Tenofovir-Induced Fanconi Syndrome Presenting with Life-Threatening Hypokalemia: Review of the Literature and Recommendations for Early Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dore, G.J.; Cooper, D.A.; Pozniak, A.L.; DeJesus, E.; Zhong, L.; Miller, M.D.; Lu, B.; Cheng, A.K. Efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in antiretroviral therapy-naive and -experienced patients coinfected with HIV-1 and hepatitis B virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bömmel, F.; Wünsche, T.; Mauss, S.; Reinke, P.; Bergk, A.; Schürmann, D.; Wiedenmann, B.; Berg, T. Comparison of adefovir and tenofovir in the treatment of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Fung, S.; Seto, W.K.; Chuang, W.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hui, A.J.; Janssen, H.L.; Chowdhury, A.; Tsang, T.Y.; et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, B.P.; Flaherty, J.F.; Shah, J. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: Clinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellin, P.; Wong, D.K.; Sievert, W.; Buggisch, P.; Petersen, J.; Flisiak, R.; Manns, M.; Kaita, K.; Krastev, Z.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Ten-year efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Montoya-Ferrer, A.; Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Poveda, J.; Sainz-Prestel, V.; Ortiz-Martin, N.; Parra-Rodriguez, A.; Selgas, R.; et al. Tenofovir nephrotoxicity: 2011 update. AIDS Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 