Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex Modulates Processing of Heat Pain Sensation as Assessed by the Offset Analgesia Paradigm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Procedures
2.2.1. Quantitative Sensory Testing Assessment
2.2.2. Stimulation Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
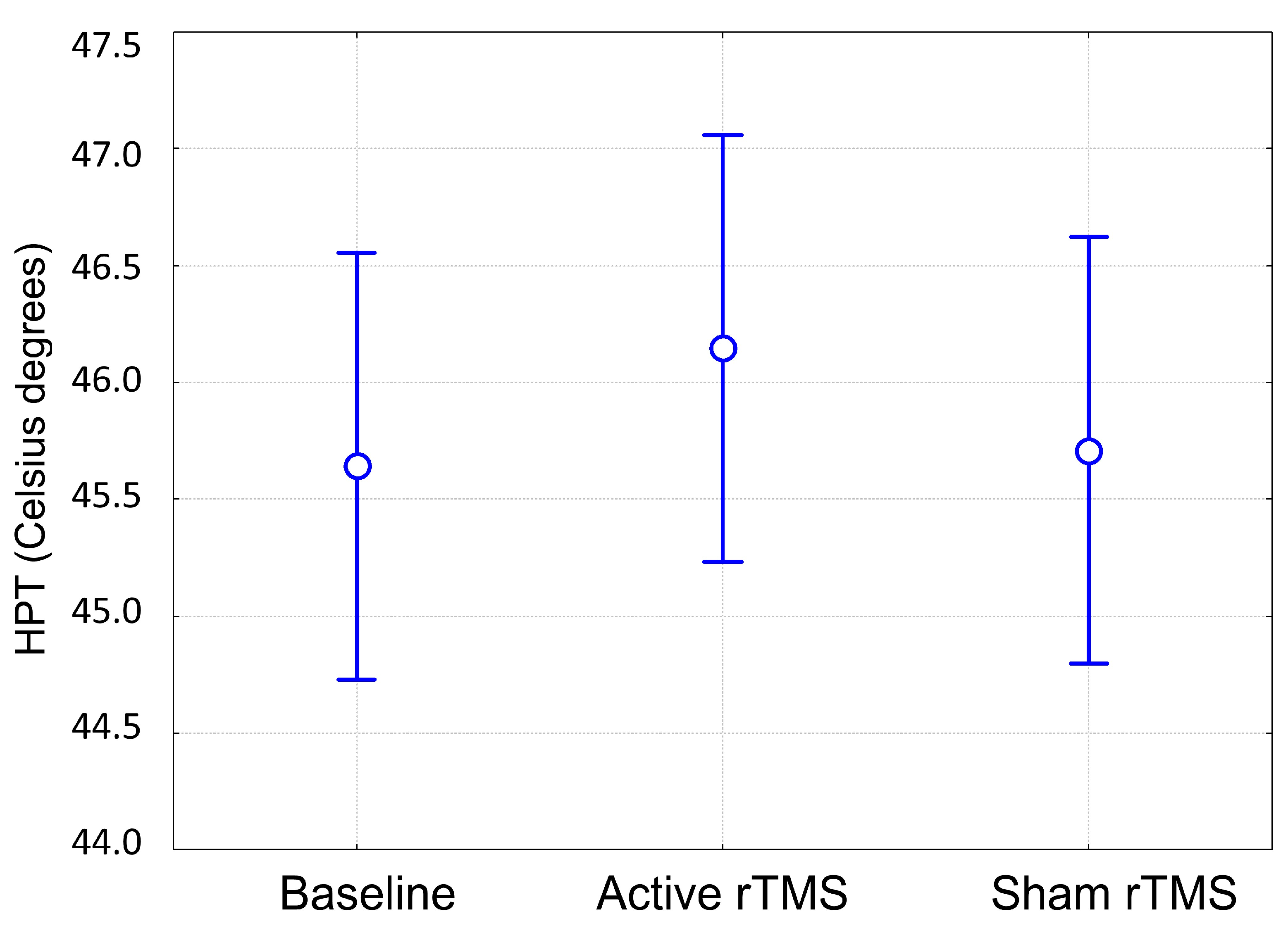
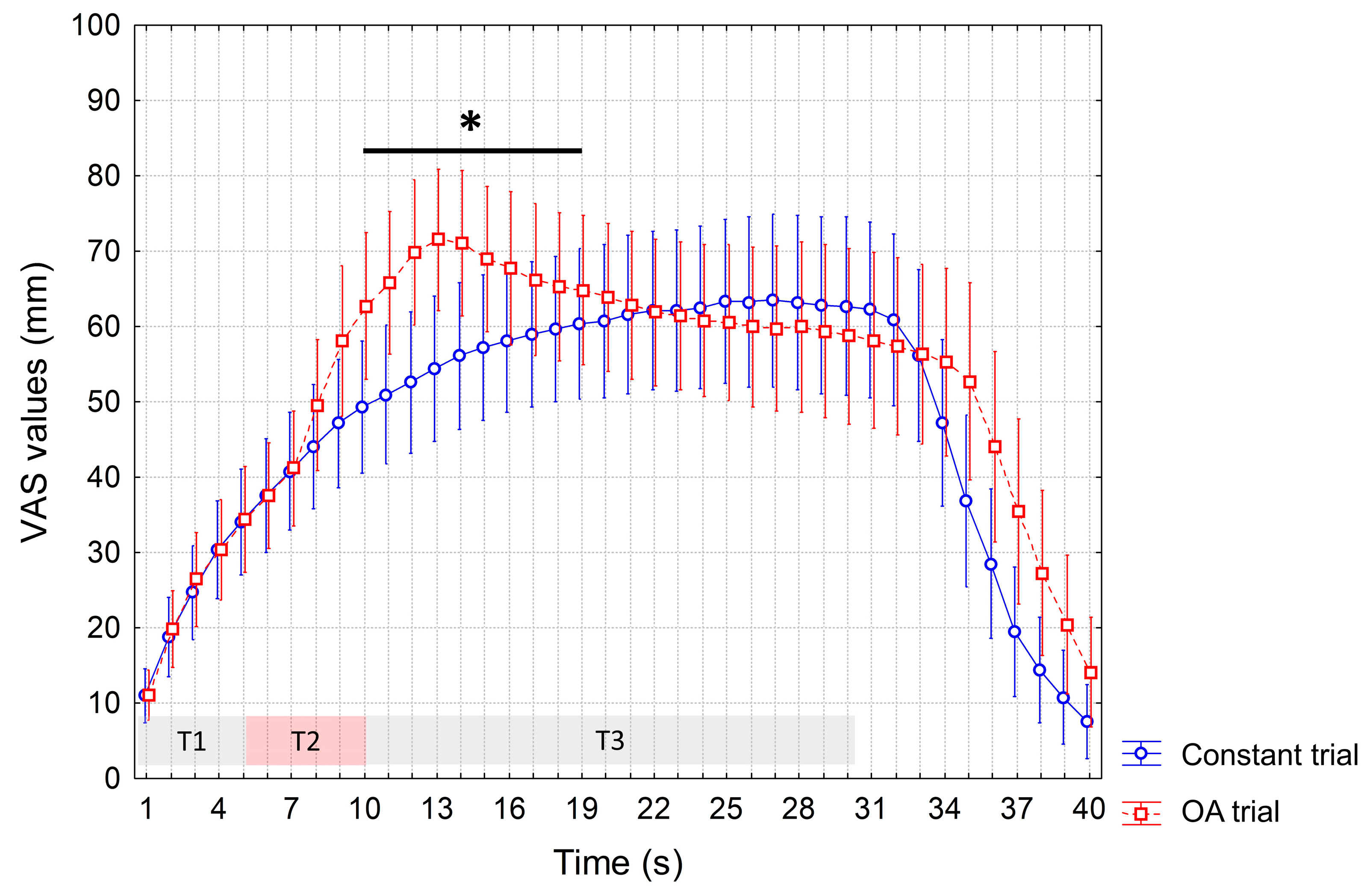
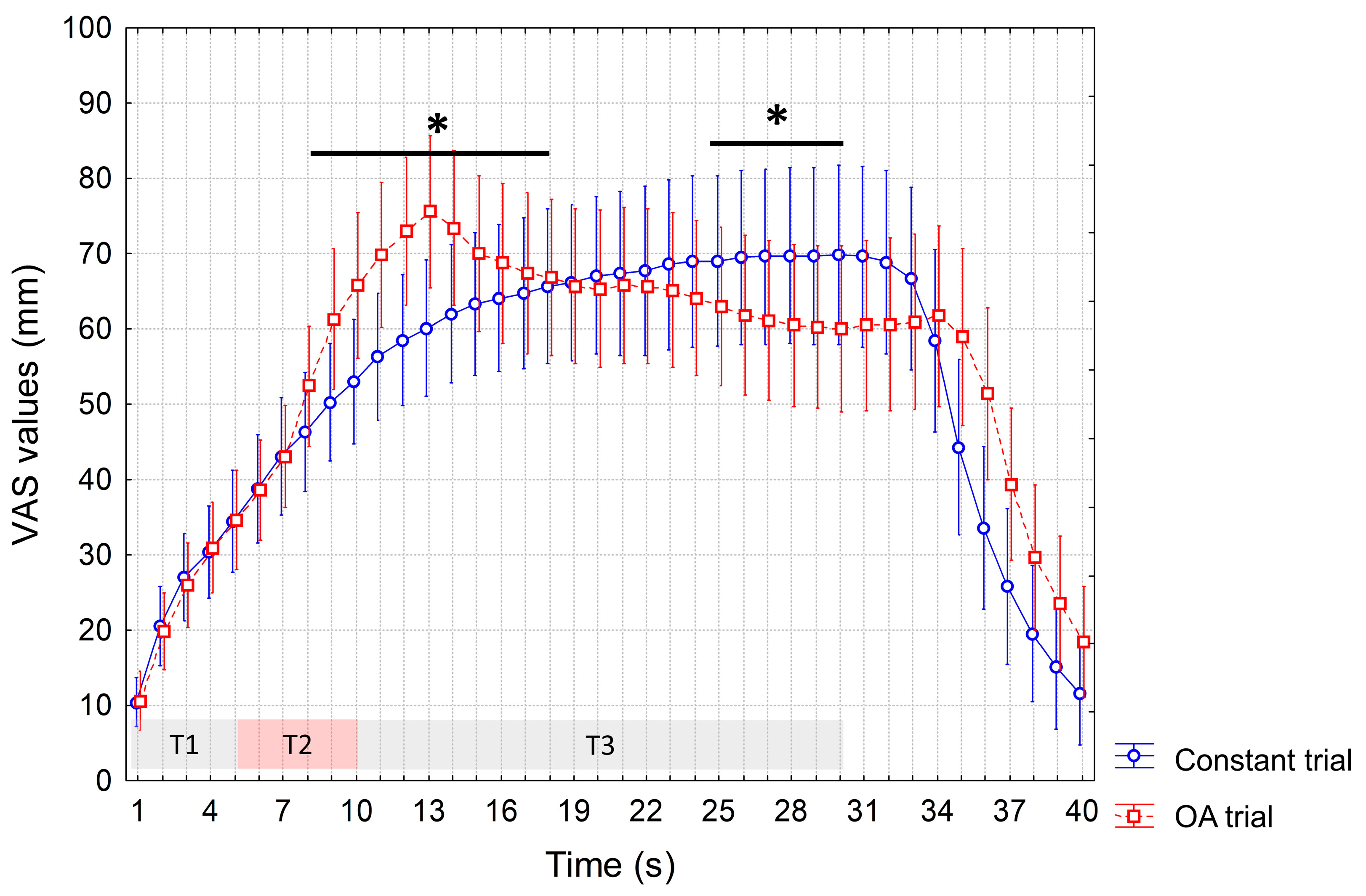
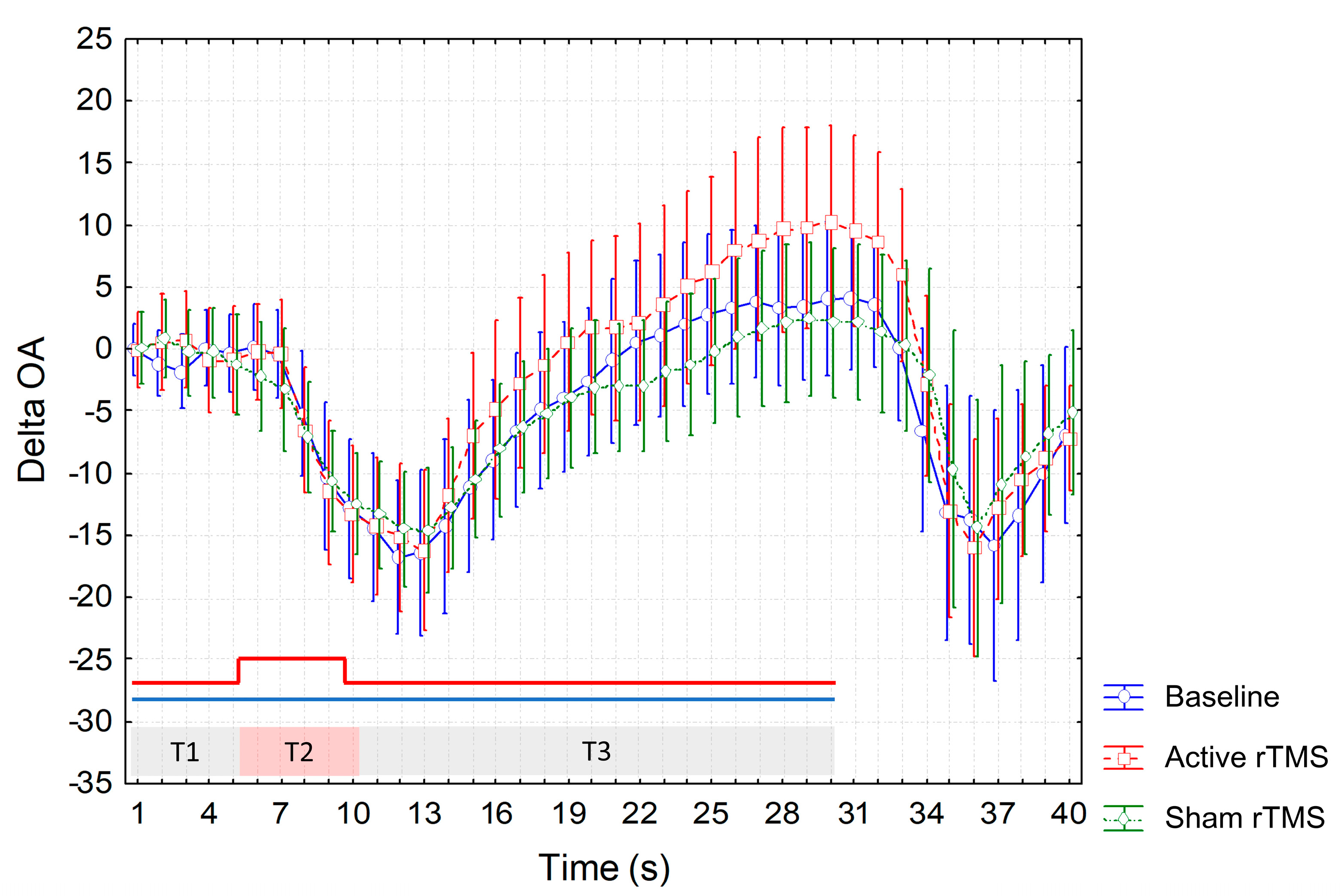
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitation and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attal, N.; Poindessous-Jazat, F.; De Chauvigny, E.; Quesada, C.; Mhalla, A.; Ayache, S.S.; Fermanian, C.; Nizard, J.; Peyron, R.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for neuropathic pain: A randomized multicentre sham-controlled trial. Brain 2021, 144, 3328–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on pain management: A systematic narrative review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DosSantos, M.F.; Ferreira, N.; Toback, R.L.; Carvalho, A.C.; DaSilva, A.F. Potential mechanisms supporting the value of motor cortex stimulation to treat chronic pain syndromes. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Summers, J.; Pridmore, S. Changes to somatosensory detection and pain thresholds following high frequency repetitive TMS of the motor cortex in individuals suffering from chronic pain. Pain 2006, 123, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Drouot, X.; Menard-Lefaucheur, I.; Zerah, F.; Bendib, B.; Cesaro, P.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J.P. Neurogenic pain relief by repetitive transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation depends on the origin and the site of pain. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Drouot, X.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J.P. Pain relief induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of precentral cortex. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 2963–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.P.