Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension after the Removal of COVID-19 Pandemic Restrictions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Methods
2.3. Stastistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Group
3.2. Fear of COVID-19, Anxiety, and Depression during the Pandemic
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farooq, S.; Tunmore, J.; Wajid Ali, M.; Ayub, M. Suicide, self-harm and suicidal ideation during COVID-19: A systematic review. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 306, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieteska-Milek, M.; Szmit, S.; Florczyk, M.; Kusmierczyk-Droszcz, B.; Ryczek, R.; Dzienisiewicz, M.; Torbicki, A.; Kurzyna, M. Fear of COVID-19, Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension during the Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Fuge, J.; Meltendorf, T.; Kahl, K.G.; Richter, M.J.; Gall, H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Kamp, J.C.; Hoeper, M.M.; Olsson, K.M. Impact of SARS-CoV-2-Pandemic on Mental Disorders and Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 668647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, G.; Dzikowska-Diduch, O.; Mroczek, E.; Mularek-Kubzdela, T.; Chrzanowski, L.; Skoczylas, I.; Tomaszewski, M.; Peregud-Pogorzelska, M.; Karasek, D.; Lewicka, E.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in the era of modern therapeutic approaches: Data from the Polish multicenter registry (BNP-PL). Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211002961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darocha, S.; Roik, M.; Kopec, G.; Araszkiewicz, A.; Furdal, M.; Lewandowski, M.; Jachec, W.; Grabka, M.; Banaszkiewicz, M.; Pietrasik, A.; et al. Balloon pulmonary angioplasty in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A multicentre registry. EuroIntervention 2022, 17, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanauskiene, T.; Cesna, S.; Grigoniene, E.; Gumbiene, L.; Daubaraite, A.; Ivanauskaite, K.; Glaveckaite, S. Balloon Pulmonary Angioplasty for Inoperable Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Insights from a Pilot Low-Volume Centre Study and a Comparative Analysis with Other Centres. Medicina 2024, 60, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, G.; Kurzyna, M.; Mroczek, E.; Chrzanowski, L.; Mularek-Kubzdela, T.; Skoczylas, I.; Kusmierczyk, B.; Pruszczyk, P.; Blaszczak, P.; Lewicka, E.; et al. Characterization of Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Data from the Polish Registry of Pulmonary Hypertension (BNP-PL). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzyna, M.; Zylkowska, J.; Fijalkowska, A.; Florczyk, M.; Wieteska, M.; Kacprzak, A.; Burakowski, J.; Szturmowicz, M.; Wawrzynska, L.; Torbicki, A. Characteristics and prognosis of patients with decompensated right ventricular failure during the course of pulmonary hypertension. Pol. Heart J. (Kardiol. Pol.) 2008, 66, 1033–1039; discussion 1031–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Somaini, G.; Hasler, E.D.; Saxer, S.; Huber, L.C.; Lichtblau, M.; Speich, R.; Bloch, K.E.; Ulrich, S. Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension and Changes during Therapy. Respiration 2016, 91, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeuffer, E.; Krannich, H.; Halank, M.; Wilkens, H.; Kolb, P.; Jany, B.; Held, M. Anxiety, Depression, and Health-Related QOL in Patients Diagnosed with PAH or CTEPH. Lung 2017, 195, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, K.M.; Meltendorf, T.; Fuge, J.; Kamp, J.C.; Park, D.H.; Richter, M.J.; Gall, H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Ferrari, P.; Schmiedel, R.; et al. Prevalence of Mental Disorders and Impact on Quality of Life in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 667602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dering, M.R.; Lepsy, N.; Fuge, J.; Meltendorf, T.; Hoeper, M.M.; Heitland, I.; Kamp, J.C.; Park, D.H.; Richter, M.J.; Gall, H.; et al. Prevalence of Mental Disorders in Patients With Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 821466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahorsu, D.K.; Lin, C.Y.; Imani, V.; Saffari, M.; Griffiths, M.D.; Pakpour, A.H. The Fear of COVID-19 Scale: Development and Initial Validation. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2020, 20, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisula, E.; Nowakowska, I. Skala Lęku Przed Koronawirusem FCV-19S (Ahorsu i in., 2020)—Polskie tłumaczenie. 2020. Available online: https://osf.io/39jr8/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Pilch, I.; Kurasz, Z.; Turska-Kawa, A. Experiencing fear during the pandemic: Validation of the fear of COVID-19 scale in Polish. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichowicz, H.M.; Wieczorek, D. Screening post-stroke depression using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Psychiatr. Pol. 2011, 45, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Hopkins, R.O.; Glissmeyer, E.W.; Kitterman, N.; Elliott, C.G. Cognitive, emotional, and quality of life outcomes in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, C.L.; Kruger, B.; Strahler, J.; Weyh, C.; Gebhardt, K.; Tello, K.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Sommer, N.; Gall, H.; Richter, M.J.; et al. Physical Activity and Mental Health of Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiejna, A.; Adamowski, T.; Piotrowski, P.; Moskalewicz, J.; Wojtyniak, B.; Swiatkiewicz, G.; Stokwiszewski, J.; Kantorska-Janiec, M.; Zagdanska, M.; Kessler, R. “Epidemiology of mental disorders and access to mental health care. EZOP—Poland”—Research methodology. Psychiatr. Pol. 2015, 49, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilling, S.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Mavranezouli, I.; Kew, K.; Taylor, C.; Clark, D.M.; Guideline Development, G. Recognition, assessment and treatment of social anxiety disorder: Summary of NICE guidance. BMJ 2013, 346, f2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronawirus Information and Recommendation. 2022. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/coronavirus/temporary-limitations (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Kopec, G.; Tyrka, A.; Jonas, K.; Magon, W.; Waligora, M.; Stepniewski, J.; Podolec, P. The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic prevents patients with pulmonary hypertension from seeking medical help. Pol. Heart J. (Kardiol. Pol.) 2020, 78, 916–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowska, J.; Meyer-Szary, J.; Mazurek-Kula, A.; Zuk, M.; Migdal, A.; Kusa, J.; Skiba, E.; Zygielo, K.; Przetocka, K.; Kordon, Z.; et al. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Children with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Parental Anxiety and Attitudes. Follow-Up Data from the Polish Registry of Pulmonary Hypertension (BNP-PL). