The Impact of Biologic Treatment on PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Disturbances in Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Group
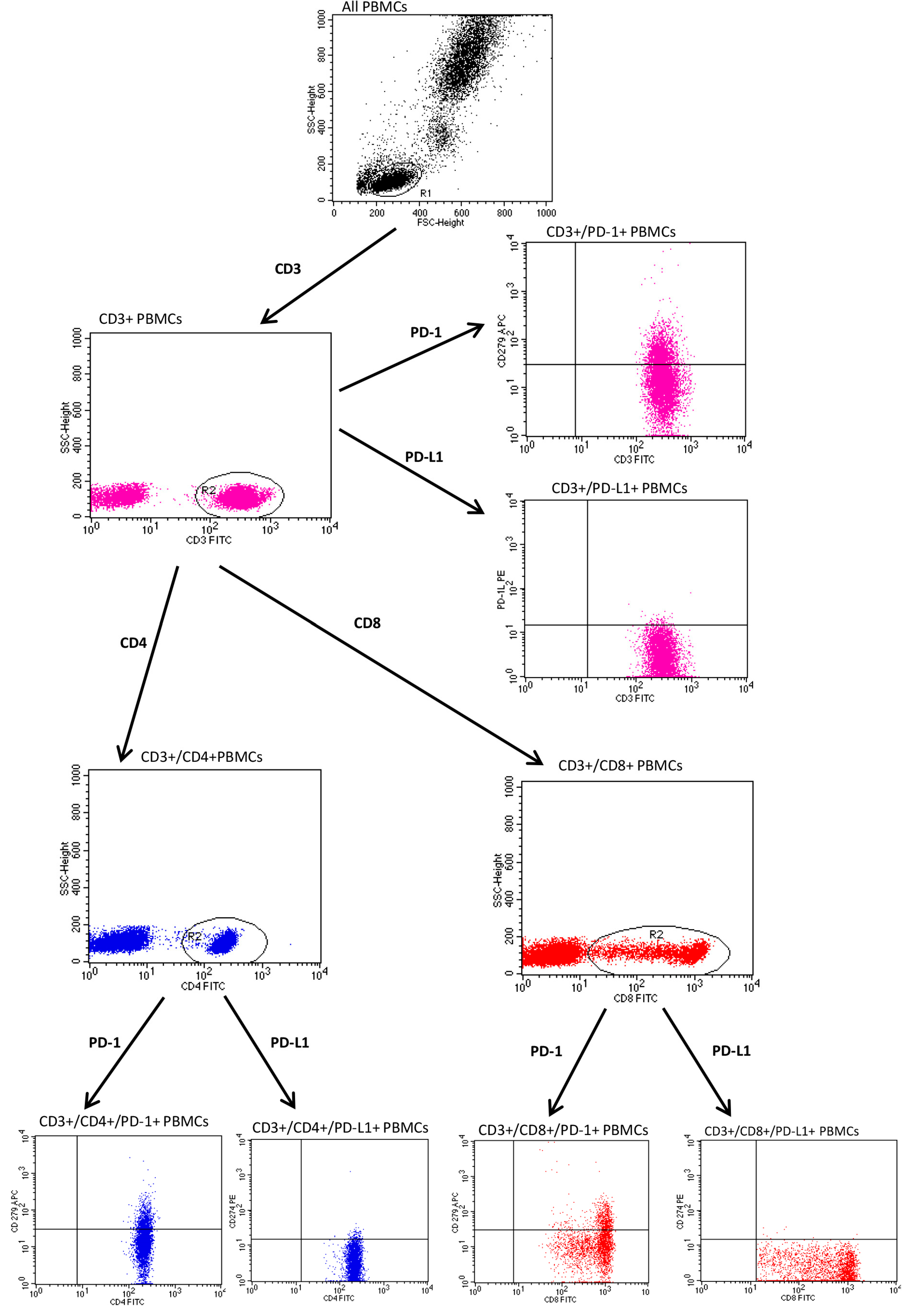
2.2. Assessment of PD-1, PD-L1
- Anti-CD3 FITC/anti-CD274 PE/anti-CD279 APC.
- Anti-CD4 FITC/anti-CD274 PE/anti CD279 APC.
- Anti-CD8 FITC/anti-CD274 PE/anti CD279 APC.
- Anti-CD19 FITC/anti-CD274 PE/anti CD279 APC.
