J.C.; Eckhardt, C.L.; Smith, K.S.; Perrin, N.; Stevens, V.J. One-year postpartum outcomes following a weight management intervention in pregnant women with obesity. Obesity 2016, 24, 2042–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, I.; Hartkopf, J.; Kullmann, S.; Schleger, F.; Hallschmid, M.; Pauluschke-Fröhlich, J.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H. Spotlight on the fetus: How physical activity during pregnancy influences fetal health: A narrative review. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapp, J.F., 3rd. The effects of maternal exercise on fetal oxygenation and feto-placental growth. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2003, 110 (Suppl. S1), S80–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, L.M.; Satin, A.J. Exercise during pregnancy: Fetal responses to current public health guidelines. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 119, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebrzydowska-Tatus, M.; Pełech, A.; Rekowska, A.K.; Satora, M.; Masiarz, A.; Kabała, Z.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Trojnar, M. Recent Insights and Recommendations for Preventing Excessive Gestational Weight Gain. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barakat, R.; Silva-José, C.; Sánchez-Polán, M.; Zhang, D.; Lobo, P.; De Roia, G.; Montejo, R. Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133726
Barakat R, Silva-José C, Sánchez-Polán M, Zhang D, Lobo P, De Roia G, Montejo R. Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133726
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarakat, Rubén, Cristina Silva-José, Miguel Sánchez-Polán, Dingfeng Zhang, Pablo Lobo, Gabriela De Roia, and Rocío Montejo. 2024. "Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133726
APA StyleBarakat, R., Silva-José, C., Sánchez-Polán, M., Zhang, D., Lobo, P., De Roia, G., & Montejo, R. (2024). Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133726











