White-Matter Lesions and Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow Evaluation by 3D Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI in Asymptomatic Divers: Correlation with Patent Foramen Ovale Ocurrence
Abstract
1. Introduction and Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Cerebral Magnetic Resonance
3. Data Analysis
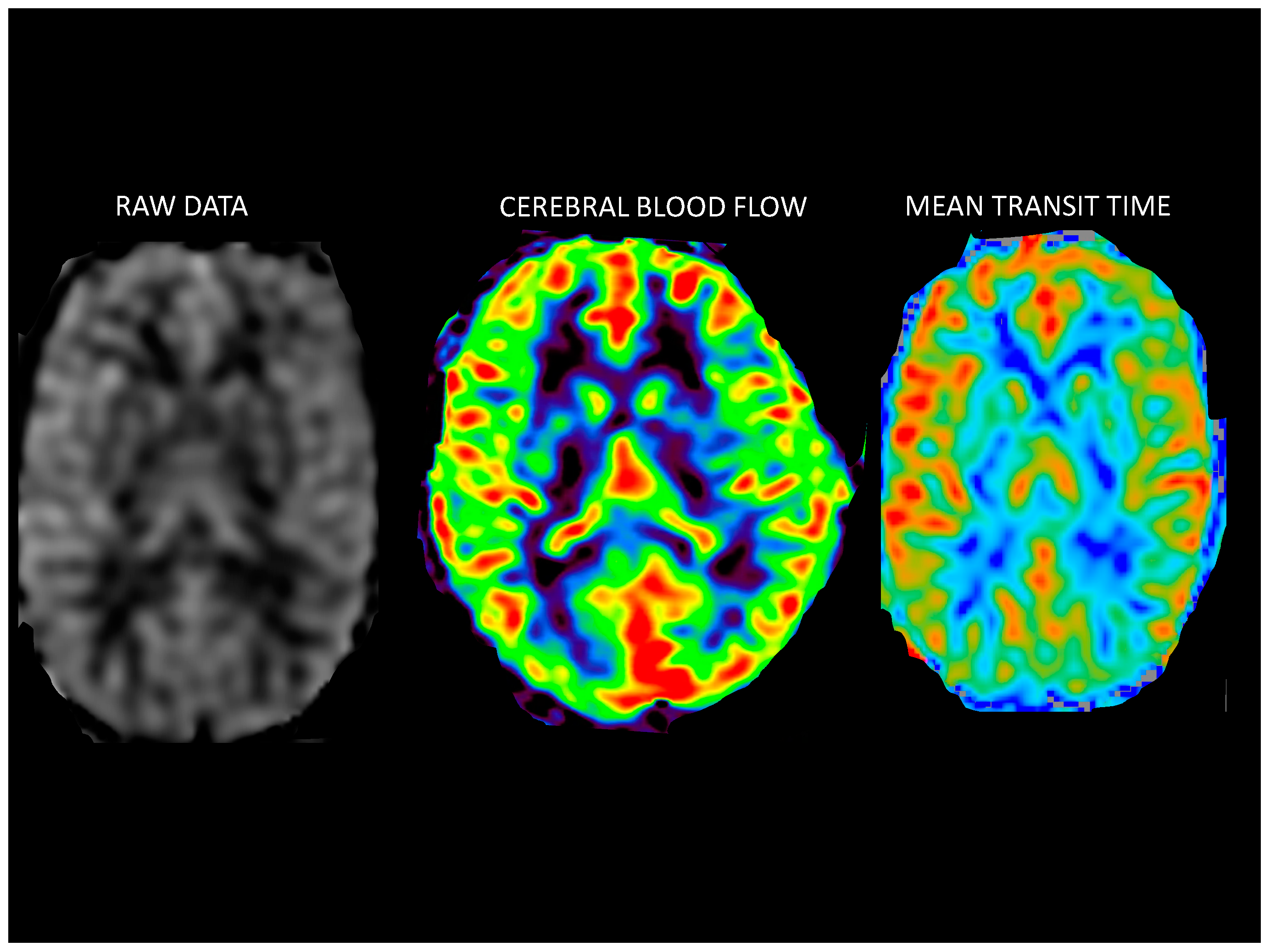
Postprocessing
4. Results
4.1. Population
4.2. Patent Foramen Ovale and White-Matter Brain Lesions
4.3. Measurement of Cerebral Blood Flow Using 3D-pASL
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A4C | Apical 4-Chamber |
| BAT | Bolus arrival time |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| CMR | Cerebral magnetic resonance |
| CRF | Cardiovascular risk factors |
| CV | Cerebral volume |
| CWML | Cerebral white-matter lesions |
| FL | Frontal lobe |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| FOV | Field of view |
| FSE | Fast spin echo |
| PFO | Patent foramen ovale |
| ROI | Regions of interest |
| SCUBA | Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus |
| TE | Time echo |
| TR | Time repetition |
| UBOs | Unidentified bright brain objects |
| 3D-ASL | Three-dimensional arterial spin labeling |
| 3D-SPGR | Three-dimensional spoiled gradient recalled acquisition in steady state |
References
- Hagen, P.T.; Scholz, D.G.; Edwards, W.D. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: An autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1984, 59, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerut, E.K.; Norfleet, W.T.; Plotnick, G.D.; Giles, T.D. Patent foramen ovale: A review of associated conditions and the impact of physiological size. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauth, M.; Rica, S.; Pohimann, S.; Kerby, T.; Forsting, M.; Daffertshofer, M.; Hennerici, M.; Sartor, K. Cohort study of multiple brain lesions in sport divers: Role of a patent foramen ovale. BMJ 1997, 314, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balestra, C.; Marroni, A.; Farkas, B.; Peetrons, P.; Vanderschueren, F.; Duboc, E.; Snoeck, T.; Germonpre, P. The fractal approach as a tool to understand asymptomatic brain hyperintense MRI signals. Fractals 2004, 12, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinck, P.A.; Svihus, R.; de Francisco, P. MR imaging of the central nervous system in divers. J. Magn Reson. Imaging 1991, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, C.; Germonpré, P. Correlation between patent Foramen Ovale, cerebral “lesions” and neuropsychometric testing in experienced sports divers: Does diving damage the brain? Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hopkins, R.O.; Beck, C.J.; Burnett, D.L.; Weaver, L.K.; Victoroff, J.; Bigler, E.D. Prevalence of white matter hyperintensities in a young healthy population. J. Neuroimaging 2006, 16, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylikoski, A.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Raininko, R.; Sarna, S.; Sulkava, R.; Tilvis, R. White matter hyperintensities on MRI in the neurologically nondiseased elderly. Analysis of cohorts of consecutive subjects aged 55 to 85 years living at home. Stroke 1995, 26, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, E.; Mortensen, E.L.; Krabbe, K.; Rostrup, E.; Larsson, H.B. Relation between age-related decline in intelligence and cerebral white-matter hyperintensities in healthy octogenarians: A