Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells Involved in Autoimmune Fibrosis: New Discoveries
Abstract
1. Introduction
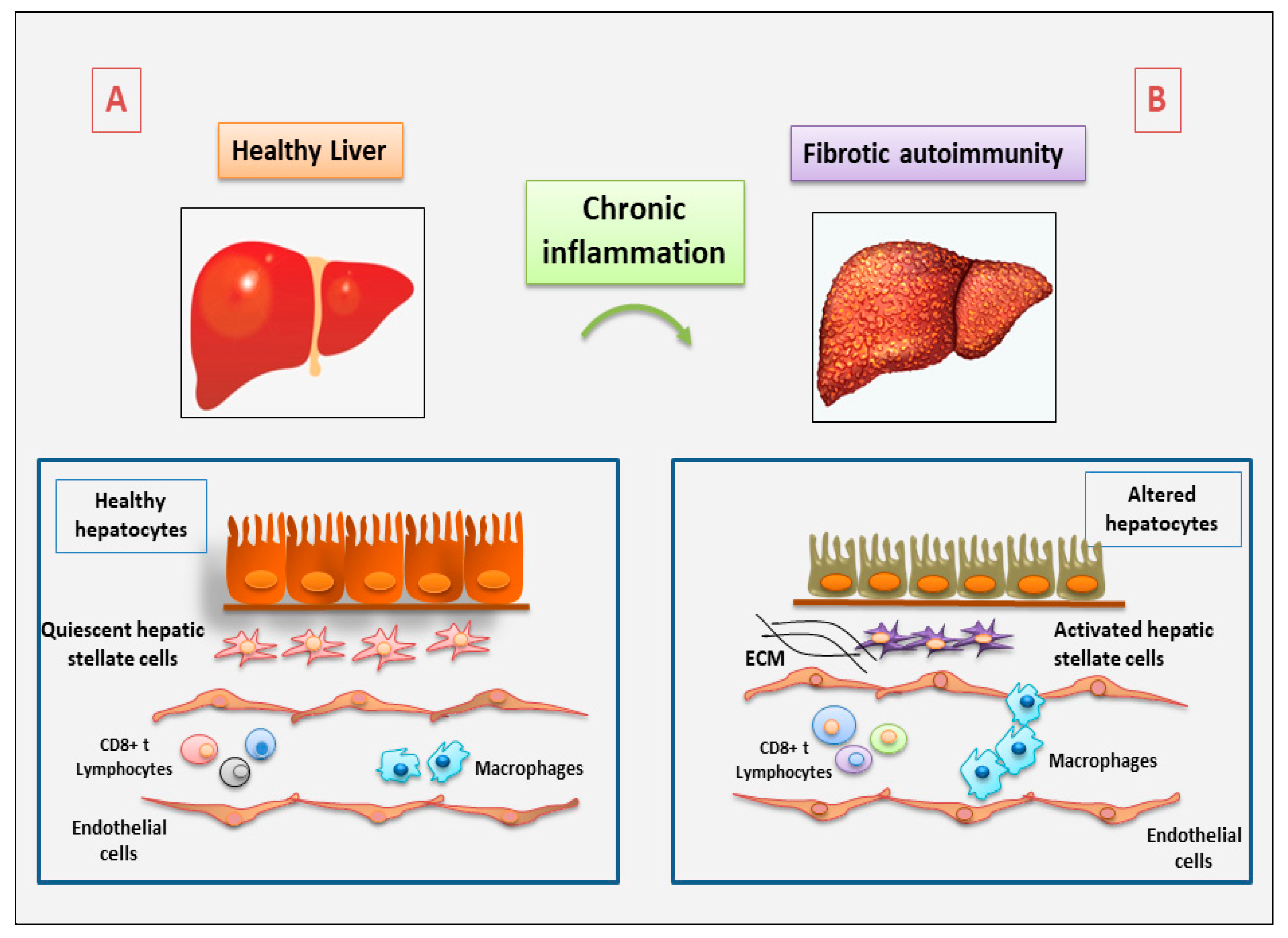
2. The Role of Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells in Fibrotic Autoimmune Diseases: New Discoveries
2.1. Current Understanding of the Involvement of Immune Cells in Fibrotic Autoimmune Diseases
2.1.1. Update on the Correlated Pro-Fibrotic Role of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells
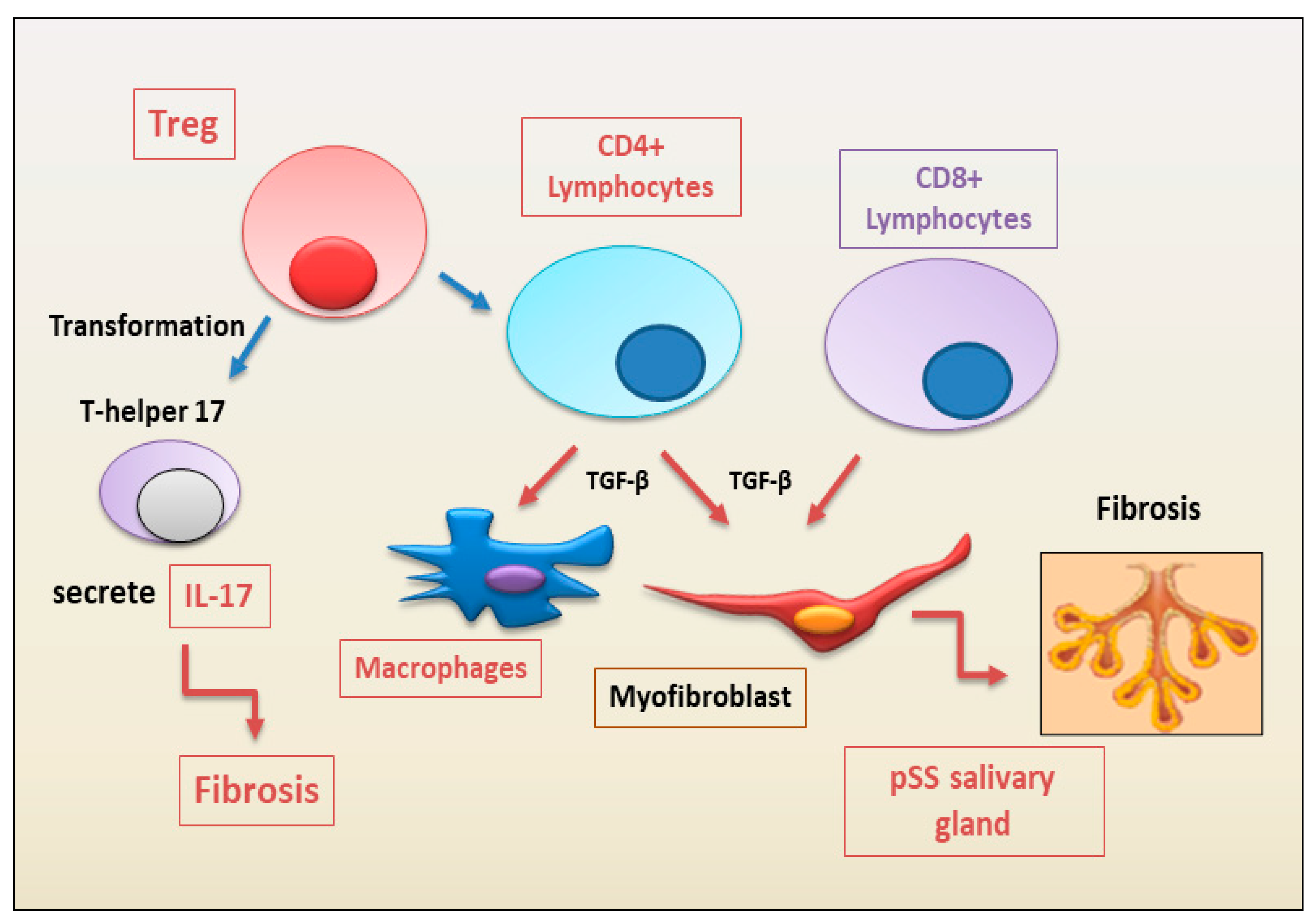
2.1.2. Autoimmune Treg Pro-Fibrotic Role
2.1.3. Emerging Pro-Fibrotic Role of T Follicular Helper Cells
2.1.4. Macrophages, Dendritic Cells, Mast Cells
2.2. Non-Immune Cells in Fibrotic Autoimmune Diseases
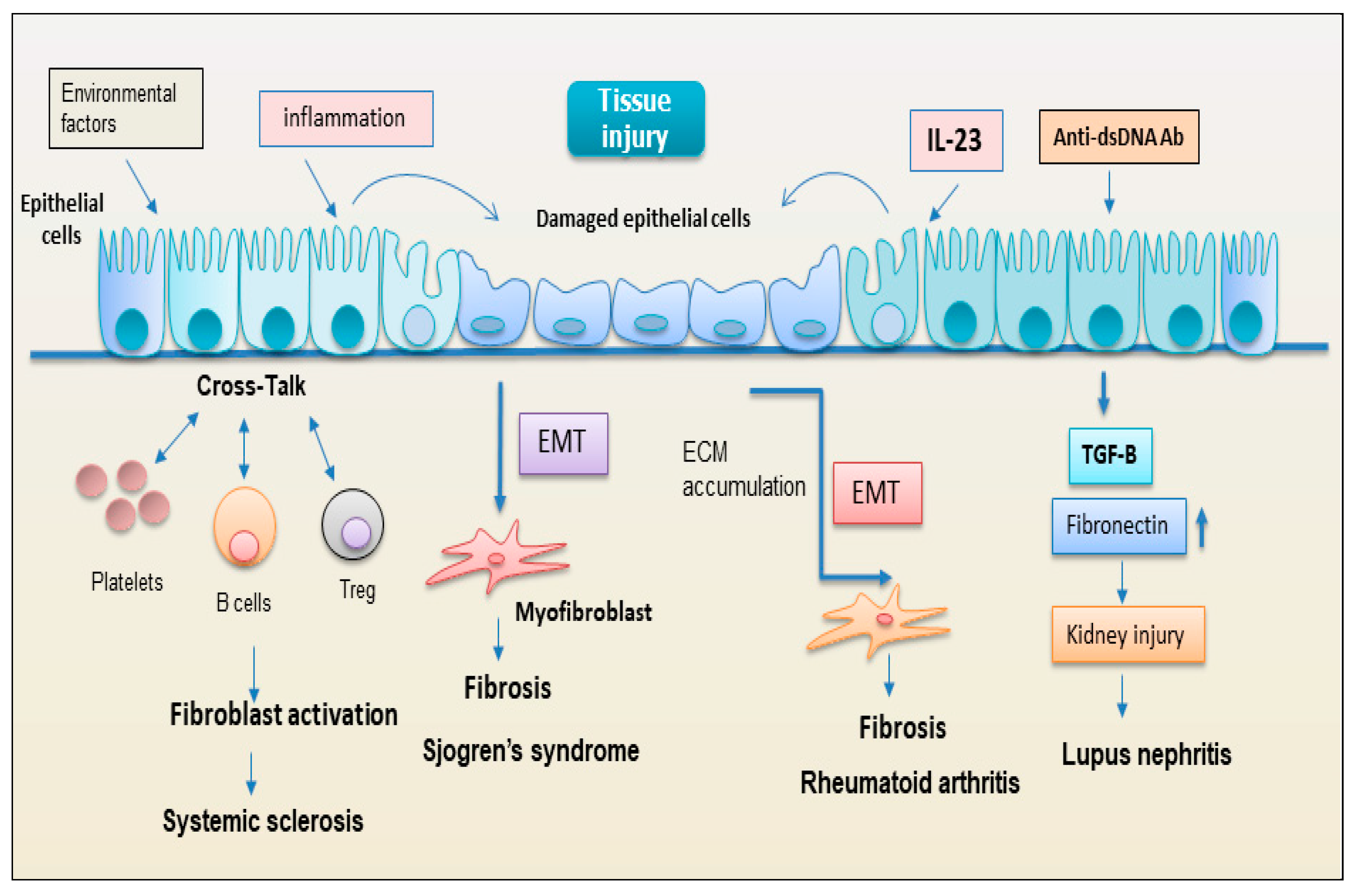
2.2.1. Epithelial Cells
2.2.2. EMT: New Player Regulating the Interplay between the Immunity and Fibrosis
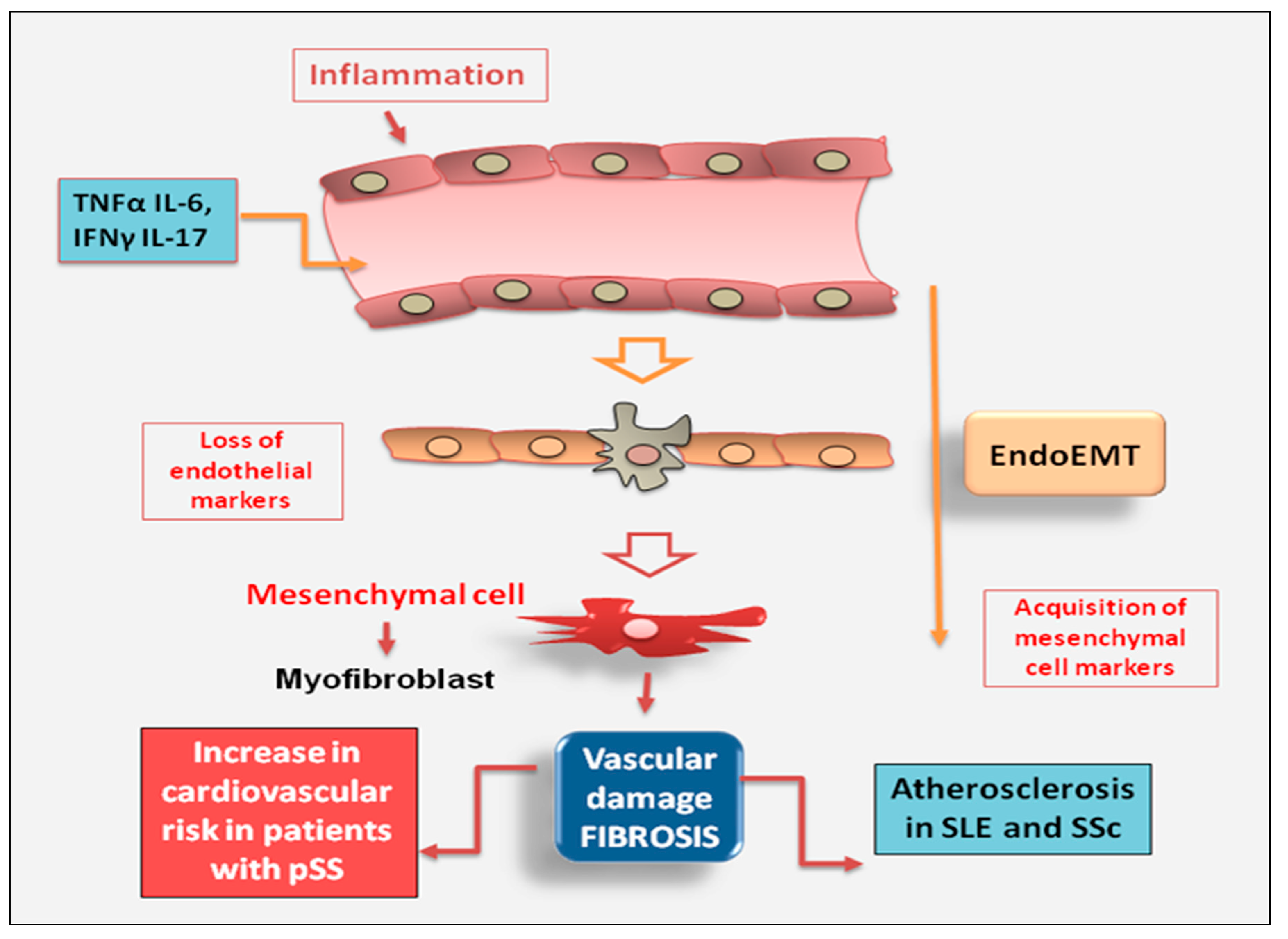
2.2.3. Endothelial Cell
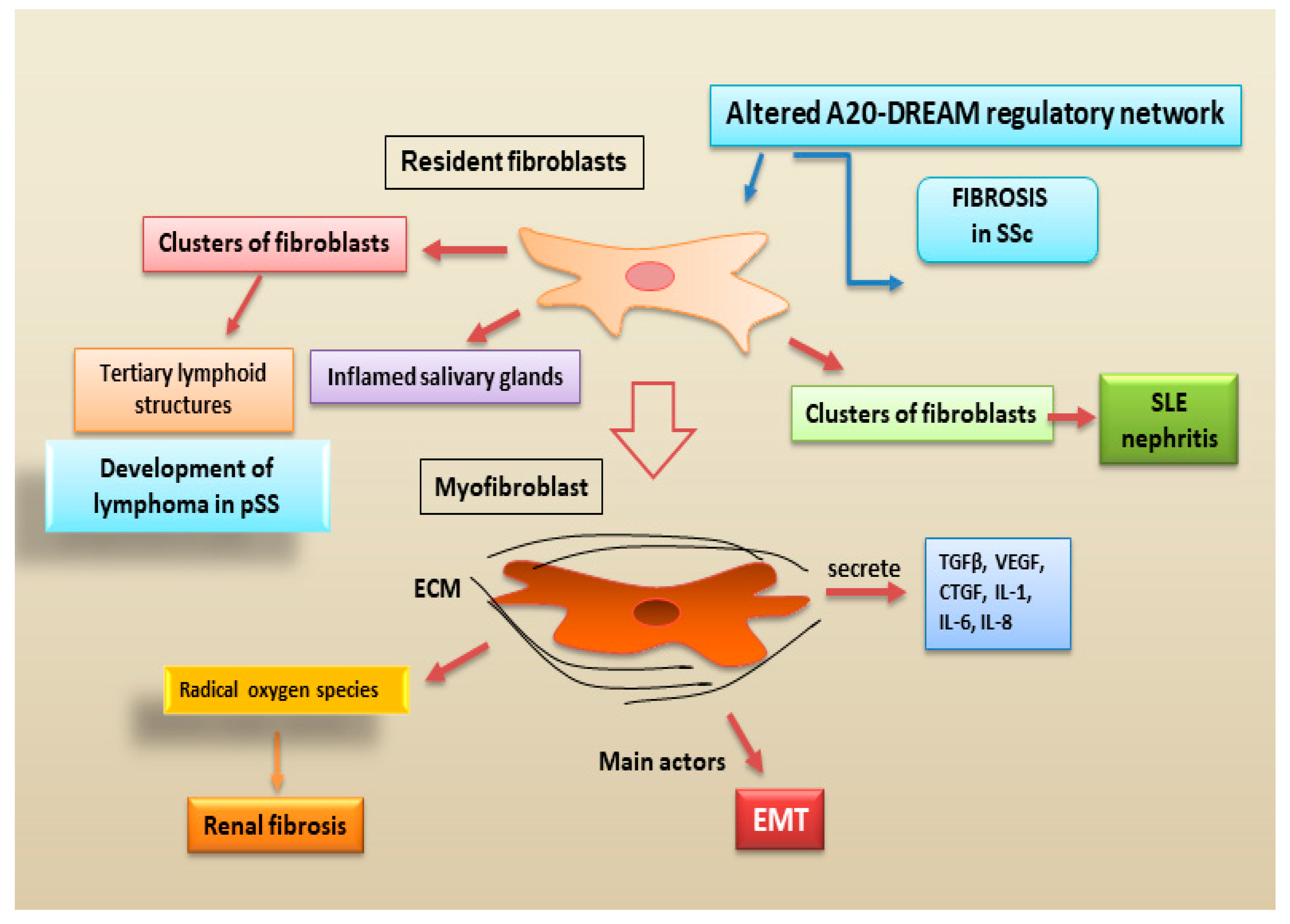
2.2.4. Fibroblasts
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, L.; Rao, X.; Sigdel, K.R. Regulation of Inflammation in Autoimmune Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7403796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizinsky, S.; Haj-Yahia, S.; Machnes Maayan, D.; Lifshitz, Y.; Maoz-Segal, R.; Offengenden, I.; Kidon, M.; Agmon-Levin, N. The innate immune perspective of autoimmune and autoinflammatory conditions. Rheumatology 2019, 58, vi1–vi8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Wei, X.; Ye, T.; Hang, L.; Mou, L.; Su, J. Interrelation Between Fibroblasts and T Cells in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, G.; Dai, S.S. The emerging role of neutrophils in autoimmune-associated disorders: Effector, predictor, and therapeutic targets. MedComm 2021, 2, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Kim, W.U. Targeted Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Disease. Immune Netw. 2022, 22, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, J.H.W.; Gyorfi, A.H.; Ramanujam, M.; Whitfield, M.L.; Konigshoff, M.; Lafyatis, R. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. T Cells in Fibrosis and Fibrotic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D. New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: The macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, I.; Joern, R.R.; Forsthuber, T.G. Memory CD4+ T Cells in Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chang, C.; Wu, H.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, R. The Emerging Epigenetic Role of CD8+T Cells in Autoimmune Diseases: A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuschiotti, P. Current perspectives on the role of CD8+ T cells in systemic sclerosis. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 195, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, N.; Chen, H.; Perugino, C.A.; Maehara, T.; Munemura, R.; Yokomizo, S.; Sameshima, J.; Diefenbach, T.J.; Premo, K.R.; Chinju, A.; et al. Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells may be drivers of tissue destruction in Sjögren’s syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, Y. Cytokines Involved in the Pathogenesis of SSc and Problems in the Devel-opment of Anti-Cytokine Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzi, E.; Tabib, T.; Papazoglou, A.; Sembrat, J.; Trejo Bittar, H.E.; Rojas, M.; Lafyatis, R. Disparate Interferon Signaling and Shared Aberrant Basaloid Cells in Single-Cell Profiling of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 595811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, L.I.; Bogdanos, D.P. The Role of T Cells in SSc: An Update. Immuno 2022, 2, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Z. Association between tubulointerstitial CD8+T cells and renal prognosis in lupus nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuerich, M.; Wang, N.; Kalbasi, A.; Graham, J.J.; Longhi, M.S. Dysfunctional Immune Regulation in Autoimmune Hepatitis: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 746436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, C.; Sacchi, D.; Sarcognato, S.; Cazzagon, N.; Grillo, F.; Baciorri, F.; Fanni, D.; Cacciatore, M.; Maffeis, V.; Guido, M. Pathology of autoimmune hepatitis. Pathologica 2021, 113, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Inverso, D.; Sironi, L.; Di Lucia, P.; Fioravanti, J.; Ganzer, L.; Fiocchi, A.; Vacca, M.; Aiolfi, R.; Sammicheli, S.; et al. Immunosurveillance of the liver by intravascular effector CD8(+) T. Cell 2015, 161, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, R.; Ohta, M.; Alvarez, C.E.; Fiel, M.I.; Bansal, M.; Mehal, W.Z.; Friedman, S.L. Immune stimulation of hepatic fibrogenesis by CD8 cells and attenuation by transgenic interleukin-10 from hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novobrantseva, T.I.; Majeau, G.R.; Amatucci, A.; Kogan, S.; Brenner, I.; Casola, S.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Koteliansky, V.; Hochman, P.S.; Ibraghimov, A. Attenuated liver fibrosis in the absence of B cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3072–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, B. T cells and liver fibrosis. Portal Hypertens. Cirrhosis 2022, 1, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, S. CD8+ T Lymphocytes: Crucial Players in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 602823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihaby, N.; Orliaguet, M.; Le Pottier, L.; Pers, J.O.; Boisramé, S. Treatment of Sjögren’s Syndrome with Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joachims, M.L.; Leehan, K.M.; Lawrence, C.; Pelikan, R.C.; Moore, J.S.; Pan, Z.; Rasmussen, A.; Radfar, L.; Lewis, D.M.; Grundahl, K.M.; et al. Single-cell analysis of glandular T cell receptors in Sjögren’s syndrome. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingueneau, M.; Boudaoud, S.; Haskett, S.; Reynolds, T.L.; Nocturne, G.; Norton, E.; Zhang, X.; Constant, M.; Park, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Cytometry by time-of-flight immunophenotyping identifies a blood Sjögren’s signature correlating with disease activity and glandular inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1809–1821.