Medication and the Risk of Falls: An Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions Reported to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Variables
2.2.1. Demographic Characterisation of the Population
2.2.2. Characterisation of the Report Rate and Report Source
2.2.3. Characterisation of ADR Reports
2.2.4. Characterisation of Fall ADRs
3. Results
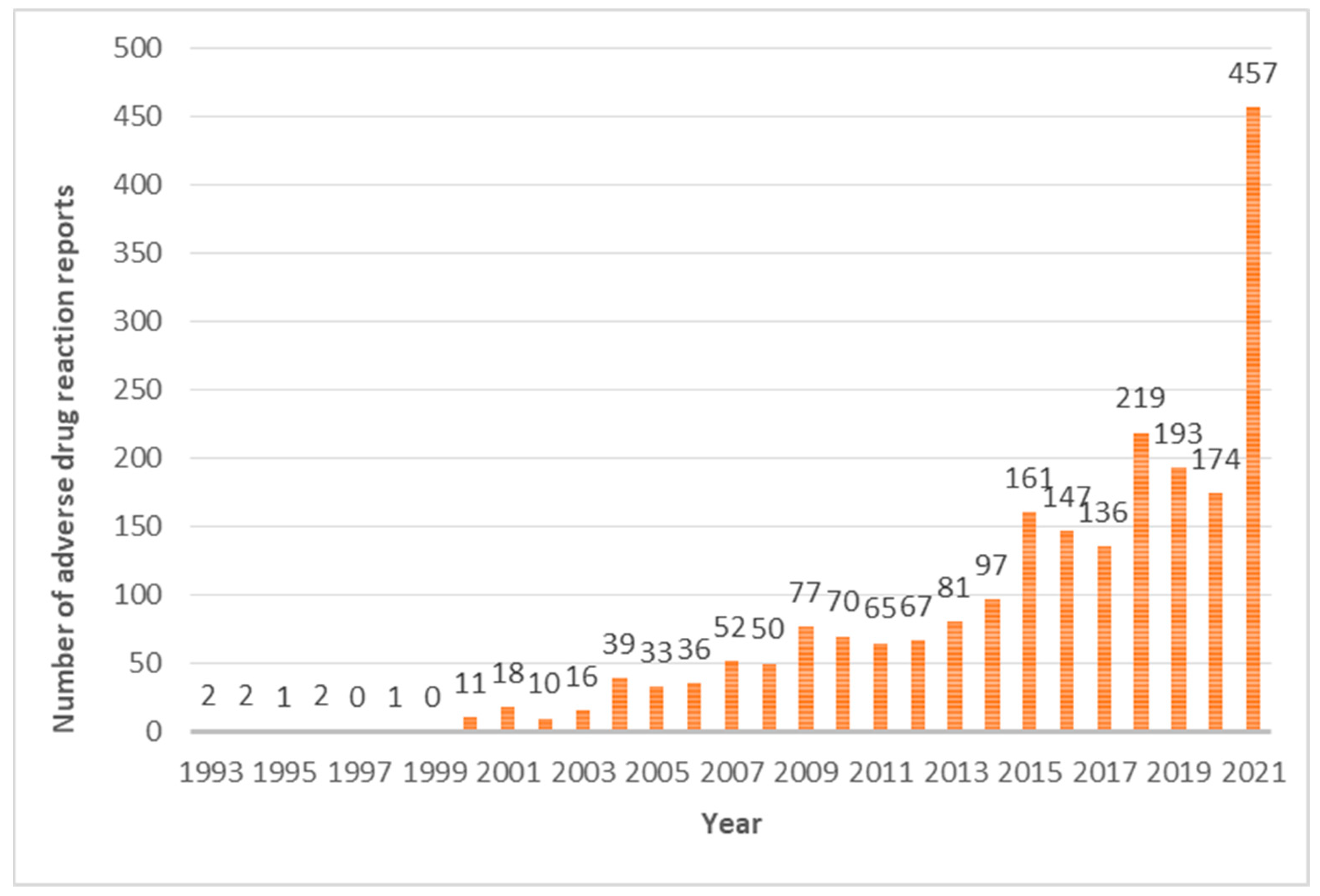
3.1. Reporting Rate
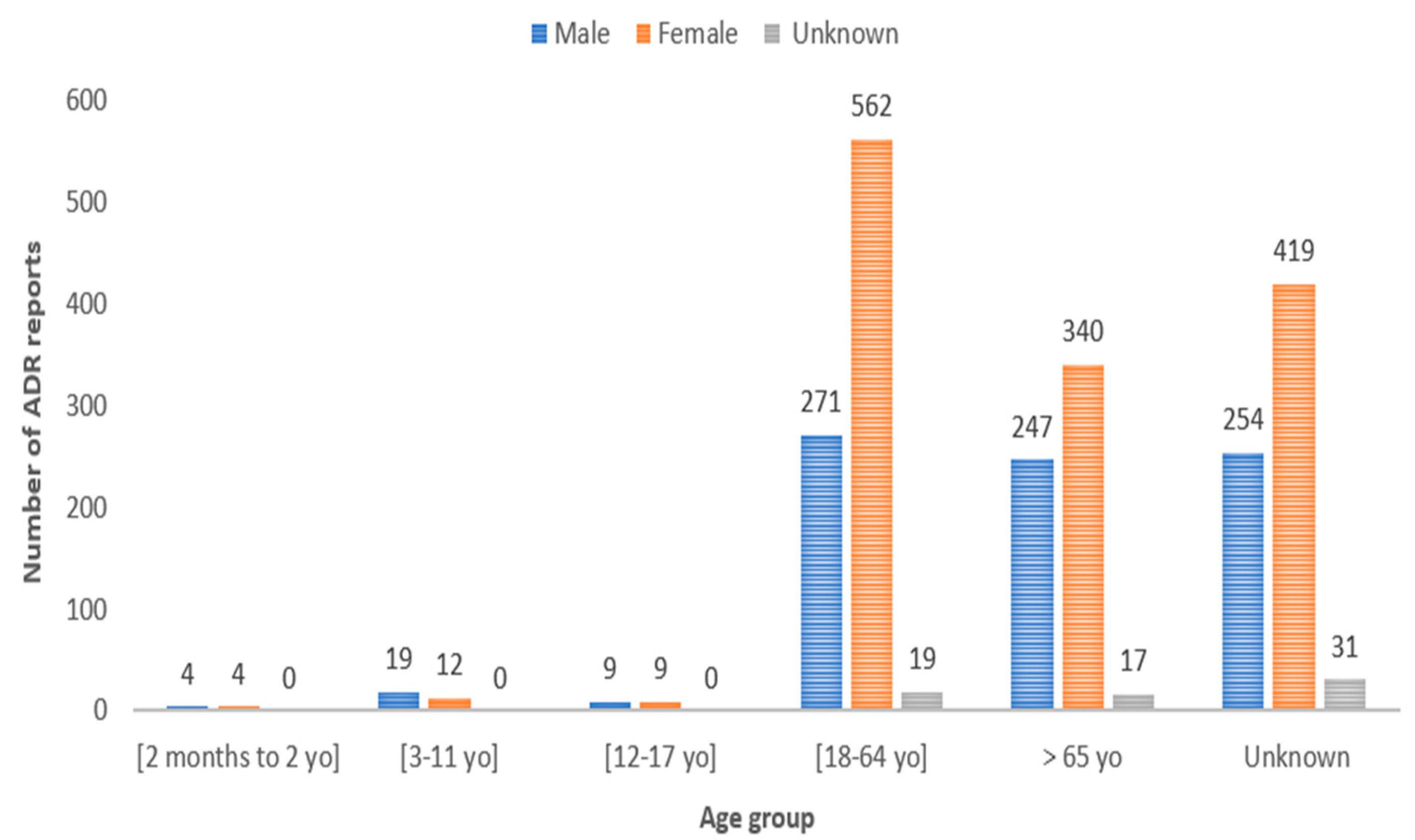
3.2. Demographic Analysis
3.3. Source of Reports and Adverse Drug Reaction Outcomes
3.4. Adverse Drug Reaction Seriousness and Causality
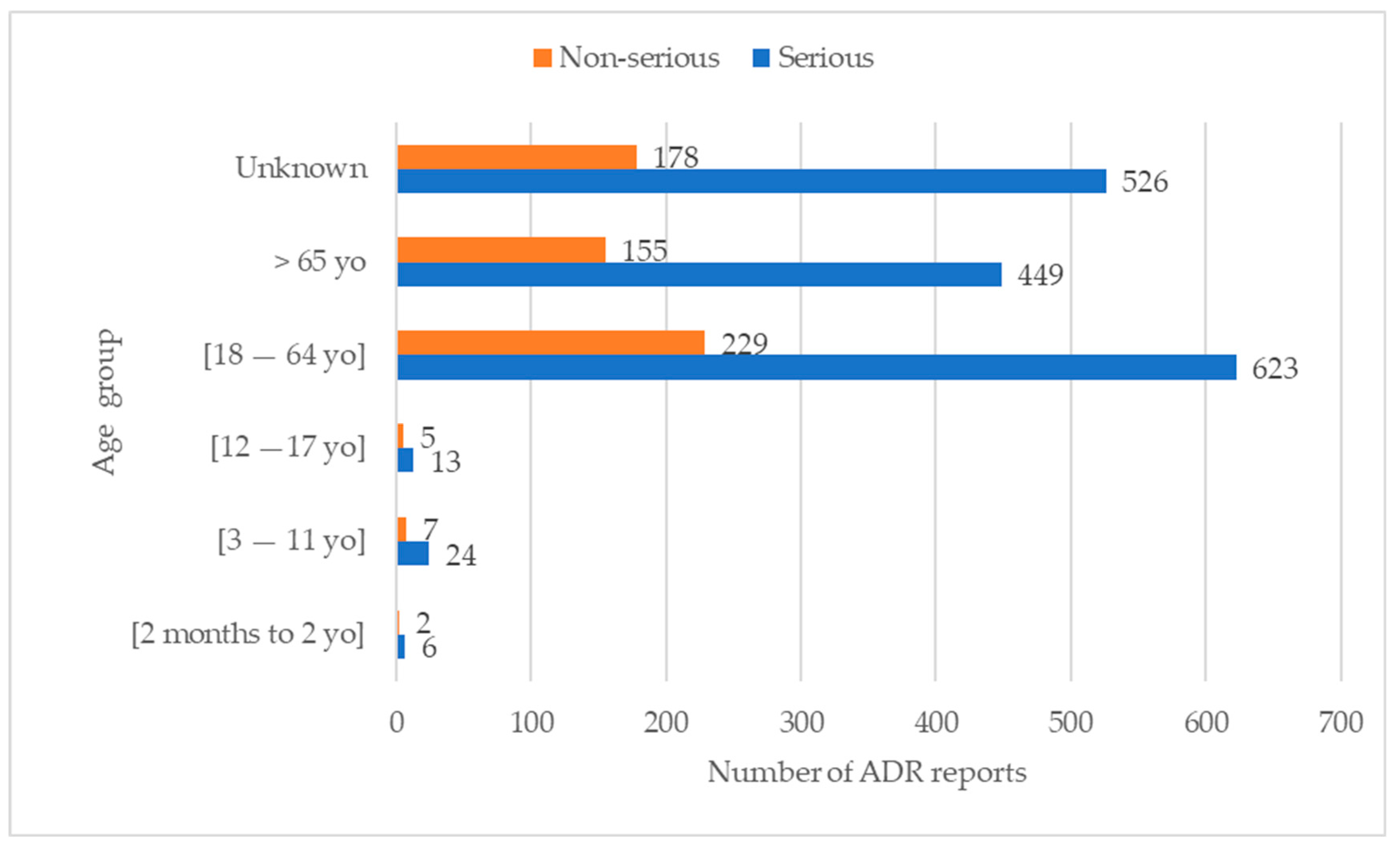
3.4.1. Relation between Age Group, Gender, and Seriousness
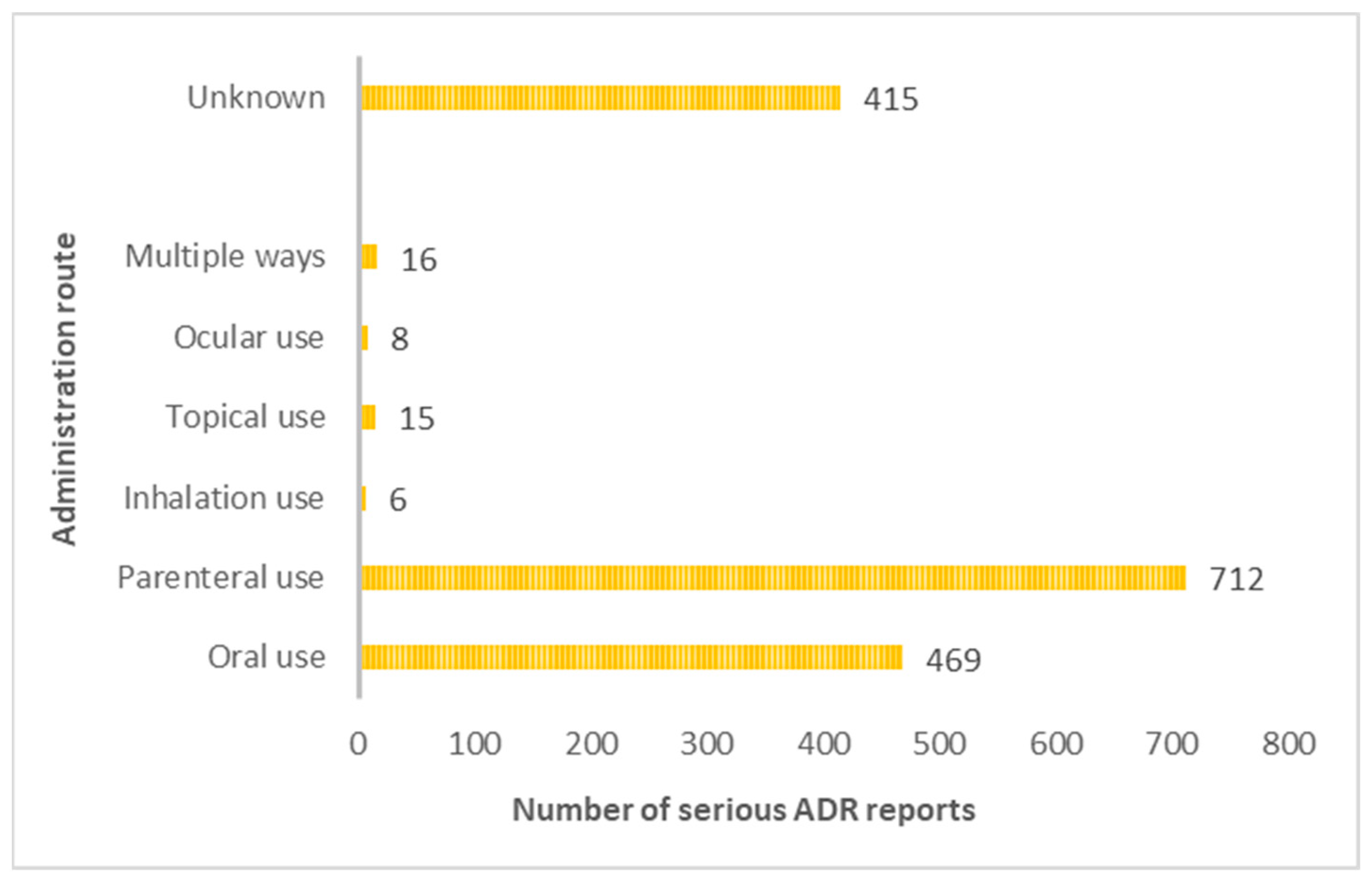
3.4.2. Routes of Administration Mostly Associated with the Occurrence of Serious Adverse Drug Reactions
3.5. Pharmacotherapeutic Classes and Suspected Drugs Associated with the Risk of Falls
3.6. Reports Mentioning the Occurrence of a Fall
3.7. Other Adverse Drug Reactions Associated with a Fall
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adverse Drug Reactions—METIS. Available online: http://www.metis.med.up.pt/index.php/Reações_adversas_a_medicamentos (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- American Geriatrics Society. Available online: https://www.americangeriatrics.org/ (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- British Geriatrics Society|Improving Healthcare for Older People. Available online: https://www.bgs.org.uk/ (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Oliveira, A.B.; Sim, A. Medications and Risk of Falls. 2021, pp. 2–4. Available online: https://www.ordemfarmaceuticos.pt/fotos/publicacoes/e_publicacao_quedas_13605605836013f2ddc4df3.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Elliott, T.R.; Westneat, S.; Karanth, S.D.; Abner, E.L.; Kucharska-Newton, A.M.; Moga, D.C. An Evaluation of Injurious Falls and Fall-Risk-Increasing-Drug (FRID) Prescribing in Ambulatory Care in Older Adults. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.R.; Mallet, L.; Rochefort, C.M.; Eguale, T.; Buckeridge, D.L.; Tamblyn, R. Medication-Related Falls in the Elderly: Causative Factors and Preventive Strategies. Drugs Aging 2012, 29, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmacovigilance|LEO Pharma. Available online: http://www.leo-pharma.pt/Home/Farmacovigilância.aspx (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Axer, H.; Axer, M.; Sauer, H.; Witte, O.W.; Hagemann, G. Falls and Gait Disorders in Geriatric Neurology. Clin. Neurol Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddock, B. Medications and Falls in the Elderly. Can. Pharm. J. 2004, 137, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimirri, S.; Aiello, R.; Mazzitello, C.; Mumoli, L.; Palleria, C.; Altomonte, M.; Citraro, R.; De Sarro, G. Vertigo/Dizziness as a Drugs′ Adverse Reaction. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4 (Suppl. S1), 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classificação Farmacoterapêutica de Medicamentos—Despacho n.o 4742/2014, de 21 de Março. Legislação Farmacêutica Compilada. Available online: https://www.infarmed.pt/documents/15786/1072289/110-AB6_Desp_4742_2014_VF.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Annual Activity Report 2021—INFARMED, I.P. Available online: https://www.infarmed.pt/documents/15786/2099374/Relatório+Anual+de+Atividades+2021/f88db1bd-40a7-7207-54a4-003b48fc6b10 (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- ADR Notifications Received in the SNF, by Origin—Evolution 1992–2021. Available online: https://www.infarmed.pt/web/infarmed/entidades/medicamentos-uso-humano/farmacovigilancia/notificacao-de-ram/evolucao-desde-1992 (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- Portugal: Resident Population: Total and by Age Group|Pordata. Available online: https://www.pordata.pt/portugal/populacao+residente+total+e+por+grupo+etario-10 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Boletín de Farmacovigilancia: Medicamentos Relacionados Con Caídas. 2019; Volume 27. Available online: https://www.euskadi.eus/contenidos/informacion/cevime_infac_2019/es_def/adjuntos/INFAC_Vol_27_10_caidas.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- INE Portal. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_indicadores&contecto=pi&indOcorrCod=0011628&selTab=tab0 (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Soldin, O.P.; Mattison, D.R. Sex Differences in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 48, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.; Caster, O.; Rochon, P.A.; den Ruijter, H. Reported Adverse Drug Reactions in Women and Men: Aggregated Evidence from Globally Collected Individual Case Reports during Half a Century. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 17, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.C.; Soares, M.; Martins, S. Adverse Reactions to Medications—Analysis of the National Pharmacovigilance System. Infarmed 2012, 6–9. Available online: https://www.infarmed.pt/documents/15786/17838/Relatorio_analise_dados_SVIG_2009_2011.pdf/465ddbbb-4725-4c7c-aced-7986338f82de?version=1.0 (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Herdeiro, M.T.; Ferreira, M.; Ribeiro-Vaz, I.; Junqueira Polónia, J.; Costa Pereira, A. The Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System. Acta Med. Port 2012, 25, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.; Ribeiro-Vaz, I.; Pereira, A.C.; Polõnia, J. A Survey of Spontaneous Reporting of Adverse Drug Reactions in 10 Years of Activity in a Pharmacovigilance Centre in Portugal. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2014, 22, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batel-Marques, F.; Mendes, D.; Alves, C.; Penedones, A.; Dias, P.; Martins, A.; Santiago, L.M.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.; Caramona, M.; Macedo, T. Pharmacovigilance in Portugal: Activity of the Centro Regional Unit. Acta Med. Port. 2015, 28, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Alba, J.E.; Jiménez-Morales, A.L.; Moran-Yela, Y.C.; Parrado-Fajardo, I.Y.; Valladales-Restrepo, L.F. Adverse Drug Reactions Associated with the Use of Biological Agents. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary of Product Characteristics—Rituximab. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/mabthera-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Summary of Product Characteristics—Adalimumab. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/humira-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Summary of Product Characteristics—Infliximab. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/remicade-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Noble, D.J.; Pronovost, P.J. Underreporting of Patient Safety Incidents Reduces Health Care’s Ability to Quantify and Accurately Measure Harm Reduction. J. Patient Saf. 2010, 6, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montané, E.; Santesmases, J. Adverse Drug Reactions. Med. Clin. 2020, 154, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Galán, M.A.; Pérez-Vilar, S.; Díez-Domingo, J.; Tuells, J.; Gomar-Fayos, J.; Morales-Olivas, F.; Pastor-Villalba, E. Adverse Reactions to Human Papillomavirus Vaccine in the Valencian Community (2007–2011). An. Pediatría (Engl. Ed.) 2014, 81, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araja, D.; Krumina, A.; Nora-Krukle, Z.; Berkis, U.; Murovska, M. Vaccine Vigilance System: Considerations on the Effectiveness of Vigilance Data Use in COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C. Reporting Suspected Adverse Reactions to COVID-19 Vaccines in Portugal: Undesirable Effects by Type of Vaccine, Gender and Age until July 2021. Biomed. Biopharm. Res. 2022, 19, 114–132. [Google Scholar]
- Summary of Product Characteristics—Diazepam. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/6274/smpc#gref (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Summary of Product Characteristics—Quetiapine. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5495/smpc#gref (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Summary of Product Characteristics—Pregabalin. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/lyrica-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Nobili, A.; Garattini, S.; Mannucci, P.M. Multiple Diseases and Polypharmacy in the Elderly: Challenges for the Internist of the Third Millennium. J. Comorbidity 2011, 1, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madurga Sanz, M. Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia: Cómo Se Trabaja En Farmacovigilancia En España. Agencia Española Medicam. Prod. Sanit. 2012, 4, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia de Medicamentos de Uso Humano (SEFV-H): Resumen Exitoso de las Actuaciones de. 2021. Available online: https://www.farmaceuticos.com/pam/actualidad/farmacovigilancia/sistema-espanol-de-farmacovigilancia-de-medicamentos-de-uso-humano-sefv-h-resumen-exitoso-de-las-actuaciones-de-2021/ (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Heckenbach, K.; Ostermann, T.; Schad, F.; Kröz, M.; Matthes, H. Medication and Falls in Elderly Outpatients: An Epidemiological Study from a German Pharmacovigilance Network. Springerplus 2014, 3, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falls in Older Persons: Risk Factors and Patient Evaluation—UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/falls-in-older-persons-risk-factors-and-patient-evaluation (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Khong, T.P.; De Vries, F.; Goldenberg, J.S.B.; Klungel, O.H.; Robinson, N.J.; Ibáñez, L.; Petri, H. Potential Impact of Benzodiazepine Use on the Rate of Hip Fractures in Five Large European Countries and the United States. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2012, 91, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medications and Falls—Do I Still Need This Medication? Is Deprescribing for You? Available online: https://www.deprescribingnetwork.ca/medications-and-falls (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Hazell, L.; Shakir, S.A.W. Under-Reporting of Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review. Drug Saf. 2006, 29, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, M.J. Factors Affecting the Development of Adverse Drug Reactions. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pharmacotherapeutic Classification | Drugs | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Immunomodulators | Glatiramer acetate; Adalimumab; Alemtuzumab; Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab; Certolizumab pegol; Cetuximab; Cyclosporine; Daratumumab; Etanercept; Everolimus fingolimod; Dimethyl fumarate; Golimumab; Infliximab; Interferon beta-1a; Interferon beta-1b; Interferon gamma-1b; Ipilimumab; Lenalidomide; Natalizumab; Nivolumab; Obinutuzumab; Ocrelizumab; Peginterferon beta-1a; Pembrolizumab; Pertuzumab; Pirfenidone; Rituximab; Tacrolimus; Thalidomide; Teriflunomide; Tocilizumab; Trastuzumab; Ustecinumab | 372 (16.78%) |