longitudinal study. Lancet 2000, 356, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Markus, H.S. The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 341, c3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbert, L.C.; Howieson, D.B.; Dodge, H.; Kaye, J.A. Cognitive impairment risk: White matter hyperintensity progression matters. Neurology 2009, 73, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbert, L.C.; Nelson, C.; Howieson, D.B.; Moore, M.M.; Kaye, J.A. Impact of white matter hyperintensity volume progression on rate of cognitive and motor decline. Neurology 2008, 71, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erten-Lyons, D.; Woltjer, R.; Kaye, J.; Mattek, N.; Dodge, H.H.; Green, S.; Tran, H.; Howieson, D.B.; Wild, K.; Silbert, L.C. Neuropathologic basis of white matter hyperintensity accumulation with advanced age. Neurology 2013, 81, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.C.; Detre, J.A.; Golay, X.; Günther, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Lu, H.; MacIntosh, B.J.; Parkes, L.M.; Smits, M.; et al. Recommended Implementation of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI for Clinical Applications: A Consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the European Consortium for ASL in Dementia. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambach, S.; Smith, M.; Morris, P.P.; Campeau, N.G.; Ho, M. Arterial Spin Labeling Applications in Pediatric and Adult Neurologic Disorders. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 698–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, M.; Uetani, H. Arterial Spin Labeling for Pediatric Central Nervous System Diseases: Techniques and Clinical Applications. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2023, 22, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Holdsworth, S.J.; Fan, A.P.; Lebel, M.R.; Zun, Z.; Shankaranarayanan, A.; Zaharchuk, G. Comparing accuracy and reproducibility of sequential and Hadamard-encoded multidelay pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling for measuring cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy subjects: A simulation and in vivo study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.M.; Chan, S.T.; Mazumder, D.; Tamborini, D.; Stephens, K.A.; Deng, B.; Farzam, P.; Chu, J.Y.; Franceschini, M.A.; Qu, J.Z.; et al. Improved accuracy of cerebral blood flow quantification in the presence of systemic physiology cross-talk using multi-layer Monte Carlo modeling. Neurophotonics 2021, 8, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; Petr, J.; Groot, P.; Vandemaele, P.; Ingala, S.; Robertson, A.D.; Václavů, L.; Groote, I.; Kuijf, H.; Zelaya, F.; et al. ExploreASL: An image processing pipeline for multi-center ASL perfusion MRI studies. Neuroimage 2020, 219, 117031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Takei, N.; Ueyama, T.; Miyawaki, S.; Koizumi, S.; Kato, S.; Takao, H.; Abe, O.; Saito, N. Arterial Transit Time-Based Multidelay Combination Strategy Improves Arterial Spin Labeling Cerebral Blood Flow Measurement Accuracy in Severe Steno-Occlusive Diseases. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T.; Bolar, D.S.; Achten, E.; Barkhof, F.; Bastos-Leite, A.J.; Detre, J.A.; Golay, X.; Günther, M.; Wang, D.J.J.; Haller, S.; et al. Current state and guidance on arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in clinical neuroimaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 2024–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promjunyakul, N.; Lahna, D.; Kaye, J.A.; Dodge, H.H.; Erten-Lyons, D.; Rooney, W.D.; Silbert, L.C. Characterizing the white matter hyperintensity penumbra with cerebral blood flow measures. Neuro Image Clin. 2015, 8, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slosman, D.O.; De Ribaupierre, S.; Chicherio, C.; Ludwig, C.; Montandon, M.L.; Allaoua, M.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C.; Grousset, A.; Mayer, E.; et al. Negative neurofunctional effects of frequency, depth and environment in recreational scuba diving: The Geneva “memory” dive study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honěk, J.; Šefc, L.; Honěk, T.; Šrámek, M.; Horváth, M.; Veselka, J. Patent Foramen Ovale in Recreational and Professional Divers: An Important and Largely Unrecognized Problem. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerzmann, M.; Seiler, C.; Lipp, E.; Guzman, R.; Lövblad, K.O.; Kraus, M.; Kucher, N. Relation between directly detected patent foramen ovale and ischemic brain lesions in sport divers. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, J.; Jung, A.; Thron, A.; Weis, J.; Willmes, K. Central nervous system lesions and cervical disc herniations in amateur divers. Lancet 1995, 345, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todnem, K.; Nyland, H.; Skeidsvol, H.L. Neurological long term consequences of deep diving. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1991, 48, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, P.; Keil, R.; Bartsch, T.; Tetzlaff, K.; Reuter, M.; Hutzelmann, A.; Friege, L.; Meyer, T.; Bettinghausen, E.; Deuschl, G. Neurologic outcome of controlled compressed-air diving. Neurology 2000, 55, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, S.E.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Koudstaal, P.J. Silent brain infarcts: A systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2007, 6, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, S.E.; Prins, N.D.; den Heijer, T.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M. Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, G.; Specht, K.; Taxt, T.; Sundal, E.; Grønning, M.; Thorsen, E.; Troland, K.; Irgens; Grüner, R. Cerebral diffusion and perfusion deficits in North Sea divers. Acta Radiol. 2010, 51, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickman, A.M.; Zahra, A.; Muraskin, J.; Steffener, J.; Holland, C.M.; Habeck, C.; Borogovac, A.; Ramos, M.A.; Brown, T.R.; Asllani, I.; et al. Reduction in cerebral blood flow in areas appearing as white matter hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 172, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernbaum, M.; Menon, B.K.; Fick, G.; Smith, E.E.; Goyal, M.; Frayne, R.; Coutts, S.B. Reduced blood flow in normal white matter predicts development of leukoaraiosis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, P.; Fletcher, E.; Harvey, D.; Carmichael, S.T.; Reed, B.; Mungas, D.; DeCarli, C. White matter hyperintensity penumbra. Stroke 2011, 42, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Stafford, R.B.; Wang, Z.; Arnold, S.E.; Wolk, D.A.; Detre, J.A. Microvascular Perfusion Based on Arterial Spin Labeled Perfusion MRI as a Measure of Vascular Risk in Alzheimer′s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 32, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Ma, L. Test–retest reliability of perfusion of the precentral cortex and precentral subcortical white matter on three-dimensional pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3788–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gordon, M.L.; Ma, Y. The Age-Related Perfusion Pattern Measured with Arterial Spin Labeling MRI in Healthy Subjects. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yan, L.; Jann, K.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Pfeuffer, J.; Qian, T.; Wang, D.J.J. Cerebral hemodynamic and white matter changes of type 2 diabetes revealed by multi-TI Arterial Spin Labeling and double inversion recovery sequence. Front. Neurol. 2017, 22, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Reduced perfusion in normal-appearing white matter in mild to moderate hypertension as revealed by 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ors, F.; Sonmez, G.; Yildiz, S.; Uzun, G.; Senol, M.G.; Mutlu, H.; Saracoglu, M. Incidence of ischemic brain lesions in hyperbaric chamber inside attendants. Adv. Ther. 2006, 23, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, E.P. Central nervous system oxygen yoxicity and hyperbaric oxygen seizures. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2016, 87, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottestad, W.; Hansen, T.A.; Ksin, J.I. Hypobaric Decompression and White Matter Hyperintensities: An Evaluation of the NATO Standard. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2021, 92, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, D.M.; Lee, V.M. Odds Ratio Meta-Analysis and Increased Prevalence of White Matter Injury in Healthy Divers. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2015, 86, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairez, O.; Cournot, M.; Minville, V.; Roncalli, J.; Austruy, J.; Elbaz, M.; Galinier, M.; Carrié, D. Risk of neurological decompression sickness in the diver with a right-to-left shunt: Literature review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009, 19, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Saidel, G.M.; LaManna, J.C. Cerebral blood flow adaptation to chronic hypoxia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 614, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyama, Y.; Brian, J.E., Jr.; Todd, M.M. Plasma viscosity and cerebral blood flow. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H1949–H1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Divers | Control Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 45.8 ± 8.6 | 41 ± 15.2 |
| Male | 32/38 (84.2%) | 12/38 (63.2%) |
| Cardiovascular RF: | 0/19 (0%) | |
| -Hypertension | 6/38 (15.8%) | |
| -Dyslipidemia | 3/38 (7.9%) | |
| -Smoking | 8/38 (21.1%) | |
| Echocardiography: | N/A | |
| -Patent foramen ovale | 10/38 (26.3%) | |
| -Degree of PFO | ||
| <10 bubbles | 8/10 (80%) | |
| 10–20 bubbles | 1/10 (10%) | |
| >20 bubbles | 1/10 (10%) | |
| Number of dives | N/A | |
| <200 | 11/38 (28.9%) | |
| 200–500 | 12/38 (31.6%) | |
| 500–1000 | 4/38 (10.5%) | |
| >1000 | 11/38 (28.9%) | |
| Type of diving | N/A | |
| -Recreational | 22/38 (57.9%) | |
| -Professional | 16/38 (42.1%) | |
| MRI: | ||
| -Ischemic defects | 4/38 (10.5%) | 0/38 (0%) |
| -Virchow–Robin | 12/38 (31.6%) | 0/38 (0%) |
| -No findings | 22/38 (57.9%) | 38/38 (100%) |
| Divers (n = 38) Mean ± SD | Controls (n = 19) Mean ± SD | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 45.84 ± 8.58 | 41.05 ± 15.24 | 0.215 |
