Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Ameliorates in LNK-Deficient Mouse Models with Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance Improvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. 16S rRNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
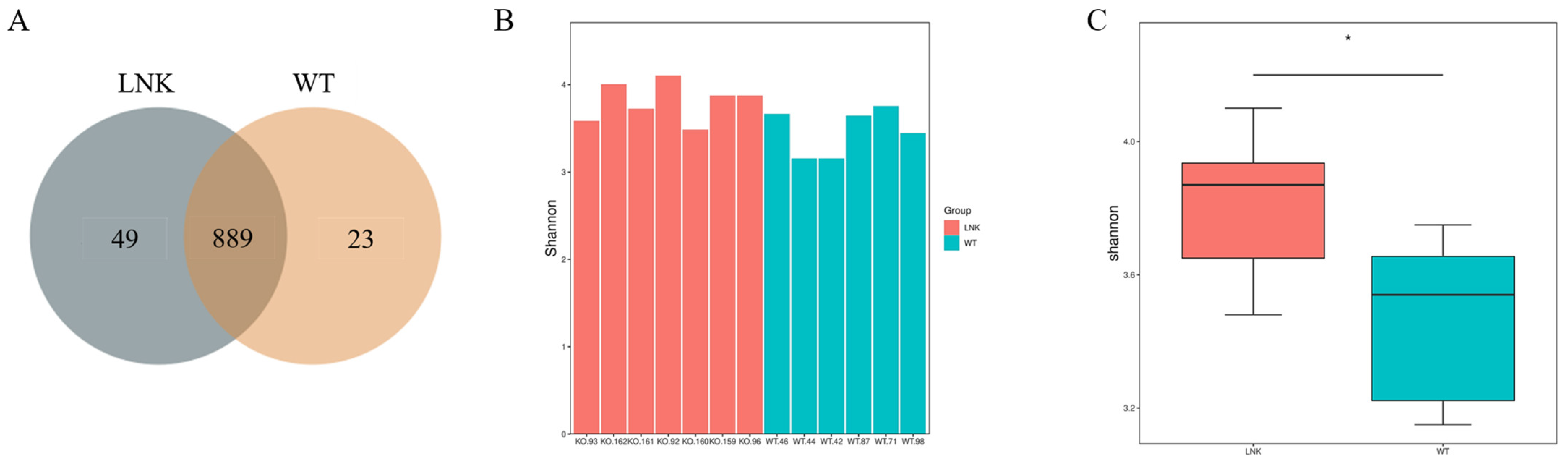
3.1. Diversity Difference of Intestinal Microbiota between LNK-/- and WT Mice
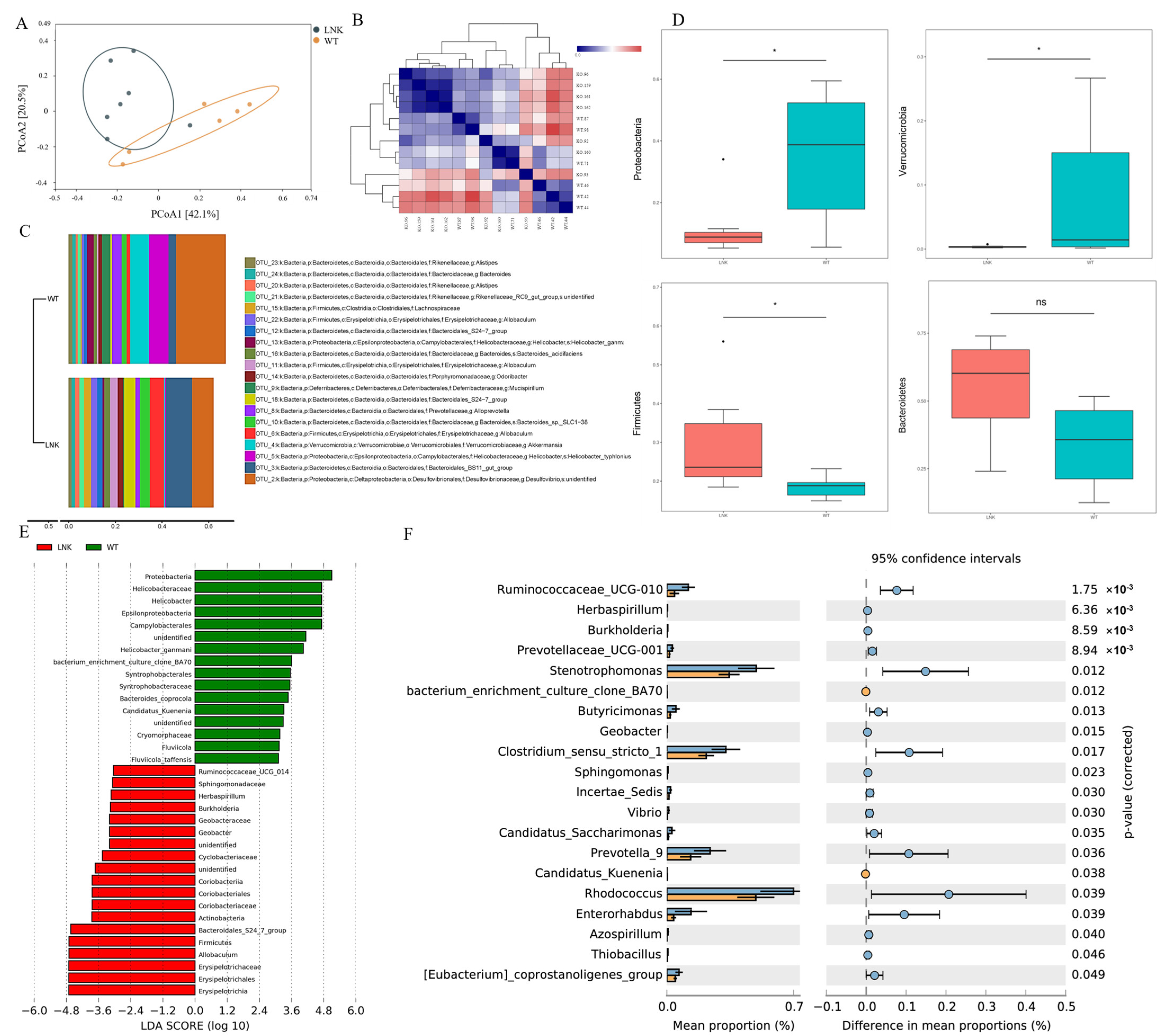
3.2. Composition and Abundance Difference of Intestinal Microbiota between LNK-/- and WT Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, C.J.; Prentki, M. Insulin resistance and insulin hypersecretion in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: Time for a conceptual framework shift. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.F.; Li, Y.M. Role of gut microbiota in the development of insulin resistance and the mechanism underlying polycystic ovary syndrome: A review. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xu, L.; Xu, C. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastrointestinal microecology. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 938608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Effects of Intestinal Flora on Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Therapeutic Significance of Polysaccharides. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 810453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, L.; Nie, H.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, M.; et al. Microecological preparation combined with a modified low-carbon diet improves glucolipid metabolism and cardiovascular complication in obese patients. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cai, Y.; Meng, C.; Ding, X.; Huang, J.; Luo, X.; Cao, Y.; Gao, F.; Zou, M. The role of the microbiome in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 172, 108645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhan, X. Metabolic profiles of oligosaccharides derived from four microbial polysaccharides by faecal inocula from type 2 diabetes patients. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Stoeva, M.K.; Justice, N.; Nemchek, M.; Sieber, C.M.K.; Tyagi, S.; Gines, J.; Skennerton, C.T.; Souza, M.; Kolterman, O.; et al. Increased circulating butyrate and ursodeoxycholate during probiotic intervention in humans with type 2 diabetes. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Chu, J.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Dai, W.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0032422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, S.; Feng, Y.; Song, Y.; Lv, N.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Perturbations of gut microbiota in gestational diabetes mellitus patients induce hyperglycemia in germ-free mice. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2020, 11, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Clément, K.; Nieuwdorp, M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: A Future Therapeutic Option for Obesity/Diabetes? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Yuan, F.