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; Decq, P.; Uchiyama, T.; Carpentier, A.; Fontaine, D.; Brugières, P.; Pollin, B.; Fève, A.; Rostaing, S.; et al. Chronic motor cortex stimulation in the treatment of central and neuropathic pain. Correlations between clinical, electrophysiological and anatomical data. Pain 1999, 82, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovsky, Y.; Sprecher, E.; Sinai, A. Motor corticospinal excitability: A novel facet of pain modulation? Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleger, B.; Janssen, F.; Schwenkreis, P.; Völker, B.; Maier, C.; Tegenthoff, M. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex attenuates pain perception in complex regional pain syndrome type I. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 356, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Johnson, S.; Pridmore, S.; Oberoi, G. Changes to cold detection and pain thresholds following low and high frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 368, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, R.; Laurent, B.; García-Larrea, L. Functional imaging of brain responses to pain. A review and meta-analysis. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2000, 30, 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Larrea, L.; Peyron, R.; Mertens, P.; Gregoire, M.C.; Lavenne, F.; Le Bars, D.; Convers, P.; Mauguière, F.; Sindou, M.; Laurent, B. Electrical stimulation of motor cortex for pain control: A combined PET-scan and electrophysiological study. Pain 1999, 83, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Gangadharan, V.; Liu, S.; Körber, C.; Tan, L.L.; Li, H.; Oswald, M.J.; Kang, J.; Martin-Cortecero, J.; Männich, D.; et al. Layer-specific pain relief pathways originating from primary motor cortex. Science 2022, 378, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, J. Neural mechanisms of offset analgesia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1099, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, J.D.; Coghill, R.C. Transient analgesia evoked by noxious stimulus offset. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 2205–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Kobinata, H.; Ikeda, E.; Ota, T.; Kurata, J. Attenuation of offset analgesia is associated with suppression of descending pain modulatory and reward systems in patients with chronic pain. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918767512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Nguyen, J.P. A practical algorithm for using rTMS to treat patients with chronic pain. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2019, 49, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.P.; Nizard, J.; Keravel, Y.; Lefaucheur, J.P. Invasive brain stimulation for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naugle, K.M.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Fillingim, R.B.; Riley, J.L., 3rd. Offset analgesia is reduced in older adults. Pain 2013, 154, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannetti, G.D.; Zambreanu, L.; Tracey, I. Similar nociceptive afferents mediate psychophysical and electrophysiological responses to heat stimulation of glabrous and hairy skin in humans. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouveau-Richard, S.; Monot, M.; Bastien, P.; de Lacharrière, O. In vivo epidermal thickness measurement: Ultrasound vs. confocal imaging. Skin. Res. Technol. 2004, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, J.T.; Everall, J.D. The thickness of the epidermis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1973, 89, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinböhl, D.; Hölzl, R.; Möltner, A.; Rommel, C.; Weber, C.; Osswald, P.M. Psychophysical measures of sensitization to tonic heat discriminate chronic pain patients. Pain 1999, 81, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.J.; Borckardt, J.J.; George, M.S. Endogenous opioids mediate left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex rTMS-induced analgesia. Pain 2012, 153, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, G.; Antoniazzi, E.; Bonomi, L.; Cavigioli, C.; D’Agostino, M.; Todisco, M.; Tassorelli, C. Age-, gender- and body site-specific reference values of thermal Quantitative Sensory Testing in the Italian population using the Q-sense device. Neurol. Sci. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolke, R.; Baron, R.; Maier, C.; Tölle, T.R.; Treede, D.R.; Beyer, A.; Binder, A.; Birbaumer, N.; Birklein, F.; Bötefür, I.C.; et al. Quantitative sensory testing in the German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain (DFNS): Standardized protocol and reference values. Pain 2006, 123, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szikszay, T.M.; Adamczyk, W.M.; Carvalho, G.F.; May, A.; Luedtke, K. Offset analgesia: Somatotopic endogenous pain modulation in migraine. Pain 2020, 161, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudejans, L.C.J.; Smit, J.M.; van Velzen, M.; Dahan, A.; Niesters, M. The influence of offset analgesia on the onset and offset of pain in patients with fibromyalgia. Pain 2015, 156, 2521–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honigman, L.; Yarnitsky, D.; Sprecher, E.; Weissman-Fogel, I. Psychophysical testing of spatial and temporal dimensions of endogenous analgesia: Conditioned pain modulation and offset analgesia. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 228, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, K.T.; Yelle, M.D.; Coghill, R.C. Differential effects of experimental central sensitization on the time-course and magnitude of offset analgesia. Pain 2012, 153, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesters, M.; Dahan, A.; Swartjes, M.; Noppers, I.; Fillingim, R.B.; Aarts, L.; Sarton, E.Y. Effect of ketamine on endogenous pain modulation in healthy volunteers. Pain 2011, 152, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André-Obadia, N.; Mertens, P.; Gueguen, A.; Peyron, R.; Garcia-Larrea, L. Pain relief by rTMS: Differential effect of current flow but no specific action on pain subtypes. Neurology 2008, 71, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisanby, S.H.; Gutman, D.; Luber, B.; Schroeder, C.; Sackeim, H.A. Sham TMS: Intracerebral measurement of the induced electrical field and the induction of motor-evoked potentials. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 49, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Safety of TMS Consensus Group. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2008–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelle, M.D.; Oshiro, Y.; Kraft, R.A.; Coghill, R.C. Temporal filtering of nociceptive information by dynamic activation of endogenous pain modulatory systems. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10264–10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Meyer, R.A.; Raja, S.N.; Campbell, J.N. Evidence for two different heat transduction mechanisms in nociceptive primary afferents innervating monkey skin. J. Physiol. 1995, 483, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treede, R.D.; Meyer, R.A.; Campbell, J.N. Myelinated mechanically insensitive afferents from monkey hairy skin: Heat-response properties. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 80, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakour, M.C.; Gibson, S.J.; Bradbeer, M.; Helme, R.D. The effect of age on A delta- and C-fibre thermal pain perception. Pain 1996, 64, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.N.; LaMotte, R.H. Latency to detection of first pain. Brain Res. 1983, 266, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovsky, Y.; Matre, D.; Sokolik, A.; Lorenz, J.; Casey, K.L. Thermoreceptive innervation of human glabrous and hairy skin: A contact heat evoked potential analysis. Pain 2005, 115, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campero, M.; Baumann, T.K.; Bostock, H.; Ochoa, J.L. Human cutaneous C fibres activated by cooling, heating and menthol. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5633–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cline, M.A.; Ochoa, J.; Torebjörk, H.E. Chronic hyperalgesia and skin warming caused by sensitized C nociceptors. Brain 1989, 112, 621–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Schmelz, M.; Ringkamp, M.; Handwerker, H.O.; Torebjörk, H.E. Innervation territories of mechanically activated C nociceptor units in human skin. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 78, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, J.; Gybels, J. C nociceptor activity in human nerve during painful and non painful skin stimulation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1981, 44, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vita, M.J.; Buckheit, K.; Gilmour, C.E.; Moskal, D.; Maisto, S.A. Development of a Novel Brief Quantitative Sensory Testing Protocol That Integrates Static and Dynamic Pain Assessments: Test-Retest Performance in Healthy Adults. Pain Med. 2022, 23, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Piasco, A.; Nissen, T.D.; Graversen, C.; Gazerani, P.; Lucas, M.F.; Dahan, A.; Drewes, A.M.; Brock, C. Reproducibility of psychophysics and electroencephalography during offset analgesia. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosentino, G.; Antoniazzi, E.; Cavigioli, C.; Tang, V.; Tammam, G.; Zaffina, C.; Tassorelli, C.; Todisco, M. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex Modulates Processing of Heat Pain Sensation as Assessed by the Offset Analgesia Paradigm. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227066
Cosentino G, Antoniazzi E, Cavigioli C, Tang V, Tammam G, Zaffina C, Tassorelli C, Todisco M. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex Modulates Processing of Heat Pain Sensation as Assessed by the Offset Analgesia Paradigm. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(22):7066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227066
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosentino, Giuseppe, Elisa Antoniazzi, Camilla Cavigioli, Vanessa Tang, Giulia Tammam, Chiara Zaffina, Cristina Tassorelli, and Massimiliano Todisco. 2023. "Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex Modulates Processing of Heat Pain Sensation as Assessed by the Offset Analgesia Paradigm" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 22: 7066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227066
APA StyleCosentino, G., Antoniazzi, E., Cavigioli, C., Tang, V., Tammam, G., Zaffina, C., Tassorelli, C., & Todisco, M. (2023). Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex Modulates Processing of Heat Pain Sensation as Assessed by the Offset Analgesia Paradigm. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(22), 7066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12227066