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinas, L.; Iyer, K.; Meszaros, G.; Quarck, R.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Jansa, P.; D’Alto, M.; Luknar, M.; Milutinov Ilic, S.; et al. PH CARE COVID survey: An international patient survey on the care for pulmonary hypertension patients during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belge, C.; Quarck, R.; Godinas, L.; Montani, D.; Escribano Subias, P.; Vachiery, J.L.; Nashat, H.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Humbert, M.; Delcroix, M. COVID-19 in pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A reference centre survey. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieteska-Milek, M.; Kusmierczyk-Droszcz, B.; Ryczek, R.; Szmit, S.; Florczyk, M.; Manczak, R.; Betkier-Lipinska, K.; Hoffman, P.; Krzesinski, P.; Torbicki, A.; et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 in patients vaccinated and unvaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 and suffering from pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2023, 133, 16406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.D.; Burger, C.D.; Delossantos, G.B.; Grinnan, D.; Ralph, D.D.; Rayner, S.G.; Ryan, J.J.; Safdar, Z.; Ventetuolo, C.E.; Zamanian, R.T.; et al. A Survey-based Estimate of COVID-19 Incidence and Outcomes among Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension or Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension and Impact on the Process of Care. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montani, D.; Certain, M.C.; Weatherald, J.; Jais, X.; Bulifon, S.; Noel-Savina, E.; Nieves, A.; Renard, S.; Traclet, J.; Bouvaist, H.; et al. COVID-19 in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: A National Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieteska-Milek, M.; Kusmierczyk-Droszcz, B.; Betkier-Lipinska, K.; Szmit, S.; Florczyk, M.; Zielinski, P.; Hoffman, P.; Krzesinki, P.; Kurzyna, M. Long COVID syndrome after SARS-CoV-2 survival in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2023, 13, e12244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigorski, D.; Sobczuk, P.; Osmola, M.; Kuc, K.; Walerzak, A.; Wilk, M.; Ciszewski, T.; Kopec, S.; Hryn, K.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 on anxiety levels among patients with cancer actively treated with systemic therapy. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzman, J. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health. Psychiatr. Pol. 2020, 54, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Total Study Group n (%) or Mean (SD) | PAH n (%) or Mean (SD) | CTEPH n (%) or Mean (SD) | PAH vs. CTEPH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 141 (100%) | 90 (64%) | 51 (36%) | |
| Females/males | 88/53 (62%/38%) | 69/21 (77%/33%) | 19/32 (37%/63%) | <0.001 * |
| Age, years | 60 (42–72) | 57 (41–69) | 68 (48–78) | 0.005 * |
| Duration of disease, years | 5.7 (2.1–9.8) | 5.8 (2.3–9.8) | 3.8 (1.2–9.8) | 0.22 |
| PAH patients | ||||
| • Idiopathic PAH | 54 (60%) | |||
| • PAH associated with CHD | 9 (10%) | |||
| • PAH associated with CTD | 17 (19%) | |||
| • Heritable PAH | 6 (7%) | |||
| • PAH porto-pulmonary | 4 (4%) | |||
| PAH monotherapy | 18 (23%) | |||
| PAH double combination therapy | 33 (42%) | |||
| PAH triple combination therapy | 27 (34%) | |||
| CTEPH-BPA | 42 (82%) | |||
| CTEPH-PEA | 12 (24%) | |||
| CTEPH PAH-like therapy (riociguat or sildenafil) | 45 (88%) | |||