354908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlitz, L.C.; Mohan, S.; Stokes, M.B.; Radhakrishnan, J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Markowitz, G.S. Tenofovir nephrotoxicity: Acute tubular necrosis with distinctive clinical, pathological, and mitochondrial abnormalities. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.W.; Steinhaus, M.C.; Szabo, S.; Dressier, R.M. Tenofovir-related nephrotoxicity: Case report and review of the literature. Pharmacotherapy 2004, 24, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Khalili, H.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S. Tenofovir-induced nephrotoxicity: Incidence, mechanism, risk factors, prognosis and proposed agents for prevention. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; He, Y.-H.; Yang, T.-T.; Yan, D.-M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.-X.; He, S.-H.; Zhou, Z.-H. Effects of long-term exposure to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-containing antiretroviral therapy on renal function in HIV-positive Chinese patients. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.W.; Kim, K.; Jun, K.I.; Kang, C.K.; Moon, S.M.; Song, K.H.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.B.; Park, S.W.; et al. Recovery of Tenofovir-induced Nephrotoxicity following Switch from Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate to Tenofovir Alafenamide in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patients. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 52, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.R.; Katlama, C.; Montaner, J.S.; Cooper, D.A.; Gazzard, B.; Clotet, B.; Lazzarin, A.; Schewe, K.; Lange, J.; Wyatt, C.; et al. The safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HIV infection in adults: The first 4 years. Aids 2007, 21, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, D.; Monge, M.; Meynard, J.L.; Fouqueray, B.; Mougenot, B.; Girard, P.M.; Ronco, P.; Rossert, J. Fanconi syndrome and renal failure induced by tenofovir: A first case report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 40, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrière, H.; Reynes, J.; Rouanet, I.; Daniel, N.; de Boever, C.M.; Mauboussin, J.M.; Leray, H.; Moachon, L.; Vincent, D.; Salmon-Céron, D. Renal tubular dysfunction associated with tenofovir therapy: Report of 7 cases. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2004, 35, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarga, P.; Barreiro, P.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; Rodriguez-Novoa, S.; Solera, C.; Medrano, J.; Rivas, P.; Albalater, M.; Blanco, F.; Moreno, V.; et al. Kidney tubular abnormalities in the absence of impaired glomerular function in HIV patients treated with tenofovir. Aids 2009, 23, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nóvoa, S.; Labarga, P.; D’Avolio, A.; Barreiro, P.; Albalate, M.; Vispo, E.; Solera, C.; Siccardi, M.; Bonora, S.; Di Perri, G.; et al. Impairment in kidney tubular function in patients receiving tenofovir is associated with higher tenofovir plasma concentrations. Aids 2010, 24, 1064–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracey, D.M.; Snelling, P.; McKenzie, P.; Strasser, S.I. Tenofovir-associated Fanconi syndrome in patients with chronic hepatitis B monoinfection. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.S.; Park, C.W.; Song, M.J. Tenofovir-associated Fanconi syndrome and nephrotic syndrome in a patient with chronic hepatitis B monoinfection. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viganò, M.; Brocchieri, A.; Spinetti, A.; Zaltron, S.; Mangia, G.; Facchetti, F.; Fugazza, A.; Castelli, F.; Colombo, M.; Lampertico, P. Tenofovir-induced Fanconi syndrome in chronic hepatitis B monoinfected patients that reverted after tenofovir withdrawal. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueaphongsukkit, T.; Gatechompol, S.; Avihingsanon, A.; Surintrspanont, J.; Iampenkhae, K.; Avihingsanon, Y.; Udomkarnjananun, S. Tenofovir alafenamide nephrotoxicity: A case report and literature review. AIDS Res. Ther. 2021, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Thibault, V.; Valantin, M.A.; Peytavin, G.; Schneider, L.; Benhamou, Y. Tenofovir/probenecid combination in HIV/HBV-coinfected patients: How to escape Fanconi syndrome recurrence? Aids 2010, 24, 1078–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libório, A.B.; Andrade, L.; Pereira, L.V.; Sanches, T.R.; Shimizu, M.H.; Seguro, A.C. Rosiglitazone reverses tenofovir-induced nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
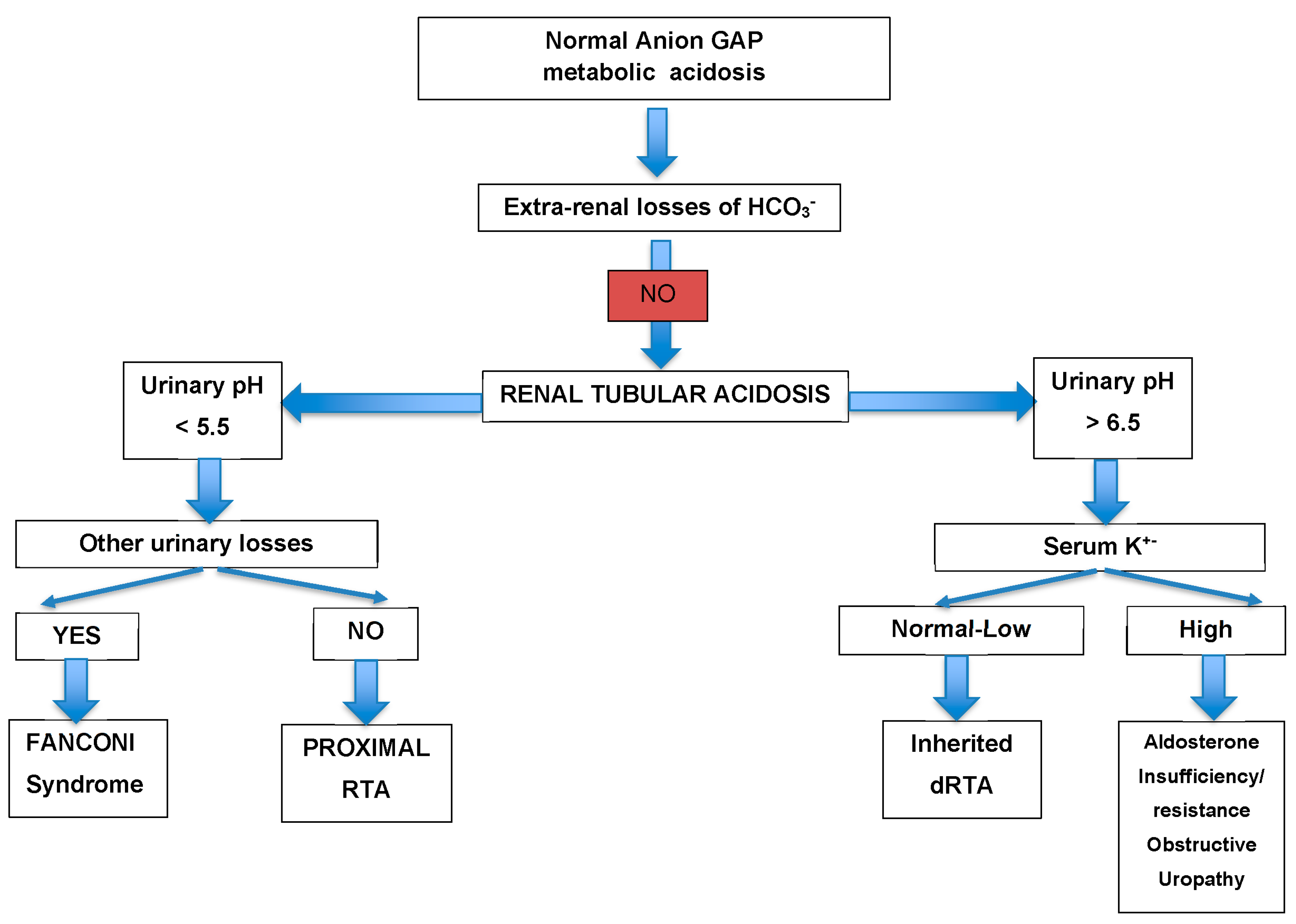
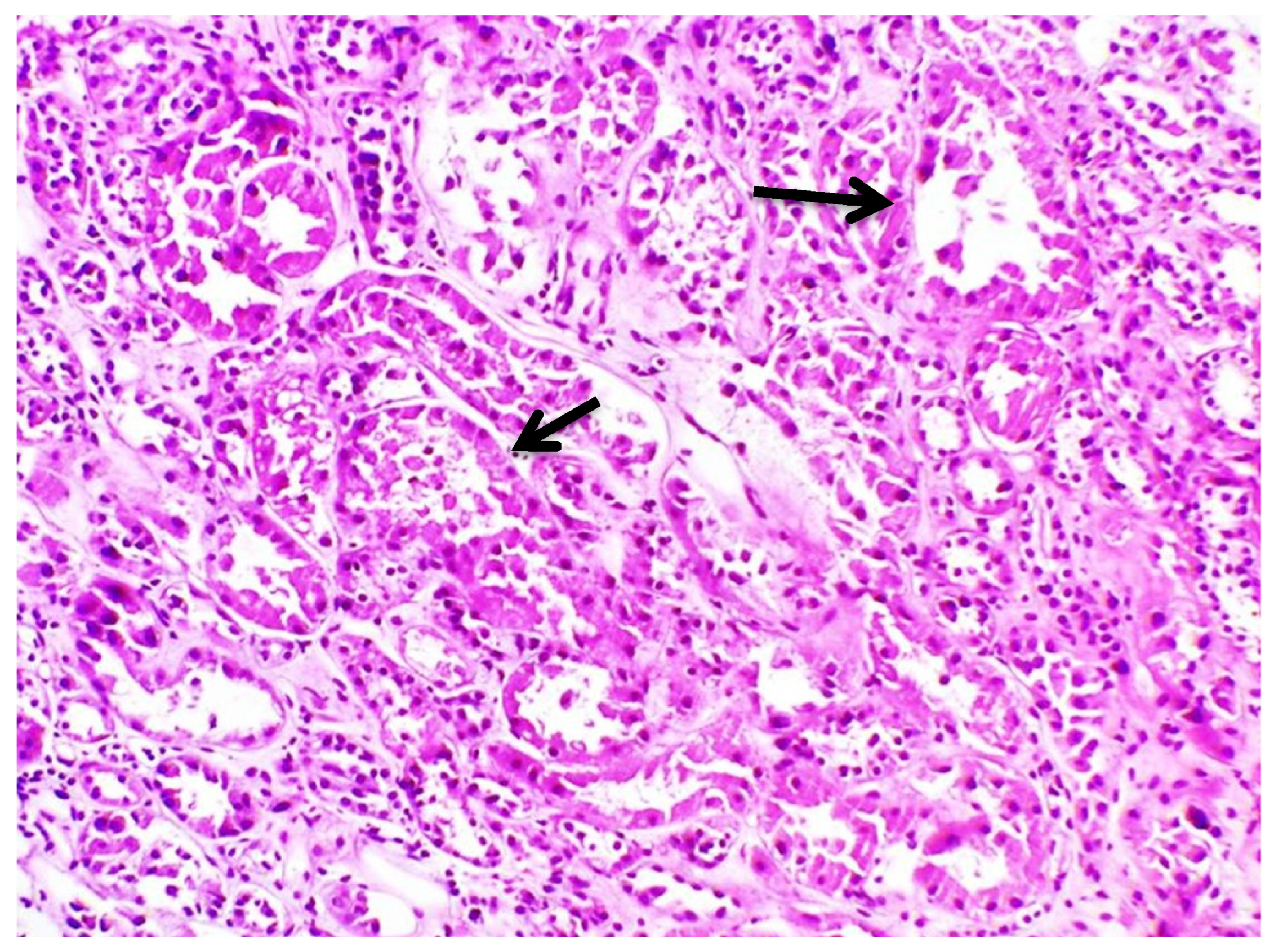
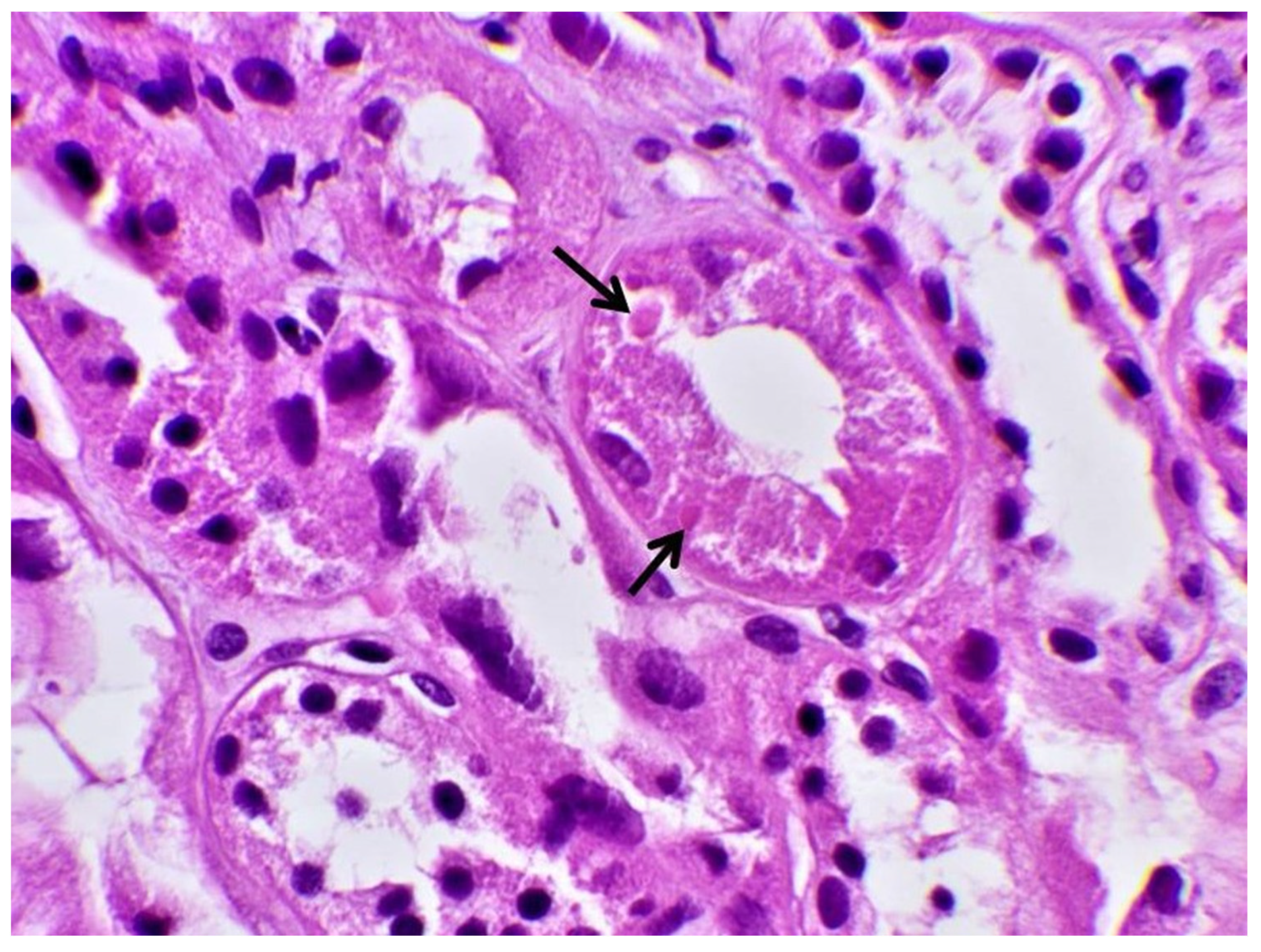
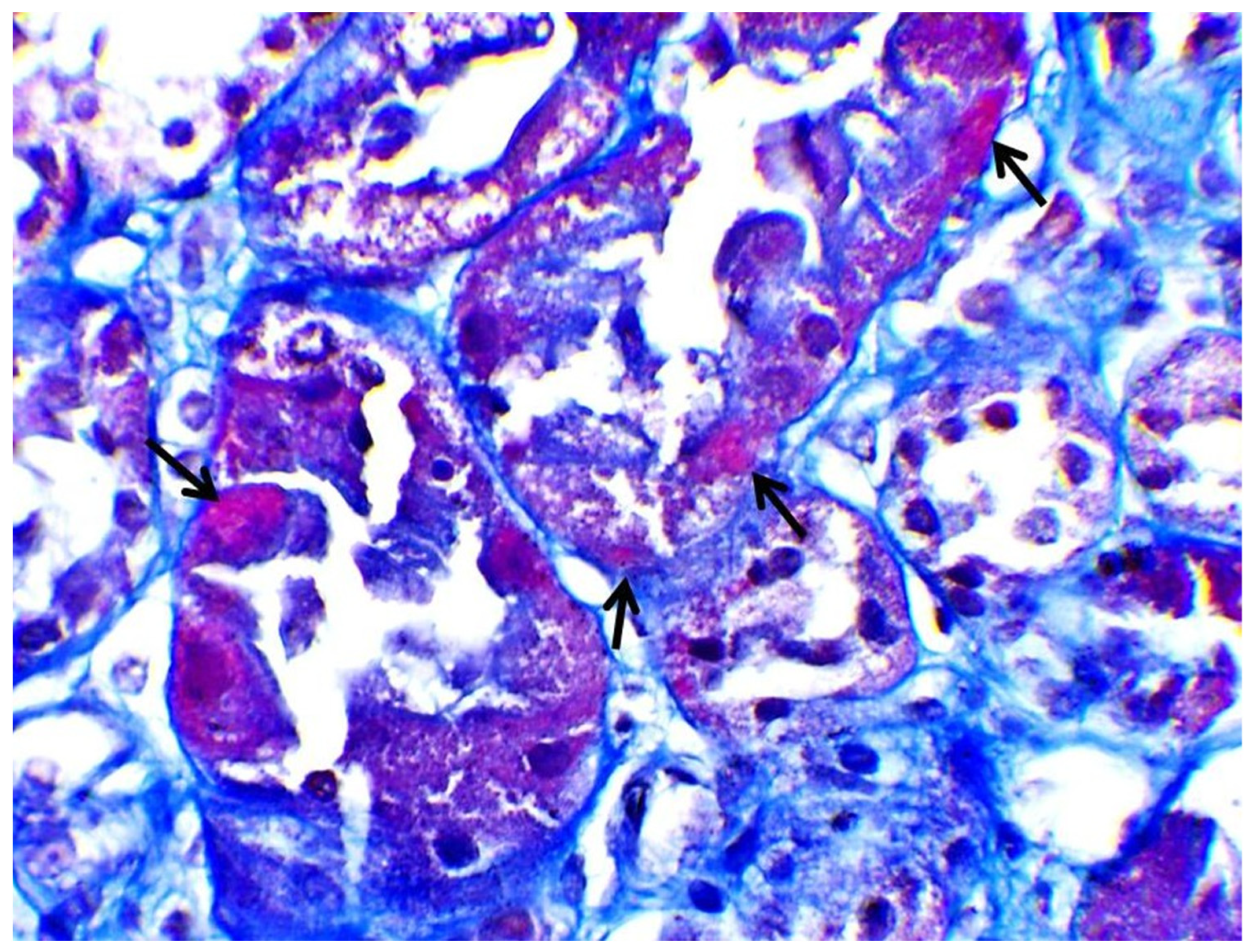
