Red Flags for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Associated with Sarcoidosis or Connective Tissue Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol Approval and Patient Consent
2.2. Patients
2.3. Electrophysiological Studies
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description and Control Group (Figure 1 and Table 1)
3.1.1. SAR-CIDP Group
3.1.2. CTD-CIDP Group
3.1.3. Control Group
3.2. Comparison between SAR-CIDP and CIDP (Table 1)
3.3. Comparison between CTD-CIDP and CIDP
3.4. Other Comparisons
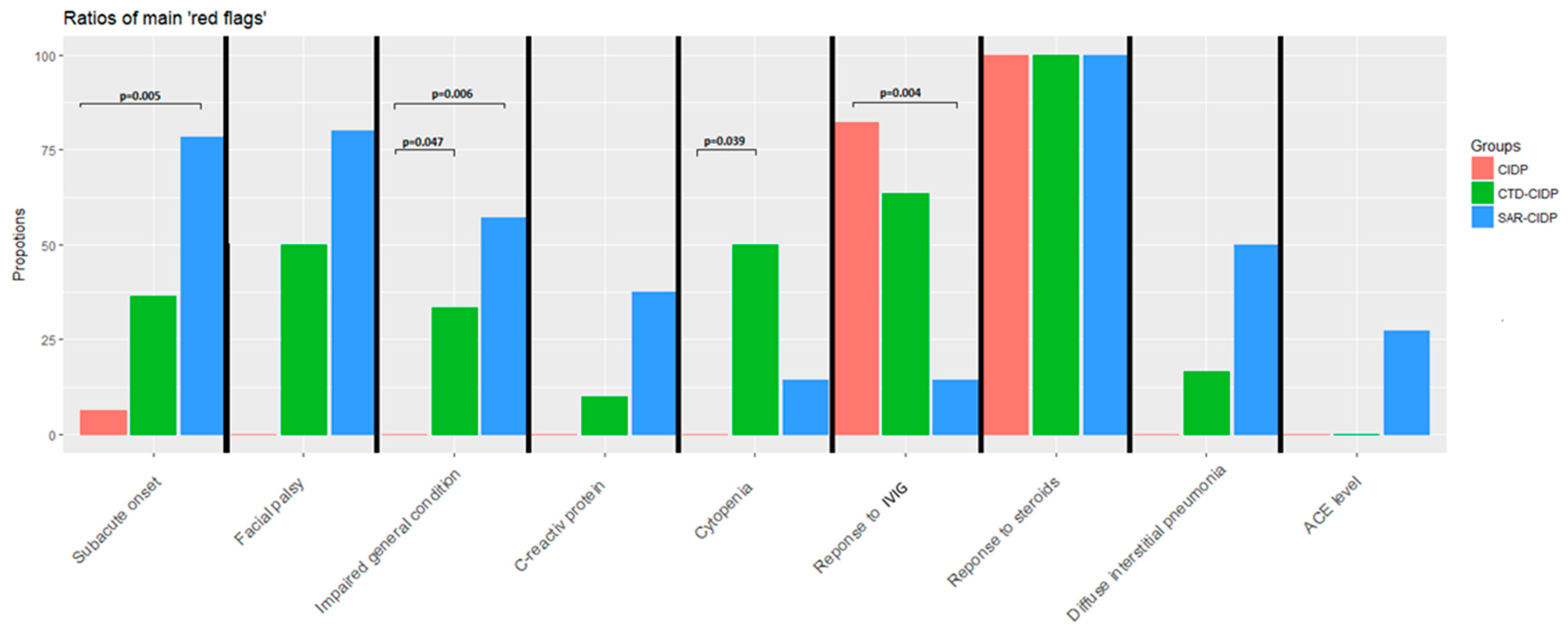
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van den Bergh, P.Y.; van Doorn, P.A.; Hadden, R.D.; Avau, B.; Vankrunkelsven, P.; Allen, J.A.; Attarian, S.; Blomkwist-Markens, P.H.; Cornblath, D.R.; Eftimov, F.; et al. European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on diagnosis and treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Report of a joint Task Force—Second revision. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3556–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajicek, J.P.; Scolding, N.J.; Foster, O.; Rovaris, M.; Evanson, J.; Moseley, I.F.; Scadding, J.W.; Thompson, E.J.; Chamoun, V.; Miller, D.H.; et al. Central nervous system sarcoidosis—Diagnosis and management. QJM 1999, 92, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Muscal, E.; Brey, R.L. Neurological Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Adults. Neurol. Clin. 2010, 28, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivadasan, A.; Muthusamy, K.; Patel, B.; Benjamin, R.; Prabhakar, A.T.; Mathew, V.; Aaron, S.; Alexander, M. Clinical Spectrum, Therapeutic Outcomes, and Prognostic Predictors in Sjogren’s Syndrome-associated Neuropathy. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2017, 20, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—First Revision. J. Peripher Nerv. Syst. 2010, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, G.; Lacroix, C.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Le Page, L.; Pico, F.; Presles, O.; Senant, J.; Remy, P.; Rondepierre, P.; Mallecourt, J. Nerve granulomas and vasculitis in sarcoid peripheral neuropathy: A clinicopathological study of 11 patients. Brain J. Neurol. 2002, 125, 264–275. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, V. Neurosarcoidosis: Clinical presentations and course in 50 patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1986, 73, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, O.P. Neurosarcoidosis: A personal perspective based on the study of 37 patients. Chest 1997, 112, 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Saifee, T.A.; Reilly, M.M.; Ako, E.; Rugg-Gunn, F.; Brandner, S.; Lunn, M.P.; Leary, S.M. Sarcoidosis presenting as acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2011, 43, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Ahad, R.; Ahmed, I.; Lee, G.; Khosla, S. Neurosarcoidosis Presenting as Acute Inflammatory Polyneuropathy (P6.142). Neurology 2016, 86, P6.142. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, T.M.; Dyck, P.J.B.; Aksamit, A.J.; Dyck, P.J. The natural history and long-term outcome of 57 limb sarcoidosis neuropathy cases. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 244, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducray, F.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Bouhour, F.; Rousset, H.; Vial, C. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and sarcoidosis: Fortuitous association? Rev. Neurol. 2007, 163, 3S85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Elkin, R.; Willcox, P.A. Neurosarcoidosis. A report of 5 cases. South Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Geneeskd. 1985, 67, 943–946. [Google Scholar]
