Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
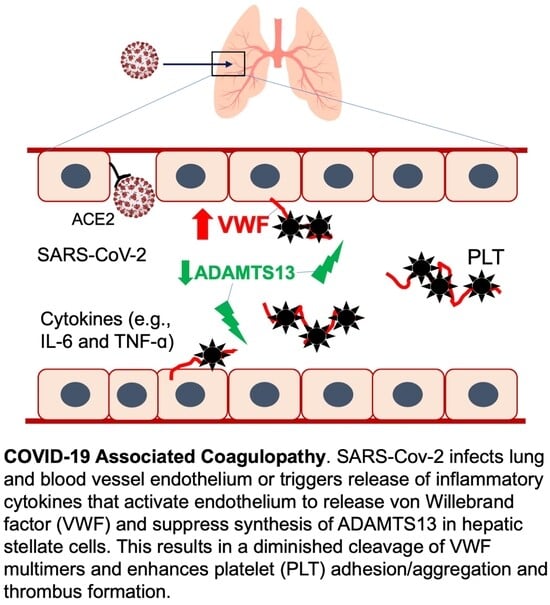
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Sampling
2.2. Plasma VWF Antigen
2.3. Plasma ADAMTS13 Antigen
2.4. Preparation of Recombinant VWF73 Peptide
2.5. Plasma ADAMTS13 Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory Characteristics of the COVID-19 Patient Cohort
3.2. Plasma Levels of VWF Antigen, ADAMTS13 Activity, and ADAMTS13 Antigen in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.3. Dynamic Changes in Plasma VWF and ADAMTS13 in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.4. Elevated VWF Levels or VWF/ADAMTS13 Antigen Ratios Predict 60-Day Mortality in Patients with Severe/Critical COVID-19
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortigoza, M.B.; Yoon, H.; Goldfeld, K.S.; Troxel, A.B.; Daily, J.P.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Cobb, G.F.; Baptiste, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma in Hospitalized Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Murakami, M. COVID-19: A New Virus, but a Familiar Receptor and Cytokine Release Syndrome. Immunity 2020, 52, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S. ACE2 receptor: A potential pharmacological target in COVID-19. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2023, 24, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutsogiannis, D.J.; Alharthy, A.; Balhamar, A.; Faqihi, F.; Papanikolaou, J.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Memish, Z.A.; Brindley, P.G.; Brochard, L.; Karakitsos, D. Mortality and Pulmonary Embolism in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome From COVID-19 vs. Non-COVID-19. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 800241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, Z.; Bignotti, A.; Zheng, X.L. Longitudinal Assessment of Plasma Syndecan-1 Predicts 60-Day Mortality in Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, A.; Pranata, R.; Lim, M.A.; Akbara, M.R.; Martha, J.W. Endotheliopathy marked by high von Willebrand factor (vWF) antigen in COVID-19 is associated with poor outcome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 117, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, H.; Townsend, L.; Morrin, H.; Ahmad, A.; Comerford, C.; Karampini, E.; Englert, H.; Byrne, M.; Bergin, C.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; et al. Persistent endotheliopathy in the pathogenesis of long COVID syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 2546–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp, S.; Coppens, M.; van Haaps, T.F.; Foppen, M.; Vlaar, A.P.; Muller, M.C.A.; Bouman, C.C.S.; Beenen, L.F.M.; Kootte, R.S.; Heijmans, J.; et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfidia, A.; Pola, R. Venous thromboembolism in COVID-19 patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1516–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, D.; Sperhake, J.P.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Steurer, S.; Edler, C.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Mushumba, H.; Kniep, I.; Schroder, A.S.; et al. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, C.; Lambert, C. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on therapeutic choices in Thrombosis-Hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1794–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.C.; Eldahshan, W.; Rutkowski, E. COVID-19-Related Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, I. Biology of endothelium. Lupus 1998, 7 (Suppl. 2), S41–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y. Current understanding of the biology of vascular endothelium. Cell Struct. Funct. 2001, 26, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gonzalez Rodriguez, E.; Ostrowski, S.R.; Cardenas, J.C.; Baer, L.A.; Tomasek, J.S.; Henriksen, H.H.; Stensballe, J.; Cotton, B.A.; Holcomb, J.B.; Johansson, P.I.; et al. Syndecan-1: A Quantitative Marker for the Endotheliopathy of Trauma. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 225, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Wada, H.; Okugawa, Y.; Tamaki, S.; Nakasaki, T.; Watanabe, R.; Gabazza, E.C.; Nishikawa, M.; Minami, N.; Shiku, H. Increased plasma thrombomodulin as a vascular endothelial cell marker in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2001, 7, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporn, L.A.; Chavin, S.I.; Marder, V.J.; Wagner, D.D. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human megakaryocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 76, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporn, L.A.; Marder, V.J.; Wagner, D.D. von Willebrand factor released from Weibel-Palade bodies binds more avidly to extracellular matrix than that secreted constitutively. Blood 1987, 69, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayadas, T.N.; Wagner, D.D. von Willebrand factor biosynthesis and processing. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 614, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.D.; Bonfanti, R. von Willebrand factor and the endothelium. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1991, 66, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, M.; Anvari, B.; Romo, G.M.; Cruz, M.A.; Dong, J.F.; McIntire, L.V.; Moake, J.L.; Lopez, J.A. Ultralarge multimers of von Willebrand factor form spontaneous high-strength bonds with the platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex: Studies using optical tweezers. Blood 2002, 99, 3971–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A.; Ball, C.; Nolasco, L.; Moake, J.F.; Dong, J.F. Effects of inflammatory cytokines on the release and cleavage of the endothelial cell-derived ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers under flow. Blood 2004, 104, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.F.; Moake, J.L.; Nolasco, L.; Bernardo, A.; Arceneaux, W.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Schade, A.J.; McIntire, L.V.; Fujikawa, K.; Lopez, J.A. ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers on the endothelial surface under flowing conditions. Blood 2002, 100, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Kisucka, J.; Brill, A.; Walsh, M.T.; Scheiflinger, F.; Wagner, D.D. ADAMTS13: A new link between thrombosis and inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chung, D.; Takayama, T.K.; Majerus, E.M.; Sadler, J.E.; Fujikawa, K. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41059–41063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwamoto, T.A.; Mori, T.; Wanaka, A.; Fukui, H.; et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood 2005, 106, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.; Nolasco, L.; Tao, Z.; Dong, J.F.; Moake, J. Human endothelial cells synthesize and release ADAMTS-13. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Zheng, X.W.; Niiya, M.; Zheng, X.L. Apical sorting of ADAMTS13 in vascular endothelial cells and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells depends on the CUB domains and their association with lipid rafts. Blood 2006, 108, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.J.; Niiya, M.; Zheng, X.W.; Shang, D.Z.; Zheng, X.L. Inflammatory cytokines inhibit ADAMTS13 synthesis in hepatic stellate cells and endothelial cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.N.; Emonts, M.; de Maat, M.P.; de Groot, R.; Lisman, T.; Hazelzet, J.A.; Leebeek, F.W. Reduced ADAMTS13 in children with severe meningococcal sepsis is associated with severity and outcome. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 103, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, R.A.; Bockmeyer, C.L.; Kentouche, K.; Sieber, M.W.; Oberle, V.; Kaufmann, R.; Deigner, H.P.; Losche, W. Transcriptional regulation of ADAMTS13. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, J.E. A new name in thrombosis, ADAMTS13. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11552–11554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, C.B.; Cao, W.; Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor interactions. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Lian, E.C.; Foroud, T.; McClintick, J.N.; McGee, B.M.; Yang, A.Y.; Siemieniak, D.R.; Stark, K.R.; Gruppo, R.; et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001, 413, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.M.; Lian, E.C. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Eng. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.R.; de Groot, R.; Scully, M.A.; Crawley, J.T. Pathogenicity of Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies in Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. eBioMedicine 2015, 2, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.N.; de Maat, M.P.; van Goor, M.L.; Bhagwanbali, V.; van Vliet, H.H.; Gomez Garcia, E.B.; Dippel, D.W.; Leebeek, F.W. High von Willebrand factor levels increase the risk of first ischemic stroke: Influence of ADAMTS13, inflammation, and genetic variability. Stroke 2006, 37, 2672–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.M.; Siegerink, B.; Luken, B.M.; Crawley, J.T.; Algra, A.; Lane, D.A.; Rosendaal, F.R. High