| Vaccines (single and conjugate) | Diphtheria and tetanus vaccine; Influenza vaccine; Pandemic influenza vaccine; Adsorbed pneumococcal polyacid conjugate vaccine; Hepatitis B vaccine; Human papillomavirus vaccine; Human papillomavirus vaccine (types 6, 11, 16, 18); Human papillomavirus vaccine (types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58); Tetanus vaccine; Meningococcal vaccine; Measles, mumps, rubella vaccine; mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 (with modified nucleoside); COVID-19 non-replicating vectored viral vaccine (chimpanzee adenovirus); COVID-19 non-replicating vectored viral vaccine (human adenovirus type 26); Live rotavirus vaccine | 359 (16.19%) |
| Cytotoxics | Alectinib; Axicabtagene ciloleucel; Axitinib; Bleomycin; Bortezomib; Bosutinib; Carboplatin; Cisplatin; Capecitabine; Cladribine; Crizotinib; Dasatinib; Radium dichloride (223Ra); Docetaxel; Doxorubicin; Erlotinib; Exemestane; Etoposide; Glasdegib; Idelalisib; Irinotecan; Lenvatinib Methotrexate; Mitotane; Nilotinib; Nintedanib; Osimertinib; Oxaliplatin; Paclitaxel; Pazopanib; Pegaspargase; Regorafenib; Ribociclib; Ruxolitinib; Selumetinib; Sorafenib; Sunitinib; Verteporfin | 125 (5.64%) |
| Psychoactive drugs | Agomelatine; Alprazolam; Amitriptyline; Aripiprazole; Bupropion; Chlorpromazine; Cloxazolam; Clozapine; Dexmedetomidine; Diazepam; Duloxetine; Escitalopram; Fluoxetine; Fluvoxamine; Haloperidol; Levomepromazine; Lithium; Loflazepat ethyl; Lorazepam; Melatonin; Mexazolam; Mirtazapine; Olanzapine; Paliperidone; Paroxetine; Quetiapine; Risperidone; Sertraline; Sulpiride; Temazepam; Trazodone; Valerian; Venlafaxine; Ziprasidone; Zuclopenthixol | 105 (4.74%) |
| Antihypertensives | Altizide + Spironolactone; Amlodipine; Amlodipine + Valsartan; Amlodipine + Olmesartan medoxomilo; Amlodipine + Olmesartan medoxomilo + Hydrochlorothiazide; Bisoprolol; Bisoprolol + Perindopril; Candesartan + Hydrochlorothiazide; Captopril; Carvedilol; Cilazapril; Cilazapril + Hydrochlorothiazide; Chlorthalidone; Doxazosin; Enalapril + Hydrochlorothiazide; Eplerenone; Spironolactone; Furosemide; Hydrochlorothiazide + Triamterene; Indapamide; Indapamide + Amlodipine; Irbesartan + Hydrochlorothiazide; Lercanidipine; Lisinopril; Lisinopril + Hydrochlorothiazide; Losartan; Methyldopa; Nebivolol; Nifedipine; Olmesartan medoxomilo; Olmesartan medoxomilo + Hydrochlorothiazide; Perindopril; Perindopril + Amlodipine; Perindopril + Indapamide; Propranolol; Ramipril; Riociguat; Sacubitril + Valsartan; Telmisartan + Hydrochlorothiazide; Valsartan; Valsartan + Hydrochlorothiazide | 104 (4.69%) |
