Physical Activity in Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Three Years after COVID-19, a Longitudinal Survey: The After-Effects of the Quarantine and the Benefits of a Return to a Healthier Life-Style
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Scoring Protocol
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
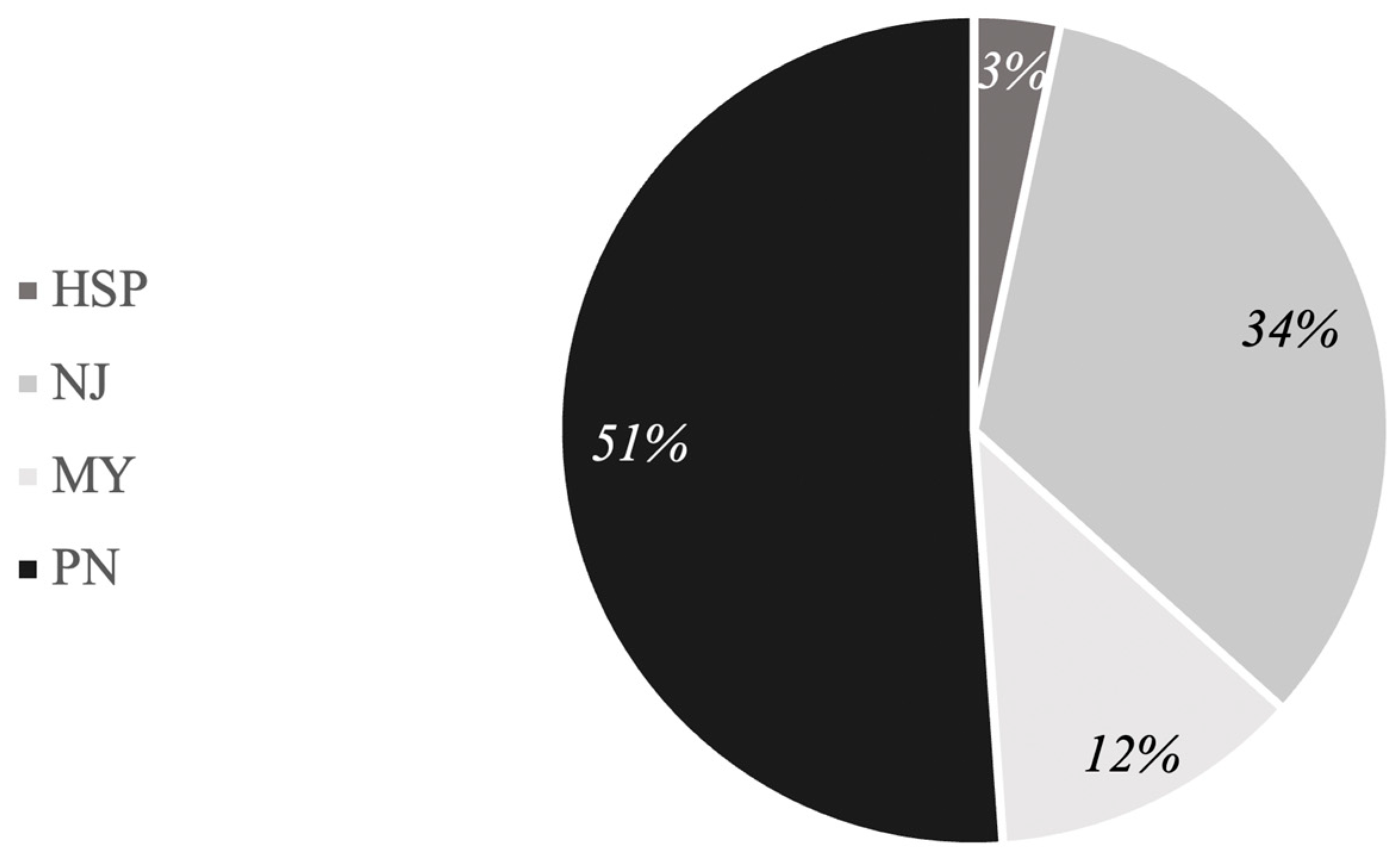
3.1. Participants
3.2. The Adapted Version of the IPAQ-SF and SF-12
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Strengths and Limitations
5.2. Practical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abasıyanık, Z.; Kurt, M.; Kahraman, T. COVID-19 and Physical Activity Behaviour in People with Neurological Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Dev. Phys. Disabil. 2022, 34, 987–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velavan, T.P.; Meyer, C.G. The COVID-19 epidemic. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2020, 25, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Seze, J.; Lebrun-Frenay, C. COVID-19, the pandemic war: Implication for neurologists. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Mao, L.; Nassis, G.P.; Harmer, P.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Li, F. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): The need to maintain regular physical activity while taking precautions. J. Sport. Health Sci. 2020, 9, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Church, T.S.; Craig, C.L.; Bouchard, C. Sitting Time and Mortality from All Causes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2009, 41, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, R.J.; Johnson, N.E. Neuromuscular Disease. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 9, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidon, A.C.; Amato, A.A. COVID-19 and neuromuscular disorders. Neurology 2020, 94, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, L.C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Nunes, P.S.; de França Costa, I.M.; Garcez, C.A.; Goes, G.M.; Neves, E.L.; de Souza Siqueira Quintans, J.; de Souza Araújo, A.A. Epidemiologic Study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: A Systematic Review. Neuroepidemiology 2016, 46, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareyson, D.; Saveri, P.; Pisciotta, C. New developments in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy and related diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollár, J.; Nagy, F.; Tóth, B.E.; Török, K.; Szita, K.; Csutorás, B.; Moizs, M.; Hortobágyi, T. Exercise Effects on Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life and Clinical-Motor Symptoms. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2020, 52, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareyson, D.; Marchesi, C. Diagnosis, natural history, and management of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, G.; Schirinzi, E.; Simoncini, C.; Ricci, G. Exercise therapy in muscle diseases: Open issues and future perspectives. Acta Myol. Myopathies Cardiomyopathies Off. J. Mediterr. Soc. Myol. 2019, 38, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Westerberg, E.; Molin, C.J.; Lindblad, I.; Emtner, M.; Punga, A.R. Physical exercise in myasthenia gravis is safe and improves neuromuscular parameters and physical performance-based measures: A pilot study. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, G.; Salort-Campana, E.; Pereon, Y.; Stojkovic, T.; Wahbi, K.; Cintas, P.; Adams, D.; Laforet, P.; Tiffreau, V.; Desguerre, I.; et al. Guidance for the care of neuromuscular patients during the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak from the French Rare Health Care for Neuromuscular Diseases Network. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabally, Y.A.; Goedee, H.S.; Attarian, S.; Hartung, H.P. Management challenges for chronic dysimmune neuropathies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Muscle Nerve 2020, 62, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anziska, Y.; Inan, S. Exercise in neuromuscular disease. Semin. Neurol. 2014, 34, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustino, V.; Parroco, A.M.; Gennaro, A.; Musumeci, G.; Palma, A.; Battaglia, G. Physical Activity Levels and Related Energy Expenditure during COVID-19 Quarantine among the Sicilian Active Population: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, G.