Assessment of Bidirectional Relationships between Mental Illness and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
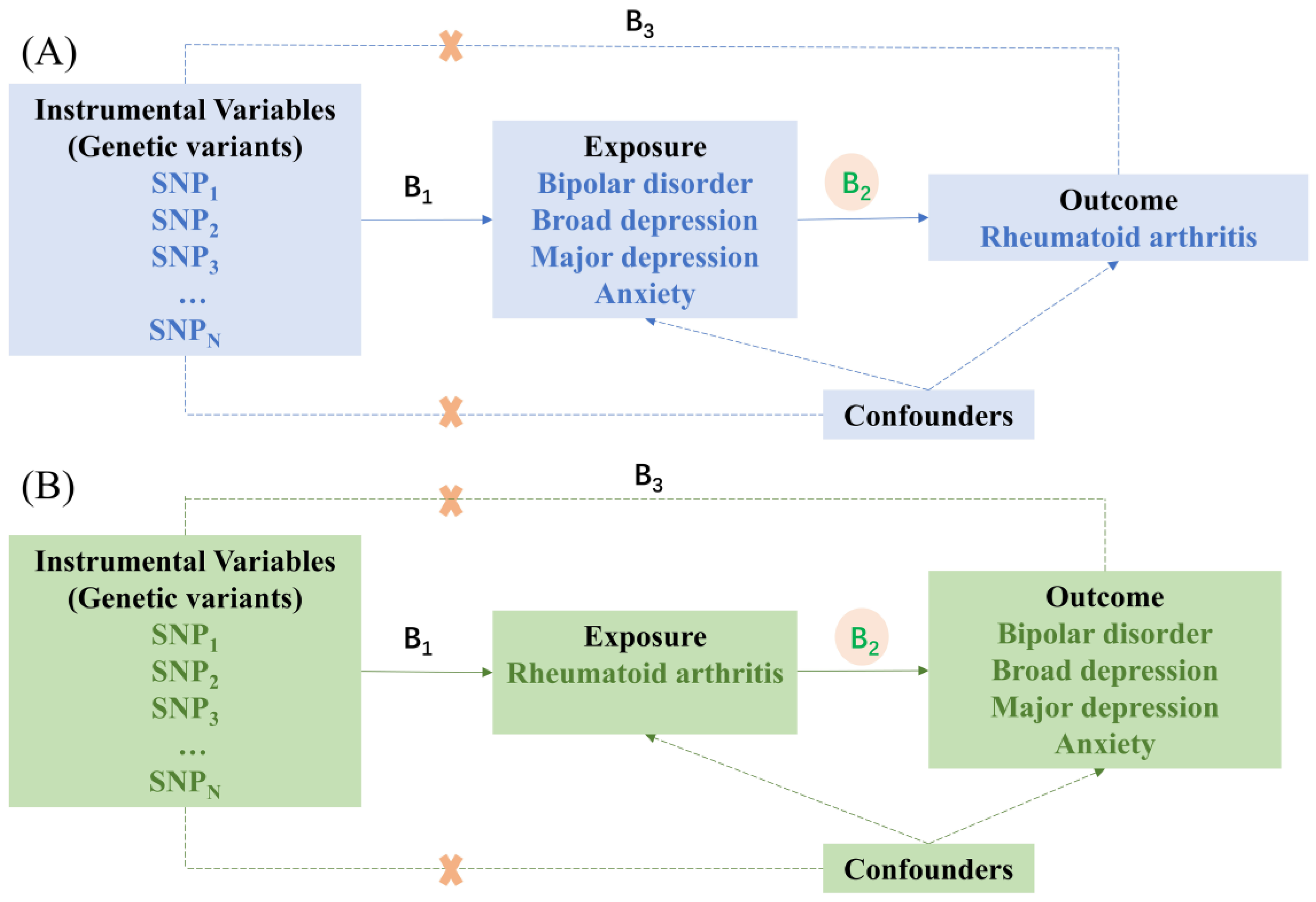
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Selection of Instrumental Variables
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. MR Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
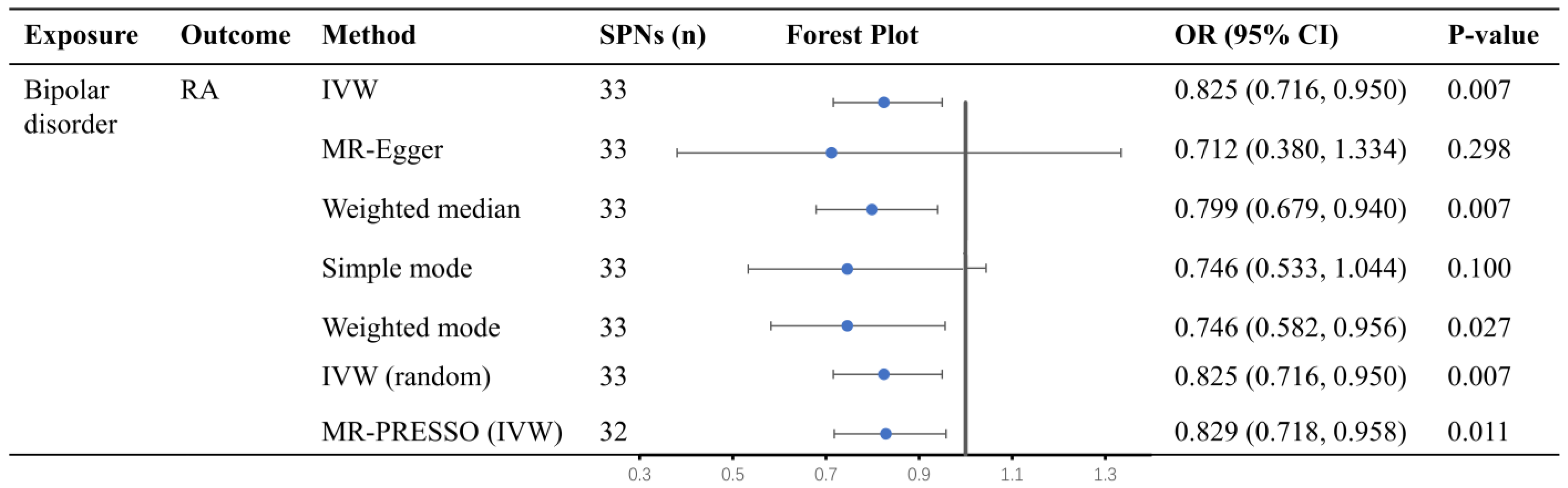
3.1. Causal Effect of Bipolar Disorder on RA
3.2. Causal Effect of Broad Depression, Major Depression, and Anxiety on RA
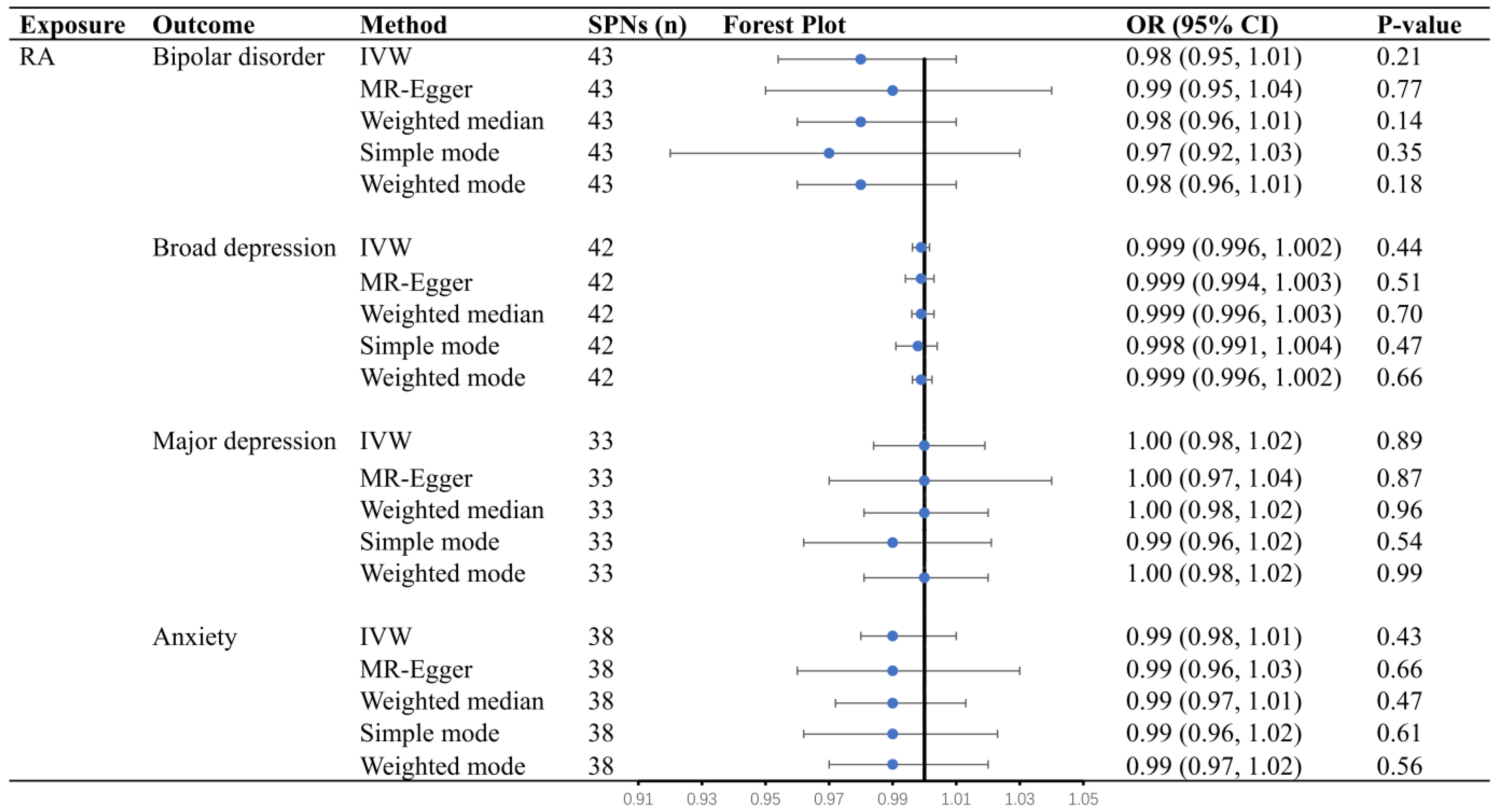
3.3. Causal Effects of RA on Bipolar Disorder, Broad Depression, Major Depression, and Anxiety
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Hoy, D.; Smith, E.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Qorbani, M.; et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Pan, W.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Ren, Y.; Ma, X. Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and insomnia symptoms among patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of quality effects model. J. Psychosom. Res. 2021, 147, 110516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, M.; De Hert, M.; Detraux, J.; Di Palo, K.; Munir, H.; Music, S.; Piña, I.; Ringen, P.A. Severe mental illness and cardiovascular disease: Jacc state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.R.; McGee, R.E.; Druss, B.G. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.C.; Guo, H.R.; Lin, M.C.; Livneh, H.; Lai, N.S.; Tsai, T.Y. Bidirectional associations between rheumatoid arthritis and depression: A nationwide longitudinal study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Li, C.K.; Liu, J.M.; Hsu, R.J.; Chuang, H.C.; Chang, F.W. Postpartum depression and subsequent autoimmune diseases in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matcham, F.; Rayner, L.; Steer, S.; Hotopf, M. The prevalence of depression in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2136–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, K.P.; Coleman JR, I.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Galloway, J.; Lewis, C.M. Investigating pleiotropy between depression and autoimmune diseases using the uk biobank. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2021, 1, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, A.; Koca, S.S.; Ozturk, A.; Mermi, O. Anxiety and depression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 26, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, E.Y.; Mok, C.C.; Cheng, C.W.; Cheung, E.F. Prevalence and determinants of psychiatric disorders in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Psychosomatics 2010, 51, e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chen, S.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lu, T.; Shen, C.C.; Hu, Y.W.; Yeh, C.M.; Chen, P.M.; Chen, T.J.; Hu, L.Y. Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of bipolar disorder: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N.; Ponvilawan, B.; Ungprasert, P. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis have a higher risk of bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 282, 112484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraich, P.; Goldner, E.M.; Somers, J.M.; Hsu, L. Prevalence and incidence studies of mood disorders: A systematic review of the literature. Can. J. Psychiatry 2004, 49, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhi, A.; Cohen, A.D.; Shovman, O.; Comaneshter, D.; Amital, H.; Amital, D. Bipolar disorder associated with rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 189, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbun, A.M.; England, B.R.; Mikuls, T.R.; Ryan, A.S.; Barton, J.L.; Shardell, M.D.; Hochberg, M.C. Relationship between depression and disease activity in united states veterans with early rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnardi, C.A.; Capelusnik, D.; Schneeberger, E.E.; Bazzarelli, M.; Berloco, L.; Blanco, E.; Benítez, C.A.; Luján Benavidez, F.; Scarafia, S.; Lázaro, M.A.; et al. Depression is a major determinant of functional capacity in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S180–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRenzo, D.D.; Craig, E.T.; Bingham Iii, C.O.; Bartlett, S.J. Anxiety impacts rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and health-related quality of life even at low levels. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Altman, N.; Krzywinski, M. Points of significance: Association, correlation and causation. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 899–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The association between disease duration and mood disorders in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 41, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, J.A.; Finan, P.H.; Zautra, A.J. Affective disturbance in rheumatoid arthritis: Psychological and disease-related pathways. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergne-Salle, P.; Pouplin, S.; Trouvin, A.P.; Bera-Louville, A.; Soubrier, M.; Richez, C.; Javier, R.M.; Perrot, S.; Bertin, P. The burden of pain in rheumatoid arthritis: Impact of disease activity and psychological factors. Eur. J. Pain 2020, 24, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Cai, L.S.; Yan, C.; Yu, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, R.W.; Huang, J.W.; Duan, X.W. Rheumatoid arthritis and risk of anxiety: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machin, A.R.; Babatunde, O.; Haththotuwa, R.; Scott, I.; Blagojevic-Bucknall, M.; Corp, N.; Chew-Graham, C.A.; Hider, S.L. The association between anxiety and disease activity and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Geng, Y.; Han, Z.; Qin, W.; Zhou, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G. Self-reported sleep disturbance is significantly associated with depression, anxiety, self-efficacy, and stigma in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Psychol. Health Med. 2022, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.G.; Schmidt, D.A.; Scarnà, A.; Semler, C.N.; Goodwin, G.M. Sleep-related functioning in euthymic patients with bipolar disorder, patients with insomnia, and subjects without sleep problems. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Kim, S.J. Inferring causality from observational studies: The role of instrumental variable analysis. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watad, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Adawi, M.; Aljadeff, G.; Amital, H.; Comaneshter, D.; Cohen, A.D.; Amital, D. Anxiety disorder among rheumatoid arthritis patients: Insights from real-life data. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 213, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian randomization. JAMA 2017, 318, 1925–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The mr-base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.C.; Conti, D.V. Commentary: The concept of ‘mendelian randomization’. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, N.; Forstner, A.J.; O’Connell, K.S.; Coombes, B.; Coleman JR, I.; Qiao, Z.; Als, T.D.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Børte, S.; Bryois, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Shirali, M.; Clarke, T.K.; Marioni, R.E.; Davies, G.; Coleman JR, I.; Alloza, C.; Shen, X.; Barbu, M.C.; et al. Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in uk biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman JR, I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, S.M.; Trontti, K.; Purves, K.L.; Als, T.D.; Grove, J.; Laine, M.; Pedersen, M.G.; Bybjerg-Grauholm, J.; Bækved-Hansen, M.; Sokolowska, E.; et al. Genetic variants associated with anxiety and stress-related disorders: A genome-wide association study and mouse-model study. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Wu, D.; Trynka, G.; Raj, T.; Terao, C.; Ikari, K.; Kochi, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 2014, 506, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; He, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qin, C. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 475. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, N.; Gao, R.C.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wu, Z.Z.; Wu, Z.G.; Wu, G.C. Causal relationship between sleep traits and risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: A two-sample mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otowa, T.; Hek, K.; Lee, M.; Byrne, E.M.; Mirza, S.S.; Nivard, M.G.; Bigdeli, T.; Aggen, S.H.; Adkins, D.; Wolen, A.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of anxiety disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Stein, M.B.; Klimentidis, Y.C.; Wang, M.J.; Koenen, K.C.; Smoller, J.W. Assessment of bidirectional relationships between physical activity and depression among adults: A 2-sample mendelian randomization study. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Cao, P.; Guo, Y.; Lu, H.; Hu, Y. Exploring the causality between hypothyroidism and non-alcoholic fatty liver: A mendelian randomization study. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 643582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Improving bias and coverage in instrumental variable analysis with weak instruments for continuous and binary outcomes. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 1582–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Smith, G.D.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Tian, Y.; Si, H.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, K.; Wu, L.; et al. Genetic Causal Association between Iron Status and Osteoarthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting pleiotropy in mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, S.; Pratt, W.S.; Rees, E.; Dahimene, S.; Ferron, L.; Owen, M.J.; Dolphin, A.C. Genetic disruption of voltage-gated calcium channels in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 134, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. Calcium