Associations between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjects, Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Definition of DM
2.4. Statistical
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
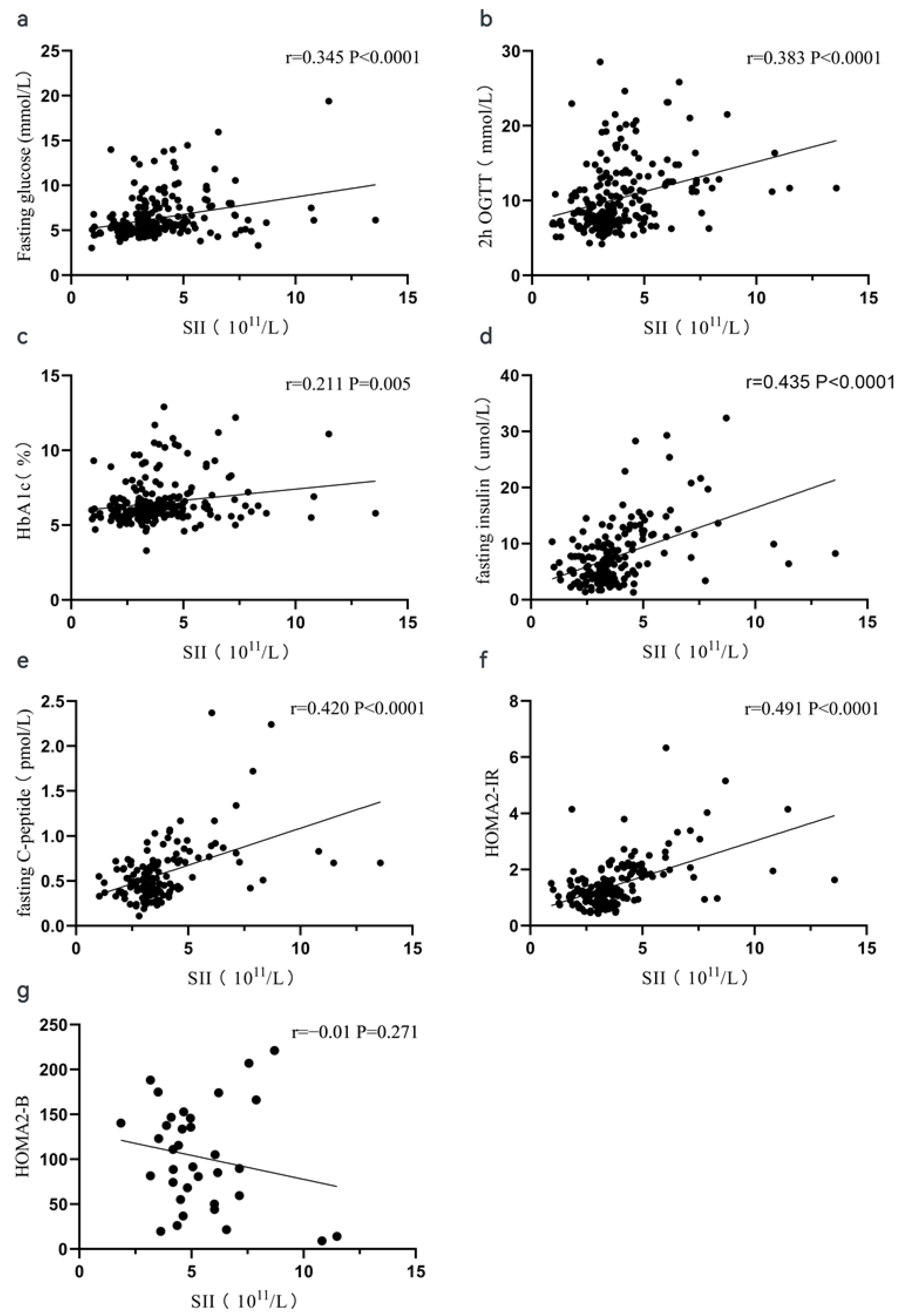
3.2. Spearman Correlation Analysis between Periphery Blood Indexes and Glucose-Related Parameters
3.3. Risk Factors for Diabetes Secondary to PDAC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, H.; Cao, S.; Xu, R. Cancer incidence, mortality, and burden in China: A time-trend analysis and comparison with the United States and United Kingdom based on the global epidemiological data released in 2020. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Andersen, D.K.; Bradley, D.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Forsmark, C.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Habtezion, A.; Korc, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, W.; Sun, Y. Contribution of biomarkers for pancreatic cancer-associated new-onset diabetes to pancreatic cancer screening. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, K.; Devereaux, B.; Dornhorst, A. Diabetes of the exocrine pancreas. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, S.; Ellenrieder, V.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Oncogenic transcription factors: Cornerstones of inflammation-linked pancreatic carcinogenesis. Gut 2013, 62, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wang, Y.; Fang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xia, F.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y. Associations between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Diabetic Complications in Adults with Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 6219545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tan, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Association Between the Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte Ratio and Diabetes Secondary to Exocrine Pancreatic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 957129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaban, M.; Zetoune, A.B.; Hesenow, S.; Hessenow, R. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio as novel risk markers for diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Wu, C.H.; Hsu, P.F.; Chen, S.C.; Huang, S.S.; Chan, W.L.; Lin, S.J.; Chou, C.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Pan, J.P.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) predicted clinical outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittoni, A.; Pecci, F.; Mentrasti, G.; Crocetti, S.; Lupi, A.; Lanese, A.; Pellei, C.; Ciotti, C.; Cantini, L.; Giampieri, R.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index: A prognostic tiebreaker among all in advanced pancreatic cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomrich, G.; Gruber, E.S.; Winkler, D.; Hollenstein, M.; Gnant, M.; Sahora, K.; Schindl, M. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) Predicts Poor Survival in Pancreatic Cancer Patients Undergoing Resection. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biyik, M.; Biyik, Z.; Asil, M.; Keskin, M. Systemic Inflammation Response Index and Systemic Immune Inflammation Index Are Associated with Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis? J. Investig. Surg. 2022, 35, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Qu, C.; Tang, B.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Gao, H.; Tian, X.; et al. Validation and modification of the AJCC 8th TNM staging system for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in a Chinese cohort: A nationwide pancreas data center analysis. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 33, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. S1), S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.K.; Korc, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Eibl, G.; Li, D.; Rickels, M.R.; Chari, S.T.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cersosimo, E.; Pisters, P.W.; Pesola, G.; McDermott, K.; Bajorunas, D.; Brennan, M.F. Insulin secretion and action in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer 1991, 67, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permert, J.; Ihse, I.; Jorfeldt, L.; von Schenck, H.; Arnqvist, H.J.; Larsson, J. Pancreatic cancer is associated with impaired glucose metabolism. Eur. J. Surg. 1993, 159, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, R.N.; Phillips, L.S.; Cobelli, C. Physiologic evaluation of factors controlling glucose tolerance in man: Measurement of insulin sensitivity and beta-cell glucose sensitivity from the response to intravenous glucose. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Fu, W.; Lee, Y.S.; Olefsky, J.M. The role of macrophages in obesity-associated islet inflammation and β-cell abnormalities. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, S.E. The role of TNF-α in insulin resistance. Endocrine 2004, 23, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, J.; Grémeaux, T.; Cormont, M.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Tanti, J.-F. Interleukin-1β-Induced Insulin Resistance in Adipocytes through Down-Regulation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Expression. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, J.J.; Klover, P.J.; Nowak, I.A.; Mooney, R.A. Interleukin-6 Induces Cellular Insulin Resistance in Hepatocytes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.T.; Zapiach, M.; Yadav, D.; Rizza, R.A. Beta-cell function and insulin resistance evaluated by HOMA in pancreatic cancer subjects with varying degrees of glucose intolerance. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zoughbi, W.; Al-Zhoughbi, W.; Huang, J.; Paramasivan, G.S.; Till, H.; Pichler, M.; Guertl-Lackner, B.; Hoefler, G. Tumor macroenvironment and metabolism. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunemaker, C.S. Considerations for Defining Cytokine Dose, Duration, and Milieu That Are Appropriate for Modeling Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2846570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, S.J.S.; Kandlakunta, H.; Her, T.; Sharma, A.; Sannapaneni, S.; Smyrk, T.C.; Velamala, P.; Garg, S.K.; Rakshit, K.; Majumder, S.; et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is associated with a unique endocrinopathy distinct from type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, L.X.; Jin, D.Y.; Yang, P.Y.; Wang, X.L. Identification of proteins implicated in the development of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics. J. Proteom. 2013, 84, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Nagpal, S.J.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chari, S.T. New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Niu, Y.; Li, X.; Qin, L.; Su, Q. White blood cell subtypes and risk of type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.T.; Harris, S.B.; Retnakaran, R.; Gerstein, H.C.; Perkins, B.A.; Zinman, B.; Hanley, A.J. White blood cell subtypes, insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction in high-risk individuals--the PROMISE cohort. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, M.; Singh, J. Endothelial dysfunction and platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Molecular insights and therapeutic strategies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, J.A.; Paneni, F.; Cosentino, F.; Creager, M.A. Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part II. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2444–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Yan, S.D.; Wautier, J.L.; Stern, D. Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products: A mechanism for chronic vascular dysfunction in diabetic vasculopathy and atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Choi, H.J.; Ha, S.J.; Lee, K.T.; Kwon, Y.G. Recruitment of monocytes/macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menart-Houtermans, B.; Rütter, R.; Nowotny, B.; Rosenbauer, J.; Koliaki, C.; Kahl, S.; Simon, M.C.; Szendroedi, J.; Schloot, N.C.; Roden, M. Leukocyte profiles differ between type 1 and type 2 diabetes and are associated with metabolic phenotypes: Results from the German Diabetes Study (GDS). Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Yan, J.; Xu, R.; Xu, M.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Lin, Z. The Clinical Values of Afamin, Triglyceride and PLR in Predicting Risk of Gestational Diabetes During Early Pregnancy. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 723650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.W.; Cheng, X.Y.; Sha, C.X.; Cui, Y.B. Clinical significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio in women with hyperglycemia. Postgrad. Med. 2020, 132, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, C.; Caffo, O.; Scarpi, E.; Aieta, M.; Conteduca, V.; Maines, F.; Bianchi, E.; Massari, F.; Veccia, A.; Chiuri, V.E.; et al. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predicts the Clinical Outcome in Patients with mCRPC Treated with Abiraterone. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | All (n = 221) | Non-DM (n = 144) | DM (n = 77) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 60 (50, 67) | 57 (49, 66) | 62 (52, 68) | 0.031 |