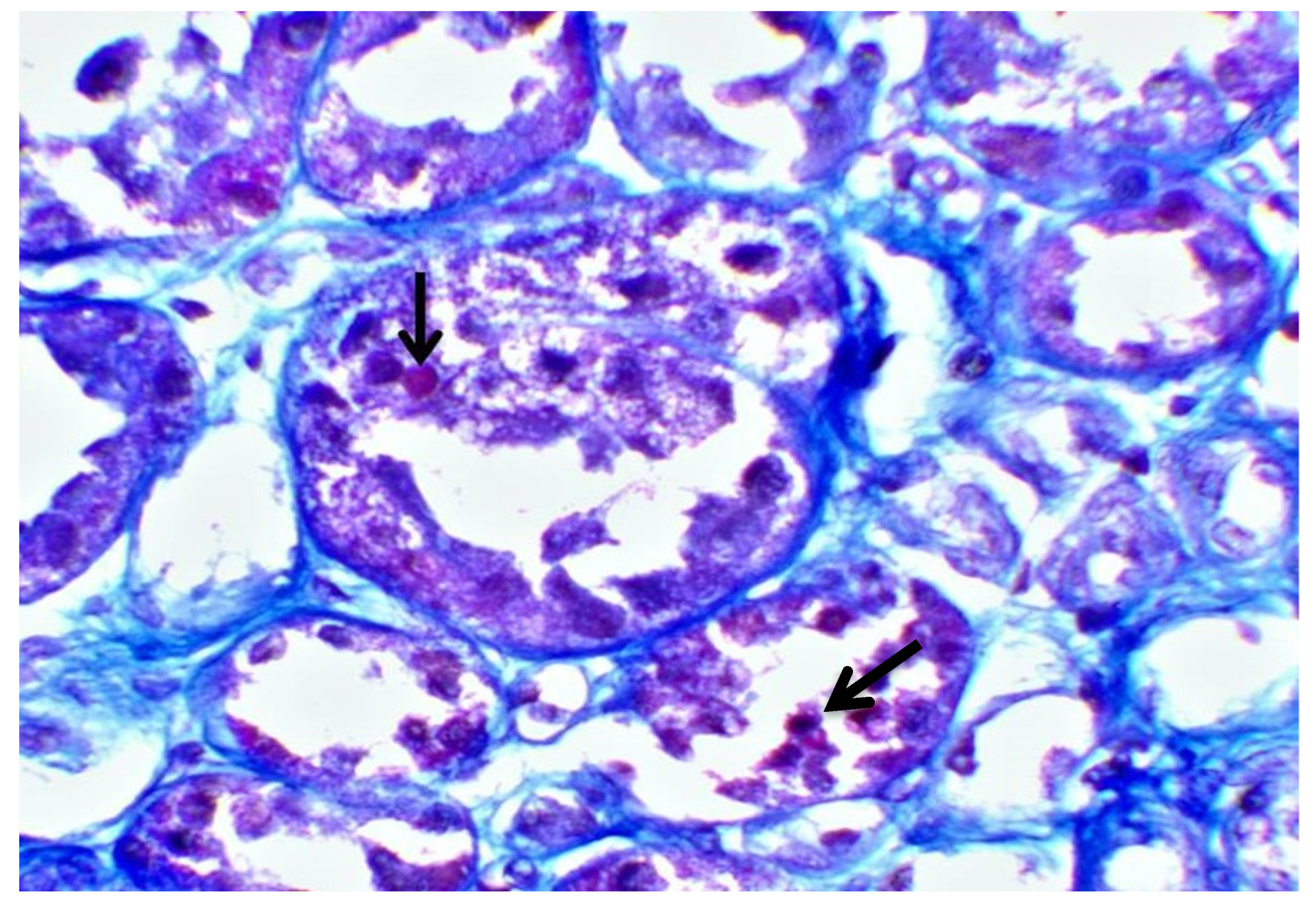
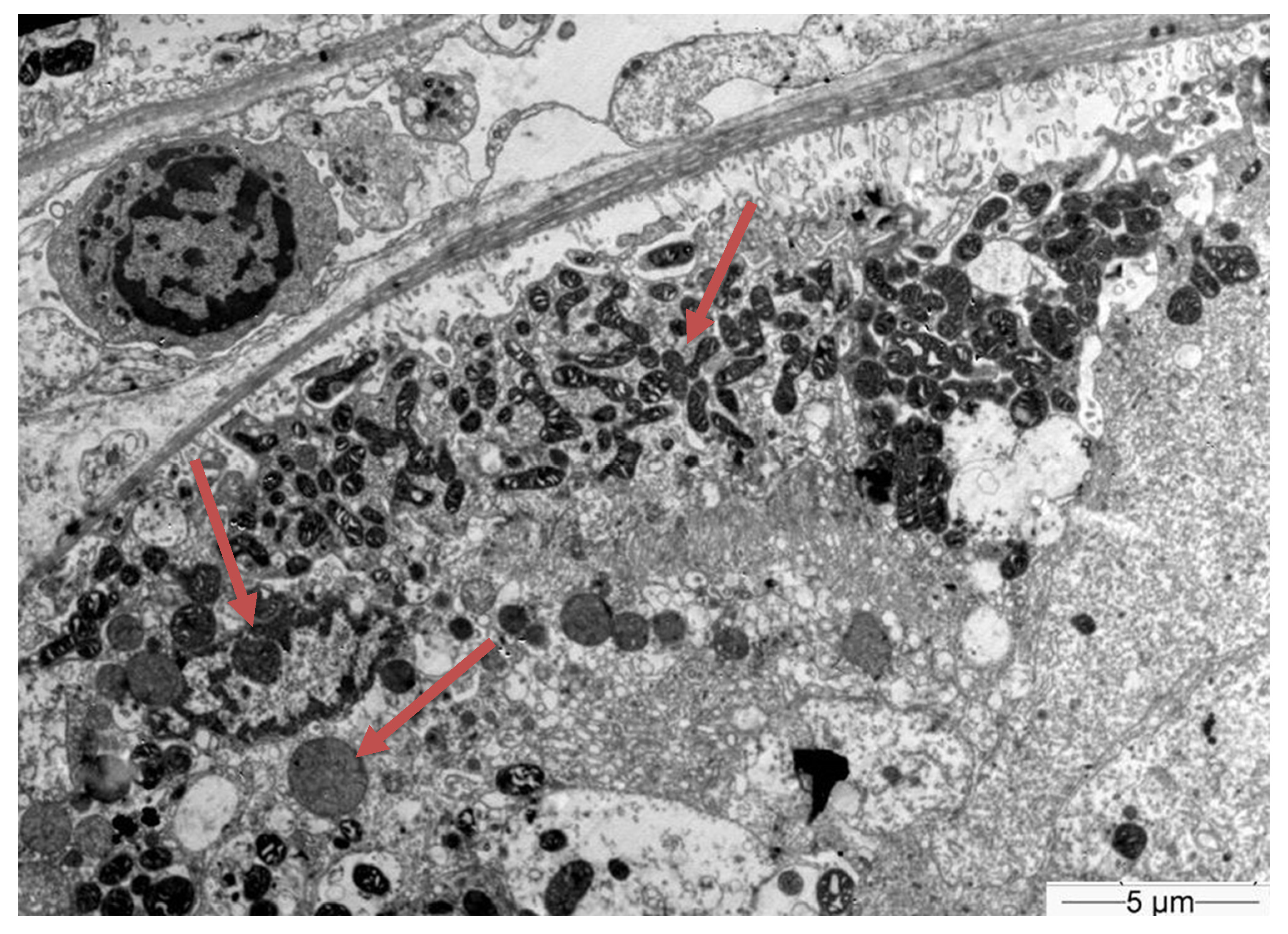
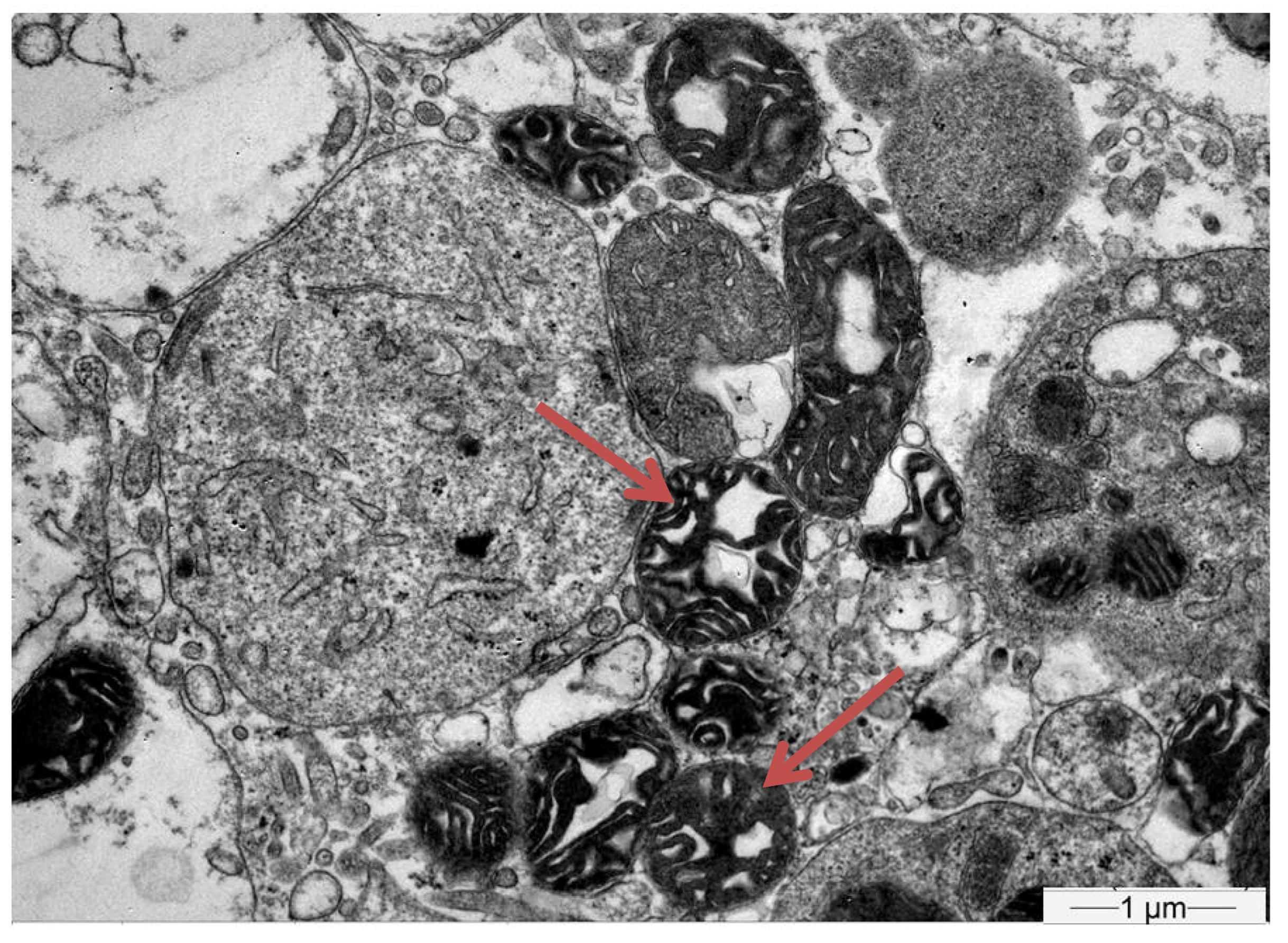
| Hb | 14 g/dL | 42–50% | Κ | 1.8 mmol/L | 3.5–5.1 mmol/L |
| Ht | 42.2% | 4.5–5.9 × 106/μL | Νa | 131 mmol/L | 136–148 mmol/L |
| RBC | 4.78 × 106/μL | 80–96/27–33/11.5–14.5 | AST | 25 U/L | 5–40 U/L |
| MCV/MCH/RDW | 90/29.9/15.5 | 4000–10,000/μL | ALT | 16 U/L | 5–40 U/L |
| WBC | 26,300/μL | (40–70%/19–48%/2–10%) | CPK | 130 U/L | 5–170/L |
| (Neutrophils/Lymphocytes/Monocytes) | (98%/1.2%/0.6%) | (40–70%/19–48%/2–10%) | LDH | 347 U/L | 135–225 U/L |
| PLTS | 201,000/μL | 140,000–400,000/μL | Glucose | 78 mg/dL | 75–115 mg/dL |
| Urea | 64 mg/dL | 18–50 mg/dL | |||
| Creatinine | 2.79 mg/dL | 0.7–1.2 mg/dL | |||
| PT | 13.4 s | 10–15 s | tBil | 0.28 mg/dL | 0.3–1.2 mg/dL |
| aPTT | 28.6 s | 26–36 s | Uric acid | 1.1 mg/dL | 3–7 mg/dL |
| INR | 1.22 | 0.8–1 | P | 0.9 mg/dL | 2.5–4.5 mg/dL |
| Fib | 5.7 | 1.8–3 | ALP | 111 U/L | 40–129 U/L |
| D-Dimers | 0.80 | Ca | 8.5 mg/dL | 8.5–10.2 mg/dL | |
| CRP | <0.33 mg/L | 0–5 mg/L | Total protein | 3.8 g/dL | 6.4–8.4 g/dL |
| TSH/fT4/T3 | 1.58/12.70 < 0.62 | albumin | 2.4 g/dL | 3.5–5 g/dL | |
| Urinalysis | Urine P | 426 mmol/L | 0.97–1.45 mmol/L | ||
| PH | 5.5 | Urine K | 87 mmol/L | 0–10 mmol/L | |
| Specific gravity | 1020 | Urine Cl | 86 mmol/L | 20–40 mmol/L | |
| Protein | +1 | Urine Na | 85 mmol/L | 0–20 mmol/L | |
| WBC | 1–2 | Urine anion gap | 86 mEq/L | 0–<10 mEq/L | |
| RBC | 15–20 | HBV | +HbsAg | ||
| HBV viral load | 0 copies | ||||
| Glucose | + | ABGS | |||