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Nishikawa, A.; Kassai, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; Kurisu, R.; Okuzono, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Takeshita, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; et al. Multiomic disease signatures converge to cytotoxic CD8 T cells in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira-Dantas, S.; Furmanak, T.; Smith, C.; Quinn, M.; Teos, L.Y.; Ertel, A.; Kurup, D.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Snyder, C.M. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 Promotes CD8+ T Cell Accumulation in Uninfected Salivary Glands but Is Not Necessary after Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstappen, G.M.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Bootsma, H. T cells in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Targets for early intervention. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Min, B. Tissue Resident Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells: Sentinels and Saboteurs in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendeeran, A.; Tenbrock, K. Regulatory T cell function in autoimmune disease. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Hao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Short-term and low-dose IL-2 therapy restores the Th17/Treg balance in the peripheral blood of patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1838–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, C.; Auffray, C.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y. Regulatory T Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Nagafuchi, Y.; Shoda, H.; Fujio, K. The Pathophysiological Roles of Regulatory T Cells in the Early Phase of SSc. Front. Immunol. 2022, 24, 900638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, K.G.; Dawson, N.A.J.; Huang, Q.; Dunne, J.V.; Levings, M.K.; Broady, R. Regulatory T cells produce profibrotic cytokines in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 946–955.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keindl, M.; Davies, R.; Bergum, B.; Brun, J.G.; Hammenfors, D.; Jonsson, R.; Lyssenko, V.; Appel, S. Impaired activation of STAT5 upon IL-2 stimulation in Tregs and elevated sIL-2R in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K. Recent progress on the Roles of Regulatory T Cells in IgG4-Related Disease. Immuno 2022, 2, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.; Qian, Q.F.; Zhou, J.R.; Sun, D.L.; Duan, Y.F.; Zhu, X.; Sartorius, K.; Lu, Y.J. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) in liver fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormandy, L.A.; Hillemann, T.; Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P.; Greten, T.F.; Korangy, F. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nurieva, R.I.; Dong, C. Transcriptional regulation of follicular T-helper (Tfh) cells. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 252, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitfeld, D.; Ohl, L.; Kremmer, E.; Ellwart, J.; Sallusto, F.; Lipp, M.; Förster, R. Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5, localize to B cell follicles, and support immunoglobulin production. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensous, N.; Charrier, M.; Duluc, D.; Contin-Bordes, C.; Truchetet, M.E.; Lazaro, E.; Duffau, P.; Blanco, P.; Richez, C. T Follicular Helper Cells in Autoimmune Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, P. Role of the frequency of blood CD4(+) CXCR5(+) CCR6(+) T cells in autoimmunity in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yu, D.; Li, X.; Yu, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. CD4+CXCR5+ follicular helper T cells in salivary gland promote B cells maturation in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelzang, A.; McGuire, H.M.; Yu, D.; Sprent, J.; Mackay, C.R.; King, C. A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Chu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xuan, D.; Zheng, S.; Zou, H. T follicular helper cells and regulatory B cells dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, T.T.; Yin, Z.J.; Wang, X.B. Elevated circulating Th17 and follicular helper CD4(+) T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. APMIS 2015, 123, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.K.; Mittereder, N.; Kuta, E.; Delaney, T.; Burwell, T.; Dacosta, K.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, L.I.; Brown, C.; Boutrin, A.; et al. T follicular helper-like cells contribute to skin fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 431, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, T.I.; van Caam, A.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Thurlings, R.M. Therapeutic Options for Systemic Sclerosis: Current and Future Perspectives in Tackling Immune-Mediated Fibrosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, Y.; Chiba, H.; Nishikiori, H.; Kamekura, R.; Yabe, H.; Kondo, S.; Miyajima, S.; Shigehara, K.; Ichimiya, S.; Takahashi, H. Aberrant populations of circulating T follicular helper cells and regulatory B cells underlying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2019, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwi, Y.; Westra, J.; van Goor, H.; Burgess, J.K.; Denton, C.P.; Mulder, D.J. Macrophages as determinants and regulators of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, E.A.; Devitt, A.; Johnson, J.R. Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeft, K.; Schaefer, G.J.L.; Kim, H.; Schumacher, D.; Bleckwehl, T.; Long, Q.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Peisker, F.; Koch, L.; Nagai, J.; et al. Platelet-instructed SPP1+ macrophages drive myofibroblast activation in fibrosis in a CXCL4-dependent manner. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Chai, J.; Wang, H.; Fu, L.; Peng, S.; Ni, X. Hepatic macrophages: Key players in the development and progression of liver fibrosis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2279–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choreño-Parra, J.A.; Cervantes-Rosete, D.; Jiménez-Alvarez, L.A.; Ramírez-Martínez, G.; Márquez-García, J.E.; Cruz-Lagunas, A.; Magaña-Sanchez, A.Y.; Lima, G.; López-Maldonado, H.; Gaytán-Guzmán, E.; et al. Dendritic cells drive profibrotic inflammation and aberrant T cell polarization in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2022, 62, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilliams, M.; Ginhoux, F.; Jakubzick, C.; Naik, S.H.; Onai, N.; Schraml, B.U.; Segura, E.; Tussiwand, R.; Yona, S. Dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages: A unified nomenclature based on ontogeny. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 4, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.S.; Ferreira, B.H.; Almeida, C.R. Molecular Mechanisms Behind the Role of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. Biology 2023, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafaja, S.; Valera, I.; Divekar, A.A.; Saggar, R.; Abtin, F.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Singh, R.R. pDCs in lung and skin fibrosis in a bleomycin-induced model and patients with systemic sclerosis. JCI Insight. 2018, 3, e98380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedoe, P.; Marges, E.; Hiemstra, P.; Ninaber, M.; Geelhoed, M. Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis: Toward Personalized-Medicine-Based Prediction and Drug Screening Models of Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD). Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Mennella, A.; Palazzo, R.; Pietraforte, I.; Stefanantoni, K.; Iannace, N.; Butera, A.; Boirivant, M.; Pica, R.; Conrad, C.; et al. Anti-CXCL4 Antibody Reactivity Is Present in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) and Correlates with the SSc Type I Interferon Signature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affandi, A.J.; Carvalheiro, T.; Ottria, A.; de Haan, J.J.; Brans, M.A.D.; Brandt, M.M.; Tieland, R.G.; Lopes, A.P.; Fernández, B.M.; Bekker, C.P.J.; et al. CXCL4 drives fibrosis by promoting several key cellular and molecular processes. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bon, L.; Affandi, A.J.; Broen, J.; Christmann, R.B.; Marijnissen, R.J.; Stawski, L.; Farina, G.A.; Stifano, G.; Mathes, A.L.; Cossu, M.; et al. Proteome-wide analysis and CXCL4 as a biomarker in systemic sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah Kioon, M.D.; Tripodo, C.; Fernandez, D.; Kirou, K.A.; Spiera, R.F.; Crow, M.K.; Gordon, J.K.; Barrat, F.J. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote systemic sclerosis with a key role for TLR8. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaam8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Stellin, L.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K.; Frydas, I.; Younes, A.; Di Emidio, P.; Ronconi, G. Advances in Mast Cell Activation by IL-1 and IL-33 in Sjogren’s Syndrome: Promising Inhibitory Effect of IL-37. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehan, K.M.; Pezant, N.P.; Rasmussen, A.; Grundahl, K.; Moore, J.S.; Radfar, L.; Lewis, D.M.; Stone, D.U.; Lessard, C.J.; Rhodus, N.L.; et al. Minor salivary gland fibrosis in Sjogren’s syndrome is elevated, associated with focus score and not solely a consequence of aging. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Sjögren’s Syndrome-Related Organs Fibrosis: Hypotheses and Realities. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, M.K.; Allington, T.M.; Schiemann, W.P. Mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by TGF-beta. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 1145–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppe, C.