| Antibacterial drugs | Amoxicillin; Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid; Azithromycin; Benzylpenicillin benzathine + Benzylpenicillin potassium + Benzylpenicillin procaine; Cefatrizine; Cefazolin; Cefuroxime; Cefotaxime; Cefotetan; Cefoxitin; Cefradin; Ceftazidime; Ceftazidime + Avibactam; Ceftriaxone; Ciprofloxacin; Clarithromycin; Clindamycin; Flucloxacillin; Imipenem + Cilastatin; Isoniazid; Levofloxacin; Metronidazole; Minocycline; Moxifloxacin; Ofloxacin; Piperacillin + Tazobactam; Rifampicin; Bismuth potassium subcitrate + Metronidazole + Tetracycline; Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim; Teicoplanin; Telithromycin; Tinidazole; Vancomycin | 94 (4.24%) |
| Anticoagulants and Antithrombotics | Acenocoumarol; Acetylsalicylic acid; Alteplase; Apixaban Clopidogrel; Dabigatran etexilate; Enoxaparin sodium; Heparin sodium; Iloprost; Rivaroxaban; Tenecteplase; Ticagrelor; Ticlopidine; Warfarin | 78 (3.52%) |
| Analgesics and antipyretics | Acetylsalicylic acid; Chlorphenamine + Paracetamol; Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC PFV) + Cannabidiol (CBD PFV), Prep from plant drugs, ext Cannabis sativa; Flupirtine; Gabapentin; Metamizole magnesium; Metamizole sodium; Paracetamol; Pregabalin | 54 (2.44%) |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Acemetacin; Cetorolac; Colecoxib; Diclofenac; Diclofenac + Misoprostol; Etodolac; Etoricoxib; Flurbiprofen; Ibuprofen; Indomethacin; Lumiracoxib; Naproxen; Naproxen + Esomeprazole; Nimesulide; Rofecoxib | 43 (1.94%) |
| Antiarrhythmics | Amiodarone; Diltiazem; Propafenone; Sotalol; Verapamil | 37 (1.67%) |
| Other central nervous system drugs | Disulfiram; Donepezil; Fampridine; Ginkgo biloba; Memantine; Rivastigmine; Varenicline; Vinpocetine | 36 (1.62%) |
| Antivirals | Abacavir + Lamivudine; Acyclovir; Amphotericin B; Boceprevir; Dolutegravir + Abacavir + Lamivudine; Efavirenz; Efavirenz + Emtricitabine + Tenofovir; Elvitegravir + Cobicistat + Emtricitabine + Tenofovir; Emtricitabine + Tenofovir; Entecavir; Ledipasvir + Sofosbuvir; Oseltamivir; Raltegravir; Remdesivir; Ribavirin; Ritonavir; Sofosbuvir; Sofosbuvir + Velpatasvir; Tenofovir; Valacyclovir; Voriconazole | 34 (1.53%) |
| Hormones and antihormones | Anastrozole; Apalutamide; Bicalutamide; Enzalutamide; Goserreline; Letrozole; Leuprorreline; Megestrol; Tamoxifen; Triptorreline | 34 (1.53%) |
| Antianemics | Ferric carboxymaltose; Cobamamide; Iron–dextran complex; Saccharose ferric oxide; Ferrous sulphate + Folic acid | 32 (1.44%) |
| Insulin, antidiabetics, and glucagon | Dapagliflozin; Diazóxido; Dulaglutido; Empagliflozin; Ertugliflozin; Exenatido; Glibenclamida; Glibenclamida + Metformin; Gliclazida; Glimepirida + Pioglitazona; Insulin degludec; Insulin humana; Insulin isofânica; Linagliptin; Metformin; Metformin + Pioglitazona; Metformin + Sitagliptin | 31 (1.40%) |