| 24-h urine protein | 2178 mg/day | PH | 7.11 | 7.35–7.45 | |
| Sat02 | 98% | 80–100% | |||
| pO2 | 113 mmHg | 80–100 mmHg | |||
| pCO2 | 18 mmHg | 35–45 mmHg | |||
| HCO3 | 6.6 mmol/L | 22–28.0 mmol/L | |||
| Glu | 3.3 mmol/L | 3.5–5.4 mmol/L | |||
| lac | 0.9 mmol/L | 0.0–2.0 mmol/L | |||
| K | 1.1 mmol/L | 3.7–4.7 mmol/L | |||
| Na | 128 mmol/L | 14–17.5 g/dL | |||
| Cl | 112 mmol/L | 101–110 mmol/L |
| Case No. 1 (2013; Gracey) [17] | Case No. 2 (2013; Gracey) [17] | Case No. 3 (2014; Vigano) [19] | Case No. 4 (2014; Vigano) [19] | Case No. 5 (2015; Hwang) [18] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | Male | Male | Male | Female |
| Age (years) | 39 | 52 | 58 | 62 | 44 |
| Origin | South-East Asian | Mediterranean | Italian | Italian | South-East Asian |
| Therapy | TDF 300 mg once daily | TDF 300 mg once daily | TDF 245 mg once daily | TDF 245 mg once daily | TDF 300 mg once daily |
| Indication | HBe-Ag (-) CHB | HBe-Ag (-) CHB | Hbe-Ag (-) CHB | Hbe-Ag (-) CHB | HBe-Ag (-) CHB |
| HBV DNA levels | 110,000 IU/mL | 6,400,000 IU/mL | <12 IU/mL | 121,780 IU/mL | 12,300 IU/mL |
| Comorbidities | Hypertension | Obesity, Dyslipidaemia, Hypertension, Sleep apnea | None | Hypertension | Low BMI, Diabetes |
| Onset | 48 months | 24 months | 30 months | 45 months | 3 months |
| Crbaseline | 96 μmol/L (EGFR: 81 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 94 μmol/L (EGFR: 77 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.90 mg/dL (EGFR: 89 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.9 mg/dL (EGFR: 88 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 1.03 mg/dL (EGFR: 58.2 mL/min/1.73 m2) |
