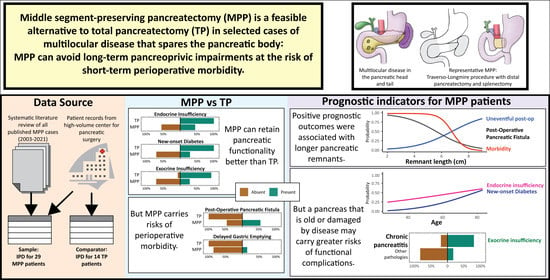
Middle Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy to Avoid Pancreatic Insufficiency: Individual Patient Data Analysis of All Published Cases from 2003–2021
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Quality Control and Risk of Bias
2.3. Extracted Data and Definitions
2.4. Outcomes and Analysis
2.4.1. Patient Baseline Characteristics
2.4.2. Surgical Resection and Intraoperative Outcomes
2.4.3. Postoperative Course
2.4.4. Long-Term Follow-Up and Survival
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review and Risk of Bias
3.2. Pre-Operative Baseline
3.3. Surgical Resections and Intraoperative Outcomes
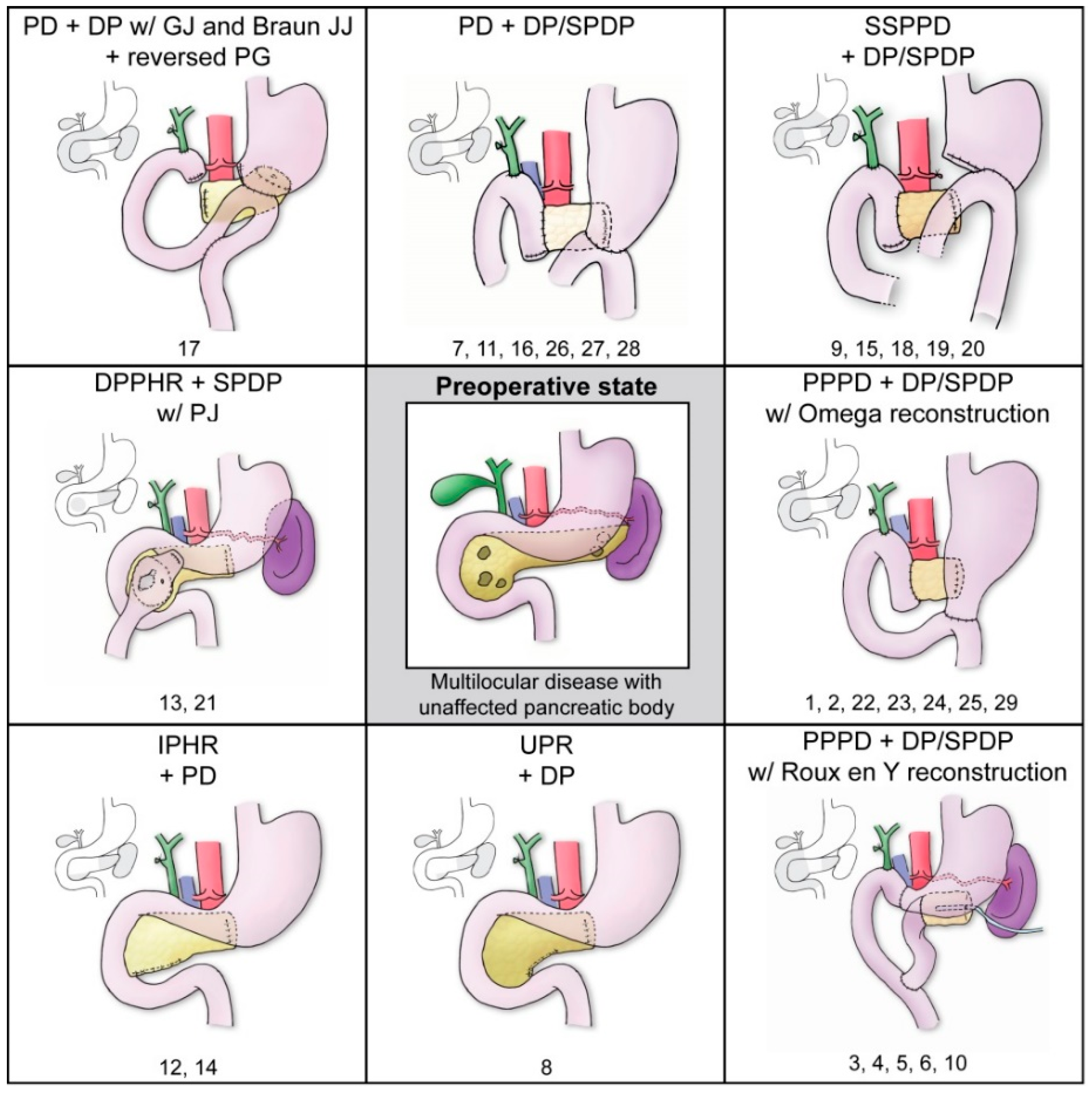
3.3.1. MPP Surgical Procedures
3.3.2. MPP Intraoperative Outcomes
3.3.3. Comparison of Intraoperative Outcomes with TP Patients
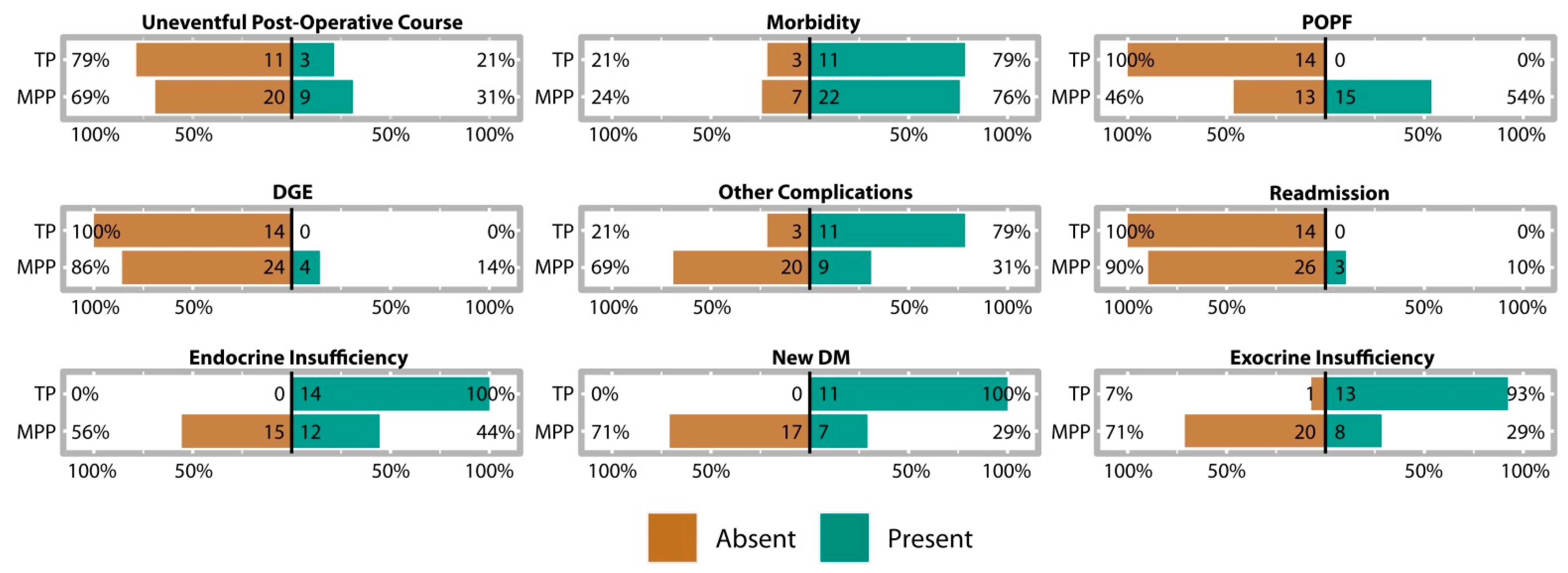
3.4. Postoperative Course and Complications
3.4.1. MPP Postoperative Outcomes
3.4.2. MPP Postoperative Pancreatic Function
3.4.3. Comparison of Postoperative Course with TP Patients
3.5. MPP Long-Term Follow-Up and Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| First Author | Primary Institution | Last Contact | Risk of Bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Score | |||
| Lloyd [18] | Methodist Hospital, Indianapolis | 8 November 2021 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Miura [29] | Teikyo University School of Medicine, Tokyo | 27 March 2019 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Low |
| Partelli [30] | University of Verona Hospital, Verona | 15 Decemeber 2020 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Low |
| Kitasato [31] | Nagasaki University Hospital, Nagasaki | 12 February 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Ohzato [32] | Sakai Municipal Hospital, Osaka | 7 January 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Sperti [33] | University of Padua Hospital, Padua | 7 January 2019 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Low |
| Chen [34] | The First People’s Hospital of Fo Shan, Guang Dong | 4 January 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Horiguchi [35] | Fujita Health University, Toyoake | 12 February 2019 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Low |
| Noda [36] | Saitama Medical Center, Saitama | 20 February 2019 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Low |
| Aryal [37] | Kagoshima University Hospital, Kagoshima | 15 February 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Nishi [38] | Ehime Prefectural Central Hospital, Matsuyama | 16 February 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Tanemura [40] | Mie University School of Medicine, Tsu | 24 February 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Usui [41] | Mie University School of Medicine, Tsu | 12 February 2019 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Lu [42] | First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Jiangsu | 2 February 2019 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Low |
| Addeo [45] | Hôpital de Hautepierre-Strasbourg University Hospital, Strasbourg | 2 February 2021 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Nitta [46] | Shizuoka Cancer Center, Shizuoka | 6 Decemeber 2020 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
| Iguchi [47] | Saiseikai Fukuoka General Hospital, Fukuoka | 31 January 2022 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Moderate |
Appendix B
| Factor | MPP | TP | Statistic | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Age ± SE | 59.97 ± 3.17 | 63.07 ± 2.76 | t38.68 = 0.74 | 0.465 |
| ASA° ≤ 2 | 18 (62%) | 9 (64%) | χ21 = 0.02 | 0.888 |
| ASA° > 2 | 11 (38%) | 5 (36%) | ||
| Female | 15 (52%) | 9 (64%) | χ21 = 0.60 | 0.437 |
| Male | 14 (48%) | 5 (36%) | ||
| Neoplastic | 12 (41%) | 8 (57%) | Fisher’s | 0.065 |
| Synchronous | 10 (34%) | 3 (21%) | ||
| Metastatic | 6 (21%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Non-Neoplastic | 1 (3%) | 3 (2%) | ||
| Diabetic | 5 (17%) | 3 (21%) | Fisher’s | 1.000 |
| Non-Diabetic | 24 (83%) | 11 (79%) |