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, G.; Huang, H.; Yang, D.; Xie, M.; et al. Overexpression of Lnk in the Ovaries Is Involved in Insulin Resistance in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3709–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhong, X.; Yang, D.; Jiang, S.; Ye, Y.; Ding, M.; Guan, G.; Yang, D.; Zhao, X. LNK promotes granulosa cell apoptosis in PCOS via negatively regulating insulin-stimulated AKT-FOXO3 pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 4617–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Ke, C.; Cai, Z.; Wu, H.; Ye, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, L.; Jiang, S.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; et al. LNK deficiency decreases obesity-induced insulin resistance by regulating GLUT4 through the PI3K-Akt-AS160 pathway in adipose tissue. Aging 2020, 12, 17150–17166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; García-Mantrana, I.; Vila-Vicent, S.; Gozalbo-Rovira, R.; Buesa, J.; Monedero, V.; Collado, M.C. Relevance of secretor status genotype and microbiota composition in susceptibility to rotavirus and norovirus infections in humans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adda-Rezig, H.; Carron, C.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Choubley, H.; Charron, É.; Rérole, A.L.; Laheurte, C.; Louvat, P.; Gaiffe, É.; Simula-Faivre, D.; et al. New Insights on End-Stage Renal Disease and Healthy Individual Gut Bacterial Translocation: Different Carbon Composition of Lipopolysaccharides and Different Impact on Monocyte Inflammatory Response. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Righi, S.; Krieg, R.; Kang, L.; Carl, D.; Wang, J.; Massey, H.D.; Sica, D.A.; Gehr, T.W.; Ghosh, S. High Fat High Cholesterol Diet (Western Diet) Aggravates Atherosclerosis, Hyperglycemia and Renal Failure in Nephrectomized LDL Receptor Knockout Mice: Role of Intestine Derived Lipopolysaccharide. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Real, J.M.; Pérez del Pulgar, S.; Luche, E.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Waget, A.; Serino, M.; Sorianello, E.; Sánchez-Pla, A.; Pontaque, F.C.; Vendrell, J.; et al. CD14 modulates inflammation-driven insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2179–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajo, K.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Nozaki, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Shinohara, Y.; Kato, S.; Mawatari, H.; Shibata, W.; Kitani, H.; et al. Hyperresponsivity to low-dose endotoxin during progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is regulated by leptin-mediated signaling. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncon-Albuquerque, R., Jr.; Moreira-Rodrigues, M.; Faria, B.; Ferreira, A.P.; Cerqueira, C.; Lourenço, A.P.; Pestana, M.; von Hafe, P.; Leite-Moreira, A.F. Attenuation of the cardiovascular and metabolic complications of obesity in CD14 knockout mice. Life Sci. 2008, 83, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Pérez, A.; Neef, A.