| Crfanconi | 127 μmol/L (EGFR: 59 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 135 μmol/L (EGFR: 51 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 1.32 mg/dL (EGFR: 55 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 3.35 mg/dL (EGFR: 18 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 3.22 mg/dL (EGFR: 15.6 mL/min/1.73 m2) |
| Potassiumserium | NA | NA | 4.7 mEq/L | 3.6 mEq/L | 2.0 mEq/L |
| Uric Acidserum | 0.21 mmol/L | 0.08 mmol/L | NA | NA | 2.5 mg/dL |
| Phosphateserum | 0.8 mmol/L | 0.68 mmol/L | 2.0 mg/dL | 1.7 mg/dL | 2.6 mg/dL |
| Microglobinuria | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Yes |
| Proteinuria | 0.6 g/24 h | 0.2 g/24 h | 0.05 g/24 | 0.3 g/24 | Severe |
| Glycosuria | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Osteoporosis (T-score) | NA | NA | Yes | No | NA |
| Biopsy | Proximal Tubular Injury | Not performed | Not performed | Not performed | Proximal Tubular Injury |
| Switch Agent | Entecavir 0.5 mg daily | Entecavir 0.5 mg daily | Entecavir 0.5 mg daily | Entecavir 0.5 mg every other day | Entecavir 0.5 mg daily |
| Time to tubular restoration | 6 months | 3 months | 3 months | 9 months | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liatsou, E.; Tatouli, I.; Mpozikas, A.; Pavlou, M.-M.; Gakiopoulou, H.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Kontogiannis, S.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Tenofovir-Induced Fanconi Syndrome Presenting with Life-Threatening Hypokalemia: Review of the Literature and Recommendations for Early Detection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227178
Liatsou E, Tatouli I, Mpozikas A, Pavlou M-M, Gakiopoulou H, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Gavriatopoulou M, Kontogiannis S, Dimopoulos MA. Tenofovir-Induced Fanconi Syndrome Presenting with Life-Threatening Hypokalemia: Review of the Literature and Recommendations for Early Detection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(22):7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227178
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiatsou, Efstathia, Ioanna Tatouli, Andreas Mpozikas, Maria-Markella Pavlou, Hariklia Gakiopoulou, Ioannis Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Maria Gavriatopoulou, Sofoklis Kontogiannis, and Meletios Athanasios Dimopoulos. 2023. "Tenofovir-Induced Fanconi Syndrome Presenting with Life-Threatening Hypokalemia: Review of the Literature and Recommendations for Early Detection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 22: 7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227178
APA StyleLiatsou, E., Tatouli, I., Mpozikas, A., Pavlou, M.-M., Gakiopoulou, H., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I., Gavriatopoulou, M., Kontogiannis, S., & Dimopoulos, M. A. (2023). Tenofovir-Induced Fanconi Syndrome Presenting with Life-Threatening Hypokalemia: Review of the Literature and Recommendations for Early Detection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(22), 7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227178