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, M.; Krasowska, D. PD1/PD-L1 pathway in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A review. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. The inflammatory response in psoriasis: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, R.V.; Chemnitz, J.M.; Frauwirth, K.A.; Lanfranco, A.R.; Braunstein, I.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Linsley, P.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Riley, J.L. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9543–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonigen, J.; Raynaud-Donzel, C.; Hureaux, J.; Kramkimel, N.; Blom, A.; Jeudy, G.; Breton, A.L.; Hubiche, T.; Bedane, C.; Legoupil, D.; et al. Anti-PD1-induced psoriasis: A study of 21 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e254–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosińska, J.; Zakrzewska, E.; Król, A.; Raczkiewicz, D.; Purkot, J.; Majdan, M.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G.; Giannopoulos, K. Differential expression of programmed death 1 (PD-1) on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2017, 127, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosińska, J.; Purkot, J.; Kowal, M.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G.; Giannopoulos, K. The expression of selected molecular markers of immune tolerance in psoriatic patients. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Kubota, N.; Konishi, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Mizuno, S.; Takahashi, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Nomura, T.; Okiyama, N. The Role of PD-L1 on Langerhans Cells in the Regulation of Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 3167–3174.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahil, S.K.; Ezejimofor, M.C.; Exton, L.S.; Manounah, L.; Burden, A.D.; Coates, L.C.; de Brito, M.; McGuire, A.; Murphy, R.; Owen, C.W.; et al. Comparing the efficacy and tolerability of biologic therapies in psoriasis: An updated network meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Wang, J. PD-1/PD-L pathway and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2005, 38, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peled, M.; Strazza, M.; Azoulay-Alfaguter, I.; Silverman, G.J.; Scher, J.U.; Mor, A. Analysis of Programmed Death-1 in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raptopoulou, A.P.; Bertsias, G.; Makrygiannakis, D.; Verginis, P.; Kritikos, I.; Tzardi, M.; Klareskog, L.; Catrina, A.I.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Boumpas, D.T. The programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 inhibitory pathway is up-regulated in rheumatoid synovium and regulates peripheral T cell responses in human and murine arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibaud, V.; Meyer, N.; Lamant, L.; Vigarios, E.; Mazieres, J.; Delord, J.P. Dermatologic complications of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Ayithan, N.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Hwang, S.T. Cutting Edge: PD-1 Regulates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasiform Dermatitis through Inhibition of IL-17A Expression by Innate γδ-Low T Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommarito, D.; Hall, C.; Taams, L.S.; Corrigall, V.M. Inflammatory cytokines compromise programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)-mediated T cell suppression in inflammatory arthritis through up-regulation of soluble PD-1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosińska, J.; Zakrzewska, E.; Raczkiewicz, D.; Purkot, J.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Kowal, M.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G.; Giannopoulos, K. Suppressed Programmed Death 1 Expression on CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells in Psoriatic Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5385102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosińska, J.; Zakrzewska, E.; Purkot, J.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Kowal, M.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G.; Giannopoulos, K. Decreased blood CD4+PD-1+ and CD8+PD-1+ T cells in psoriatic patients with and without arthritis. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2018, 35, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Unit or Category | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with psoriasis: | ||
| Age, min–max, median (IQR) | Years | 18–68, 43 (34–52) |
| Gender, n (%) | Male | 60 (71.4) |