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 Reduces Obesity-Associated Inflammation by Restoring the Lymphocyte-Macrophage Balance and Gut Microbiota Structure in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, M.; Prabhu, D.; Sathishkumar, C.; Prabu, P.; Rokana, N.; Kumar, R.; Raghavan, S.; Soundarajan, A.; Grover, S.; Batish, V.K.; et al. Improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity by probiotic strains of Indian gut origin in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhao, S. Effect of monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition on intestinal permeability in chronic stress model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummesson, A.; Carlsson, L.M.; Storlien, L.H.; Bäckhed, F.; Lundin, P.; Löfgren, L.; Stenlöf, K.; Lam, Y.Y.; Fagerberg, B.; Carlsson, B. Intestinal permeability is associated with visceral adiposity in healthy women. Obesity 2011, 19, 2280–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, L.W.; Al-Sadi, R.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1β and the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermüller, B.; Frisina, N.; Meischel, M.; Singer, G.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S.; Lichtenegger, H.; Kolb, D.; Klymiuk, I.; Till, H.; Castellani, C. Examination of intestinal ultrastructure, bowel wall apoptosis and tight junctions in the early phase of sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Biochemical Evaluation of the Antioxidant Effects of Hydroxytyrosol on Pancreatitis-Associated Gut Injury. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom Dieck, H.; Schön, C.; Wagner, T.; Pankoke, H.C.; Fluegel, M.; Speckmann, B. A Synbiotic Formulation Comprising Bacillus subtilis DSM 32315 and L-Alanyl-L-Glutamine Improves Intestinal Butyrate Levels and Lipid Metabolism in Healthy Humans. Nutrients 2021, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.X.; Zhao, W.; Solomon, C.; Rowland, K.J.; Ackerley, C.; Robine, S.; Holzenberger, M.; Gonska, T.; Brubaker, P.L. The intestinal epithelial insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor links glucagon-like peptide-2 action to gut barrier function. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, S.; Zhao, X. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Ameliorates in LNK-Deficient Mouse Models with Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance Improvement. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051767
Chen J, Xu J, Sun Y, Xue Y, Zhao Y, Yang D, Li S, Zhao X. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Ameliorates in LNK-Deficient Mouse Models with Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance Improvement. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051767
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jingbo, Jiawen Xu, Yan Sun, Yuhuan Xue, Yang Zhao, Dongzi Yang, Shuijie Li, and Xiaomiao Zhao. 2023. "Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Ameliorates in LNK-Deficient Mouse Models with Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance Improvement" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051767
APA StyleChen, J., Xu, J., Sun, Y., Xue, Y., Zhao, Y., Yang, D., Li, S., & Zhao, X. (2023). Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Ameliorates in LNK-Deficient Mouse Models with Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance Improvement. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051767