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Kranz, J.; Zhang, X.; Ziegler, S.; Perales-Patón, J.; Jansen, J.; Reimer, K.C.; Smith, J.R.; Dobie, R.; et al. Decoding myofibroblast origins in human kidney fibrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 589, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Organ Fibrosis and Autoimmunity: The Role of Inflammation in TGFβ-Dependent EMT. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Autoimmunity in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Identification of New Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Saigusa, R. Systemic sclerosis: Is the epithelium a missing piece of the pathogenic puzzle? J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 94, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Healy, H.; Kassianos, A.J. The Emerging Role of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in the Immunological Pathophysiology of Lupus Nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 578952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Lamas, S.; Ortiz, A.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Ng, C.Y.; Ho, S.K.; Cheung, K.F.; Chan, K.W.; Zhang, Q.; Chau, M.K.; Chan, T.M. Anti-dsDNA antibody induces soluble fibronectin secretion by proximal renal tubular epithelial cells and downstream increase of TGF-beta1 and collagen synthesis. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 58, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Lau, J.; Roden, A.C.; Matteson, E.L.; Sun, J.; Luo, F.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Vassallo, R. IL-23 amplifies the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mechanically conditioned alveolar epithelial cells in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease through mTOR/S6 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L1006–L1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, J.; Robuffo, I.; Spalletta, S.; Giambuzzi, G.; De Iuliis, V.; Toniato, E.; Martinotti, S.; Conti, P.; Flati, V. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition as a Possible Therapeutic Target in Fibrotic Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 607483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Poe, D.; Yang, Y.; Hyatt, T.; Xing, J. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through directional destabilization of multidimensional attractor. eLife 2022, 11, e74866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Novoa, J.M.; Nieto, M.A. Inflammation and EMT: An alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, G.D.; Fonticoli, L.; Rajan, T.S.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Trubiani, O.; Pizzicannella, J.; Diomede, F. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): The Type-2 EMT in Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration and Organ Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Dai, F.; Feng, L.; Zou, H.; Feng, L.; Xu, M. Communication Between Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity and Cancer Stem Cells: New Insights Into Cancer Progression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 617597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovisa, S. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Fibrosis: Concepts and Targeting Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 737570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. TGF-β1 signaling and tissue fibrosis. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a022293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.O.; Wan, Y.Y.; Sanjabi, S.; Robertson, A.K.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 99–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, I.; Moreno-Càceres, J.; Sánchez, A.; Dewidar, B.; Giannelli, G.; Ten Dijke, P. IT-LIVER Consortium. TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.C.; Borok, Z. TGF-β-induced EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. 2007, 293, L525–L534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, S.A. Role of endothelial to mesenchymal transition in the pathogenesis of the vascular alterations in systemic sclerosis. ISRN Rheumatol. 2013, 2013, 835948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebmeier, S.; Horsley, V. Origin of fibrosing cells in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Vomero, M.; Navarini, L.; Dolo, V.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschetti, L.; Piantoni, S.; Vizzardi, E.; Sciatti, E.; Riccardi, M.; Franceschini, F.; Cavazzana, I. Endothelial Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Systemic Sclerosis: A Common Trigger for Different Microvascular Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 849086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, A.; Małecki, R.; Kulus, M.; Madej, M.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Doroszko, A. Cardiovascular Risk and Endothelial Dysfunction in Primary Sjogren Syndrome Is Related to the Disease Activity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, M.; Miossec, P. Effects of Interleukin 17 on the cardiovascular system. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostmans, Y.; Cutolo, M.; Giddelo, C.; Decuman, S.; Melsens, K.; Declercq, H.; Vandecasteele, E.; De Keyser, F.; Distler, O.; Gutermuth, J.; et al. The role of endothelial cells in the vasculopathy of systemic sclerosis: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBleu, V.S.; Taduri, G.; O’Connell, J.; Teng, Y.; Cooke, V.G.; Woda, C.; Sugimoto, H.; Kalluri, R. Origin and Function of Myofibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Korsunsky, I.; Marshall, J.L.; Gao, A.; Watts, G.F.M.; Major, T.; Croft, A.P.; Watts, J.; Blazar, P.E.; Lange, J.K.; et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature 2020, 582, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J. Insights into the role of fibroblasts in human autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 141, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bale, S.; Wei, J.; Yalavarthi, B.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Yan, J.J.; Abdala-Valencia, H.; Xu, D.; Sun, H.; Marangoni, R.G.; et al. Fibroblast A20 governs fibrosis susceptibility and its repression by DREAM promotes fibrosis in multiple organs. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuora, S. Fibroblast A20 and its suppressor DREAM regulate fibrosis in SSc. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K. Fibroblasts in Sjögren’s Syndrome, Fibroblasts—Advances in Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Cancer; Bertoncelj, M.F., Lakota, K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, K. Crosstalk between fibroblasts and T cells in immune networks. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1103823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Cozzi, M.; Barinotti, A.; Radin, M.; Cecchi, I.; Fenoglio, R.; Mancardi, D.; Wilson Jones, G.; Rossi, D.; Roccatello, D. Renal Fibrosis in Lupus Nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.; Woods, E.L.; Dally, J.; Kong, D.; Steadman, R.; Moseley, R.; Midgley, A.C. Myofibroblasts: Function, Formation, and Scope of Molecular Therapies for Skin Fibrosis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabib, T.; Morse, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Lafyatis, R. SFRP2/DPP4 and FMO1/LSP1 Define Major Fibroblast Populations in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Caam, A.; Vonk, M.; van den Hoogen, F.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P. Unraveling SSc Pathophysiology; The Myofibroblast. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falke, L.L.; Gholizadeh, S.; Goldschmeding, R.; Kok, R.J.; Nguyen, T.Q. Diverse Origins of the Myofibroblast—Implications for Kidney Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schunk, S.J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Speer, T. WNT-β-Catenin Signalling—A Versatile Player in Kidney Injury and Repair. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antigen Location | Antigen | Fibrosis Autoimmune Diseases |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear | Ro-RNP complex | Systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome |
| La antigen | Systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome | |
| Small nuclear RNP | Systemic lupus erythematosus, Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | |
| Chromatin | Autoimmune hepatitis, Systemic sclerosis | |
| dsDNA | Systemic lupus erythematosus, Autoimmune hepatitis | |
| Topoisomerase I | Systemic sclerosis | |
| Centromere | Systemic sclerosis | |
| Modified proteins | Citrullinated proteins | Rheumatoid arthritis, Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| Carbamylated proteins | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| Extracellular | RF (IgG) | Rheumatoid arthritis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sisto, M.; Lisi, S. Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells Involved in Autoimmune Fibrosis: New Discoveries. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12113801
Sisto M, Lisi S. Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells Involved in Autoimmune Fibrosis: New Discoveries. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(11):3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12113801
Chicago/Turabian StyleSisto, Margherita, and Sabrina Lisi. 2023. "Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells Involved in Autoimmune Fibrosis: New Discoveries" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 11: 3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12113801
APA StyleSisto, M., & Lisi, S. (2023). Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells Involved in Autoimmune Fibrosis: New Discoveries. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(11), 3801. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12113801