| Radiologic contrast media | Iobitridol; Iodixanol; Io-hexol; Iomeprol; Iopromide; Ioversol | 30 (1.35%) |
| Antiepileptics and anticonvulsants | Eslicarbazepine acetate; Valproic acid; Carbamazepine; Phenytoin; Gabapentin; Lacosamide; Levetiracetam; Perampanel; Pregabalin; Primidone; Topiramate; Valproate semisodium; Zonisamide | 28 (1.26%) |
| Drugs that act on the bone and calcium metabolism | Alendronic acid + Colecalciferol; Ibandronic acid; Zoledronic acid; Ibandronic acid + Colecalciferol; Colecalciferol; Denosumab; Raloxifene; Strontium ranelate; Teriparatide | 25 (1.13%) |
| Other drugs used in genitourinary disorders | Alfuzosin; Throspium chloride; Doxazosin; Dutasteride + Tansulosin; Finasteride; Oxybutynin; Silodosin; Tadalafil; Tansulosin; Terazosin; Vardenafil | 23 (1.04%) |
| Others | 307 (15.47%) |
| Pharmacotherapeutic Classification | Drugs | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Immunomodulators | Adalimumab; Bevacizumab; Fingolimod; Dimethyl fumarate; Golimumab; Interferon beta-1a; Interferon beta-1b; Interferon gamma-1b; Ipilimumab; Natalizumab; Peginterferon beta-1a; Pirfenidone; Rituximab; Tocilizumab | 99 (28.86%) |
| Vaccines (single and conjugate) | Adsorbed pneumococcal polyoside conjugate vaccine; Diphtheria and tetanus vaccine; COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (with modified nucleoside); COVID-19 non-replicating viral vector vaccine (chimpanzee adenovirus); COVID-19 non-replicating viral vector vaccine (human adenovirus type 26); Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine | 47 (13.70%) |
| Anticoagulants and Antithrombotics | Acenocoumarol; Acetylsalicylic acid; Apixaban; Dabigatran etexilate; Enoxaparin sodium; Rivaroxaban; Warfarin | 34 (9.91%) |
| Psychoactive drugs | Agomelatine; Chlorpromazine; Duloxetine; Loflazepato de etilo; Lorazepam; Mirtazapine; Olanzapine; Paliperidona; Quetiapine; Risperidona; Sertraline; Trazodona; Zuclopentixol | 24 (7.00%) |
| Other central nervous system drugs | Donepezil; Fampridine; Rivastigmine | 12 (3.50%) |
| Insulin, antidiabetics, and glucagon | Ertugliflozin; Exenatide; Glibenclamide; Gliclazide; Insulin degludec; Insulin isophane; Linagliptin; Metformin; Sitagliptin | 9 (2.62%) |
| Antiepileptics and anticonvulsants | Valproic acid; Carbamazepine; Perampanel; Pregabalin; Primidone; Zonisamide | 8 (2.33%) |
| Antihypertensives | Hydrochlorothiazide + Triamterene; Olmesartan medoxomilo; Perindopril + Indapamide; Sacubitril + Valsartan | 7 (2.04%) |
| Drugs that act on bone and calcium metabolism | Alendronic Acid + Cholecalciferol; Denosumab; Raloxifene; Teriparatide | 7 (2.04%) |
| Antiparkinsonians | Levodopa + Carbidopa; Opicapona | 6 (1.75%) |
