Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Mice Inbred Strains
2.2. Source of T. cruzi and Experimental Infection
2.3. Quantitative Determination of Kinin B1 Receptor Levels and T. cruzi DNA in Cardiac Tissues by Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. Histopathological Analysis of Heart Tissues
2.6. Determination of Parasite Nests by Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Electrocardiographic Measurements
2.8. Creatine-Kinase MB Detection
2.9. Cell Cultures and Invasion Assays with T. cruzi
2.10. ELISA for IFN-γ Detection
2.11. Intracellular Staining for IFN-γ and Granzyme B Detection
2.12. In Vivo Cytotoxicity Assay
2.13. Reagents
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
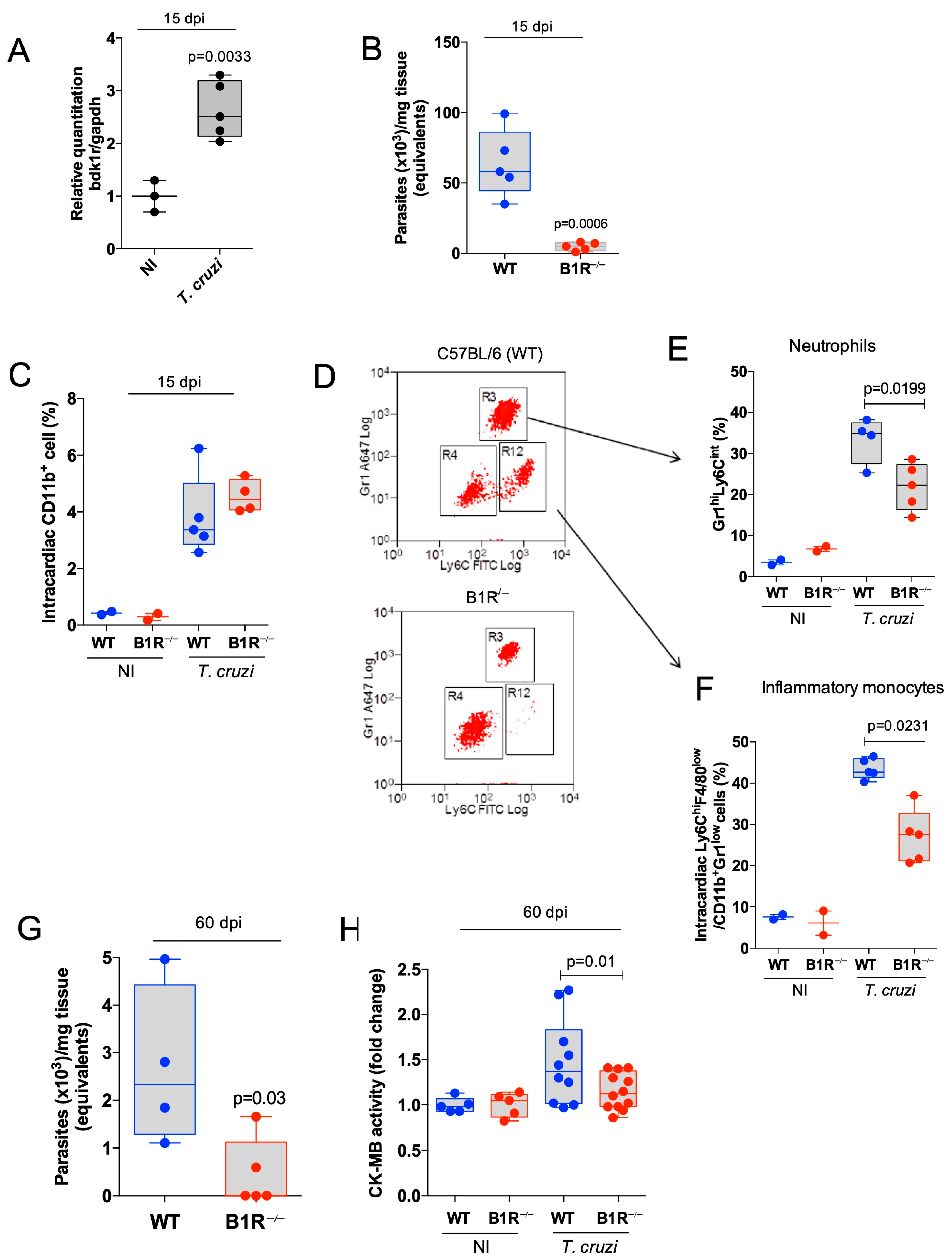
3.1. Global Ablation of the Mouse b1r Gene Reduces Heart Parasitism and Inhibits Intracardiac Infiltration of Proinflammatory Leukocytes in the Acute Stage of CD
3.2. Chronic Myocarditis and Heart Fibrosis Are Attenuated in B1R−/− Infected Mice
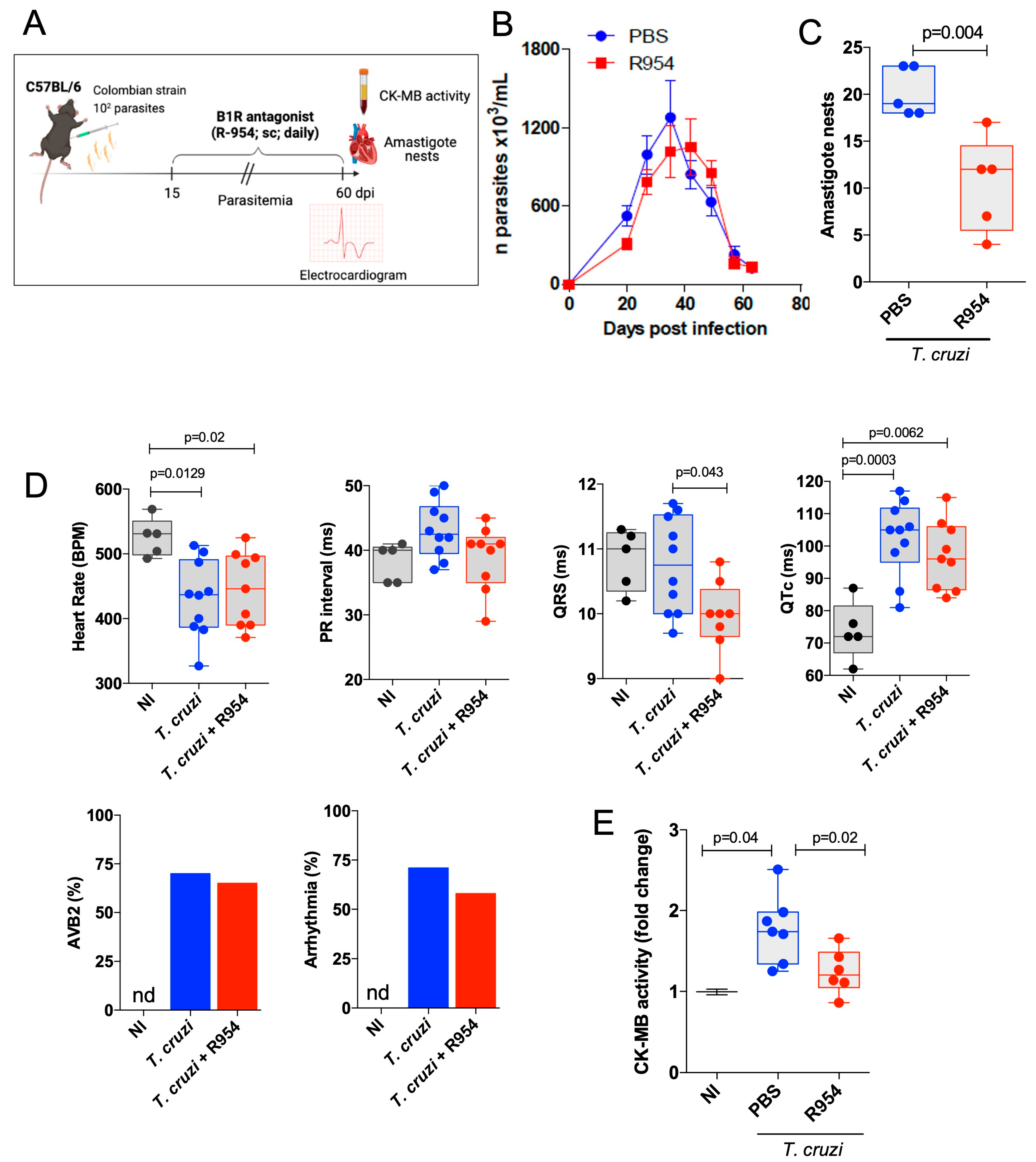
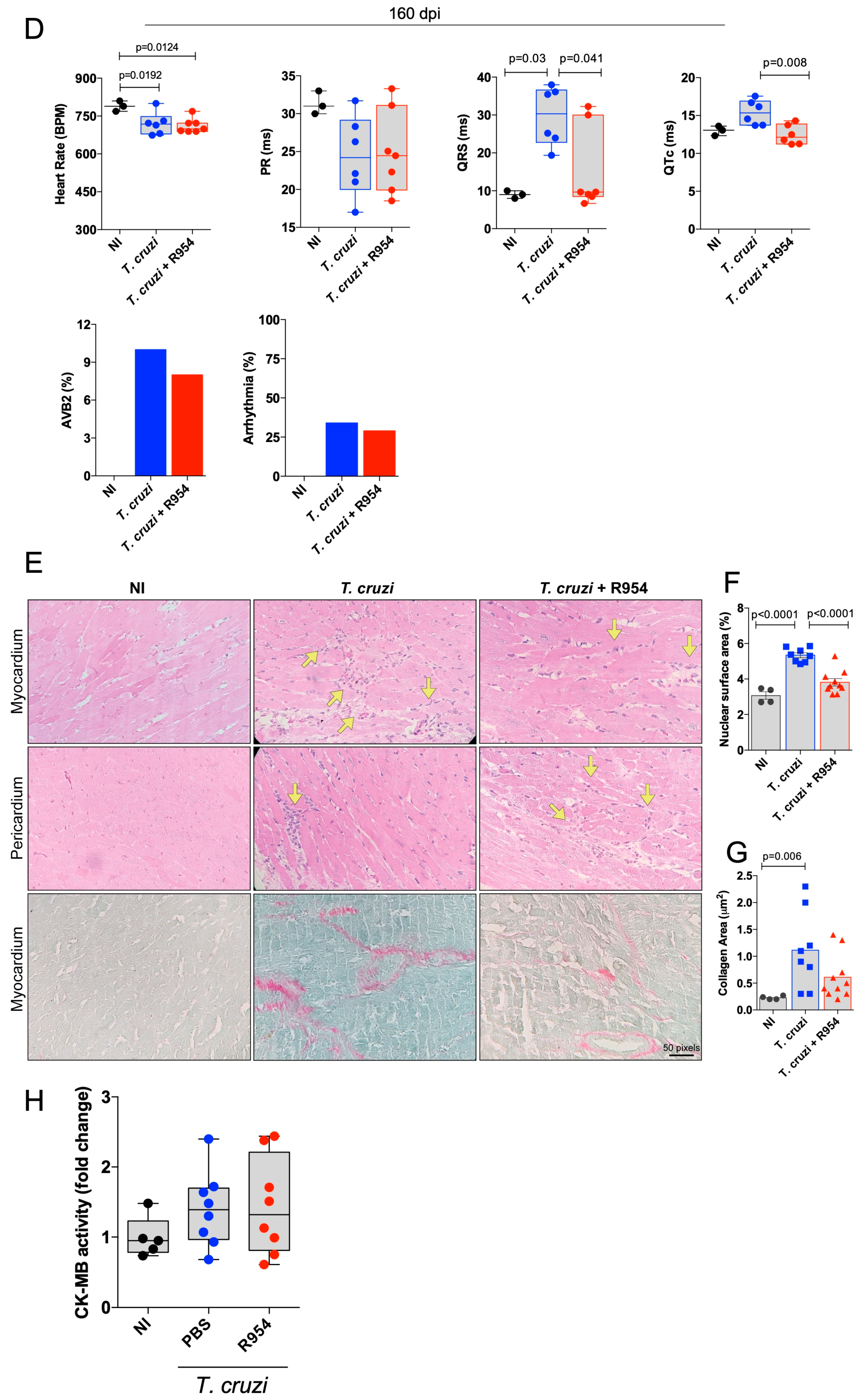
3.3. Therapeutical Effects of R-954 during Chronic Chagas Disease
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ribeiro, A.L.; Nunes, M.P.; Teixeira, M.M.; Rocha, M.O. Diagnosis and management of Chagas disease and cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikanai-Yasuda, M.A.; Carvalho, N.B. Oral transmission of Chagas disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez de Ayala, A.; Perez-Molina, J.A.; Norman, F.; Lopez-Velez, R. Chagasic cardiomyopathy in immigrants from Latin America to Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, M.C.P.; Beaton, A.; Acquatella, H.; Bern, C.; Bolger, A.F.; Echeverria, L.E.; Dutra, W.O.; Gascon, J.; Morillo, C.A.; Oliveira-Filho, J.; et al. Chagas Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Current Clinical Knowledge and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 138, e169–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro Dos Santos, R.; Rassi, S.; Feitosa, G.; Grecco, O.T.; Rassi, A., Jr.; da Cunha, A.B.; de Carvalho, V.B.; Guarita-Souza, L.C.; de Oliveira, W., Jr.; Tura, B.R.; et al. Cell therapy in Chagas cardiomyopathy (Chagas arm of the multicenter randomized trial of cell therapy in cardiopathies study): A multicenter randomized trial. Circulation 2012, 125, 2454–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.D.; Llewellyn, M.S.; Yeo, M.; Acosta, N.; Gaunt, M.W.; Miles, M.A. Recent, independent and anthropogenic origins of Trypanosoma cruzi hybrids. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Serrano, A.; Hutchinson, C.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Almeida, I.C.; Carrington, M. Comparison and Evolution of the Surface Architecture of Trypanosomatid Parasites. In Trypanosomes: After the Genome; Barry, J.D., Mottram, J.C., McCulloch, R., Acosta-Serrano, A., Eds.; Horizon Scientific Press: Norwich, UK, 2007; pp. 319–338. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.C.; Ward, A.; Olmo, F.; Jayawardhana, S.; Francisco, A.F.; Lewis, M.D.; Kelly, J.M. Intracellular DNA replication and differentiation of Trypanosoma cruzi is asynchronous within individual host cells in vivo at all stages of infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellasco, L.; Svensjo, E.; Bulant, C.A.; Blanco, P.J.; Nogueira, F.; Domont, G.; de Almeida, N.P.; Nascimento, C.R.; Silva-Dos-Santos, D.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; et al. Sheltered in Stromal Tissue Cells, Trypanosoma cruzi Orchestrates Inflammatory Neovascularization via Activation of the Mast Cell Chymase Pathway. Pathogens 2022, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, A.D.; Collins, M.H.; Rosenberg, C.S.; Tarleton, R.L. Highly competent, non-exhausted CD8+ T cells continue to tightly control pathogen load throughout chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, C.N.; Feijo, D.F.; Dutra, F.F.; Carneiro, V.C.; Freitas, G.B.; Alves, L.S.; Mesquita, J.; Fortes, G.B.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Souza, H.S.; et al. Oxidative stress fuels Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfstein, J. Subverting bradykinin-evoked inflammation by co-opting the contact system: Lessons from survival strategies of Trypanosoma cruzi. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2018, 25, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, D.; Serra, R.; Svensjo, E.; Lima, A.P.; Ramos, E.S., Jr.; Fortes, F.S.; Morandini, A.C.; Morandi, V.; Soeiro Mde, N.; Tanowitz, H.B.; et al. Trypanosoma cruzi invades host cells through the activation of endothelin and bradykinin receptors: A converging pathway leading to chagasic vasculopathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, C.R.; Andrade, D.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Serra, R.R.; Vellasco, L.; Brasil, G.; Ramos-Junior, E.S.; da Mota, J.B.; Almeida, L.N.; Andrade, M.V.; et al. Mast Cell Coupling to the Kallikrein-Kinin System Fuels Intracardiac Parasitism and Worsens Heart Pathology in Experimental Chagas Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Ducret, A.; Langen, H.; Nogoceke, E.; Santos, R.H.B.; Silva Nunes, J.P.; Benvenuti, L.; Levy, D.; Bydlowski, S.P.; Bocchi, E.A.; et al. Impairment of Multiple Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism Pathways in the Heart of Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 755782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tarleton, R.L. Parasite persistence correlates with disease severity and localization in chronic Chagas’ disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverio, J.C.; Pereira, I.R.; Cipitelli Mda, C.; Vinagre, N.F.; Rodrigues, M.M.