| MPP | TP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathology | Head | Tail | Total | Head | Tail | Total |
| AC | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BD-IPMN | 5 | 4 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| CC | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CP | 1 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| IPMN | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCA | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD-IPMN | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| dBDC | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| mDFSP | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| mPCC | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| mRC | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| mRCC | 3 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MT-IPMN | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 13 |
| PDAC | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PNEN | 7 | 7 | 14 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Retention Cyst | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SCA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| SPN | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Response | Factor | All Surgeries | Multi-Visceral Excluded | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F-Value | p-Value | df | F-Value | p-Value | ||
| Log operation time (log min) * | Surgery Type | 1 | 31.99 | <0.001 | 1 | 27.19 | <0.001 |
| Age Group | 1 | 5.01 | 0.031 | 1 | 6.41 | 0.016 | |
| ASA° | 1 | 1.07 | 0.307 | 1 | 0.92 | 0.344 | |
| Sex | 1 | 0.73 | 0.398 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.849 | |
| Residuals | 38 | 33 | |||||
| Blood loss (mL) † | Surgery Type | 1 | 0.09 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.700 |
| Age Group | 1 | 0.97 | 0.331 | 1 | 0.14 | 0.708 | |
| ASA° | 1 | 6.36 | 0.017 | 1 | 5.78 | 0.023 | |
| Sex | 1 | 1.77 | 0.193 | 1 | 2.17 | 0.152 | |
| Residuals | 33 | 28 | |||||
| Remnant length (cm) ‡ | Surgery Type | 1 | 2.43 | 0.129 | 1 | 2.82 | 0.105 |
| Age Group | 1 | 0.49 | 0.488 | 1 | 1.09 | 0.306 | |
| ASA° | 1 | 0.03 | 0.853 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.847 | |
| Sex | 1 | 1.78 | 0.192 | 1 | 2.06 | 0.163 | |
| Residuals | 32 | 26 | |||||
| Outcome | Selected Model | ΔAICc | χ2 | df | p | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of stay | Surgical outcomes | −10.3 | 18.99 | 21, 24 | <0.001 | 0.53 |
| Uneventful course | Surgical outcomes | +0.9 | 6.88 | 21, 24 | 0.076 | 0.33 |
| Uneventful course | Pathological dignity | +1.0 | 1.41 | 23, 24 | 0.235 | 0.08 |
| Morbidity | Surgical outcomes | −10.1 | 17.97 | 21, 24 | <0.001 | 0.74 |
| POPF | Surgical outcomes | −2.1 | 9.99 | * 20, 23 | 0.019 | 0.45 |
| DGE | Null | 0.0 | ||||
| Other complications | Null | 0.0 | ||||
| Readmission | Surgical outcomes | −2.7 | 10.54 | 21, 24 | 0.015 | 0.66 |
| Endocrine insufficiency | Patient characteristics | +1.3 | 6.73 | * 19, 22 | 0.081 | 0.34 |
| New-onset DM | Patient characteristics | +1.2 | 7.10 | * 17, 20 | 0.069 | 0.40 |
| New-onset DM | Pathological dignity | +1.6 | 0.87 | * 19, 20 | 0.350 | 0.06 |
| Exocrine insufficiency | Pathological dignity | −3.2 | 5.61 | * 22, 23 | 0.018 | 0.29 |
| Exocrine insufficiency † | Surgical outcomes | +0.1 | 8.53 | * 15, 18 | 0.036 | 0.56 |
| Predictor | Outcome | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Endocrine insufficiency | 2.78 (1.02–10.35) | 1.79 | 0.074 |
| New-onset DM | 6.22 (1.44–76.29) | 1.91 | 0.056 | |
| ASA° | Endocrine insufficiency | 0.10 (0.01–1.06) | −1.76 | 0.078 |
| New-onset DM | 0.15 (0.01–1.87) | −1.37 | 0.171 | |
| Sex | Endocrine insufficiency | 1.10 (0.12–9.10) | 0.09 | 0.927 |
| New-onset DM | 0.57 (0.03–6.61) | −0.43 | 0.666 |
| Predictor | Outcome | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation time | Length of stay | 1.36 (1.09–1.72) | 2.60 | 0.009 |
| Uneventful course | 1.09 (0.35–3.26) | 0.16 | 0.875 | |
| Morbidity | 0.75 (0.05–11.90) | −0.24 | 0.813 | |
| POPF | 1.23 (0.45–3.85) | 0.40 | 0.689 | |
| Readmission | 0.15 (0.00–2.26) | −0.91 | 0.366 | |
