Does PLEX® Elite 9000 OCT Identify and Characterize Most Posterior Pole Lesions in Highly Myopic Patients?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohno-Matsui, K. Pathologic Myopia: Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 5, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flitcroft, D.I.; He, M.; Jonas, J.B.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Rahi, J.; Resnikoff, S.; Vitale, S.; Yannuzzi, L. IMI—Defining and Classifying Myopia: A Proposed Set of Standards for Clinical and Epidemiologic Studies. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, M20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno-Matsui, K.; Wu, P.-C.; Yamashiro, K.; Vutipongsatorn, K.; Fang, Y.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Lai, T.Y.Y.; Ikuno, Y.; Cohen, S.Y.; Gaudric, A.; et al. IMI Pathologic Myopia. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Medrano, J.; Montero, J.A.; Flores-Moreno, I.; Arias, L.; García-Layana, A.; Ruiz-Moreno, J.M. Myopic maculopathy: Current status and proposal for a new classification and grading system (ATN). Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 69, 80–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaide, R.F. Staphyloma. Part 1. In Pathologic Myopia; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Curtin, B.J. The posterior staphyloma of pathologic myopia. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1977, 75, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Matsui, K. Proposed Classification of Posterior Staphylomas Based on Analyses of Eye Shape by Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Wide-Field Fundus Imaging. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, J.; Tapasztó, B.; Aclimandos, W.A.; Kestelyn, P.; Jonas, J.B.; De Faber, J.-T.H.N.; Januleviciene, I.; Grzybowsk, A.; Nagy, Z.Z.; Pärssinen, O. Update and guidance on management of myopia. European Society of Ophthalmology in cooperation with International Myopia Institute. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 853–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, B.J.; Karlin, D.B. Axial length measurements and fundus changes of the myopic eye I. the posterior fundus. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1970, 68, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, M.P.; Weiter, J.J.; Jalkh, A.E.; Trempe, C.L.; Pruett, R.C.; Schepens, C.L. Natural History of Choroidal Neovascularization in Degenerative Myopia. Ophthalmology 1984, 91, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno-Matsui, K.; Kawasaki, R.; Jonas, J.B.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Saw, S.-M.; Verhoeven, V.J.M.; Klaver, C.C.W.; Moriyama, M.; Shinohara, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; et al. International Photographic Classification and Grading System for Myopic Maculopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 159, 877–883.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, R.; Sivaprasad, S.; Han, L.T.; Mathew, R.; Kiousis, G.; Yang, Y. Myopic foveoschisis: A clinical review. Eye 2015, 29, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Fang, Y.; Jonas, J.B.; Du, R.; Shinohara, K.; Tanaka, N.; Yokoi, T.; Onishi, Y.; Uramoto, K.; Kamoi, K.; et al. Ridge-shaped macula in young myopic patients and its differentiation from typical dome-sahped macula in elderly myopic patients. Retina 2020, 40, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, M.; Kishi, S. Foveal retinoschisis and retinal detachment in severely myopic eyes with posterior staphyloma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 128, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuno, Y.; Jo, Y.; Hamasaki, T.; Tano, Y. Ocular Risk Factors for Choroidal Neovascularization in Pathologic Myopia. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveziel, N.; Yu, Y.; Reynolds, R.; Tai, A.; Meng, W.; Caillaux, V.; Calvas, P.; Rosner, B.; Malecaze, F.; Souied, E.H.; et al. Genetic Factors for Choroidal Neovascularization Associated with High Myopia. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyère, E.; Miere, A.; Cohen, S.Y.; Martiano, D.; Sikorav, A.; Popeanga, A.; Semoun, O.; Querques, G.; Souied, E.H. Neovascularization secondary to high myopia imaged by optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2017, 37, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, M.; Ooto, S.; Hata, M.; Yamashiro, K.; Tamura, H.; Akagi-Kurashige, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Ueda-Arakawa, N.; Takahashi, A.; Kuroda, Y.; et al. Detection of Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 165, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, A.; Liu, Z.; Young, C.A.