| Gender (Male, %) | 131 | 76 (52.8) | 55 (59.3) | 0.007 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.63 (21.15, 26.04) | 23.11 (21.15, 25.51) | 26.34 (21.78, 26.25) | 0.071 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 5.51 (4.91, 6.85) | 5.18 (4.77, 5.65) | 7.57 (5.87, 9.55) | <0.0001 |
| 2 h OGTT (mmol/L) | 8.70 (6.98, 12.41) | 7.40 (6.53, 8.55) | 13.70 (12.30, 17.44) | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.1 (5.6, 6.7) | 5.9 (5.6, 6.2) | 6.8 (6.2, 8.6) | <0.0001 |
| Fasting insulin (umol/L) a | 6.21 (3.62, 9.96) | 5.83 (3.60, 9.47) | 7.50 (3.58, 12.08) | 0.157 |
| Fasting C-peptide (pmol/L) b | 0.49 (0.38, 0.71) | 0.47 (0.38, 0.67) | 0.53 (0.39, 0.77) | 0.250 |
| HOMA2-B a | 87.30 ± 41.94 | 95.89 ± 36.17 | 68.91 ± 47.53 | <0.0001 |
| HOMA2-IR a | 1.21 (0.88, 1.82) | 1.12 (0.84, 1.61) | 1.43 (1.03, 2.10) | 0.003 |
| Tumor volume (cm3) | 4.00 (1.52, 10.40) | 2.55 (1.00, 8.75) | 7.92 (2.88, 13.68) | <0.0001 |
| Location, (body and tail %) | 101 (45.7) | 65 (45.1) | 36 (46.8) | 0.818 |
| AJCC stage (Ⅲ~Ⅳ, %) | 39 (18) | 18 (12.5) | 21 (34.8) | 0.006 |
| CA19-9 | 18.00 (9.41, 55.00) | 17.50 (9.80, 44.96) | 19.00 (7.52, 77.00) | 0.699 |
| Total bilirubin (umol/L) | 11.10 (8.40, 13.40) | 10.80 (8.20, 13.08) | 11.50 (8.80, 14.30) | 0.211 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 18.00 (12.00, 28.00) | 18.00 (13.00, 25.00) | 18.00 (11.50, 32.00) | 0.371 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 43.20 (40.65, 46.10) | 43.10 (40.9, 45.88) | 43.40 (39.60, 46.25) | 0.838 |
| Creatinine (umol/L) | 66.00 (56.00, 77.00) | 63.00 (54.25, 76.75) | 67.00 (58.50, 77.50) | 0.073 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.16 (0.87, 1.49) | 1.10 (0.85, 1.48) | 1.21 (0.94, 1.54) | 0.144 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.26 ± 0.95 | 4.31 ± 0.96 | 4.18 ± 0.93 | 0.322 |
| High density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 1.20 (0.99, 1.52) | 1.22 (1.03, 1.52) | 1.15 (0.94, 1.46) | 0.089 |
| Low density lipoprotein (mmol/L) | 2.48 (2.01, 2.95) | 2.49 (1.99, 2.98) | 2.48 (2.21, 2.94) | 0.913 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 132.29 ± 14.61 | 131.28 ± 14.59 | 134.17 ± 14.56 | 0.161 |
| White blood cell(109/L) | 5.37 (4.58, 6.34) | 5.12 (4.32, 5.99) | 5.84 (4.96, 7.52) | <0.0001 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 145.00 (120.75, 182.25) | 132.50 (114.25, 168.00) | 170.00 (141.00, 200.00) | <0.0001 |
| Neutrophil (109/L) | 3.31 (2.73, 4.26) | 2.10 (2.40, 3.90) | 3.82 (2.91, 4.80) | <0.0001 |
| Lymphocyte (109/L) | 1.46 (1.14, 1.76) | 1.46 (1.15, 1.73) | 1.48 (1.10, 1.89) | 0.967 |
| Monocyte (109/L) | 0.39 (0.31, 0.51) | 0.37 (0.29, 0.45) | 0.46 (0.34, 0.59) | <0.0001 |
| NLR | 2.41 (1.85, 3.02) | 2.31 (1.81, 2.79) | 2.55 (1.91, 3.59) | 0.003 |
| PLR | 107.69 (83.06, 134.06) | 103.62 ± 33.71 | 131.18 ± 62.49 | <0.0001 |
| SII (1011/L) | 3.42 (2.96, 4.58) | 3.19 (2.50, 3.71) | 4.41 (3.43, 6.23) | <0.0001 |