VWF, low ADAMTS13, and oral contraceptives increase the risk of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction in young women. Blood 2012, 119, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, M.; Uemura, S.; Uemura, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Ishizashi, H.; Imagawa, K.; Iwama, H.; Takeda, Y.; Kawata, H.; Nakajima, T.; et al. Acute myocardial infarction as a systemic prothrombotic condition evidenced by increased von Willebrand factor protein over ADAMTS13 activity in coronary and systemic circulation. Heart Vessels 2008, 23, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, S.; Goda, H. Increased VWF antigen levels and decreased ADAMTS13 activity in preeclampsia. Hematology 2013, 18, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genet, G.F.; Johansson, P.I.; Meyer, M.A.; Solbeck, S.; Sorensen, A.M.; Larsen, C.F.; Welling, K.L.; Windelov, N.A.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Ostrowski, S.R. Trauma-induced coagulopathy: Standard coagulation tests, biomarkers of coagulopathy, and endothelial damage in patients with traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.T.; McDaniel, J.K.; Cao, W.; Shroyer, M.; Wagener, B.M.; Zheng, X.L.; Pittet, J.F. Low Plasma ADAMTS13 Activity Is Associated with Coagulopathy, Endothelial Cell Damage and Mortality after Severe Paediatric Trauma. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tecson, K.M.; McCullough, P.A. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to COVID-19-associated vascular inflammation and coagulopathy. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgushina, N.; Gorodnova, E.; Beznoshenco, O.; Romanov, A.; Menzhinskaya, I.; Krechetova, L.; Sukhikh, G. Von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS-13 Are Associated with the Severity of COVID-19 Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Benoit, S.W.; de Oliveira, M.H.S.; Lippi, G.; Favaloro, E.J.; Benoit, J.L. ADAMTS13 activity to von Willebrand factor antigen ratio predicts acute kidney injury in patients with COVID-19: Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 induced secondary thrombotic microangiopathy. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 43, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, N.; Montagnana, M.; Pizzolo, F.; Friso, S.; Salvagno, G.L.; Forni, G.L.; Gianesin, B.; Morandi, M.; Lunardi, C.; Lippi, G.; et al. A relative ADAMTS13 deficiency supports the presence of a secondary microangiopathy in COVID 19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 193, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Rodriguez, M.; Castro Quismondo, N.; Zafra Torres, D.; Gil Alos, D.; Ayala, R.; Martinez-Lopez, J. Increased von Willebrand factor antigen and low ADAMTS13 activity are related to poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, O152–O155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Baronciani, L.; Artoni, A.; Colpani, P.; Biganzoli, M.; Cozzi, G.; Novembrino, C.; Boscolo Anzoletti, M.; De Zan, V.; Pagliari, M.T.; et al. The ADAMTS13-von Willebrand factor axis in COVID-19 patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.; Marco, P. Von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 activity as clinical severity markers in patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, B.S.; Darmon, M.; Dekimpe, C.; Dupont, T.; Dumas, G.; Yvin, E.; Beranger, N.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Azoulay, E.; Veyradier, A. Imbalance of von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 axis is rather a biomarker of strong inflammation and endothelial damage than a cause of thrombotic process in critically ill COVID-19 patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, W.; Ziade, M.A.; Arya, A.; Saleh, H.; Ali, S.; Rao, S.R.; Fdl Alla, O.; Ali, M.; Zouhbi, M.A.; Abdelrahman, A. Reduced ADAMTS13 Activity in Correlation with Pathophysiology, Severity, and Outcome of COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 117, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Cao, W.; McDaniel, J.K.; Pham, H.P.; Raju, D.; Nawalinski, K.; Frangos, S.; Kung, D.; Zager, E.; Kasner, S.E.; et al. Plasma ADAMTS13 activity and von Willebrand factor antigen and activity in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raife, T.J.; Cao, W.; Atkinson, B.S.; Bedell, B.; Montgomery, R.R.; Lentz, S.R.; Johnson, G.F.; Zheng, X.L. Leukocyte proteases cleave von Willebrand factor at or near the ADAMTS13 cleavage site. Blood 2009, 114, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lawson, H.L.; Harish, V.C.; Huff, J.D.; Knovich, M.A.; Owen, J. Creation of a recombinant peptide substrate for fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based protease assays. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 358, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.J.; Bir, N.; Rahn, P.; Dotson, R.; Brohi, K.; Chesebro, B.B.; Mackersie, R.; Carles, M.; Wiener-Kronish, J.; Pittet, J.F. Protein C depletion early after trauma increases the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia. J. Trauma. 2009, 67, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmer, E.; Houston, B.L.; Kumar, A.; Abou-Setta, A.M.; Friesen, C.; Marshall, J.C.; Rock, G.; Turgeon, A.F.; Cook, D.J.; Houston, D.S.; et al. The efficacy and safety of plasma exchange in patients with sepsis and septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeriani, E.; Porfidia, A.; Ageno, W.; Spoto, S.; Pola, R.; Di Nisio, M. High-dose versus low-dose venous thromboprophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 17, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patell, R.; Bogue, T.; Koshy, A.; Bindal, P.; Merrill, M.; Aird, W.C.; Bauer, K.A.; Zwicker, J.I. Postdischarge thrombosis and hemorrhage in patients with COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannis, D.; Allen, S.L.; Tsang, J.; Flint, S.; Pinhasov, T.; Williams, S.; Tan, G.; Thakur, R.; Leung, C.; Snyder, M.; et al. Postdischarge thromboembolic outcomes and mortality of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The CORE-19 registry. Blood 2021, 137, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacciotti, E.; Barile Agati, L.; Calderaro, D.; Aguiar, V.C.R.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; de Oliveira, C.C.C.; Lins Dos Santos, J.; Volpiani, G.G.; Sobreira, M.L.; Joviliano, E.E.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus no anticoagulation for post-discharge thromboprophylaxis after hospitalisation for COVID-19 (MICHELLE): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuker, A.; Tseng, E.K.; Schunemann, H.J.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blair, C.; Dane, K.; DeSancho, M.T.; Diuguid, D.; Griffin, D.O.; Kahn, S.R.; et al. American Society of Hematology living guidelines on the use of anticoagulation for thromboprophylaxis for patients with COVID-19: March 2022 update on the use of anticoagulation in critically ill patients. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4975–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.; Gajic, O. Response to Aspirin Therapy in COVID-19: Prevention of NETosis. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arefizadeh, R.; Moosavi, S.H.; Towfiqie, S.; Mohsenizadeh, S.A.; Pishgahi, M. Effect of Ticagrelor Compared to Clopidogrel on Short-term Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention; a Randomized Clinical Trial. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2023, 11, e14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Iagnocco, A.; Giacomelli, R. Cytokine storm syndrome in severe COVID-19. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doevelaar, A.A.N.; Bachmann, M.; Holzer, B.; Seibert, F.S.; Rohn, B.J.; Zgoura, P.; Witzke, O.; Dittmer, U.; Brenner, T.; Paniskaki, K.; et al. Generation of potentially inhibitory autoantibodies to ADAMTS13 in coronavirus disease 2019. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, R.; McKinnon, T.A.J.; Zhang, X.F. Contribution of the von Willebrand factor/ADAMTS13 imbalance to COVID-19 coagulopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 322, H87–H93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovits, G.; Reti, M.; Muller, V.; Ivanyi, Z.; Gal, J.; Gopcsa, L.; Remenyi, P.; Szathmary, B.; Lakatos, B.; Szlavik, J.; et al. Associations between the von Willebrand Factor-ADAMTS13 Axis, Complement Activation, and COVID-19 Severity and Mortality. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, F.; Blair, R.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Mudd, J.; Currey, J.M.; Iwanaga, N.; He, J.; Mi, R.; et al. Endothelial cell infection and dysfunction, immune activation in severe COVID-19. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8076–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Lei, T.; Patel, P.S.; Lee, C.H.; Monaghan-Nichols, P.; Xin, H.B.; Qiu, J.; Fu, M. Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0139621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colunga Biancatelli, R.M.L.; Solopov, P.A.; Sharlow, E.R.; Lazo, J.S.; Marik, P.E.; Catravas, J.D. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 induces COVID-19-like acute lung injury in Kappa18-hACE2 transgenic mice and barrier dysfunction in human endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L477–L484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuovo, G.J.; Magro, C.; Shaffer, T.; Awad, H.; Suster, D.; Mikhail, S.; He, B.; Michaille, J.J.; Liechty, B.; Tili, E. Endothelial cell damage is the central part of COVID-19 and a mouse model induced by injection of the S1 subunit of the spike protein. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 51, 151682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioh, F.W.; Fong, S.W.; Young, B.E.; Wu, K.X.; Siau, A.; Krishnan, S.; Chan, Y.H.; Carissimo, G.; Teo, L.L.; Gao, F.; et al. Convalescent COVID-19 patients are susceptible to endothelial dysfunction due to persistent immune activation. eLife 2021, 10, e64909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogarty, H.; Ward, S.E.; Townsend, L.; Karampini, E.; Elliott, S.; Conlon, N.; Dunne, J.; Kiersey, R.; Naughton, A.; Gardiner, M.; et al. Sustained VWF-ADAMTS-13 axis imbalance and endotheliopathy in long COVID syndrome is related to immune dysfunction. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2022, 20, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockmeyer, C.L.; Claus, R.A.; Budde, U.; Kentouche, K.; Schneppenheim, R.; Losche, W.; Reinhart, K.; Brunkhorst, F.M. Inflammation-associated ADAMTS13 deficiency promotes formation of ultra-large von Willebrand factor. Haematologica 2008, 93, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, X.L. Low ADAMTS-13 predicts adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients with suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 5, e12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiscia, G.; Favuzzi, G.; De Laurenzo, A.; Cappucci, F.; Fischetti, L.; Colaizzo, D.; Chinni, E.; Florio, L.; Miscio, G.; Piscitelli, A.P.; et al. The Prognostic Value of ADAMTS-13 and von Willebrand Factor in COVID-19 Patients: Prospective Evaluation by Care Setting. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Mansouritorghabeh, H.; Parsa-Kondelaji, M. High levels of Von Willebrand factor markers in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 22, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrijevic, D.; Andrijevic, L.; Antic, J.; Rakic, G.; Pastor, K. Hemogram-based decision tree models for discriminating COVID-19 from RSV in infants. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrijevic, D.; Antic, J.; Rakic, G.; Katanic, J.; Andrijevic, L.; Pastor, K. Clinical Hematochemical Parameters in Differential Diagnosis between Pediatric SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Virus Infection: An Automated Machine Learning Approach. Children 2023, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, F.; Scully, M.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Cataland, S.; Knobl, P.; Wu, H.; Artoni, A.; Westwood, J.P.; Mansouri Taleghani, M.; Jilma, B.; et al. Caplacizumab for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.R.; Peyvandi, F.; Coppo, P.; Knobl, P.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Metjian, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Pavenski, K.; Callewaert, F.; et al. Caplacizumab Treatment for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Knobl, P.; Kentouche, K.; Rice, L.; Windyga, J.; Schneppenheim, R.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Kajiwara, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Maggiore, C.; et al. Recombinant ADAMTS-13: First-in-human pharmacokinetics and safety in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2017, 130, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Bignotti, A.; Yada, N.; Ye, Z.; Liu, S.; Han, Z.; Zheng, X.L. Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227174
Zhang Q, Bignotti A, Yada N, Ye Z, Liu S, Han Z, Zheng XL. Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(22):7174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227174
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Quan, Antonia Bignotti, Noritaka Yada, Zhan Ye, Szumam Liu, Zhe Han, and X. Long Zheng. 2023. "Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 22: 7174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227174
APA StyleZhang, Q., Bignotti, A., Yada, N., Ye, Z., Liu, S., Han, Z., & Zheng, X. L. (2023). Dynamic Assessment of Plasma von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Predicts Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(22), 7174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227174