- Fahoum, F.; Drory, V.E.; Issakov, J.; Neufeld, M.Y. Neurosarcoidosis presenting as Guillain-Barré-like syndrome. A case report and review of the literature. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2009, 11, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriby, D.; Stojkovic, T.; De Seze, J.; Hurtevent, J.F.; Vermersch, P. Chronic polyradiculoneuritis disclosing sarcoidosis. Rev. Neurol. 2002, 158, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Findik, S.; Bulbul, R.; Ozbenli, T.; Aslan, E.; Sandikci, U.; Aydin, D.; Atici, A.G.; Ozkaya, S. Sarcoidosis and Gullain-Barré syndrome. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2011, 111, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.; Sheron, N.; Semple, S. Sarcoidosis presenting with an acute Guillain-Barré syndrome. Postgrad Med. J. 1989, 65, 765–767. [Google Scholar]
- Rizk, C. A Case of Neurosarcoidosis Masquerading as Subacute Inflammatory Demylelinating Polyneuropathy. Neurology 2016, 86 (Suppl. 16), P3.371. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, N.S.; Irodenko, V.S.; Margeta, M.; Layzer, R.B. Sarcoid polyneuropathy masquerading as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, G.T.; Moser, K.M. Sarcoidosis with a Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome and clinical response to corticosteroids. Am. J. Med. 1967, 43, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Vital, A.; Lagueny, A.; Ferrer, X.; Louiset, P.; Canron, M.H.; Vital, C. Sarcoid neuropathy: Clinico-pathological study of 4 new cases and review of the literature. Clin. Neuropathol. 2008, 27, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zuniga, G.; Ropper, A.H.; Frank, J. Sarcoid peripheral neuropathy. Neurology 1991, 41, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, D.; Hammans, S.R.; Legg, N.J. Chronic relapsing inflammatory polyneuropathy complicating sicca syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 159–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bregante, S.; Gualandi, F.; van Lint, M.T.; Schenone, A.; Bacigalupo, A.; Marmont, A.M. Sjögren’s syndrome associated chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) treated with autologous and subsequently allogeneic haematopoietic SCT (HSCT). Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmin, R.; Sockalingam, S.; Shahrizaila, N.; Cheah, T.-E.; Zain, A.; Goh, K.-J. Successful treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with oral cyclophosphamide. Lupus 2012, 21, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedra, J.; Foltz, V.; Viala, K.; Tan, S.; Fautrel, B. Lewis-Sumner syndrome in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: Link between rheumatoid arthritis and demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathies. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianmehr, N.; Haghighi, A.; Moghaddasi, M.; Mofidi, M. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) as a first presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Res. 2017, 2, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn-Lubetzki, I.; Abramsky, O. Acute and chronic demyelinating inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Association with autoimmune diseases and lymphocyte response to human neuritogenic protein. Arch. Neurol. 1986, 43, 604–608. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, Y.-D.; Lin, W.-S.; Ws, L.; Yd, H. Sjögren’s syndrome with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurol. India 2011, 59, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luostarinen, L. Mixed connective tissue disease associated with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: CASE REPORT. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 28, 328–330. [Google Scholar]