| Female | 24 (28.6) | |
| Weight, min–max, median (IQR) | kg | 47–125, 85 (74–95) |
| BMI, min–max, median (IQR) | kg/m2 | 17.72–46.88, 27.51 (24.44–31.25) |
| Smoking status, n (%) | Non-smokers | 30 (38.0) |
| Smokers | 54 (62.0) | |
| Psoriasis type, n (%) | I (the onset <40 years old) | 72 (88.1) |
| II (the onset >40 years old) | 12 (11.9) | |
| Duration of psoriasis, min–max, median (IQR) | Years | 1–50, 20 (14–26) |
| PASI, min–max, median (IQR) | 5.5–47.0, 18.0 (13.1–21.3) | |
| BSA, min–max, median (IQR) | 6–80.0, 23.3 (15.0–39.8) | |
| PsA, n (%) | Yes | 27 (30.9) |
| Control group: | ||
| Age, min–max, median (IQR) | Years | 24–65, 40 (33–52) |
| Gender, n (%) | Male | 20 (69.0) |
| Female | 9 (31.0) | |
| Specificity | Fluorochrome | Producer | Clone | Isotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse anti-human-CD3 | FITC | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA | MEM-57 | Mouse IgG2a, κ |
| Mouse anti-human-CD4 | FITC | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NY, USA | RPA-T4 | Mouse IgG1, κ |
| Mouse anti-human-CD8 | FITC | BD, Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NY, USA | SK1 | Mouse BALB/c IgG1, κ |
| Mouse anti-human-CD19 | FITC | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NY, USA | HIB19 | Mouse IgG1, κ |
| Mouse anti-human-CD279 | APC | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NY, USA | MIH4 | Mouse IgG1, κ |
| Mouse anti-human-CD274 | PE | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NY, USA | MIH1 | Mouse BALB/c IgG1, κ |
| PBMC Subtype | Psoriasis | Control | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | ||
| CD3/PD-1 | 13.78 (11.03–18.42) | 17.26 (14.51–21.00) | 0.021 |
| CD3/PD-L1 | 1.23 (0.74–2.72) | 3.26 (1.67–8.20) | <0.001 |
| CD4/PD-1 | 13.58 (9.94–17.46) | 18.10 (13.77–25.25) | 0.002 |
| CD4/PD-L1 | 2.14 (1.14–4.49) | 4.30 (3.28–5.28) | 0.001 |
| CD8/PD-1 | 13.70 (9.78–17.32) | 14.90 (8.80–18.61) | 0.576 |
| CD8/PD-L1 | 0.58 (0.28–1.57) | 1.72 (0.87–3.10) | <0.001 |
| CD19/PD-1 | 2.48 (1.44–4.34) | 10.65 (6.14–12.20) | <0.001 |
| CD19/PD-L1 | 5.94 (1.39–11.11) | 10.95 (4.67–20.00) | 0.002 |
| PBMC Subtype | PASI | BSA | Duration of Psoriasis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| CD3/PD-1 | −0.101 | 0.361 | −0.132 | 0.233 | 0.261 | 0.018 |
| CD3/PD-L1 | −0.018 | 0.873 | 0.069 | 0.532 | −0.080 | 0.473 |
| CD4/PD-1 | −0.033 | 0.767 | −0.039 | 0.727 | 0.263 | 0.017 |
| CD4/PD-L1 | −0.008 | 0.944 | 0.075 | 0.500 | −0.138 | 0.216 |
| CD8/PD-1 | −0.149 | 0.177 | −0.087 | 0.429 | 0.200 | 0.072 |
| CD8/PD-L1 | 0.094 | 0.393 | 0.062 | 0.574 | −0.011 | 0.925 |
| CD19/PD-1 | −0.096 | 0.384 | 0.043 | 0.697 | 0.203 | 0.068 |
| CD19/PD-L1 | −0.014 | 0.898 | 0.244 | 0.025 | −0.063 | 0.576 |
| PBMC Subtype | Before Treatment | During Treatment | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | ||
| CD3/PD-1 | 13.59 (10.08–20.77) | 13.72 (9.32–16.24) | 0.078 |
| CD3/PD-L1 | 1.33 (0.92–2.36) | 3.74 (1.85–11.11) | 0.002 |
| CD4/PD-1 | 15.64 (10.00–17.69) | 12.11 (9.78–16.32) | 0.471 |
| CD4/PD-L1 | 2.11 (1.43–3.37) | 3.1 (1.42–6.03) | 0.428 |
| CD8/PD-1 | 14.73 (10.04–21.10) | 12.84 (7.00–15.73) | 0.041 |
| CD8/PD-L1 | 0.59 (0.28–1.36) | 1.65 (0.63–5.84) | 0.006 |
| CD19/PD-1 | 3.74 (1.79–4.36) | 2.91 (1.14–6.11) | 0.737 |
| CD19/PD-L1 | 4.77 (1.77–10.00) | 9.6 (2.67–13.39) | 0.302 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adamczyk, M.; Bartosińska, J.; Raczkiewicz, D.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Krasowska, D. The Impact of Biologic Treatment on PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Disturbances in Psoriasis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134179
Adamczyk M, Bartosińska J, Raczkiewicz D, Michalak-Stoma A, Krasowska D. The Impact of Biologic Treatment on PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Disturbances in Psoriasis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134179
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdamczyk, Michał, Joanna Bartosińska, Dorota Raczkiewicz, Anna Michalak-Stoma, and Dorota Krasowska. 2023. "The Impact of Biologic Treatment on PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Disturbances in Psoriasis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134179
APA StyleAdamczyk, M., Bartosińska, J., Raczkiewicz, D., Michalak-Stoma, A., & Krasowska, D. (2023). The Impact of Biologic Treatment on PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Disturbances in Psoriasis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134179