signalling and psychiatric disease: Bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 357, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.J.; Geddes, J.R.; Tunbridge, E.M. The emerging neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, N.; Takahashi, T.; Hata, H.; Nomura, T.; Tagami, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Sakihama, T.; Matsutani, T.; Negishi, I.; Nakatsuru, S.; et al. Altered thymic T-cell selection due to a mutation of the ZAP-70 gene causes autoimmune arthritis in mice. Nature 2003, 426, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowin, T.; Tingting, R.; Zurmahr, J.; Classen, T.; Schneider, M.; Pongratz, G. Cannabidiol (CBD): A killer for inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jin, K.; Qiu, J.; Hu, B.; Jadhav, R.R.; Sheth, K.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Arachidonic acid-regulated calcium signaling in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis promotes synovial inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, W.U. The role of calcium-calcineurin-nfat signaling pathway in health and autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.H.; Marques, T.R.; Jauhar, S.; Nour, M.M.; Goodwin, G.M.; Young, A.H.; Howes, O.D. The dopamine hypothesis of bipolar affective disorder: The state of the art and implications for treatment. Mol. Psychiatry. 2017, 22, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, V.V.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. Prolactin and autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Reis, J.E.; Santos, G.; Pereira, M.P.; Loureiro, G.; Martins, F.; Fonseca, J.E. Abstracts from the european workshop for rheumatology research, 20–22 February 2014, Lisbon, Portugal. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73 (Suppl. S1), A1–A98. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Rosenfeld, G.; Keiser, H.; Peeva, E. Prolactin alters the mechanisms of B cell tolerance induction. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellino, S.; Cosentino, M.; Luini, A.; Bombelli, R.; Lowin, T.; Cutolo, M.; Marino, F.; Straub, R.H. Increased Expression of Dopamine Receptors in Synovial Fibroblasts from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inhibitory Effects of Dopamine on Interleukin-8 and Interleukin-6. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellino, S.; Cosentino, M.; Wolff, C.; Schmidt, M.; Grifka, J.; Straub, R.H. Catecholamine-producing cells in the synovial tissue during arthritis: Modulation of sympathetic neurotransmitters as new therapeutic target. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinberg, M.; Ottesen, N.M.; Meluken, I.; Sørensen, N.; Pedersen, O.; Kessing, L.V.; Miskowiak, K.W. Remitted affective disorders and high familial risk of affective disorders associate with aberrant intestinal microbiota. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2018, 139, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; An, J.; Ding, T.; Xue, H.; Li, X.F.; Wang, C. Pos0396 the level of peripheral regulatory t cells is associated with the changes of intestinal microbiota in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccaro, L.F.; Schilliger, Z.; Dayer, A.; Perroud, N.; Piguet, C. Inflammation, anxiety, and stress in bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder: A narrative