- McCombe, P.A.; Klestov, A.C.; Tannenberg, A.E.; Chalk, J.B.; Pender, M. Sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 28, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, H.; Kamakura, K.; Masaki, T.; Hirata, A.; Nakamura, R.; Motoyoshi, K. Motor dominant neuropathy in Sjögren’s syndrome: Report of two cases. Intern. Med. 2002, 41, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pou Serradell, A.; Viñas Gaya, J. 3 cases of rare peripheral neuropathies associated with primary Gougerot-Sjögren syndrome. Rev. Neurol. 1993, 149, 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Rigamonti, A.; Lauria, G.; Balgera, R.; Agostoni, E.C. Subacute inflammatory polyradiculopathy associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2009, 39, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvito, L.; Wong, S.L.; Rajabally, Y.A. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with alopecia totalis and Sjögren syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2012, 45, 762–763. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22499108 (accessed on 17 December 2017).
- Sindern, E.; Stark, E.; Haas, J.; Steck, A.J. Serum antibodies to GM1 and GM3-gangliosides in systemic lupus erythematosus with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1991, 83, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Vina, E.; Fang, A.J.; Wallace, D.J.; Weisman, M.H. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Prognosis and outcome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 35, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappia, M.; Valentino, P.; Bono, F.; Vita, G.; Aguglia, U.; Messina, C.; Quattrone, A. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. Neurol. 1995, 35, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zoilo, M.A.; Eduardo, B.; Enrique, F.; del Rocio, M.V.M. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy in a boy with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.; Catoggio, L.J.; Gallagher, P.J.; Maddison, P.J. Salivary gland biopsy in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis 1989, 6, 47–50. [Google Scholar]

| Total (n = 44) | SAR-CIDP (n = 16) | CTD-CIDP (n = 11) | CIDP (n = 17) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of onset, median [Q1–Q3] | 60 * [50–68] | 66 [56–73] | 62 [53–67] | 54 [48–60] | |
| Sex (%F) | 52 | 44 | 82 | 41 | |
| Atypical presentation, n (%) | 25 * (60%) | 14 (100%) | 5 (45%) | 6 (35%) | |
| CIDP diagnosis according to NCS (definite, probable, possible, undefined, n (%)) *,¤,† | |||||
| Definite | 22 (54%) | 5 (36%) | 4 (36%) | 13 (81%) | |
| Probable | 3 (7%) | 2 (14%) | 0 | 1 (6%) | |
| Possible | 8 (19%) | 3 (21%) | 3 (27%) | 2 (13%) | |
| Undefined | 8 (19%) | 4 (29%) | 4 (36%) | 0 | |
| CIDP diagnosis after supportive criteria (definite, probable, possible, undefined, n (%)) *,¤,† | |||||
| Definite | 30 (73%) | 8 (57%) | 6 (55%) | 16 (100%) | |
| Probable | 2 (5%) | 1 (7%) | 1 (9%) | 0 | |
| Possible | 1 (2%) | 1 (7%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Undefined | 8 (20%) | 4 (29%) | 4 (36%) | 0 | |
| Weight loss, n (%) | 7 *,¤,† (24%) | 4 (57%) | 3 (33%) | 0 | |
| Extra neurological involvement (n,%) | 8 (50%) | 9 (82%) | |||
| Acute or subacute onset, n (%) | 16 *,† (38%) | 11 (79%) | 4 (36%) | 1 (6%) | |
| CSF pleiocytosis, n (%) | 5 (19%) | 3 (30%) | 1 (13%) | 1 (12%) | |