| WHO functional class | 2.4 (±0.6) | 2.5 (±0.6) | 2.3 (±0.7) | 0.4 |
| WHO FC 1 | 9 (6.4%) | 2 (2%) | 6 (12%) | |
| WHO FC 2 | 71 (50%) | 47 (52%) | 22 (43%) | |
| WHO FC 3 | 59 (42%) | 37 (41%) | 23 (45%) | |
| WHO FC 4 | 2 (1.4%) | 4 (4.4%) | 0 | |
| 6 MWD, m | 457 (330–540) | 459 (333–542) | 453 (330–523) | 0.41 |
| NTproBNP (pg/mL) | 237 (99–810) | 249 (107–673) | 201 (89–994) | 0.61 |
| 1-year risk of death due to PH, points # | 1.6 (1.0–2.6) | 1.6 (1.0–2.5) | 1.6 (1.0–2.6) | 0.86 |
| COVID-19 vaccination | 107 (76%) | 68 (76%) | 39 (76%) | 1.0 |
| History of COVID-19 | 26 (18%) | 15 (17%) | 11 (22%) | 0.5 |
| History of depression or anxiolytic treatment | 19 (13%) | 13 (14%) | 6 (12%) | 0.8 |
| Concomitant disease | 93 (66%) | 56 (62%) | 37 (73%) | 0.27 |
| Arterial hypertension | 62 (44%) | 36 (40%) | 26 (51%) | 0.22 |
| Diabetes | 18 (13%) | 13 (14%) | 5 (10%) | 0.60 |
| Coronary artery disease | 23 (16%) | 10 (11%) | 4 (8%) | 0.77 |
| COPD | 14 (9.9%) | 13 (14%) | 10 (20%) | 0.48 |
| Neoplasm | 16 (11%) | 8 (9%) | 8 (16%) | 0.27 |
| Obesity, BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 | 41 (29%) | 24 (27%) | 17 (33%) | 0.44 |
| All Patients n (%); Median (IQR) or Mean (SD) n = 141 | PAH n (%); Median (IQR) or Mean (SD) n = 90 | CTEPH n (%); Median (IQR) or Mean (SD) n = 51 | PAH vs. CTEPH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fear of COVID-19, points | 18 (12–23) | 19 (12–23) | 17 (11–21) | 0.32 |
| HADS-A, points | 5 (3–8) | 5 (3–8) | 5 (2–8) | 0.54 |
| HADS-D, points | 3 (1–7) | 2 (1–7) | 4 (0–7) | 0.64 |
| HADS-A ≥ 8 points | 37 (26%) | 24 (27%) | 13 (25%) | 0.69 |
| HADS-A ≥ 11 points | 10 (7%) | 6 (6.7%) | 4 (7.8%) | 1.0 |
| HADS-D ≥ 8 points | 23 (16%) | 16 (18%) | 7 (14%) | 0.64 |
| HADS-D ≥ 11 points | 4 (2.8%) | 2 (2%) | 0 | 0.54 |
| All n = 141 | PAH (n = 90) | CTEPH (n = 51) | P (PAH vs. CTEPH) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
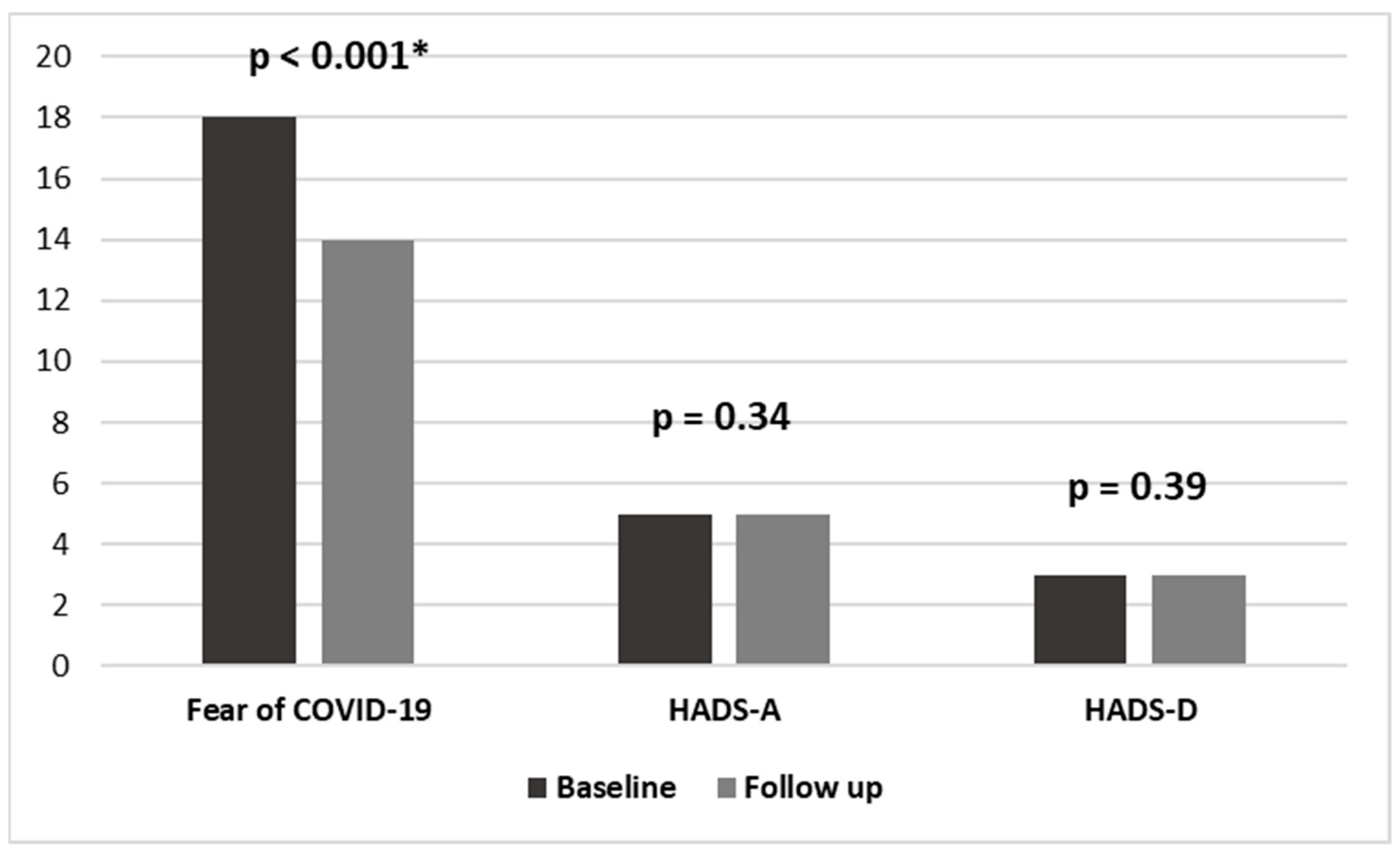
| ∆ FCV-19S | −4 (−7–0), p < 0.001 * | −4 (−7–0), p < 0.001 * | −3 (−7–2), p = 0.04 * | 0.68 |
| ∆ HADS-A ∆ HADS-D | −2 (−4–0), p = 0.34 * 0 (−2–1), p = 0.39 * | 0 (−2–1), p = 0.22 * 0 (−1–1), p = 0.69 * | 0 (−2–2), p = 0.99 * 0 (−2–1), p = 0.37 * | 0.36 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wieteska-Miłek, M.; Witowicz, A.; Szmit, S.; Florczyk, M.; Peller, M.; Dzienisiewicz, M.; Kurzyna, M. Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension after the Removal of COVID-19 Pandemic Restrictions. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123532
Wieteska-Miłek M, Witowicz A, Szmit S, Florczyk M, Peller M, Dzienisiewicz M, Kurzyna M. Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension after the Removal of COVID-19 Pandemic Restrictions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123532
Chicago/Turabian StyleWieteska-Miłek, Maria, Anna Witowicz, Sebastian Szmit, Michał Florczyk, Michał Peller, Milena Dzienisiewicz, and Marcin Kurzyna. 2024. "Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension after the Removal of COVID-19 Pandemic Restrictions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123532
APA StyleWieteska-Miłek, M., Witowicz, A., Szmit, S., Florczyk, M., Peller, M., Dzienisiewicz, M., & Kurzyna, M. (2024). Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension after the Removal of COVID-19 Pandemic Restrictions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3532. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123532