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, G.; Zheng, D. Prevalence of myopic macular degeneration worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Fotouhi, A.; Yekta, A.; Pakzad, R.; Ostadimoghaddam, H.; Khabazkhoob, M. Global and regional estimates of prevalence of refractive errors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2018, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Gómez, C.; Fernández-Robredo, P.; Salinas-Alamán, Á.; Montañés, J.M.; Berasategui, J.M.E.; Guillén-Grima, F.; Ruiz-Moreno, J.M.; Garcia-Layana, A. Prevalence and Causes of Bilateral Blindness and Visual Impairment among Institutionalized Elderly People in Pamplona, Spain. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 20, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco-Martin, R.M.; Belani-Raju, M.; de la Fuente-Gomez, D.; Sanabria, M.R.; Fernández, I. Progression of myopic maculopathy in a Caucasian cohort of highly myopic patients with long follow-up: A multistate analysis. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruão, M.; Andreu-Fenoll, M.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Gallego-Pinazo, R. Prevalence of Different Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in a Spanish Cohort With High Myopia. J. Vitreoretin. Dis. 2017, 1, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Tham, Y.-C.; Cheung, C.Y.; Sidhartha, E.; Siantar, R.G.; Lim, S.-H.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheng, C.-Y. Factors affecting signal strength in spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witmer, M.T.; Margo, C.E.; Drucker, M. Tilted Optic Disks. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2010, 55, 403–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno-Matsui, K.; Akiba, M.; Moriyama, M. Macular pits and scleral dehiscence in highly myopic eyes with macular chorioretinal atrophy. Retin. Cases Brief Rep. 2013, 7, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.-H.; Yuan, M.-Z.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X. Macular Bruch’s membrane defects and other myopic lesions in high myopia. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 15, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, H.; Hajizadeh, F.; Riazi-Esfahani, M. Optical Coherence Tomographic Findings in Highly Myopic Eyes. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2010, 5, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Wei, L.; Zhang, K.; He, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, X. Cilioretinal Arteries in Highly Myopic Eyes: A Photographic Classification System and Its Association With Myopic Macular Degeneration. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 595544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiuyan, Z.; Qingmei, T.; Qiuxin, W.; Tailiang, L.; Jing, X.; Guodong, T.; Ting, Y.; Shasha, L.; Xi, C.; Chenying, Q.; et al. Thickness, vessel density of retina and choroid on OCTA in young adults (18–24 years old). Microvasc. Res. 2021, 136, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.W.; Baek, S.K.; Lee, Y.H. Repeatability of Manual Measurement of Foveal Avascular Zone Area in Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Images in High Myopia. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 34, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhu, D.; Ma, Q.; Ye, X.; Lu, F. Macular Thickness Profiles of Intraretinal Layers in Myopia Evaluated by Ultrahigh-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 53–61.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, U.C.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, B.H.; Oh, B.-L. Decreased choroidal and scleral thicknesses in highly myopic eyes with posterior staphyloma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.W.; Phua, V.; Lee, S.Y.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheung, C.M.G. Is Choroidal or Scleral Thickness Related to Myopic Macular Degeneration? Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruko, I.; Iida, T.; Sugano, Y.; Oyamada, H.; Akiba, M.; Sekiryu, T. Morphologic Analysis in Pathologic Myopia Using High-Penetration Optical Coherence Tomography. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Ito, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Kawano, K.; Terasaki, H. Scleral thickness in highly myopic eyes measured by enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography. Eye 2013, 27, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.S.H.; Cheong, K.X.; Lim, L.W.; Li, K.Z. Topographic variation of choroidal and retinal thicknesses at the macula in healthy adults. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarman, A.E.G.; Tedja, M.S.; Brussee, C.; Enthoven, C.A.; van Rijn, G.A.; Vingerling, J.R.; Keunen, J.E.E.; Boon, C.J.F.; Geerards, A.J.M.; Luyten, G.P.M.; et al. Prevalence of Myopic Macular Features in Dutch Individuals of European Ancestry With High Myopia. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022, 140, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, K.; Shimada, N.; Moriyama, M.; Yoshida, T.; Jonas, J.B.; Yoshimura, N.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Posterior Staphylomas in Pathologic Myopia Imaged by Widefield Optical Coherence Tomography. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisina, R.; Baldi, A.; Cesana, B.M.; Semeraro, F.; Parolini, B. Morphological and clinical characteristics of myopic posterior staphyloma in Caucasians. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fang, Y.; Uramoto, K.; Nagaoka, N.; Shinohara, K.; Yokoi, T.; Tanaka, N.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Clinical features of lacquer cracks in eyes with pathologic myopia. Retina 2019, 39, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Nagaoka, N.; Shinohara, K.; Onishi, Y.; Ishida, T.; Yoshida, T.; Xu, X.; Jonas, J.B.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Progression of Myopic Maculopathy during 18-Year Follow-up. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhu, Z.; Odouard, C.; Xiao, O.; Guo, X.; He, M. Wide-Field En Face Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Features of Extrafoveal Retinoschisis in Highly Myopic Eyes. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Verma, S.; Azad, S.V.; Chawla, R.; Bhayana, A.A.; Surve, A.; Vohra, R.; Venkatesh, P. Dome-shaped macula—Review of literature. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2021, 66, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Deng, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Luan, M.; Fan, Y.; Xiong, S.; et al. Design and Pilot data of the high myopia registration study: Shanghai Child and Adolescent Large-scale Eye Study (SCALE-HM). Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, e489–e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel Levin, M.; Freund, K.B.; Gunnemann, F.; Greaves, G.; Sadda, S.; Sarraf, D. Myopic macular pits: A case series with multimodal imaging. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, S0008418221003483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-da-Costa, P.; Falcão, M.; Carneiro, Â. Infrared Reflectance Pattern of Macular Pits in Pathologic Myopia. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, e1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, K.B. Peripapillary Detachment in Pathologic Myopia. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toranzo, J.; Cohen, S.Y.; Erginay, A.; Gaudric, A. Peripapillary Intrachoroidal Cavitation in Myopia. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, N. Characteristics of Peripapillary Detachment in Pathologic Myopia. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2006, 124, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.S.; Peng, X.Y.; Chen, C.X.; Xu, L.; Jonas, J.B. Peripapillary Intrachoroidal Cavitations. The Beijing Eye Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayanagi, K.; Ikuno, Y.; Gomi, F.; Tano, Y. Retinal vascular microfolds in highly myopic eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 139, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yokoi, T.; Shinohara, K.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Possible connection of short posterior ciliary arteries to choroidal neovascularisations in eyes with pathologic myopia. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querques, G.; Corvi, F.; Balaratnasingam, C.; Casalino, G.; Parodi, M.B.; Introini, U.; Freund, K.B.; Bandello, F. Lacquer Cracks and Perforating Scleral Vessels in Pathologic Myopia: A Possible Causal Relationship. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 759–766.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falavarjani, K.; Shenazandi, H.; Naseri, D.; Anvari, P.; Kazemi, P.; Aghamohammadi, F.; Alissmail, F.; Alemzadeh, S. Foveal avascular zone and vessel density in healthy subjects: An optical coherence tomography angiography study. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2018, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, D.; Ryu, G.; Sagong, M. Analysis of Foveal Microvascular Structures Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Age-stratified Healthy Koreans. J. Korean Ophthalmol. Soc. 2017, 58, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafe, N.A.; Phasukkijwatana, N.; Chen, X.; Sarraf, D. Retinal Capillary Density and Foveal Avascular Zone Area Are Age-Dependent: Quantitative Analysis Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, D.; Wu, A.; Wu, L. The foveal avascular zone area in healthy eyes measured by ocular coherence tomography angiography using a full spectrum probabilistic algorithm. Int. Ophthalmol. 