| CBF THALAMUS L | 38.91 ± 10.74 | 51.57 ± 9.79 | <0.001 |
| CBF THALAMUS R | 38.97 ± 9.69 | 51.57 ± 9.54 | <0.001 |
| CBF CAUDATE L | 34.35 ± 6.72 | 41.58 ± 5.8 | <0.001 |
| CBF CAUDATE R | 33.25 ± 7.18 | 42.15 ± 4.98 | <0.001 |
| CBF FIntL | 65.95 ± 11.62 | 75.79 ± 13.33 | 0.006 |
| CBF FIntR | 69.44 ± 13.06 | 79.05 ± 13.65 | 0.013 |
| CBF FLML | 58.25 ± 12.51 | 73.38 ± 15.21 | <0.001 |
| CBF FLMR | 56.88 ± 13.16 | 71.87 ± 13.58 | <0.001 |
| CBF LLFL | 59.04 ± 11.63 | 73.24 ± 13.49 | <0.001 |
| CBF RLFL | 59.83 ± 12.26 | 72.61 ± 11.41 | <0.001 |
| CBF ULFL | 53.79 ± 11.29 | 67.72 ± 15.3 | <0.001 |
| CBF URFL | 54.13 ± 11.9 | 67.31 ± 13.19 | <0.001 |
| TT URFL | 1353.59 ± 128.17 | 1339.77 ± 89.76 | 0.676 |
| TT ULFL | 1344.63 ± 145.44 | 1340.79 ± 81.96 | 0.915 |
| TT RLFL | 1263.81 ± 146.61 | 1249.69 ± 104.41 | 0.71 |
| TT LLFL | 1251.58 ± 139.16 | 1241.44 ± 84.27 | 0.772 |
| TT FLMR | 1452.69 ± 169.67 | 1400.69 ± 75.76 | 0.116 |
| TT FLML | 1454.68 ± 168.61 | 1383.85 ± 73.58 | 0.032 |
| TT FIntR | 1198.93 ± 87.99 | 1191.55 ± 88.16 | 0.767 |
| TTFIntL | 1208.42 ± 82.60 | 1181.89 ± 72.04 | 0.467 |
| TT CAUDATE R | 1220.75 ± 91.03 | 1188.55 ± 82.3 | 0.2 |
| TT CAUDATE L | 1210.77 ± 102.33 | 1187.33 ± 93.77 | 0.406 |
| TT THALAMUS R | 1297.75 ± 124.02 | 1290.8 ± 106.67 | 0.836 |
| TT THALAMUS L | 1299.42 ± 124.84 | 1290.83 ± 101.66 | 0.796 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabrera, J.Á.; Urmeneta Ulloa, J.; Jímenez de la Peña, M.; Rubio Alonso, M.; López Gavilán, M.; Bayona Horta, S.; Pizarro, G.; Simon, K.; Migoya, T.; Martínez de Vega, V. White-Matter Lesions and Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow Evaluation by 3D Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI in Asymptomatic Divers: Correlation with Patent Foramen Ovale Ocurrence. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082866
Cabrera JÁ, Urmeneta Ulloa J, Jímenez de la Peña M, Rubio Alonso M, López Gavilán M, Bayona Horta S, Pizarro G, Simon K, Migoya T, Martínez de Vega V. White-Matter Lesions and Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow Evaluation by 3D Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI in Asymptomatic Divers: Correlation with Patent Foramen Ovale Ocurrence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082866
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabrera, José Ángel, Javier Urmeneta Ulloa, Mar Jímenez de la Peña, Margarita Rubio Alonso, Miguel López Gavilán, Silvia Bayona Horta, Gonzalo Pizarro, Karlos Simon, Teresa Migoya, and Vicente Martínez de Vega. 2023. "White-Matter Lesions and Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow Evaluation by 3D Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI in Asymptomatic Divers: Correlation with Patent Foramen Ovale Ocurrence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082866
APA StyleCabrera, J. Á., Urmeneta Ulloa, J., Jímenez de la Peña, M., Rubio Alonso, M., López Gavilán, M., Bayona Horta, S., Pizarro, G., Simon, K., Migoya, T., & Martínez de Vega, V. (2023). White-Matter Lesions and Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow Evaluation by 3D Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI in Asymptomatic Divers: Correlation with Patent Foramen Ovale Ocurrence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2866. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082866