| White Blood Cell | Neutrophil | Lymphocyte | Monocyte | Platelet | NLR | PLR | SII | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting glucose | 0.181 ** | 0.215 ** | −0.058 | 0.154 * | 0.110 | 0.251 *** | 0.150 * | 0.345 *** |
| 2 h OGTT | 0.174 ** | 0.206 ** | −0.060 | 0.151 * | 0.210 ** | 0.223 *** | 0.236 ** | 0.383 *** |
| Fasting insulin | 0.288 *** | 0.313 *** | 0.015 | 0.161 * | 0.214 ** | 0.211 ** | 0.160 * | 0.435 *** |
| Fasting C-peptide | 0.371 *** | 0.382 *** | 0.059 | 0.281 ** | 0.154 | 0.248 ** | 0.084 | 0.420 *** |
| HbA1c | 0.178 ** | 0.167 * | 0.059 | 0.197 ** | 0.110 | 0.109 | 0.037 | 0.211 ** |
| HOMA2-IR | 0.358 *** | 0.409 *** | 0.025 | 0.220 ** | 0.173 * | 0.294 *** | 0.113 | 0.491 *** |
| HOMA2-B | −0.045 | 0.029 | −0.049 | −0.06 | −0.013 | 0.012 | 0.002 | −0.01 |
| Tumor volumes | 0.361 *** | 0.445 *** | −0.107 | 0.284 *** | 0.039 | 0.479 *** | 0.147 * | 0.478 *** |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multiple Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | |
| Age | 1.027 (1.002, 1.053) | 0.035 | 1.043 (1.01, 1.077) | 0.008 |
| Gender (male) | 2.237 (1.236, 4.047) | 0.008 | 1.743 (0.827, 3.672) | 0.144 |
| Body mass index | 0.998 (0.991, 1.005) | 0.527 | NA | |
| Tumor volumes | 1.040 (1.011, 1.070) | 0.006 | 0.999 (0.957, 1.043) | 0.970 |
| Tumor location (body and tail) | 1.067 (0.613, 1.859) | 0.818 | NA | |
| AJCC stage (Ⅲ~Ⅳ) | 2.625 (1.299, 5.307) | 0.007 | 2.021 (0.596, 6.853) | 0.259 |
| CA19-9 | 1.001 (0.999, 1.002) | 0.290 | NA | |
| Total bilirubin | 1.026 (0.976, 1.079) | 0.316 | NA | |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 1.018 (1.001, 1.035) | 0.040 | 1.019 (0.998, 1.039) | 0.072 |
| Albumin | 0.992 (0.942, 1.044) | 0.756 | NA | |
| Creatinine | 1.013 (0.996, 1.031) | 0.141 | NA | |
| Triglyceride | 1.232 (0.831, 1.827) | 0.299 | NA | |
| Cholesterol | 0.862 (0.642, 1.156) | 0.321 | NA | |
| High density lipoprotein | 0.600 (0.283, 1.273) | 0.183 | NA | |
| Low density lipoprotein | 0.866 (0.604, 1.242) | 0.435 | NA | |
| Hemoglobin | 1.014 (0.994, 1.034) | 0.162 | NA | |
| White blood cell | 1.395 (1.165, 1.668) | <0.0001 | 1.215 (0.775, 1.906) | 0.396 |
| NLR | 1.846 (1.361, 2.503) | <0.0001 | 0.593 (0.321, 1.093) | 0.094 |
| PLR | 1.016 (1.008, 1.025) | <0.0001 | 1.006 (0.984, 1.029) | 0.598 |
| Systemic immune-inflammation index | 2.156 (1.674, 2.776) | <0.0001 | 2.382 (1.157, 4.903) | 0.019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Tan, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Y. Associations between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030756
Chen G, Tan C, Liu X, Wang X, Tan Q, Chen Y. Associations between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030756
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guanhua, Chunlu Tan, Xubao Liu, Xing Wang, Qingquan Tan, and Yonghua Chen. 2023. "Associations between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030756
APA StyleChen, G., Tan, C., Liu, X., Wang, X., Tan, Q., & Chen, Y. (2023). Associations between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030756