2021, 41, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Lim, L.W.; Chow, V.S.; Chay, I.W.; Tan, S.; Cheong, K.X.; Tan, G.T.; Sadda, S.R. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Evaluation of the Parafoveal Vasculature and Its Relationship With Ocular Factors. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, OCT224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Dong, L.; Guo, Y.; Panda-Jonas, S. Advances in myopia research anatomical findings in highly myopic eyes. Eye Vis. 2020, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vurgese, S.; Panda-Jonas, S.; Jonas, J.B. Scleral Thickness in Human Eyes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Meng, J.; Wei, L.; Zhang, K.; He, W.; Lu, Y. Cilioretinal Arteries and Macular Vasculature in Highly Myopic Eyes. Ophthalmol. Retina 2020, 4, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
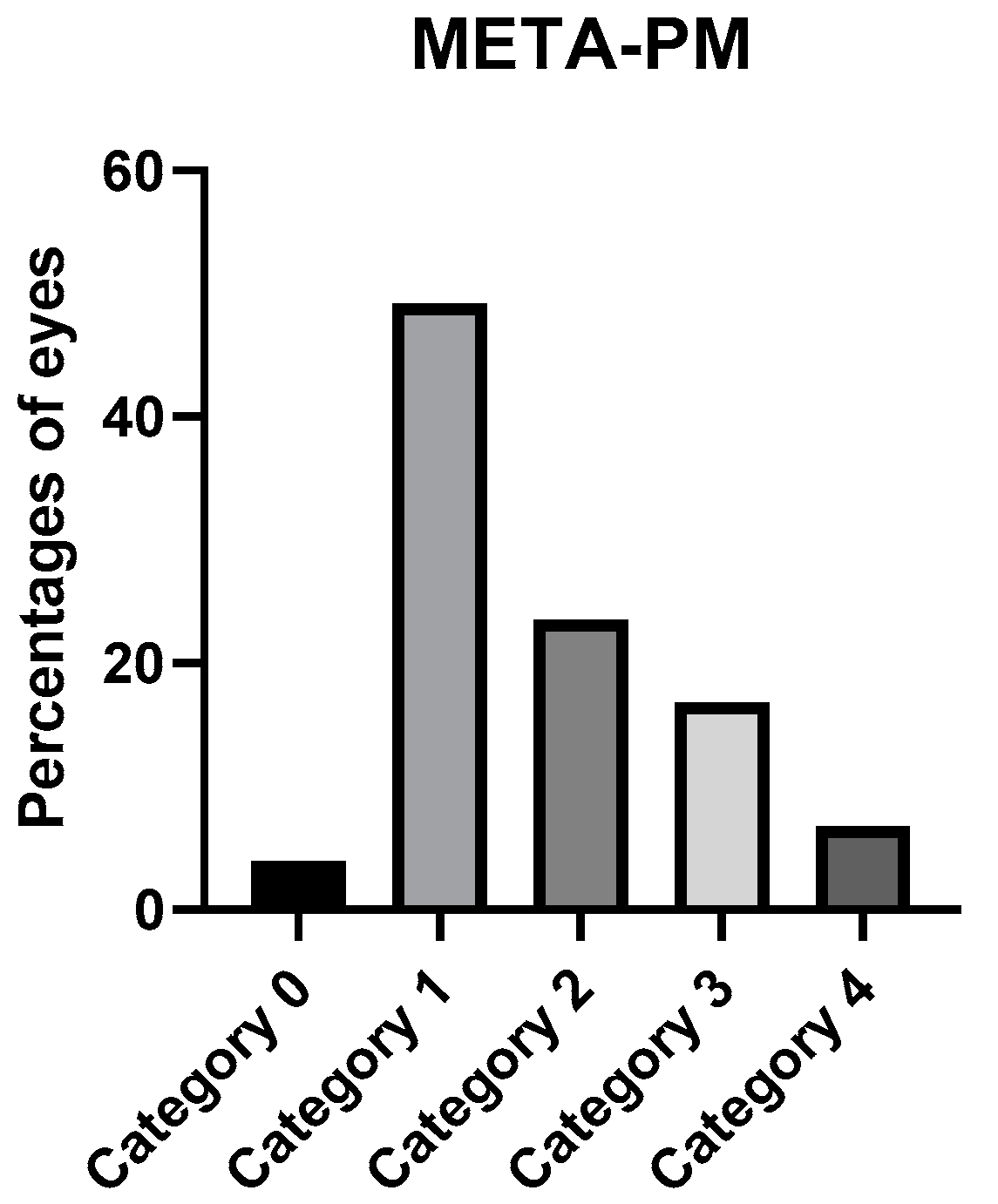
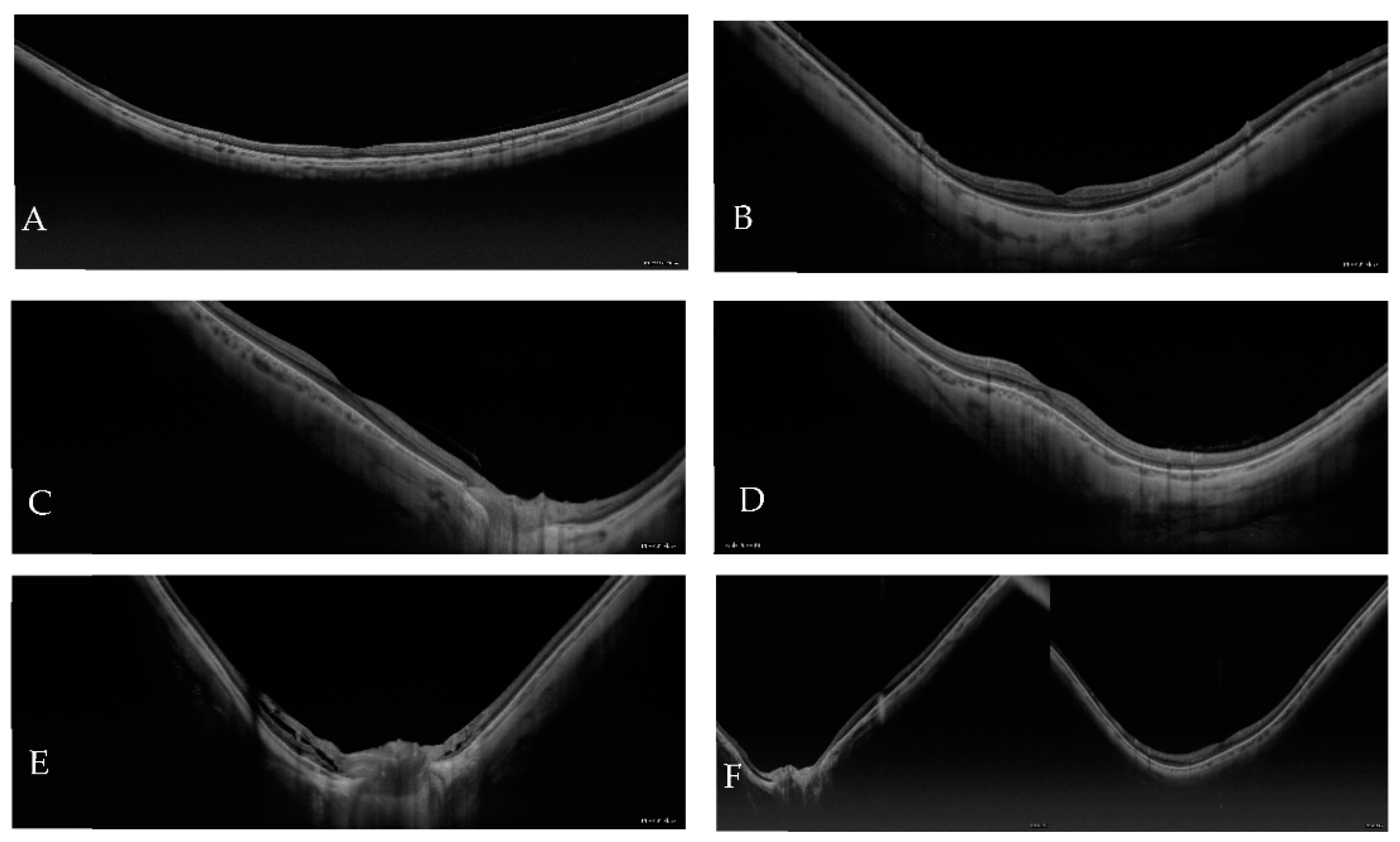
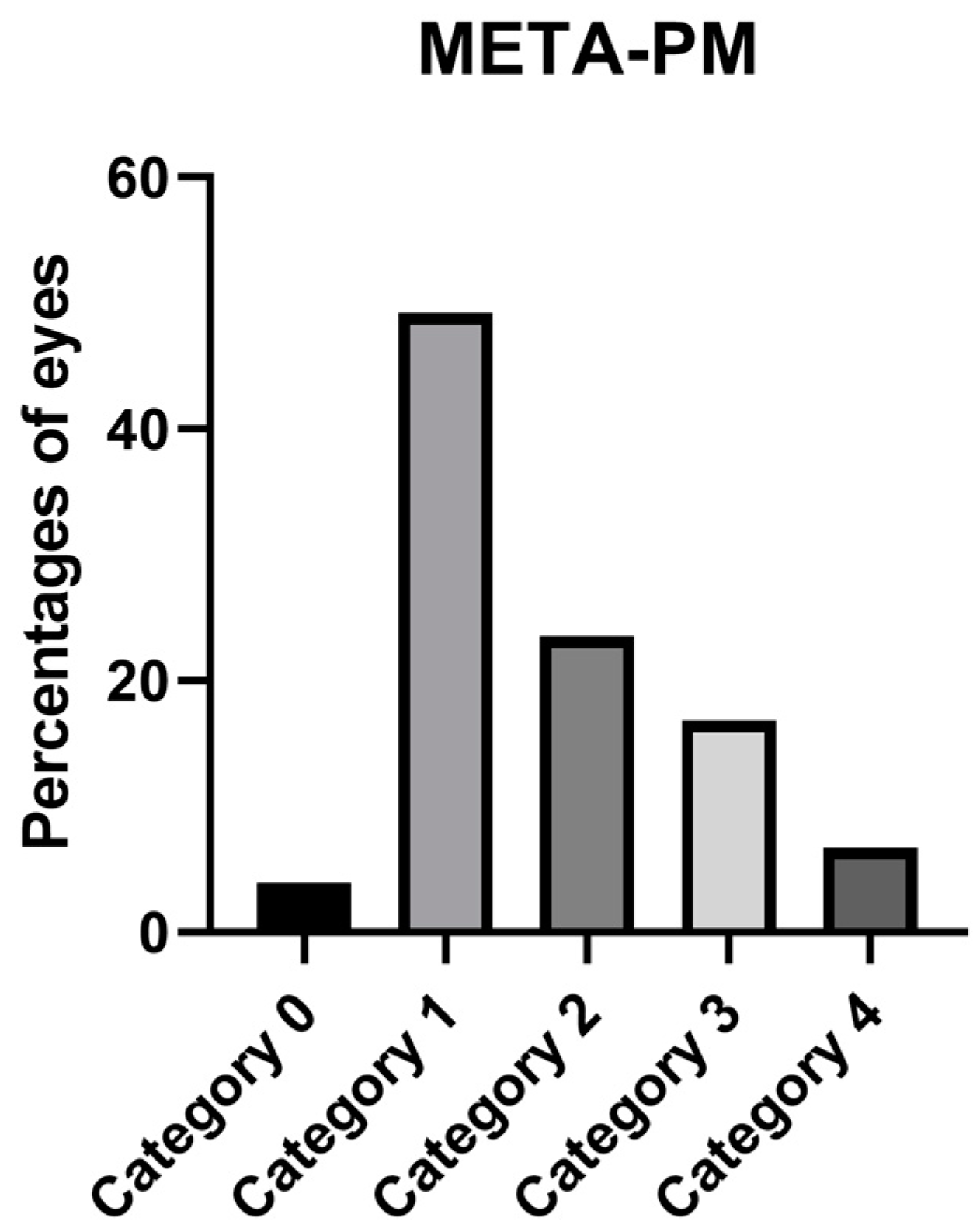
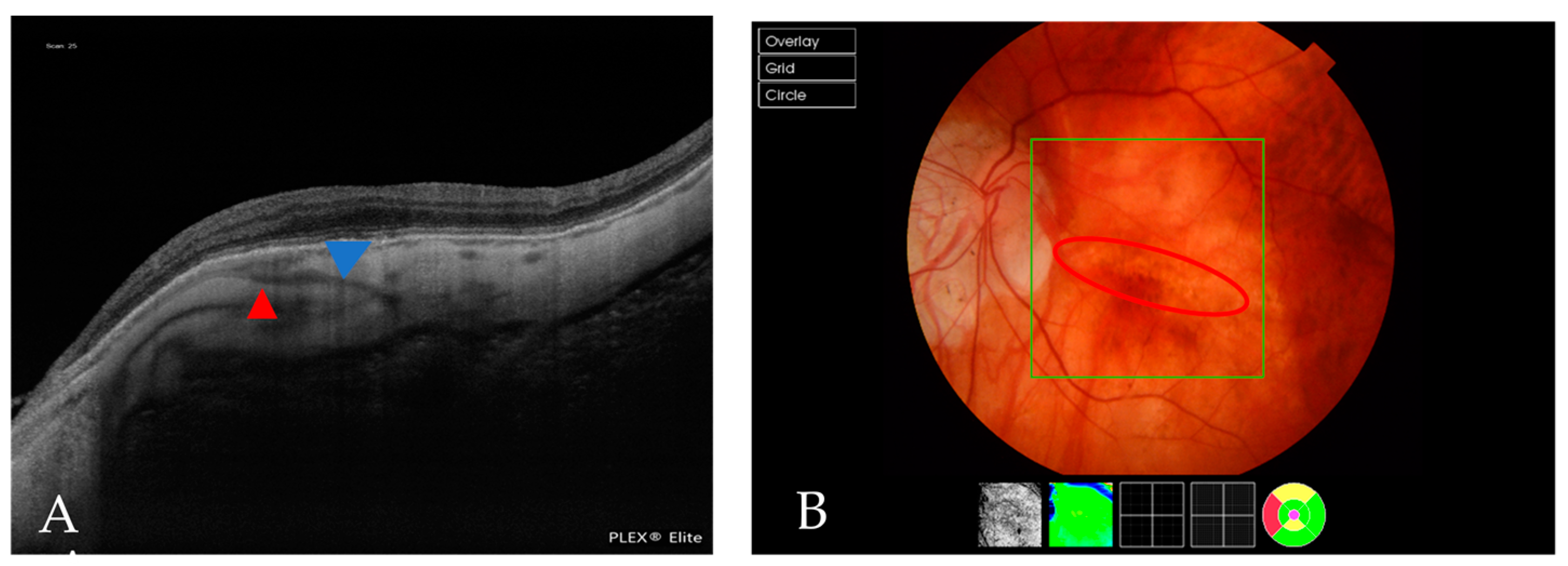
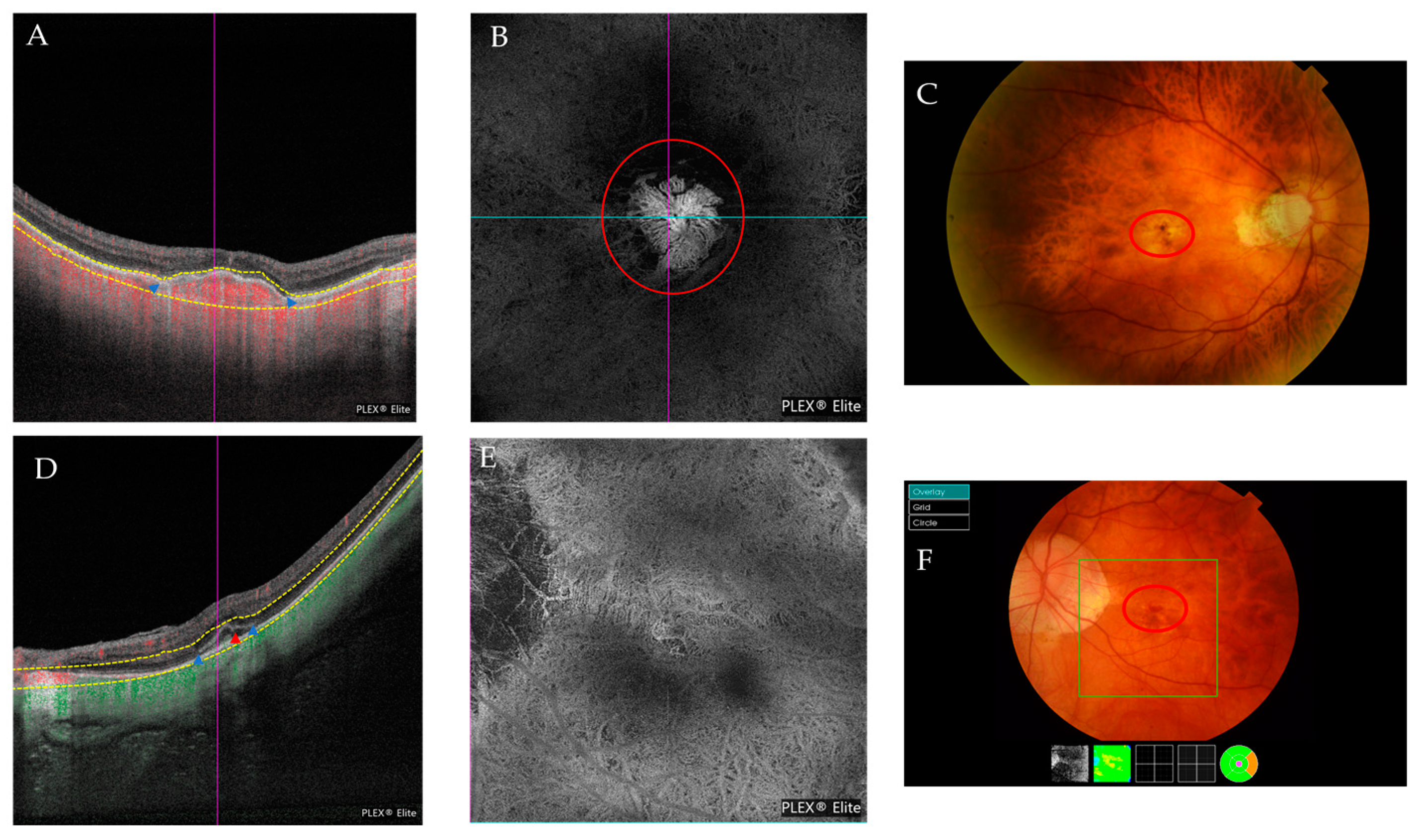
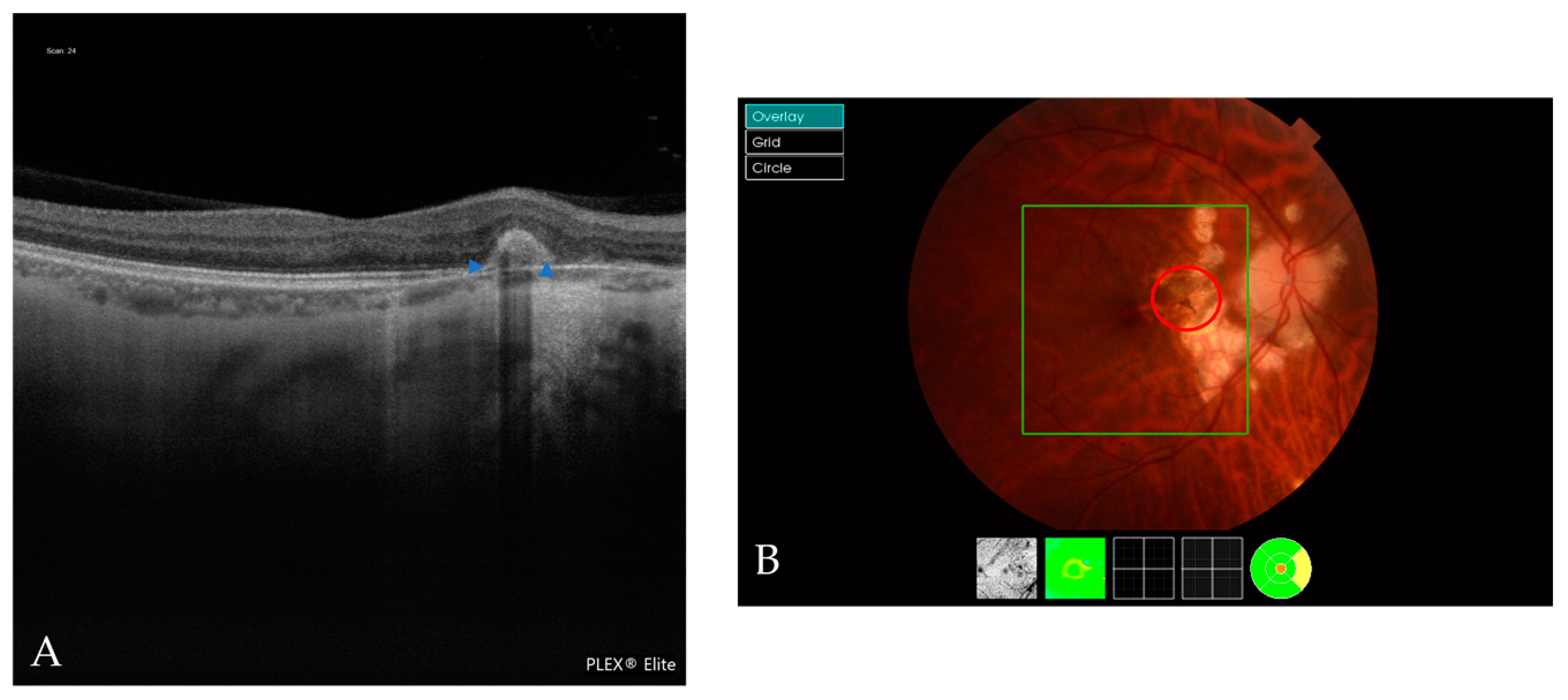
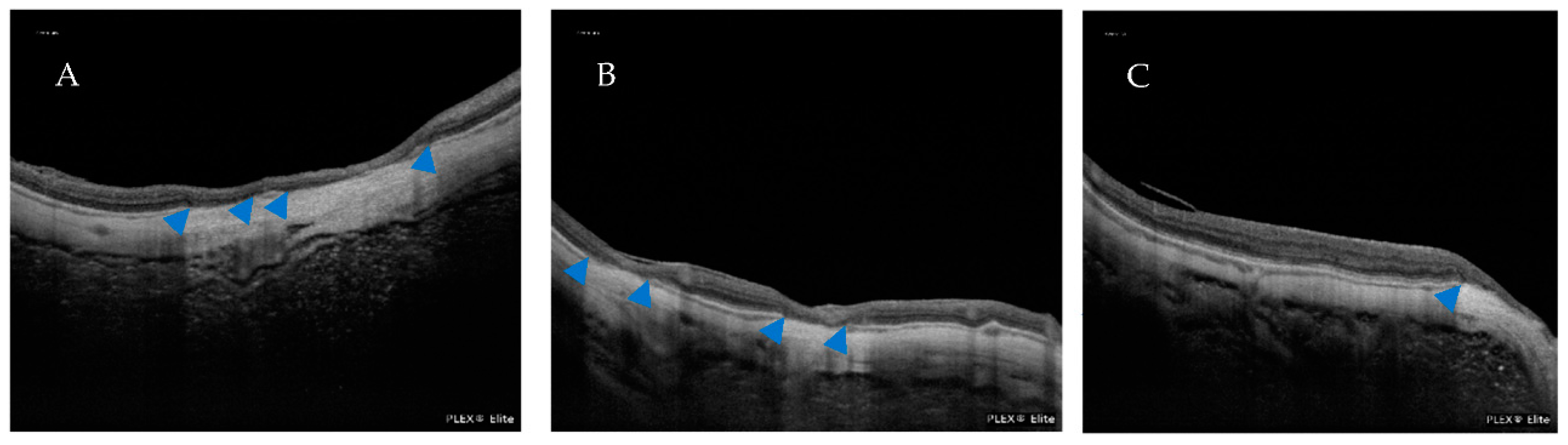
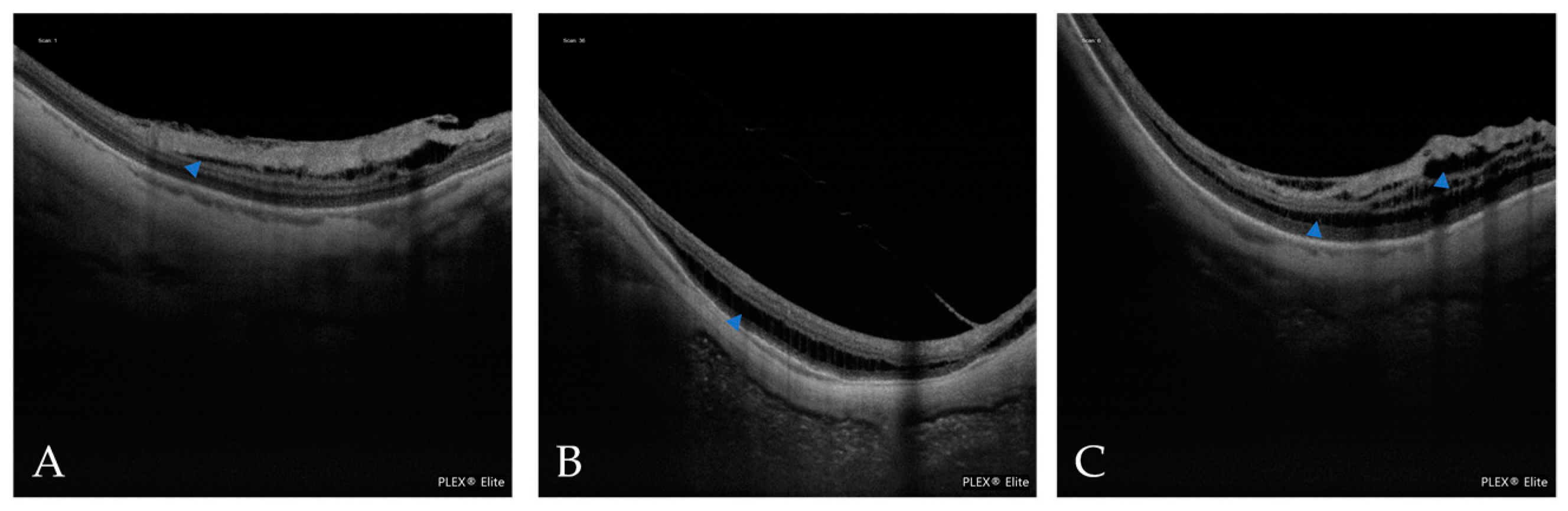

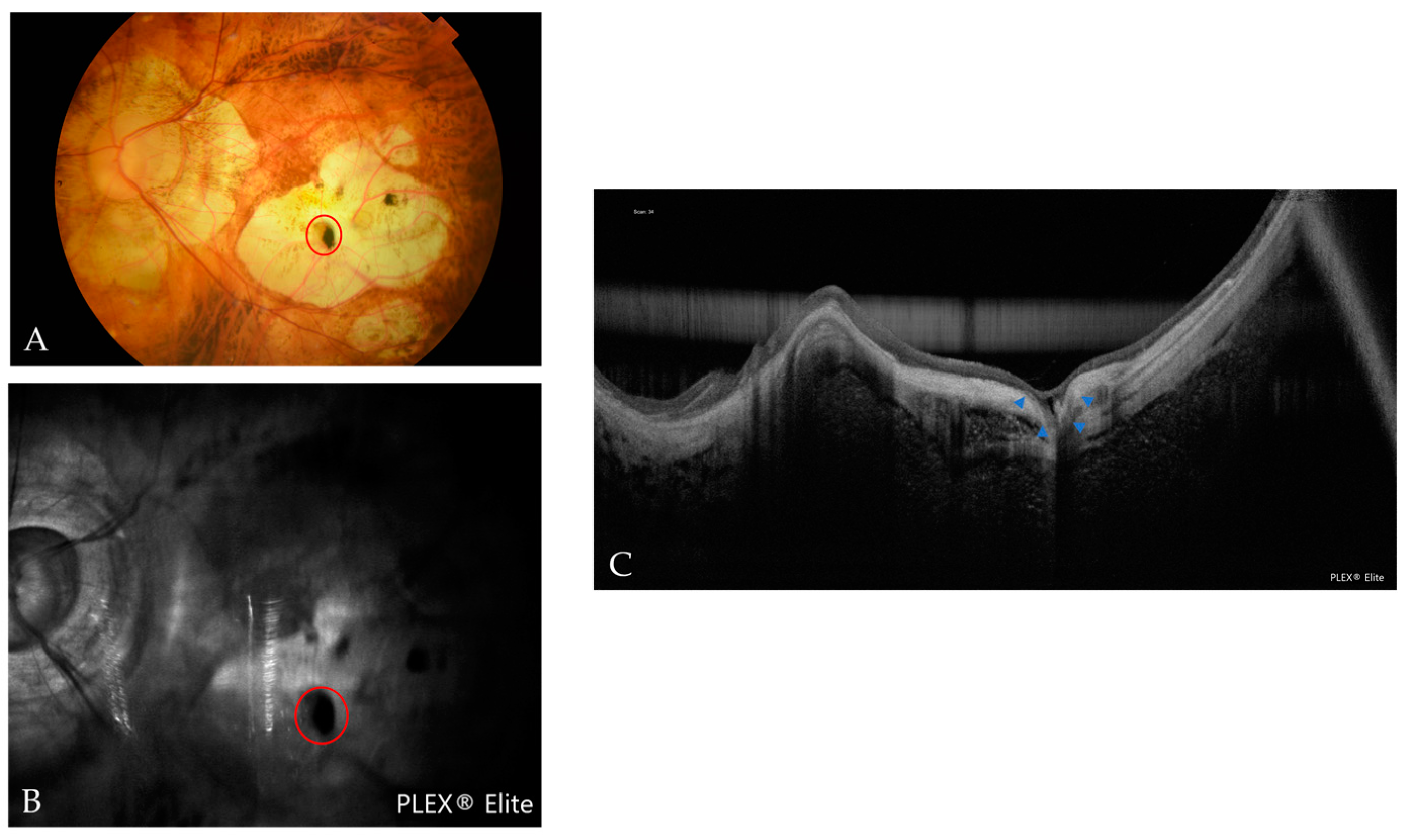
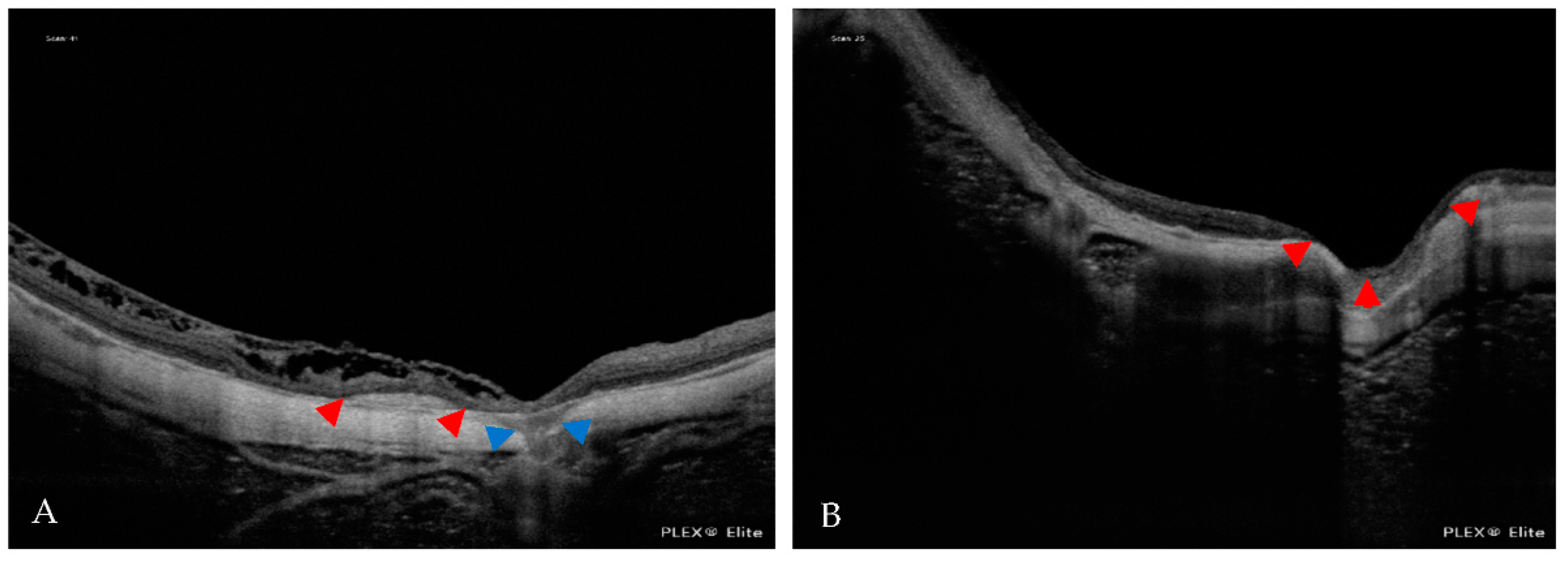



| Atrophic Classification | No. of Eyes | Tractional Classification | No. of Eyes | Neovascular Classification | No. of Eyes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 7 | T0 | 160 | N0 | 136 |
| A1 | 87 | T1 | 6 | N1 | 12 |
| A2 | 41 | T2 | 9 | N2a | 7 |
| A3 | 32 | T3 | 2 | N2s | 27 |
| A4 | 12 | T4 | 2 |
| IMI OCT Classification | No. of Eyes |
|---|---|
| No MM | 88 |
| Ia | 19 |
| Ib | 27 |
| II | 12 |
| III | 5 |
| IIIa | 17 |
| IIIb | 11 |
| Authors and Countries | Xiuyan et al. [30] China | Lee et al. [31] Republic of Korea | Arlanzón et al. Spain (Present Study) |
| No. of eyes | 154 | 30 | 179 |
| Baseline age (years) mean ± SD | 21.80 ± 1.32 | 55.5 ± 13.5 | 50.58 ± 14.98 |
| Mean spherical equivalent ± SD | −4.06 ± 2.26 D | −9.98 ± 5.03 D | −6.74 ± 6.44D |
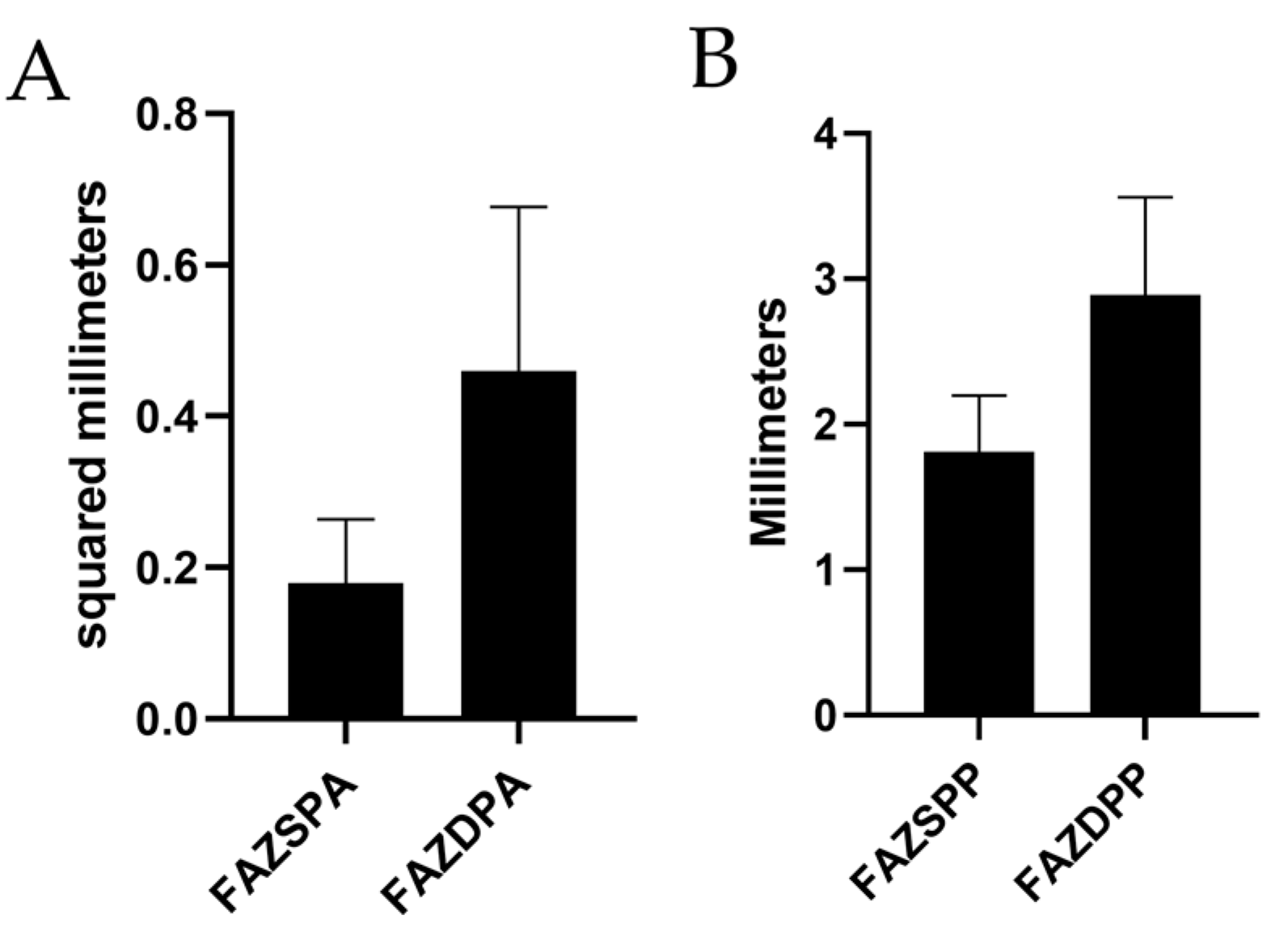
| SPFAZA (mm) | 0.1835 ± 0.0477 | 0.37 ± 0.15 | 0.18 ± 0.084 |