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Lannes-Vieira, J. CD8+ T-cells expressing interferon gamma or perforin play antagonistic roles in heart injury in experimental Trypanosoma cruzi-elicited cardiomyopathy. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, W.O.; Menezes, C.A.; Magalhaes, L.M.; Gollob, K.J. Immunoregulatory networks in human Chagas disease. Parasite Immunol. 2014, 36, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.A. Microvascular changes as a cause of chronic cardiomyopathy in Chagas’ disease. Am. Heart J. 1990, 120, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.A.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Wittner, M.; Bilezikian, J.P. Pathophysiological insights into the cardiomyopathy of Chagas’ disease. Circulation 1990, 82, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.L.; Fukasawa, S.; De Brito, T.; Parzianello, L.C.; Bellotti, G.; Ramires, J.A. Different microcirculatory and interstitial matrix patterns in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and Chagas’ disease: A three dimensional confocal microscopy study. Heart 1999, 82, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, Z.A.; Andrade, S.G.; Correa, R.; Sadigursky, M.; Ferrans, V.J. Myocardial changes in acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Ultrastructural evidence of immune damage and the role of microangiopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 144, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanowitz, H.B.; Huang, H.; Jelicks, L.A.; Chandra, M.; Loredo, M.L.; Weiss, L.M.; Factor, S.M.; Shtutin, V.; Mukherjee, S.; Kitsis, R.N.; et al. Role of endothelin 1 in the pathogenesis of chronic chagasic heart disease. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 2496–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliberti, J.; Viola, J.P.; Vieira-de-Abreu, A.; Bozza, P.T.; Sher, A.; Scharfstein, J. Cutting edge: Bradykinin induces IL-12 production by dendritic cells: A danger signal that drives Th1 polarization. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5349–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, A.C.; Schmitz, V.; Morrot, A.; de Arruda, L.B.; Nagajyothi, F.; Granato, A.; Pesquero, J.B.; Muller-Esterl, W.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Scharfstein, J. Bradykinin B2 Receptors of dendritic cells, acting as sensors of kinins proteolytically released by Trypanosoma cruzi, are critical for the development of protective type-1 responses. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfstein, J.; Ramos, P.I.P.; Barral-Netto, M. G Protein-Coupled Kinin Receptors and Immunity Against Pathogens. Adv. Immunol. 2017, 136, 29–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaier, A.H. The contact activation and kallikrein/kinin systems: Pathophysiologic and physiologic activities. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.P.; Almeida, P.C.; Tersariol, I.L.; Schmitz, V.; Schmaier, A.H.; Juliano, L.; Hirata, I.Y.; Muller-Esterl, W.; Chagas, J.R.; Scharfstein, J. Heparan sulfate modulates kinin release by Trypanosoma cruzi through the activity of cruzipain. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5875–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Nsa Allogho, S.; Rizzi, A.; Gobeil, F.J. Bradykinin receptors and their antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 348, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, V.; Svensjo, E.; Serra, R.R.; Teixeira, M.M.; Scharfstein, J. Proteolytic generation of kinins in tissues infected by Trypanosoma cruzi depends on CXC chemokine secretion by macrophages activated via Toll-like 2 receptors. J. Leukoc Biol. 2009, 85, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, V.; Almeida, L.N.; Svensjo, E.; Monteiro, A.C.; Kohl, J.; Scharfstein, J. C5a and bradykinin receptor cross-talk regulates innate and adaptive immunity in Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3613–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Hess, J.F.; Bachvarov, D.R. The B1 receptors for kinins. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 357–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.A.; Sales, V.M.; Motta, F.L.; Fonseca, R.G.; Alenina, N.; Guadagnini, D.; Schadock, I.; Silva, E.D.; Torres, H.A.; dos Santos, E.L.; et al. Kinin B1 receptor in adipocytes regulates glucose tolerance and predisposition to obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calixto, J.B.; Medeiros, R.; Fernandes, E.S.; Ferreira, J.; Cabrini, D.A.; Campos, M.M. Kinin B1 receptors: Key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangsree, S.; Brovkovych, V.; Minshall, R.D.; Skidgel, R.A. Kininase I-type carboxypeptidases enhance nitric oxide production in endothelial cells by generating bradykinin B1 receptor agonists. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H1959–H1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdos, E.G.; Sloane, E.M. An enzyme in human blood plasma that inactivates bradykinin and kallidins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1962, 11, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, F.; Skidgel, R.A. Carboxypeptidase M is a positive allosteric modulator of the kinin B1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33226–33240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, C.P.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Prindle, T.; Fulton, W.B.; Wang, S.; McCray, P.B., Jr.; Chappell, M.; Hackam, D.J.; Jia, H. Attenuation of pulmonary ACE2 activity impairs inactivation of des-Arg(9) bradykinin/BKB1R axis and facilitates LPS-induced neutrophil infiltration. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L17–L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, P.V.; Sidime, F.; Tarazona, D.D.; Valdivia, F.; Levano, K.S. A Closer Look at ACE2 Signaling Pathway and Processing during COVID-19 Infection: Identifying Possible Targets. Vaccines 2022, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanueli, C.; Maestri, R.; Corradi, D.; Marchione, R.; Minasi, A.; Tozzi, M.G.; Salis, M.B.; Straino, S.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Olivetti, G.; et al. Dilated and failing cardiomyopathy in bradykinin B(2) receptor knockout mice. Circulation 1999, 100, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messadi-Laribi, E.; Griol-Charhbili, V.; Gaies, E.; Vincent, M.P.; Heudes, D.; Meneton, P.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Richer, C. Cardioprotection and kallikrein-kinin system in acute myocardial ischaemia in mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, L.; Waeckel, L.; Vincent, M.P.; Chollet, C.; Gobeil, F., Jr.; Marre, M.; Bruneval, P.; Richer, C.; Roussel, R.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; et al. Selective kinin receptor agonists as cardioprotective agents in myocardial ischemia and diabetes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, D.; Walther, T.; Savvatis, K.; Escher, F.; Sobirey, M.; Riad, A.; Bader, M.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Tschope, C. Gene deletion of the kinin receptor B1 attenuates cardiac inflammation and fibrosis during the development of experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, W.L., Jr.; Hanson, W.L.; Waits, V.B. The influence of gonadectomy of host on parasitemia and mortality of mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Parasitol. 1975, 61, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorraro, F.; Cabrera, W.H.; Ribeiro, O.G.; Jensen, J.R.; De Franco, M.; Ibanez, O.M.; Starobinas, N. Trypanosoma cruzi infection in genetically selected mouse lines: Genetic linkage with quantitative trait locus controlling antibody response. Mediators. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 952857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, K.L.; Tarleton, R.L. Rapid quantitation of Trypanosoma cruzi in host tissue by real-time PCR. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 129, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Gomes-Neto, J.F.; Barbosa, C.D.; Granato, A.; Reis, B.S.; Santos, B.M.; Fucs, R.; Canto, F.B.; Nakaya, H.I.; Nobrega, A.; et al. Crucial role for T cell-intrinsic IL-18R-MyD88 signaling in cognate immune response to intracellular parasite infection. eLife 2017, 6, e30883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.D.; Canto, F.B.; Gomes, A.; Brandao, L.M.; Lima, J.R.; Melo, G.A.; Granato, A.; Neves, E.G.A.; Dutra, W.O.; Oliveira, A.C.; et