Association of a Bioimpedance Profile with Optical Coherence Tomography Features in Diabetic Macular Edema
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participant Characteristics
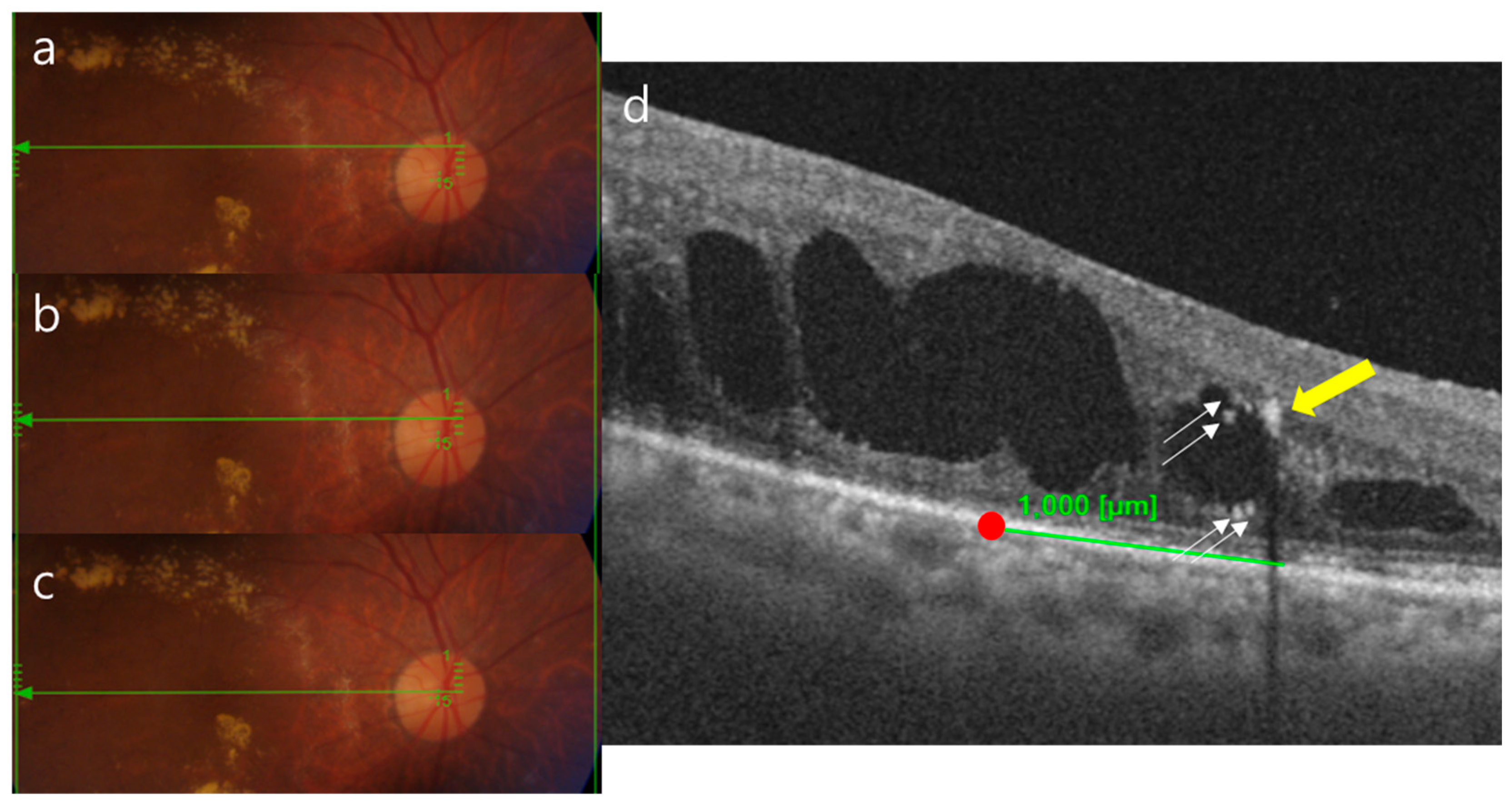
2.3. Ophthalmic Examinations
2.4. Body Composition Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Systemic Factors, Bioimpedance Parameters, and OCT Features in the No DR, DR without DME, and DR with DME Groups
3.3. Comparison of Systemic Parameters and Bioimpedance Parameters in the HRF Subdivision Groups (Table 2)
3.4. Correlation of ECW/TBW and CSRT, CSCT (Figure 3)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, J.E.; Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema and related vision loss. Eye Vis. 2015, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, A.; Reichenbach, A.; Wiedemann, P. Pathomechanisms of cystoid macular edema. Ophthalmic Res. 2004, 36, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogli, S.; Mogavero, S.; Egan, C.G.; Del Re, M.; Danesi, R. Pathophysiology and pharmacological targets of VEGF in diabetic macular edema. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 103,149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolz, M.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Deak, G.; Mylonas, G.; Kriechbaum, K.; Scholda, C.; Diabetic Retinopathy Research Group Vienna. Optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci: A morphologic sign of lipid extravasation in diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jang, H.; Choi, Y.A.; Kim, H.C.; Chung, H. Association between soluble CD14 in the aqueous humor and hyperreflective foci on optical coherence tomography in patients with diabetic macular edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Torresin, T.; Bini, S.; Convento, E.; Pilotto, E.; Parrozzani, R.; Midena, E. Imaging retinal inflammatory biomarkers after intravitreal steroid and anti-VEGF treatment in diabetic macular oedema. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Baseline spectral domain optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci as a predictor of visual outcome and recurrence for central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2016, 36, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, K.; Murakami, T.; Tsujikawa, A.; Miyamoto, K.; Sakamoto, A.; Ota, M.; Yoshimura, N. Characteristics of optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci in retinal vein occlusion. Retina 2012, 32, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbrain, M.L.; Huygh, J.; Dabrowski, W.; De Waele, J.J.; Staelens, A.; Wauters, J. The use of bio-electrical impedance analysis (BIA) to guide fluid management, resuscitation and deresuscitation in critically ill patients: A bench-to-bedside review. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2014, 46, 381391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-T.; Tsai, M.-J.; Tu, S.-T.; Hsieh, M.-C. Association of abnormal renal profiles and proliferative diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema in an Asian population with type 2 diabetes. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Ohkoshi, K.; Takei, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Shimura, M.; Ueda, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Hirano, T.; Takayama, K.; et al. Functional and anatomical changes in diabetic macular edema after hemodialysis initiation: One-year follow-up multicenter study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y.; Liang, A.; Xie, J.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Clinical relevance of body fluid volume status in diabetic patients with macular edema. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 857532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.R.; Bae, J.H.; Lee, C.S.; Al-Sawat, A.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, M.R.; Jin, H.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Serial measurements of body composition using bioelectrical impedance and clinical usefulness of phase angle in colorectal cancer. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2022, 37, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-N.; Kim, K.-A.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yim, J.-E. Independent association of phase angle with fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c in Korean type 2 diabetes patients. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2020, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-J.; Cheng, C.-K.; Wang, Y.-C. Association of body fluid expansion with optical coherence tomography measurements in diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 3606–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.-H.; Kim, S.; Ku, B.; Cho, J.; Kim, K.; Yoo, H.-R.; Kim, J.U. Glucose-independent segmental phase angles from multi-frequency bioimpedance analysis to discriminate diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zur, D.; Iglicki, M.; Busch, C.; Invernizzi, A.; Mariussi, M.; Loewenstein, A.; International Retina Group. OCT biomarkers as functional outcome predictors in diabetic macular edema treated with dexamethasone implant. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.H.; de Craen, A.J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Gunn, D.A.; Stokkel, M.P.M.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Maier, A.B. Accuracy of direct segmental multi-frequency bioimpedance analysis in the assessment of total body and segmental body composition in middle-aged adult population. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.J.; Liu, Z.; Khamaisi, M.; King, G.L.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Hughes, T.M.; Craft, S.; Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W.; et al. Diabetic microvascular disease: An endocrine society scientific statement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4343–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukackiene, D.; Laucyte-Cibulskiene, A.; Vickiene, A.; Rimsevicius, L.; Miglinas, M. Risk stratification for patients awaiting kidney transplantation: Role of bioimpedance derived edema index and nutrition status. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2759–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Kase, S.; Takahashi, M.; Saito, M.; Yokoi, M.; Sugawara, C.; Katsuta, S.; Ishida, S.; Kase, M. Relationship between diabetic macular edema and choroidal layer thickness. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Matsuura, T.; Ogata, N. Effects of panretinal photocoagulation on choroidal thickness and choroidal blood flow in patients with severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retina 2016, 36, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsu, H.; Yamashita, H.; Noma, H.; Mimura, T.; Yamashita, T.; Hori, S. Increased levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 in the aqueous humor of diabetics with macular edema. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 133, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, N.F.; Mauricio, S.F.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Carmo, A.S.; Coury, N.C.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Generoso, S.V. Association between standardized phase angle, nutrition status, and clinical outcomes in surgical cancer patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.J.; Lieth, E.; Khin, S.A.; Antonetti, D.A.; Buchanan, A.G.; Gardner, T.W. Neural apoptosis in the retina during experimental and human diabetes. Early onset and effect of insulin. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.H.; van Dijk, H.W.; Jiao, C.; Kok, P.H.B.; Jeong, W.; Demirkaya, N.; Garmager, A.; Wit, F.; Kucukevcilioglu, M.; van Velthoven, M.E.J.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2655–E2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M.; Chen, M.; Medina, R.J.; McKay, G.J.; Jenkins, A.; Gardiner, T.A.; Lyons, T.J.; Hammes, H.-P.; Simó, R.; et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 51, 156–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsamba, J.; Eroju, P.; Drenos, F.; Mathews, E. Body composition characteristics of Type 1 diabetes children and adolescents: A hospital-based case-control study in Uganda. Children 2022, 9, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, M.; Reber, H.; Kahaly, G. Bioimpedance phase angle indicates catabolism in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2015, 32, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Bernardes, R.; Lobo, C. Blood-retinal barrier. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 21, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urias, E.A.; Urias, G.A.; Monickaraj, F.; McGuire, P.; Das, A. Novel therapeutic targets in diabetic macular edema: Beyond VEGF. Vis. Res. 2017, 139, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Bini, S.; Midena, G.; Berton, M.; Pilotto, E.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective intraretinal spots in diabetics without and with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: An in vivo study using spectral domain OCT. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 491835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujosevic, S.; Berton, M.; Bini, S.; Casciano, M.; Cavarzeran, F.; Midena, E. Hyperreflective retinal spots and visual function after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment in center-involving diabetic macular edema. Retina 2016, 36, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugisho, O.O.; Rupenthal, I.D.; Squirrell, D.M.; Bould, S.J.; Danesh-Meyer, H.V.; Zhang, J.; Green, C.R.; Acosta, M.L. Intravitreal pro-inflammatory cytokines in non-obese diabetic mice: Modelling signs of diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeleri, C.M.; Cavaglieri, C.R.; de Souza, M.F.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Antunes, M.; Nabbuco, H.C.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Silva, A.M.; Cyrino, E.S. Phase angle is related with inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers in older women. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 102, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.C.; Vora, R.A.; Duker, J.S.; Reichel, E. Solid-appearing retinal cysts in diabetic macular edema: A novel optical coherence tomography finding. Retin. Cases Brief Rep. 2013, 7, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colín-Ramírez, E.; Castillo-Martínez, L.; Orea-Tejeda, A.; Lafuente, E.A.; Villanueva, F.T.; González, V.R.; David, R.N.; García, J.D. Body composition and echocardiographic abnormalities associated to anemia and volume overload in heart failure patients. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarpia, L.; Marra, M.; Montagnese, C.; Alfonsi, L.; Pasanisi, F.; Contaldo, F. Prognostic significance of bioelectrical impedance phase angle in advanced cancer: Preliminary observations. Nutrition 2009, 25, 930–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Silva, M.C.G.; Barros, A.J. Bioelectric impedance and individual characteristics as prognostic factors for post-operative complications. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | No DR, n = 24 | DR without DME, n = 38 | DR with DME, n = 38 | p a | p b | p c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 59.26 ± 8.51 | 57.06 ± 11.09 | 60.75 ± 9.94 | 0.204 | 0.309 | 0.325 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.20 ± 2.91 | 24.39 ± 3.33 | 23.68 ± 2.12 | 0.282 | 0.577 | 0.806 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.99 ± 0.94 | 8.25 ± 2.09 | 8.27 ± 1.76 | 0.101 | 0.508 | 0.304 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 82.40 ± 15.08 | 82.75 ± 15.54 | 77.87 ± 14.63 | 0.998 | 0.680 | 0.754 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 0.86 ± 0.22 | 1.11 ± 1.05 | 1.06 ± 0.56 | 0.435 | 0.967 | 0.563 |
| Ocular parameters | ||||||
| CSRT, µm | 238.17 ± 24.02 | 233.74 ± 24.99 | 350.13 ± 79.16 | 0.950 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| CSCT, µm | 218.00 ± 43.61 | 258.29 ± 41.69 | 296.57 ± 37.79 | 0.002 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| BCM parameters | ||||||
| ICW (L) | 20.98 ± 3.79 | 25.31 ± 5.46 | 22.42 ± 4.28 | 0.003 | 0.039 | 0.491 |
| ECW (L) | 12.79 ± 2.01 | 15.15 ± 3.09 | 14.48 ± 2.45 | 0.004 | 0.558 | 0.05 |
| TBW (L) | 33.77 ± 5.66 | 40.46 ± 8.32 | 36.90 ± 6.55 | 0.003 | 0.114 | 0.236 |
| ECW/TBW, % | 37.99 ± 1.77 | 37.58 ± 2.31 | 39.35 ± 2.49 | 0.790 | 0.007 | 0.047 |
| PhA (°) | 6.69 ± 0.69 | 6.05 ± 1.15 | 5.45 ± 0.84 | 0.048 | 0.032 | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Absent HRF, n = 29 | Moderate HRF, n = 23 | Significant HRF, n = 24 | p a | p b | p c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 57.58 ± 10.86 | 61.12 ± 10.45 | 59.26 ± 10.52 | 0.993 | 0.269 | 0.197 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.44 ± 3.44 | 23.94 ± 1.92 | 23.46 ± 2.19 | 0.870 | 0.530 | 0.269 |
| HbA1c, % | 8.17 ± 1.92 | 7.71 ± 1.79 | 8.00 ± 2.12 | 0.581 | 0.363 | 0.821 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 83.65 ± 23.05 | 81.88 ± 26.21 | 73.64 ± 28.47 | 0.973 | 0.611 | 0.386 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 1.08 ± 1.07 | 0.96 ± 0.48 | 1.19 ± 0.65 | 0.894 | 0.710 | 0.901 |
| ICW | 25.55 ± 5.21 | 21.60 ± 4.26 | 23.03 ± 4.73 | 0.270 | 0.306 | 0.015 |
| ECW | 15.25 ± 3.01 | 13.71 ± 2.37 | 15.04 ± 2.62 | 0.812 | 0.778 | 0.439 |
| TBW | 40.81 ± 7.96 | 35.32 ± 6.53 | 38.07 ± 7.14 | 0.430 | 0.446 | 0.058 |
| ECW/TBW, % | 37.47 ± 2.31 | 38.94 ± 1.85 | 39.68 ± 2.86 | 0.146 | 0.084 | 0.001 |
| PhA | 6.13 ± 1.08 | 5.68 ± 0.94 | 5.20 ± 0.81 | 0.391 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.; Seong, M.; Kang, M.H.; Thng, Z.X.; Cho, H.; Shin, Y.U. Association of a Bioimpedance Profile with Optical Coherence Tomography Features in Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206676
Hwang S, Seong M, Kang MH, Thng ZX, Cho H, Shin YU. Association of a Bioimpedance Profile with Optical Coherence Tomography Features in Diabetic Macular Edema. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(20):6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206676
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Sunjin, Mincheol Seong, Min Ho Kang, Zheng Xian Thng, Heeyoon Cho, and Yong Un Shin. 2023. "Association of a Bioimpedance Profile with Optical Coherence Tomography Features in Diabetic Macular Edema" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 20: 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206676
APA StyleHwang, S., Seong, M., Kang, M. H., Thng, Z. X., Cho, H., & Shin, Y. U. (2023). Association of a Bioimpedance Profile with Optical Coherence Tomography Features in Diabetic Macular Edema. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(20), 6676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12206676