| DPFAZA (mm) | 0.3299 ± 0.0601 | 0.43 ± 0.16 | 0.46 ± 0.217 |
| Authors and Countries | Xiuyan et al. [30] China | Liu et al. [32] China | Park et al. [33] Republic of Korea | Wong et al. [34] Singapore | Maruko et al. [35] Japan | Hayashi et al. [36] Japan | Tan et al. [37] China | Arlanzón et al. Spain (Present Study) |
| No. of eyes | 154 | 30 | 237 | 92 | 58 | 75 | 38 | 179 |
| Baseline age (years) mean ± SD | 21.80 ± 1.32 | 24.43 ± 3.43 | 63.0 ± 11.6 | 60.2 ± 8.4 | 65.5 ± NA | 62.3 ± 11.3 | NA | 50.58 ± 14.98 |
| Mean spherical equivalent ± SD in diopter | −4.06 ± 2.26 | −7.85 ± 1.37 | −15.4 ± 5.4 | −12.5 ± 5.1 | −12.8 ± 3.6 | −12.9 ± 4.1 | −7.35 ± 1.1 | −6.74 ± 6.44 |
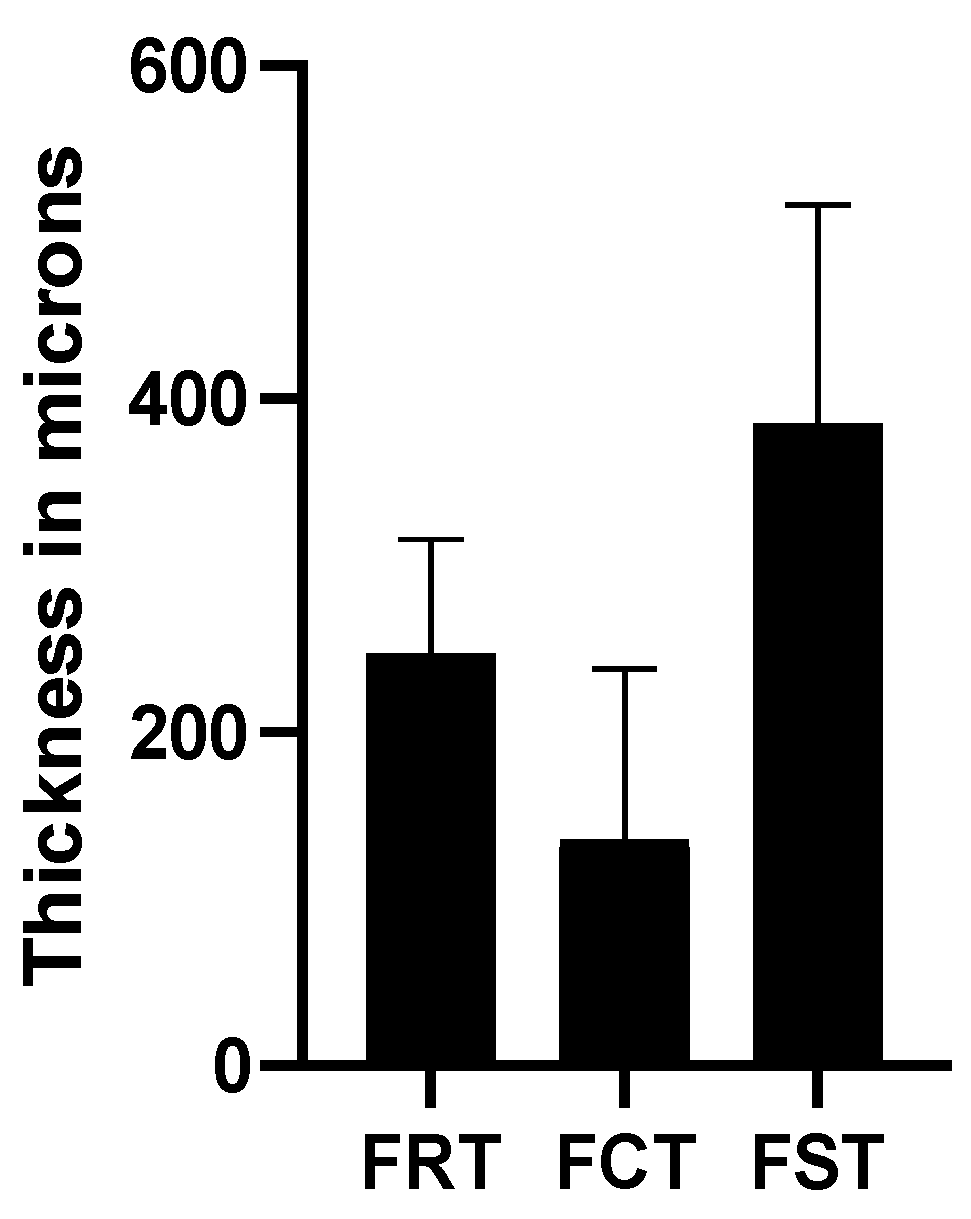
| Retinal thickness (μm) | 252.14 ± 17.33 | 240.91 ± 13.36 | NA | NA | 206 ± 92 | NA | NA | 247.06 ± 68.87 |
| Choroidal thickness (μm) | 232.16 ± 56.65 | NA | 29.2 ± 21.7 with staphyloma 46.9 ± 39.3 without staphyloma | 82.0 ± 57.12 in mild MMD 31.5 ± 0.5 in severe MMD | 52 ± 38 | NA | 253.8 ± 71.0 | 135.95 ± 102.44 |
| Scleral thickness (μm) | NA | NA | 268.7 ± 95.9 with staphyloma 316.2 ± 76.5 without staphyloma | 297.0 ± 73.8 in mild MMD 261.6 ± 78.5 in severe MMD | 335 ± 130 | 284.0 ± 70.4 | NA | 385.40 ± 131.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arlanzon-Lope, P.; Campos, M.A.; Fernandez-Bueno, I.; Coco-Martin, R.M. Does PLEX® Elite 9000 OCT Identify and Characterize Most Posterior Pole Lesions in Highly Myopic Patients? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051846
Arlanzon-Lope P, Campos MA, Fernandez-Bueno I, Coco-Martin RM. Does PLEX® Elite 9000 OCT Identify and Characterize Most Posterior Pole Lesions in Highly Myopic Patients? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051846
Chicago/Turabian StyleArlanzon-Lope, Pablo, Miguel Angel. Campos, Ivan Fernandez-Bueno, and Rosa M. Coco-Martin. 2023. "Does PLEX® Elite 9000 OCT Identify and Characterize Most Posterior Pole Lesions in Highly Myopic Patients?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051846
APA StyleArlanzon-Lope, P., Campos, M. A., Fernandez-Bueno, I., & Coco-Martin, R. M. (2023). Does PLEX® Elite 9000 OCT Identify and Characterize Most Posterior Pole Lesions in Highly Myopic Patients? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1846. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051846