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Battaglia, G.; Pippi, R.; D’Agata, V.; Palma, A.; Di Rosa, M.; Musumeci, G. The impact of physical activity on psychological health during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, G.; Camussi, E.; Piccinelli, C.; Senore, C.; Armaroli, P.; Ortale, A.; Garena, F.; Giordano, L. Did social isolation during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic have an impact on the lifestyles of citizens? Epidemiol. Prev. 2020, 44, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascherini, G.; Catelan, D.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Petri, C.; Scaletti, C.; Gulisano, M. Changes in physical activity levels, eating habits and psychological well-being during the Italian COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: Impact of socio-demographic factors on the Florentine academic population. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, M.; Mennitti, C.; Gentile, A.; Correale, L.; Buzzachera, C.F.; Ferraris, C.; Montomoli, C.; Frisso, G.; Borrelli, P.; Scudiero, O. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Job Activity, Dietary Behaviours and Physical Activity Habits of University Population of Naples, Federico II-Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallè, F.; Sabella, E.A.; Ferracuti, S.; De Giglio, O.; Caggiano, G.; Protano, C.; Valeriani, F.; Parisi, E.A.; Valerio, G.; Liguori, G.; et al. Sedentary Behaviors and Physical Activity of Italian Undergraduate Students during Lockdown at the Time of COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, F.; Cenacchi, V.; Vegro, V.; Pavei, G. COVID-19 lockdown: Physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep in Italian medicine students. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021, 21, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Corrado, D.; Magnano, P.; Muzii, B.; Coco, M.; Guarnera, M.; De Lucia, S.; Maldonato, N.M. Effects of social distancing on psychological state and physical activity routines during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sport Sci. Health 2020, 16, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, M.; Rosselli, M.; Pellegrino, A.; Boddi, M.; Stefani, L.; Toncelli, L.; Modesti, P.A. Gender differences in the impact on physical activity and lifestyle in Italy during the lockdown, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, I.; Bianco, A.; Bonfiglio, C.; Sorino, P.; Mirizzi, A.; Campanella, A.; Buongiorno, C.; Liuzzi, R.; Osella, A.R. Decreased levels of physical activity: Results from a cross-sectional study in southern Italy during the COVID-19 lockdown. J. Sport. Med. Phys. Fit. 2021, 61, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, V.; Battaglia, G.; Giustino, V.; Gagliardo, A.; D’Aleo, M.; Giannini, O.; Palma, A.; Brighina, F. Significant reduction of physical activity in patients with neuromuscular disease during COVID-19 pandemic: The long-term consequences of quarantine. J. Neurol. 2020, 268, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjaka, M.; Feka, K.; Bianco, A.; Tishukaj, F.; Giustino, V.; Parroco, A.M.; Palma, A.; Battaglia, G. The Effect of COVID-19 Lockdown Measures on Physical Activity Levels and Sedentary Behaviour in a Relatively Young Population Living in Kosovo. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. HealthyAtHome—Physical Activity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hammami, A.; Harrabi, B.; Mohr, M.; Krustrup, P. Physical activity and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Specific recommendations for home-based physical training. Manag. Sport Leis. 2020, 27, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J., Jr.; Kosinski, M.; Keller, S.D. A 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey: Construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med. Care 1996, 34, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, N.M.; Hills, A.P.; Hunter, G.R.; Weinsier, R.L.; Schutz, Y. Metabolic equivalent: One size does not fit all. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Leon, A.S.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Montoye, H.J.; Sallis, J.F.; Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr. Compendium of physical activities: Classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 1993, 25, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.J.; Wullems, J.A.; Stebbings, G.K.; Morse, C.I.; Stewart, C.E.; Onambele-Pearson, G.L. Reliability and validity of the international physical activity questionnaire compared to calibrated accelerometer cut-off points in the quantification of sedentary behaviour and physical activity in older adults. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rääsk, T.; Mäestu, J.; Lätt, E.; Jürimäe, J.; Jürimäe, T.; Vainik, U.; Konstabel, K. Comparison of IPAQ-SF and Two Other Physical Activity Questionnaires with Accelerometer in Adolescent Boys. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagell, P.; Westergren, A.; Årestedt, K. Beware of the origin of numbers: Standard scoring of the SF-12 and SF-36 summary measures distorts measurement and score interpretations. Res. Nurs. Health 2017, 40, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilagut, G.; Forero, C.G.; Pinto-Meza, A.; Haro, J.M.; de Graaf, R.; Bruffaerts, R.; Kovess, V.; de Girolamo, G.; Matschinger, H.; Ferrer, M.; et al. The mental component of the short-form 12 health survey (SF-12) as a measure of depressive disorders in the general population: Results with three alternative scoring methods. Value Health J. Int. Soc. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2013, 16, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisnie, J.C.; Sajobi, T.T.; Wang, M.; Patten, S.B.; Fiest, K.M.; Bulloch, A.G.M.; Pringsheim, T.; Wiebe, S.; Jette, N. Effects of depression and anxiety on quality of life in five common neurological disorders. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.A.M.; Camelo, C.G.; Sampaio, P.; Fonseca, A.; Estephan, E.P.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pirola, R.N.; Silva, L.H.L.; Lima, K.D.F.; Albuquerque, M.A.V.; et al. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients with inherited neuromuscular disorders. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2022, 80, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, T.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Salimei, C.; Cerroni, R.; Liguori, C.; Scalise, S.; Alwardat, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Pierantozzi, M.; Stefani, A.; et al. Physical Activity Changes and Correlate Effects in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease during COVID-19 Lockdown. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, A.; Roushdy, T.; Essam, M.; Fathy, M.; Dawood, N.L.; Abushady, E.M.; Elrassas, H.; Helmi, A.; Hamid, E. Mental Health, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease During COVID-19 Pandemic. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2020, 35, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, N.; Campbell, N.; De Leeuw, J.; Owen, M.; Schenke, K.C. The effects of COVID-19 restrictions on physical activity and mental health of children and young adults with physical and/or intellectual disabilities. Disabil. Health J. 2021, 14, 101064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moumdjian, L.; Smedal, T.; Arntzen, E.C.; van der Linden, M.L.; Learmonth, Y.; Pedullà, L.; Tacchino, A.; Novotna, K.; Kalron, A.; Yazgan, Y.Z.; et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on physical activity and associated technology use in persons with multiple sclerosis: An international RIMS-SIG Mobility survey study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-de-Quel, Ó.; Suárez-Iglesias, D.; López-Flores, M.; Pérez, C.A. Physical activity, dietary habits and sleep quality before and during COVID-19 lockdown: A longitudinal study. Appetite 2021, 158, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, G.; Bellafiore, M.; Bianco, A.; Paoli, A.; Palma, A. Effects of a dynamic balance training protocol on podalic support in older women. Pilot Study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 22, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Menon, P.; Govender, R.; Abu Samra, A.M.; Allaham, K.K.; Nauman, J.; Östlundh, L.; Mustafa, H.; Smith, J.E.M.; AlKaabi, J.M. Systematic review of the effects of pandemic confinements on body weight and their determinants. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 298–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, V.; Alonge, P.; Rini, N.; Militello, M.; Lupica, A.; Torrente, A.; Brighina, F. Efgartigimod beyond myasthenia gravis: The role of FcRn-targeting therapies in stiff-person syndrome. J. Neurol. 