al. Cytotoxic CD4(+) T cells driven by T-cell intrinsic IL-18R/MyD88 signaling predominantly infiltrate Trypanosoma cruzi-infected hearts. eLife 2022, 11, e74636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, B.; Gabra, B.H.; Sirois, P. Inhibitory effect of a novel bradykinin B1 receptor antagonist, R-954, on enhanced vascular permeability in type 1 diabetic mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 80, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; de Alencar, B.C.; Tzelepis, F.; Klezewsky, W.; da Silva, R.N.; Neves, F.S.; Cavalcanti, G.S.; Boscardin, S.; Nunes, M.P.; Santiago, M.F.; et al. Impaired innate immunity in Tlr4(-/-) mice but preserved CD8+ T cell responses against Trypanosoma cruzi in Tlr4-, Tlr2-, Tlr9- or Myd88-deficient mice. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.R.; Abreu, R.D.S.; Vilar-Pereira, G.; Degrave, W.; Meuser-Batista, M.; Ferreira, N.V.C.; da Cruz Moreira, O.; da Silva Gomes, N.L.; Mello de Souza, E.; Ramos, I.P.; et al. TGF-beta inhibitor therapy decreases fibrosis and stimulates cardiac improvement in a pre-clinical study of chronic Chagas’ heart disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfstein, J.; Schmitz, V.; Morandi, V.; Capella, M.M.; Lima, A.P.; Morrot, A.; Juliano, L.; Muller-Esterl, W. Host cell invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi is potentiated by activation of bradykinin B(2) receptors. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorov, A.G.; Andrade, D.; Pesquero, J.B.; Araujo Rde, C.; Bader, M.; Stewart, J.; Gera, L.; Muller-Esterl, W.; Morandi, V.; Goldenberg, R.C.; et al. Trypanosoma cruzi induces edematogenic responses in mice and invades cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells in vitro by activating distinct kinin receptor (B1/B2) subtypes. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.C.; Schmitz, V.; Svensjo, E.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Almeida, I.C.; Todorov, A.; de Arruda, L.B.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Pesquero, J.B.; Morrot, A.; et al. Cooperative activation of TLR2 and bradykinin B2 receptor is required for induction of type 1 immunity in a mouse model of subcutaneous infection by Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6325–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, C.N.; Medei, E.; Bozza, M.T. ROS and Trypanosoma cruzi: Fuel to infection, poison to the heart. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdos, E.G.; Tan, F.; Skidgel, R.A. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors are allosteric enhancers of kinin B1 and B2 receptor function. Hypertension 2010, 55, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanueli, C.; Bonaria Salis, M.; Stacca, T.; Pintus, G.; Kirchmair, R.; Isner, J.M.; Pinna, A.; Gaspa, L.; Regoli, D.; Cayla, C.; et al. Targeting kinin B(1) receptor for therapeutic neovascularization. Circulation 2002, 105, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.V.; Segatto, M.; Menezes, Z.; Macedo, A.M.; Gelape, C.; de Oliveira Andrade, L.; Nagajyothi, F.; Scherer, P.E.; Teixeira, M.M.; Tanowitz, H.B. Evidence for Trypanosoma cruzi in adipose tissue in human chronic Chagas disease. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, V.M.; Goncalves-Zillo, T.; Castoldi, A.; Burgos, M.; Branquinho, J.; Batista, C.; Oliveira, V.; Silva, E.; Castro, C.H.M.; Camara, N.; et al. Kinin B(1) Receptor Acts in Adipose Tissue to Control Fat Distribution in a Cell-Nonautonomous Manner. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, A.R.; Soto, J.; Olsen, C.D.; Pires, K.M.; Schell, J.C.; Larrieu-Lahargue, F.; Litwin, S.E.; Kakoki, M.; Takahashi, N.; Smithies, O.; et al. Loss of bradykinin signaling does not accelerate the development of cardiac dysfunction in type 1 diabetic akita mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3536–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, J.S.; Wang, K.; Engman, D.M. Captopril ameliorates myocarditis in acute experimental Chagas disease. Circulation 2003, 107, 2264–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll-Palhares, K.; Silverio, J.C.; Silva, A.A.; Michailowsky, V.; Marino, A.P.; Silva, N.M.; Carvalho, C.M.; Pinto, L.M.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Lannes-Vieira, J. TNF/TNFR1 signaling up-regulates CCR5 expression by CD8+ T lymphocytes and promotes heart tissue damage during Trypanosoma cruzi infection: Beneficial effects of TNF-alpha blockade. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2008, 103, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisimura, L.M.; Ferreira, R.R.; Coelho, L.L.; Souza, E.M.; Gonzaga, B.M.; Ferrao, P.M.; Waghabi, M.C.; Mesquita, L.B.; Pereira, M.C.S.; Moreira, O.D.C.; et al. Increased angiogenesis parallels cardiac tissue remodelling in experimental acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2022, 117, e220005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, I.R.; Vilar-Pereira, G.; Marques, V.; da Silva, A.A.; Caetano, B.; Moreira, O.C.; Machado, A.V.; Bruna-Romero, O.; Rodrigues, M.M.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; et al. A human type 5 adenovirus-based Trypanosoma cruzi therapeutic vaccine re-programs immune response and reverses chronic cardiomyopathy. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, I.R.; Vilar-Pereira, G.; Silva, A.A.; Moreira, O.C.; Britto, C.; Sarmento, E.D.; Lannes-Vieira, J. Tumor necrosis factor is a therapeutic target for immunological unbalance and cardiac abnormalities in chronic experimental Chagas’ heart disease. Mediators. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 798078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Pereira, G.; Castano Barrios, L.; Silva, A.A.D.; Martins Batista, A.; Resende Pereira, I.; Cruz Moreira, O.; Britto, C.; Mata Dos Santos, H.A.; Lannes-Vieira, J. Memory impairment in chronic experimental Chagas disease: Benznidazole therapy reversed cognitive deficit in association with reduction of parasite load and oxidative stress in the nervous tissue. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Kaneshiro, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Azumi, T.; Iwasaki, H. Negative dromotropic effect of diazepam on the AV node of dog heart in situ. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1979, 241, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, M.A.; Ferreira, L.R.P.; Teixeira, P.C.; Moretti, A.I.S.; Santos, R.H.B.; Frade, A.F.; Kuramoto, A.; Debbas, V.; Benvenuti, L.A.; Gaiotto, F.A.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 and 9 Enzymatic Activities are Selectively Increased in the Myocardium of Chronic Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy Patients: Role of TIMPs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 836242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, F.R.; Lalu, M.M.; Mariano, F.S.; Milanezi, C.M.; Cena, J.; Gerlach, R.F.; Santos, J.E.; Torres-Duenas, D.; Cunha, F.Q.; Schulz, R.; et al. Increased activities of cardiac matrix metalloproteinases matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 are associated with mortality during the acute phase of experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, A.C.; Vicentino, A.R.R.; Andrade, D.; Pereira, I.R.; Saboia-Vahia, L.; Moreira, O.d.C.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Mota, J.B.d.; Maciel, L.; Vilar-Pereira, G.; et al. Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082888
Oliveira AC, Vicentino ARR, Andrade D, Pereira IR, Saboia-Vahia L, Moreira OdC, Carvalho-Pinto CE, Mota JBd, Maciel L, Vilar-Pereira G, et al. Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082888
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Ana Carolina, Amanda Roberta Revoredo Vicentino, Daniele Andrade, Isabela Resende Pereira, Leonardo Saboia-Vahia, Otacílio da Cruz Moreira, Carla Eponina Carvalho-Pinto, Julia Barbalho da Mota, Leonardo Maciel, Glaucia Vilar-Pereira, and et al. 2023. "Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082888
APA StyleOliveira, A. C., Vicentino, A. R. R., Andrade, D., Pereira, I. R., Saboia-Vahia, L., Moreira, O. d. C., Carvalho-Pinto, C. E., Mota, J. B. d., Maciel, L., Vilar-Pereira, G., Pesquero, J. B., Lannes-Vieira, J., Sirois, P., Campos de Carvalho, A. C., & Scharfstein, J. (2023). Genetic Ablation and Pharmacological Blockade of Bradykinin B1 Receptor Unveiled a Detrimental Role for the Kinin System in Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082888