| Cytotoxics | Cladribine; Idelalisib; Lenvatinib; Nintedanib; Ribociclib; Ruxolitinib | 6 (1.75%) |
| Antivirals | Entecavir; Ledipasvir + Sofosbuvir | 4 (1.17%) |
| Hormones and antihormones | Enzalutamide; Goserrelin; Letrozole; Triptorrelin | 4 (1.17%) |
| Others | 33 (9.62%) |
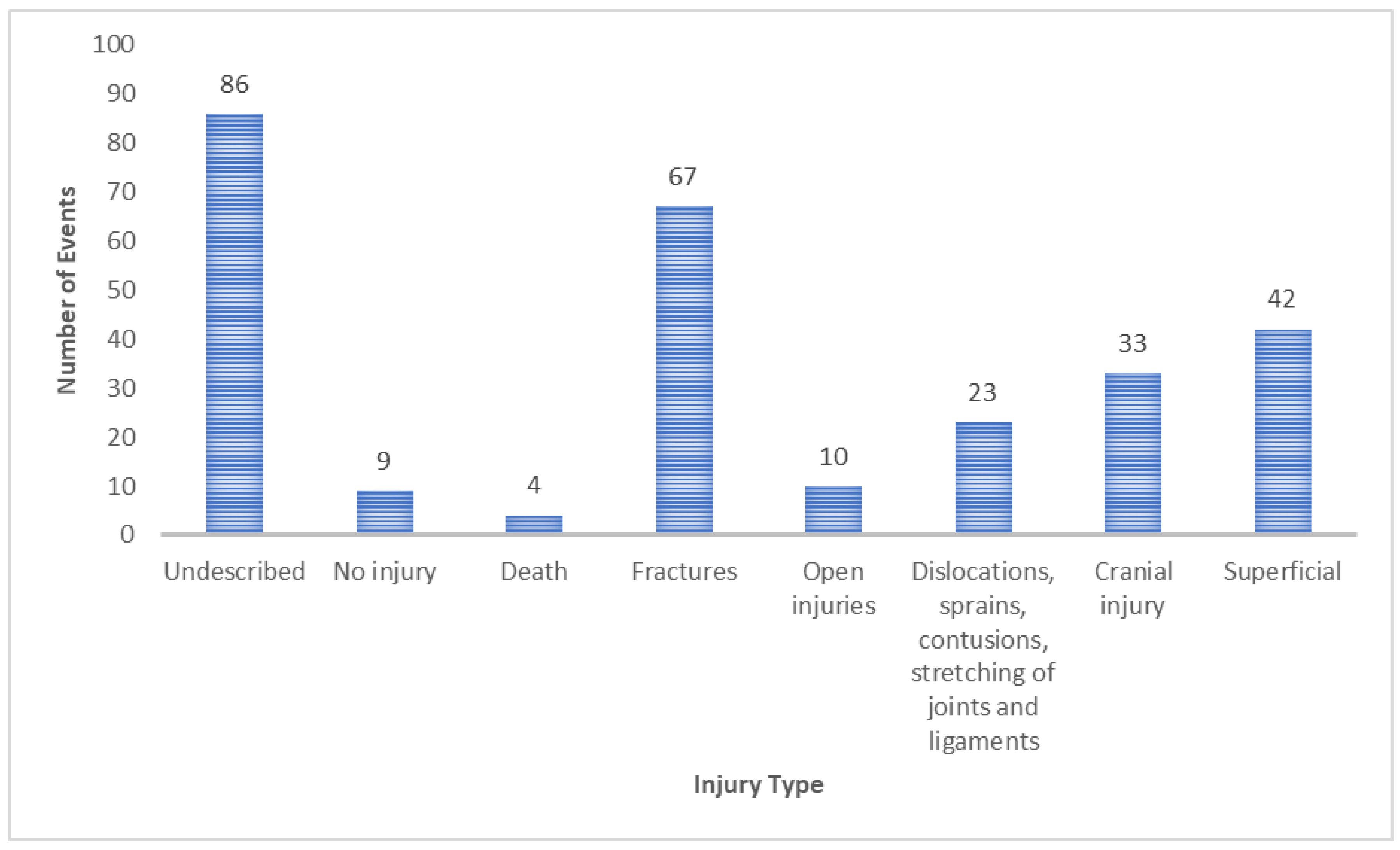
| Type of Injury | Affected Area | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Fractures | Head | 4 (1.46%) |
| Hip and thigh | 8 (2.92%) | |
| Lower limb | 31 (11.31%) | |
| Trunk | 12 (4.38%) | |
| Upper limb | 10 (3.65%) | |
| Multiple and unspecified body region | 2 (0.73%) | |
| Superficial | Head | 14 (5.11%) |
| Hip and thigh | 1 (0.36%) | |
| Lower limb | 7 (2.55%) | |
| Trunk | 6 (2.19%) | |
| Upper limb | 7 (2.55%) | |
| Multiple and unspecified body region | 7 (2.55%) | |
| Head injury | Head | 33 (12.04%) |
| Dislocations, sprains, contusions, stretching of joints and ligaments | Head | 2 (0.73%) |
| Hip and thigh | 1 (0.36%) | |
| Lower limb | 7 (2.55%) | |
| Trunk | 1 (0.36%) | |
| Upper limb | 5 (1.82%) | |
| Multiple and unspecified body region | 7 (2.55%) | |
| Open injuries | Head | 6 (2.19%) |
| Hip and thigh | 0 | |
| Lower limb | 2 (0.73%) | |
| Trunk | 0 | |
| Upper limb | 1 (0.36%) | |
| Multiple and unspecified body region | 1 (0.36%) | |
| No injury | 9 (3.28%) | |
| Death | 4 (1.46%) | |
| Undescribed | 86 (31.39%) |
| Other ADRs a Associated with Falls | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Hypotension | 977 (28.57%) |
| Visual disturbances b | 532 (15.56%) |
| Gait disorders c | 529 (15.47%) |
| Dizziness | 377 (11.02%) |
| Vertigo | 358 (10.47%) |
| Altered state of consciousness d | 150 (5.70%) |
| Syncope | 188 (5.50%) |
| Bradycardia | 118 (3.45%) |
| Sleepiness | 75 (2.19%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, D.; Silvestre, S.; Monteiro, C.; Duarte, A.P. Medication and the Risk of Falls: An Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions Reported to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237268
Rodrigues D, Silvestre S, Monteiro C, Duarte AP. Medication and the Risk of Falls: An Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions Reported to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237268
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Daniela, Samuel Silvestre, Cristina Monteiro, and Ana Paula Duarte. 2023. "Medication and the Risk of Falls: An Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions Reported to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237268
APA StyleRodrigues, D., Silvestre, S., Monteiro, C., & Duarte, A. P. (2023). Medication and the Risk of Falls: An Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions Reported to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237268