| Exocrine insufficiency * | 0.05 (0.00–1.15) | −1.15 | 0.248 | |
| Blood loss | Length of stay | 1.33 (1.02–1.75) | 2.25 | 0.025 |
| Uneventful course | 0.57 (0.15–1.65) | −0.99 | 0.323 | |
| Morbidity | 1.25 (0.22–6.57) | 0.29 | 0.775 | |
| POPF | 2.20 (0.75–8.14) | 1.37 | 0.171 | |
| Readmission | 22.32 (0.83–>100) | 1.17 | 0.243 | |
| Exocrine insufficiency * | 0.38 (0.00–7.64) | −0.52 | 0.606 | |
| Remnant length | Length of stay | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | −1.60 | 0.111 |
| Uneventful course | 2.73 (0.94–10.67) | 1.67 | 0.096 | |
| Morbidity | 0.03 (0.00–0.26) | −2.26 | 0.024 | |
| POPF | 0.28 (0.05–0.98) | −1.77 | 0.077 | |
| Readmission | 0.03 (0.00–0.69) | −1.25 | 0.210 | |
| Exocrine insufficiency * | 2.38 (0.30–36.70) | 0.73 | 0.466 |
| Pathological Dignity | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | z-Value | p-Value |
| Exocrine insufficiency | 0.11 (0.01–0.70) | −2.20 | 0.028 |
| Outcome (Model) | Factor | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of stay (negative binomial) χ238, 42 = 25.41, p < 0.001, r2 = 0.45 | Surgery Type | 2.02 (1.40–2.88) | 3.82 | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.40 (1.15–1.68) | 3.68 | <0.001 | |
| ASA° | 1.24 (0.88–1.77) | 1.20 | 0.232 | |
| Sex | 0.74 (0.53–1.03) | −1.77 | 0.076 | |
| Uneventful stay (logistic regression) χ238, 42 = 5.13, p = 0.274, r2 = 0.16 | Surgery Type | 1.30 (0.28–7.18) | 0.33 | 0.744 |
| Age | 0.47 (0.21–0.95) | −2.00 | 0.045 | |
| ASA° | 1.31 (0.26–6.49) | 0.33 | 0.738 | |
| Sex | 1.52 (0.35–6.72) | 0.57 | 0.571 | |
| Morbidity (logistic regression) χ238, 42 = 2.04, p = 0.728, r2 = 0.07 | Surgery Type | 1.03 (0.19–4.94) | 0.04 | 0.972 |
| Age | 1.32 (0.62–2.81) | 0.74 | 0.462 | |
| ASA° | 1.20 (0.24–6.77) | 0.22 | 0.829 | |
| Sex | 0.43 (0.09–1.84) | −1.13 | 0.258 | |
| Other complications (logistic regression) χ238, 42 = 9.14, p = 0.058, r2 = 0.26 | Surgery Type | 0.13 (0.02–0.53) | −2.67 | 0.008 |
| Age | 1.12 (0.56–2.37) | 0.31 | 0.753 | |
| ASA° | 0.77 (0.17–3.35) | −0.35 | 0.726 | |
| Sex | 0.84 (0.21–3.38) | −0.25 | 0.802 | |
| Exocrine insufficiency * (logistic regression) χ237, 41 = 19.50, p < 0.001, r2 = 0.50 | Surgery Type | 0.02 (0.00–0.17) | −3.17 | 0.002 |
| Age | 0.79 (0.37–1.67) | −0.64 | 0.523 | |
| ASA° | 0.42 (0.05–2.63) | −0.90 | 0.367 | |
| Sex | 1.22 (0.24–6.69) | 0.24 | 0.812 |
| Patient 12 | Patient 15 | Patient 17 | Patient 19 | Patient 22 | Patient 23 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study ID | 8 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 14 |
| Age | 69 | 83 | 80 | 67 | 81 | 48 |
| Sex | m | m | f | m | f | m |
| ASA° | ≤2 | >2 | >2 | >2 | ≤2 | ≤2 |
| Indication | Neoplasia | Synchronous | Synchronous | Metastatic | Metastatic | Metastatic |
| Dignity of Pancreatic Disease | Malignant (splenic lymphoma) * | Malignant (dBDC) | Malignant (dBDC) | Malignant (mRC) | Malignant (mRCC) | Malignant (mDFSP) |
| DFS (months) | 0 | 110 | 51 | 0 | NA | NA |
| PFS (months) | NA | NA | NA | 3 | NA | NA |
| Local Recurrence | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Malignancy Recurrence | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OS (months) | 16 | 110 | 58 | 36 | 41.3 | 8.7 |
| Cause of Death | Malignant lymphoma | Cerebral infarction | Recurrent dBDC | Disease progression | Malignancy progressed to diffuse metastases | Malignancy progressed to diffuse metastases |
References
- Rockey, E.W. Total Pancreatectomy for Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 1943, 118, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, S.; Tamburrino, D.; Partelli, S.; Salvia, R.; Germenia, S.; Bassi, C.; Pederzoli, P.; Falconi, M. Total pancreatectomy: Indications, different timing, and perioperative and long-term outcomes. Surgery 2011, 149, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, W.; Gluth, A.; Hinz, U.; Bergmann, F.; Spronk, P.E.R.; Hackert, T.; Werner, J.; Büchler, M.W. Total pancreatectomy for primary pancreatic neoplasms: Renaissance of an unpopular operation. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latenstein, A.E.J.; Scholten, L.; Al-Saffar, H.A.; Björnsson, B.; Butturini, G.; Capretti, G.; Chatzizacharias, N.A.; Dervenis, C.; Frigerio, I.; Gallagher, T.K.; et al. Clinical Outcomes after Total Pancreatectomy. Ann. Surg. 2020, 276, e536–e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchegiani, G.; Perri, G.; Burelli, A.; Zoccatelli, F.; Andrianello, S.; Luchini, C.; Donadello, K.; Bassi, C.; Salvia, R. High-risk Pancreatic Anastomosis vs. Total Pancreatectomy after Pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann. Surg. 2021, 276, e905–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; König, A.-K.; von Winkler, N.; Mehrabi, A.; Berchtold, C.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; Schneider, M.; Hoffmann, K.; Kulu, Y.; Feisst, M.; et al. Completion Pancreatectomy After Pancreatoduodenectomy: Who Needs It? Ann. Surg. 2022, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wente, M.N.; Veit, J.A.; Bassi, C.; Dervenis, C.; Fingerhut, A.; Gouma, D.J.; Izbicki, J.R.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Padbury, R.T.; Sarr, M.G.; et al. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH)-An International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery 2007, 142, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, M.; Al-Saeedi, M.; Hinz, U.; Mehrabi, A.; Schneider, M.; Berchtold, C.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; Schmidt, T.; Kulu, Y.; Hoffmann, K.; et al. Categorization of Differing Types of Total Pancreatectomy. JAMA Surg. 2022, 157, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, S.; Oehme, F.; Tahirukaj, E.; Kolbinger, F.R.; Müssle, B.; Welsch, T.; Weitz, J.; Distler, M. More is More? Total Pancreatectomy for Periampullary Cancer as an Alternative in Patients with High-Risk Pancreatic Anastomosis: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 8309–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maker, A.V.; Sheikh, R.; Bhagia, V. Perioperative management of endocrine insufficiency after total pancreatectomy for neoplasia. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchegiani, G.; Ballarin, R.; Malleo, G.; Andrianello, S.; Allegrini, V.; Pulvirenti, A.; Paini, M.; Secchettin, E.; Boriero, F.; Di Benedetto, F.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of Pancreatic Texture Using a Durometer: A New Tool to Predict the Risk of Developing a Postoperative Fistula. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 2876–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willens, D.; Cripps, R.; Wilson, A.; Wolff, K.; Rothman, R. Interdisciplinary Team Care for Diabetic Patients by Primary Care Physicians, Advanced Practice Nurses, and Clinical Pharmacists. Clin. Diabetes 2011, 29, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, H.G.; Mayer, B.; Vasilescu, C.; Poch, B. Long-term Metabolic Morbidity and Steatohepatosis Following Standard Pancreatic Resections and Parenchyma-sparing, Local Extirpations for Benign Tumor: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomir, M.P.; Sabo, A.A.; Petrescu, G.E.D.; Li, Y.; Dumitrascu, T. Central pancreatectomy: A comprehensive, up-to-date meta-analysis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2019, 404, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrini, O.; Schmidt, C.M.; Pitt, H.A.; Guiramand, J.; Aguilar-Saavedra, J.R.; Aboudi, S.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Delpero, J.R. Side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreatic head/uncinate: Resection or enucleation? Hpb 2011, 13, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J.; Alhalabi, K.T.; Hinz, U.; Mayer, P.; Tjaden, C.; Büchler, M.W.; Hackert, T.; Loos, M. Enucleation for low-grade branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Long-term follow-up. Surgery 2022, 172, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siassi, M.; Klein, P.; Hohenberger, W. Organ-preserving surgery for multicentric carcinoma of the pancreas. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1999, 25, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, F.P., Jr.; Kang, J. Multifocal paillary-cystic neoplasm of the pancreas. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2003, 95, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Lambert, P.C.; Abo-Zaid, G. Meta-analysis of individual participant data: Rationale, conduct, and reporting. BMJ 2010, 340, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 2020–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.A.; Clarke, M.; Rovers, M.; Riley, R.D.; Simmonds, M.; Stewart, G.; Tierney, J.F. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data: The PRISMA-IPD statement. JAMA–J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2015, 313, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology: A Proposal for Reporting–Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) Group B. JAMA Neurol. 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkum, E.; Klotz, R.; Seide, S.; Hüttner, F.J.; Kowalewski, K.F.; Nickel, F.; Khajeh, E.; Knebel, P.; Diener, M.K.; Probst, P. Systematic reviews in surgery—Recommendations from the Study Center of the German Society of Surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.H.; Sultan, S.; Haffar, S.; Bazerbachi, F. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. Evid. Based Med. 2018, 23, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dripps, R.D.; Lamont, A.; Eckenhoff, J.E. The role of anesthesia in surgical mortality. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1961, 178, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, E.E.; Simon, M.; Vinta, S.R.; Zehm, C.F.; Shabot, S.M.; Minhajuddin, A.; Abouleish, A.E. Adding Examples to the ASA-Physical Status Classification Improves Correct Assignment to Patients. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouleish, A.E.; Leib, M.L.; Cohen, N.H. ASA Provides Examples to Each ASA Physical Status Class. ASA Newsl. 2015, 79, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, F.; Takada, T.; Amano, H.; Yoshida, M.; Toyota, N.; Wada, K. Middle-Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2007, 204, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.C.; Hsu, J.T.; Chen, H.Y.; Jwo, S.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Jan, Y.Y.; Yeh, C.N. Multifocal intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas-A case report. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partelli, S.; Boninsegna, L.; Salvia, R.; Bassi, C.; Pederzoli, P.; Falconi, M. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy for multicentric body-sparing lesions of the pancreas. Am. J. Surg. 2009, 198, e49–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitasato, A.; Tajima, Y.; Kuroki, T.K.; Tsutsumi, R.; Tsuneoka, N.; Adachi, T.; Mishima, T.; Kanematsu, T.K. Limited pancreatectomy for metastatic pancreatic tumors from renal cell carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2010, 57, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohzato, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Fukunaga, M.; Imamura, H.; Furukawa, H. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy for multifocal metastatic renal cell carcinoma located in the head, body and tail of the pancreas. A case report. J. Pancreas 2010, 11, 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Sperti, C.; Polizzi, M.L.; Moro, M.; Beltrame, V.; Pedrazzoli, S. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy: An interesting procedure for pancreas-sparing resection. J. Pancreas 2010, 11, 258–261. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.W.; Wang, F.J.; Lai, E.C.H.; Lau, W.Y. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy for synchronous ampullary carcinoma and solid-pseudopapillary tumor of distal pancreas. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2011, 2, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, A.; Ishihara, S.; Ito, M.; Asano, Y.; Furusawa, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Miyakawa, S. Middle-segment-preserving pancreatectomy for biliary-pancreatic tumors. Surg. Tech. 2011, 58, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, H.; Kato, T.; Kamiyama, H.; Toyama, N.; Konishi, F. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy for advanced transverse colon cancer invading the duodenun and non-functioning endocrine tumor in the pancreatic tail. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 4, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, R.; Enami, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kusano, T.; Maeshiro, T.; Umekita, N.; Yakushiji, A. Simultaneous pancreaticoduodenectomy and distal pancreatectomy for 2 IPMNs in the head and the tail. Pancreas 2011, 40, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Shen, B.Y.; Peng, C.H.; Na, L.M.; Cheng, D.F. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy: Report of two cases and review of the literature. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, B.; Komokata, T.; Kadono, J.; Motodaka, H.; Shimamoto, Y.; Kitazono, I.; Nakazono, T.; Motoi, S.; Furoi, A.; Imoto, Y. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy with reversed pancreaticogastrostomy: Report of a case. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, M.; Kawasaki, H.; Fujii, M.; Nagahashi, M.; Obatake, M.; Shirai, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Harada, M. Middle-preserving pancreatectomy for multifocal intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: Report of a case. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshi, A.; Mitsuhiro, I.; Hiromitsu, A.; Naoyuki, Y.; Taiichiro, S.; Hiroki, S.; Takeaki, K.; Tatsuya, S.; Futoshi, O.; Hiroharu, S.; et al. Middle Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy for Recurrent Metastasis of Renal Cell Carcinoma after Pancreatoduodenectomy: A Case Report. Case Rep. Surg. 2014, 2014, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanemura, A.; Mizuno, S.; Okura, Y.; Inoue, H.; Takaki, H.; Nishimura, K.; Uchida, K.; Isaji, S. Margin-negative limited resection of metastatic pancreatic tumors from rectal cancer preoperatively diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsies: Report of two cases. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, M.; Kuriyama, N.; Uchida, K.; Kishiwada, M.; Mizuno, S.; Sakurai, H.; Tabata, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Isaji, S. Laparoscopy assisted middle-segment-preserving pancreatectomy for multiple pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Report of a case. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2014, 7, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yin, J.; Wei, J.; Dai, C.; Wu, J.; Gao, W.; Xu, Q.; Dai, H.; Li, Q.; Guo, F.; et al. Small amounts of tissue preserve pancreatic function: Long-term follow-up study of middle-segment preserving pancreatectomy. Medicine 2016, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Sugiura, T.; Okamura, Y.; Ito, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ashida, R.; Uesaka, K. Middle segment-preserving pancreatectomy for metachronous intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm after pancreatoduodenectomy: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 3, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patyutko, Y.; Kotelnikov, A.; Kriger, A.; Proskuryakov, I.; Galkin, G.; Polyakov, A.; Fainstein, I. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas: Experience of surgical treatment. Pirogov Russ. J. Surg. = Khirurgiya 2019, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addeo, P.; Julliard, O.; Imperiale, A.; Goichot, B.; Bachellier, P. Middle-segment preserving pancreatectomy for multifocal neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 35, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Okamura, Y.; Ito, T.; Ashida, R.; Ohgi, K.; Otsuka, S.; Sasaki, K.; Uesaka, K. Middle segment-preserving pancreatectomy for multifocal pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma located in the head and tail of the pancreas: A case report. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 2020, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, T.; Iseda, N.; Hirose, K.; Ninomiya, M.; Honboh, T.; Maeda, T.; Sawada, F.; Tachibana, Y.; Akashi, T.; Sekiguchi, N.; et al. Indocyanine green fluorescence to ensure perfusion in middle segment-preserving pancreatectomy: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.J.; Blanco, G.; Webber, J.; Marudanayagam, R.; Sutcliffe, R.P.; Muiesan, P.; Bramhall, S.R.; Isaac, J.; Mirza, D.F. How severe is diabetes after total pancreatectomy? A case-matched analysis. Hpb 2014, 16, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struyvenberg, M.R.; Fong, Z.V.; Martin, C.R.; Tseng, J.F.; Clancy, T.E.; Fernández-Del Castillo, C.; Tillman, H.J.; Bellin, M.D.; Freedman, S.D. Impact of Treatments on Diabetic Control and Gastrointestinal Symptoms after Total Pancreatectomy. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulvirenti, A.; Pea, A.; Rezaee, N.; Gasparini, C.; Malleo, G.; Weiss, M.J.; Cameron, J.L.; Wolfgang, C.L.; He, J.; Salvia, R. Perioperative outcomes and long-term quality of life after total pancreatectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2019, 106, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholten, L.; Stoop, T.F.; Del Chiaro, M.; Busch, O.R.; van Eijck, C.; Molenaar, I.Q.; de Vries, J.H.; Besselink, M.G. Systematic review of functional outcome and quality of life after total pancreatectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2019, 106, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoop, T.F.; Ateeb, Z.; Ghorbani, P.; Scholten, L.; Arnelo, U.; Besselink, M.G.; Del Chiaro, M. Impact of Endocrine and Exocrine Insufficiency on Quality of Life After Total Pancreatectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleo, G.; Pulvirenti, A.; Marchegiani, G.; Butturini, G.; Salvia, R.; Bassi, C. Diagnosis and management of postoperative pancreatic fistula. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2014, 399, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, C.; Marchegiani, G.; Dervenis, C.; Sarr, M.; Abu Hilal, M.; Adham, M.; Allen, P.; Andersson, R.; Asbun, H.J.; Besselink, M.G.; et al. The 2016 update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 Years After. Surgery 2017, 161, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wente, M.N.; Bassi, C.; Dervenis, C.; Fingerhut, A.; Gouma, D.J.; Izbicki, J.R.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Padbury, R.T.; Sarr, M.G.; Traverso, L.W.; et al. Delayed gastric emptying (DGE) after pancreatic surgery: A suggested definition by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS). Surgery 2007, 142, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ref. | Study ID | First Author | Year | Country | Indication | Pathological Dignity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | NA | * Siassi | 1999 | Germany | NA | NA |
| [18] | 1 | Lloyd | 2003 | USA | Neoplasia | Benign |
| [29] | 2 | † Miura | 2007 | Japan | Synchronous | Malignant |
| [30] | NA | ‡ Chiang | 2009 | Taiwan | NA | NA |
| [31] | 3 | Partelli | 2009 | Italy | Neoplasia | Benign |
| Neoplasia | Benign | |||||
| Neoplasia | Malignant | |||||
| Synchronous | Benign | |||||
| Synchronous | Benign | |||||
| [32] | 4 | Kitasato | 2010 | Japan | Metastatic | Malignant |
| [33] | 5 | Ohzato | 2010 | Japan | Metastatic | Malignant |
| [34] | 6 | Sperti | 2010 | Italy | Synchronous | Benign |
| [35] | 7 | Chen | 2011 | China | Synchronous | Malignant |
| [36] | 8 | Horiguchi | 2011 | Japan | Neoplasia | Malignant |
| Neoplasia | Malignant | |||||
| Neoplasia | Malignant | |||||
| Synchronous | Malignant | |||||
| [37] | 9 | Noda | 2011 | Japan | Synchronous | Malignant |
| [38] | NA | ‡ Otani | 2011 | Japan | NA | NA |
| [39] | NA | ‡ Cheng | 2013 | China | NA | NA |
| [40] | 10 | Aryal | 2014 | Japan | Synchronous | Malignant |
| [41] | 11 | Nishi | 2014 | Japan | Neoplasia | Benign |
| [42] | NA | * Takeshi | 2014 | Japan | NA | NA |
| [43] | 12 | Tanemura | 2014 | Japan | Metastatic | Malignant |
| [44] | 13 | Usui | 2014 | Japan | Neoplasia | Benign |
| [45] | 14 | Lu | 2016 | China | Non-neoplastic | Benign |
| Neoplasia | Malignant | |||||
| Metastatic | Malignant | |||||
| Metastatic | Malignant | |||||
| Metastatic | Malignant | |||||