review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner MC, F.; Wirgenes, K.V.; Shadrin, A.A.; Lunding, S.H.; Rødevand, L.; Hjell, G.; Ormerod, M.B.E.G.; Haram, M.; Agartz, I.; Djurovic, S.; et al. Limited association between infections, autoimmune disease and genetic risk and immune activation in severe mental disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 116, 110511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.H.; Vecera, C.M.; Pinjari, O.F.; Machado-Vieira, R. Inflammatory signaling mechanisms in bipolar disorder. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, D.; Calvacchi, S.; Petrelli, F.; Giannini, D.; Bilia, S.; Alunno, A.; Puxeddu, I. One year in review 2021: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 39, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblat, J.D. Targeting the immune system in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2909–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, J.M.; Wootton, R.E.; Treur, J.L.; Sallis, H.M.; Jones, H.J.; Zammit, S.; van den Brink, W.; Goodwin, G.M.; de Haan, L.; Munafò, M.R. Smoking and the risk for bipolar disorder: Evidence from a bidirectional mendelian randomisation study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2021, 218, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Xie, Z.; Wen, C.; Mao, Y. Genetic predisposition to smoking is associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A Mendelian randomization study. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamukcu, M.; Duran, T.; Ulusoy, H.; Altinbaş, K. Investigation of the correlation between mood disorder symptoms and disease activity and functional status in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 3008–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman, J.S.; D’Agostino McGowan, L.; Greevy, R.A.; Morrow, J.A.; Griffin, M.R.; Roumie, C.L.; Grijalva, C.G. Mental health conditions and the risk of chronic opioid therapy among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective veterans affairs cohort study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho de Oliveira Ribeiro, N.; Rafael de Mello Schier, A.; Ornelas, A.C.; Pinho de Oliveira, C.M.; Nardi, A.E.; Silva, A.C. Anxiety, depression and suicidal ideation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in use of methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide and biological drugs. Compr. Psychiatry. 2013, 54, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.J.; Huang, K.Y.; Tung, C.H.; Hsu, B.B.; Wu, C.H.; Lu, M.C.; Lai, N.S. Risk factors, including different biologics, associated with depression and anxiety in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional observational study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, B.L.; Whittle, S.L.; van der Heijde, D.M.; Buchbinder, R. The efficacy and safety of antidepressants in inflammatory arthritis: A cochrane systematic review. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.A.; Malspeis, S.; Hahn, J.; Wang, J.; Roberts, A.L.; Kubzansky, L.D.; Costenbader, K.H. Depression and subsequent risk for incident rheumatoid arthritis among women. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phenotype | GWAS Reference | Case Ascertainment | Ethnicity | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bipolar disorder | Mullins, N et al., 2021 [32] | Cases were individuals diagnosed with the international consensus criteria for defined bipolar disorder (The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IVS, International Classification of diseases-9, or International Classification of diseases-10), using structured diagnostic interviews, clinician-managed checklists, or medical history reviews. | European ancestry | 41,917 cases and 371,549 controls |