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescimanno, G.; Lupica, A.; Tomasello, V.; Di Stefano, V.; Brighina, F.; Marrone, O. Challenges in the identification of nocturnal respiratory events in adult patients affected by spinal muscular atrophy. Sleep Med. 2023, 112, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, M.; Gray, M.M.; Gest, C.; Motz, P.; Sawyer, T.; Umoren, R. Telecoaching Improves Positive Pressure Ventilation Performance During Simulated Neonatal Resuscitations. Telemed. Rep. 2022, 3, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Neto, L.; Elsangedy, H.M.; de Oliveira Tavares, V.D.; Teixeira, C.V.L.S.; Behm, D.G.; Da Silva-Grigoletto, M.E. # Traininginhome-Home-based training during COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: Physical exercise and behavior-based approach. Rev. Bras. Fisiol. Exerc. 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, E.; Muse, H.; Wallace, K.; Wilkinson, M.; Heslop Marshall, K.; Nair, A.; Clark, S.; Vogiatzis, I. Feasibility and acceptability of a physical activity behavioural modification tele-coaching intervention in lung transplant recipients. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2022, 19, 14799731221116588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetlin, R.D.; Gutmann, L.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Ullrich, I.H.; Yeater, R.A. Resistance training effectiveness in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Recommendations for exercise prescription. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mhandi, L.; Millet, G.Y.; Calmels, P.; Richard, A.; Oullion, R.; Gautheron, V.; Feasson, L. Benefits of interval-training on fatigue and functional capacities in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Muscle Nerve 2008, 37, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupica, A.; Di Stefano, V.; Iacono, S.; Pignolo, A.; Quartana, M.; Gagliardo, A.; Fierro, B.; Brighina, F. Impact of COVID-19 in AChR Myasthenia Gravis and the Safety of Vaccines: Data from an Italian Cohort. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| During the Pandemic (T0) | Follow Up (T1) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 54.98 ± 13.437 | 57.65 ± 12.859 | 0.212 |
| Gender (males) | 49/91 (53.8%) | 49/91 (53.8%) | 1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.9 ± 4.9 | 23.87 ± 4.98 | 0.579 |
| MET—minutes/week of walking PAs | 252.03 ± 597.1 | 656.7 ± 2324.75 | <0.001 *** |
| MET—minutes/week of moderate-intensity PAs | 174.5 ± 538.9 | 1747.69 ± 13,570.4 | 0.003 ** |
| MET—minutes/week of vigorous-intensity PAs | 52.75 ± 381.6 | 134.51 ± 705.8 | 0.251 |
| MET—minutes/week of MVPAs | 227.25 ± 817.54 | 1882.2 ± 13,581.2 | 0.002 ** |
| MET—minutes/week of total PA | 479.29 ± 1244.76 | 2538.9 ± 15,821.7 | <0.001 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leale, I.; Giustino, V.; Trapani, P.; Alonge, P.; Rini, N.; Cutrò, I.; Leone, O.; Torrente, A.; Lupica, A.; Palma, A.; et al. Physical Activity in Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Three Years after COVID-19, a Longitudinal Survey: The After-Effects of the Quarantine and the Benefits of a Return to a Healthier Life-Style. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010265
Leale I, Giustino V, Trapani P, Alonge P, Rini N, Cutrò I, Leone O, Torrente A, Lupica A, Palma A, et al. Physical Activity in Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Three Years after COVID-19, a Longitudinal Survey: The After-Effects of the Quarantine and the Benefits of a Return to a Healthier Life-Style. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010265
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeale, Ignazio, Valerio Giustino, Paolo Trapani, Paolo Alonge, Nicasio Rini, Ivana Cutrò, Olga Leone, Angelo Torrente, Antonino Lupica, Antonio Palma, and et al. 2024. "Physical Activity in Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Three Years after COVID-19, a Longitudinal Survey: The After-Effects of the Quarantine and the Benefits of a Return to a Healthier Life-Style" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010265
APA StyleLeale, I., Giustino, V., Trapani, P., Alonge, P., Rini, N., Cutrò, I., Leone, O., Torrente, A., Lupica, A., Palma, A., Roccella, M., Brighina, F., Di Stefano, V., & Battaglia, G. (2024). Physical Activity in Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Three Years after COVID-19, a Longitudinal Survey: The After-Effects of the Quarantine and the Benefits of a Return to a Healthier Life-Style. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010265