| [46] | NA | * Yamada | 2017 | Japan | NA | NA |
| [47] | NA | ‡ Patyutko | 2019 | Russia | NA | NA |
| [48] | 15 | Addeo | 2020 | France | Neoplasia | Malignant |
| [49] | 16 | Nitta | 2020 | Japan | Neoplasia | Malignant |
| [50] | 17 | Iguchi | 2021 | Japan | Synchronous | Malignant |
| NA | NA | NA | 2020 | Germany | Synchronous | Benign |
| DP | SPDP | Operation Time (min) | Blood Loss (mL) | Remnant Length (cm) | Remnant Volume (% Original) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | ||
| Proximal operation | Duodenum-preserving pancreatic head resection (Beger, Bern, Frey) | 0 (0%) | 2 (7%) | 506.5 ± 136.5 | 1110.0 ± 90.0 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 18.4 |
| Inferior pancreatic head resection | 1 (3%) | 1 (3%) | 454.0 ± 86.0 | 1160.0 ± 260.0 | NA | NA | |
| Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Kausch-Whipple procedure) | 6 (21%) | 1 (3%) | 512.6 ± 34.6 | 1440.7 ± 632.6 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 33.8 ± 4.0 | |
| Pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy (Traverso-Longmire procedure) | 9 (31%) | 3 (10%) | 378.8 ± 38.0 | 981.6 ± 431.0 | 5.7 ± 0.6 | 28.6 ± 3.7 | |
| Subtotal stomach-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy | 4 (14%) | 1 (3%) | 520.0 ± 48.0 | 885.8 ± 215.0 | 6.3 ± 0.7 | 33.4 ± 8.3 | |
| Uncinate process resection | 1 (3%) | 0 (0%) | 440.0 | 1720.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | |
| Surgical extent | Pancreas only | 17 (59%) | 6 (21%) | 430.3 ± 24.0 | 975.8 ± 215.4 | 5.9 ± 0.4 | 31.0 ± 3.2 |
| Multi-visceral | 4 (14%) | 2 (7%) | 533.2 ± 62.1 | 1685.0 ± 777.3 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 31.8 ± 4.7 |
| Survived | Died | Test | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indication: Metastatic | 1 (17%) | 3 (50%) | Fisher’s | 0.351 |
| Indication: Neoplasms | 4 (67%) | 1 (17%) | ||
| Indication: Synchronous | 1 (17%) | 2 (33%) | ||
| Dignity: Benign | 3 (50%) | 0 (0%) | Fisher’s | 0.182 |
| Dignity: Malignant | 3 (50%) | 6 (100%) | ||
| Malignancy recurrence: No | 6 (100%) | 2 (33%) | Fisher’s | 0.061 |
| Malignancy recurrence: Yes | 0 (0%) | 4 (67%) | ||
| ASA° ≤ 2 | 5 (83%) | 3 (50%) | Fisher’s | 0.546 |
| ASA° > 2 | 1 (17%) | 3 (50%) | ||
| Age | 56.0 ± 7.8 | 71.3 ± 5.4 | t8.88 = 1.61 | 0.141 |
| Operation time (min) | 462.2 ± 47.5 | 428.5 ± 65.7 | t9.10 = 0.42 | 0.688 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 630.0 ± 212.8 | 1575.8 ± 720.4 | t5.87 = 1.26 | 0.256 |
| Remnant length (cm) | 7.1 ± 0.6 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | t8.00 = 2.46 | 0.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pausch, T.M.; Liu, X.; Dincher, J.; Contin, P.; Cui, J.; Wei, J.; Heger, U.; Lang, M.; Tanaka, M.; Heap, S.; et al. Middle Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy to Avoid Pancreatic Insufficiency: Individual Patient Data Analysis of All Published Cases from 2003–2021. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052013
Pausch TM, Liu X, Dincher J, Contin P, Cui J, Wei J, Heger U, Lang M, Tanaka M, Heap S, et al. Middle Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy to Avoid Pancreatic Insufficiency: Individual Patient Data Analysis of All Published Cases from 2003–2021. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052013
Chicago/Turabian StylePausch, Thomas M., Xinchun Liu, Josefine Dincher, Pietro Contin, Jiaqu Cui, Jishu Wei, Ulrike Heger, Matthias Lang, Masayuki Tanaka, Stephen Heap, and et al. 2023. "Middle Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy to Avoid Pancreatic Insufficiency: Individual Patient Data Analysis of All Published Cases from 2003–2021" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052013
APA StylePausch, T. M., Liu, X., Dincher, J., Contin, P., Cui, J., Wei, J., Heger, U., Lang, M., Tanaka, M., Heap, S., Kaiser, J., Klotz, R., Probst, P., Miao, Y., & Hackert, T. (2023). Middle Segment-Preserving Pancreatectomy to Avoid Pancreatic Insufficiency: Individual Patient Data Analysis of All Published Cases from 2003–2021. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052013