| CSF protein level g/L, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.62 [0.5–1.1] | 0.64 [0.6–0.9] | 0.41 [0.4–0.7] | 0.76 [0.5–1.1] | |
| Presence of motor conduction blocs on NCS | 19 (51%) | 7 (47%) | 2 (20%) | 10 (83%) | |
| Response to treatment | |||||
| Steroids (n,%) | 22 (100%) | 13 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (100%) | |
| IVIG (n,%) | 22 *,† (63%) | 1 (14%) | 7 (64%) | 14 (82%) | |
| Plasmapheresis (n,%) | 2 (67%) | 0/1 | Not prescribed | 2 (100%) | |
| Patient | Tissue with Granuloma | Other Tissue with Granuloma | Zajicek Criteria | Nerve Biopsy | Granuloma in Nerve Biopsy | Muscle Biopsy | Granuloma in Muscle Biopsy | Granuloma in Accesory Salivatory Glands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Possible | X | No | X | No | No | ||
| 2 | lung | Probable | X | No | X | No | -- | |
| 3 | nerve | muscle | Definite | X | Yes | X | Yes | Yes |
| 4 | muscle | Probable | -- | X | Yes | No | ||
| 5 | skin | Probable | -- | -- | Yes | |||
| 6 | nerve | Definite | X | Yes | X | No | No | |
| 7 | muscle | Probable | -- | X | Yes | No | ||
| 8 | muscle | Probable | X | No | X | Yes | -- | |
| 9 | nerve | muscle | Definite | X | Yes | X | Yes | -- |
| 10 | nerve | Definite | X | Yes | -- | -- | ||
| 11 | nerve | muscle, stomac | Definite | X | Yes | X | Yes | -- |
| 12 | muscle | Probable | X | No | X | Yes | No | |
| 13 | nerve | muscle | Definite | X | Yes | -- | -- | |
| 14 | nerve | muscle | Definite | X | Yes | X | Yes | -- |
| 15 | nerve | Definite | X | Yes | X | Yes | NP | |
| 16 | nerve | Definite | X | Yes | -- | -- |
| Extra-Neurological Involvement | SAR-CIDP | CTD-CIDP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Nb | Type | Nb | |
| Total | 50% | 82% | ||
| Lung | Intersitial pneumonitis | 3 | DIP | 3 |
| Cardiac | Pericarditis | 1 | Pericarditis | 2 |
| Adenopathy | Thoracic | 3 | ||
| Skin | Erythema nodosum | 1 | Livedo | 2 |
| Scar modification | 1 | |||
| Nail involvement | 1 | |||
| Ocular | Uveitis | 1 | ||
| Episcleritis | 1 | |||
| Digestive tract | Gastritis | 1 | Hepatitis | 1 |
| Oesophagus hypomotility | 1 | |||
| Sicca | 7 | |||
| Rheumatologic | Arthralgia | 3 | ||
| Raynaud syndrome | 2 | |||
| Thyroiditis | 2 | |||
| Hematologic | Cytopenia | 1 | ||
| Myelofibrosis | 1 | |||
| Muscle | Myositis | 1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vialatte de Pémille, C.; Noël, N.; Adam, C.; Labeyrie, C.; Not, A.; Beaudonnet, G.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Adams, D.; Cauquil, C. Red Flags for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Associated with Sarcoidosis or Connective Tissue Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093281
Vialatte de Pémille C, Noël N, Adam C, Labeyrie C, Not A, Beaudonnet G, Echaniz-Laguna A, Adams D, Cauquil C. Red Flags for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Associated with Sarcoidosis or Connective Tissue Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093281
Chicago/Turabian StyleVialatte de Pémille, Clément, Nicolas Noël, Clovis Adam, Céline Labeyrie, Adeline Not, Guillemette Beaudonnet, Andoni Echaniz-Laguna, David Adams, and Cécile Cauquil. 2023. "Red Flags for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Associated with Sarcoidosis or Connective Tissue Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093281
APA StyleVialatte de Pémille, C., Noël, N., Adam, C., Labeyrie, C., Not, A., Beaudonnet, G., Echaniz-Laguna, A., Adams, D., & Cauquil, C. (2023). Red Flags for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Associated with Sarcoidosis or Connective Tissue Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093281