| Broad depression | Howard, D.M et al., 2018 [33] | Cases were individuals included by self-reported, help-seeking behavior for mental health difficulties. | European ancestry | 113,769 cases and 208,811 controls |
| Major depression | Howard, D.M, et al., 2019 [34] | Cases were ascertained by structured diagnostic interviews, national inpatient electronic records, self-reported major depression symptoms or treatment or electronic records, and self-reported diagnosis or treatment for clinical depression by a medical professional. | European ancestry | 246,363 cases and 561,190 controls |
| Anxiety | Otowa, T et al., 2016 [39] | Cases were individuals diagnosed with anxiety by a psychiatrist. It satisfies the genetic effects shared across the five core anxiety disorders: generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder (PD), social phobia, agoraphobia, and specific phobia. | European ancestry | 7016 cases and 14,745 controls |
| RA | Okada, Y et al., 2014 [36] | All cases met the diagnostic criteria of RA of the American Rheumatology Association in 1987 [40] or were diagnosed with RA by experts. | European ancestry | 14,361 cases and 43,923 controls |
| Exposure | Outcome | Method | No. of SNPs | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad depression | Rheumatoid arthritis | Inverse variance weighted | 2 | 11.76 (0.23, 600.62) | 0.22 |
| Major depression | Rheumatoid arthritis | Inverse variance weighted | 60 | 1.14 (0.87, 1.50) | 0.35 |
| MR-Egger | 60 | 0.66 (0.24, 1.85) | 0.44 | ||
| Weighted median | 60 | 1.08 (0.76, 1.55) | 0.66 | ||
| Simple mode | 60 | 0.61 (0.27, 1.35) | 0.23 | ||
| Weighted mode | 60 | 0.83 (0.49, 1.41) | 0.49 | ||
| Anxiety | Rheumatoid arthritis | Inverse variance weighted | 7 | 1.12 (0.89, 1.40) | 0.35 |
| MR-Egger | 7 | 0.80 (0.19, 3.40) | 0.78 | ||
| Weighted median | 7 | 1.19 (0.92, 1.55) | 0.19 | ||
| Simple mode | 7 | 1.16 (0.75, 1.78) | 0.52 | ||
| Weighted mode | 7 | 1.19 (0.79, 1.78) | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, S.; Wang, R.; Hua, L.; Song, J.; Qian, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ding, X. Assessment of Bidirectional Relationships between Mental Illness and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030944
Xiang S, Wang R, Hua L, Song J, Qian S, Jin Y, Zhang B, Ding X. Assessment of Bidirectional Relationships between Mental Illness and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030944
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Shate, Rongyun Wang, Lijiangshan Hua, Jie Song, Suhai Qian, Yibo Jin, Bingyue Zhang, and Xinghong Ding. 2023. "Assessment of Bidirectional Relationships between Mental Illness and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030944
APA StyleXiang, S., Wang, R., Hua, L., Song, J., Qian, S., Jin, Y., Zhang, B., & Ding, X. (2023). Assessment of Bidirectional Relationships between Mental Illness and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030944






