Automatic Masseter Muscle Accurate Segmentation from CBCT Using Deep Learning-Based Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Image Acquisition
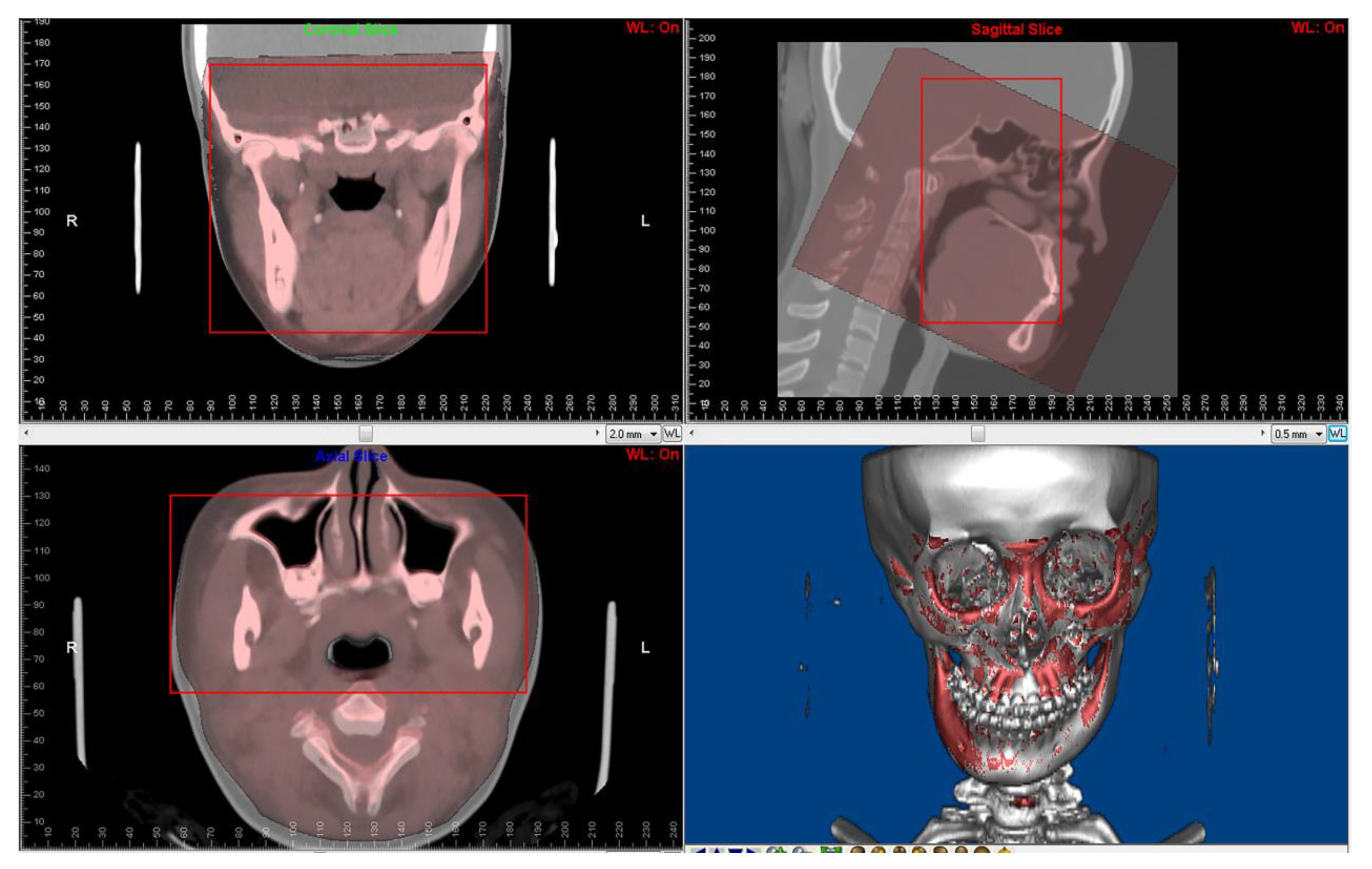
2.3. CBCT to CT Superimposition
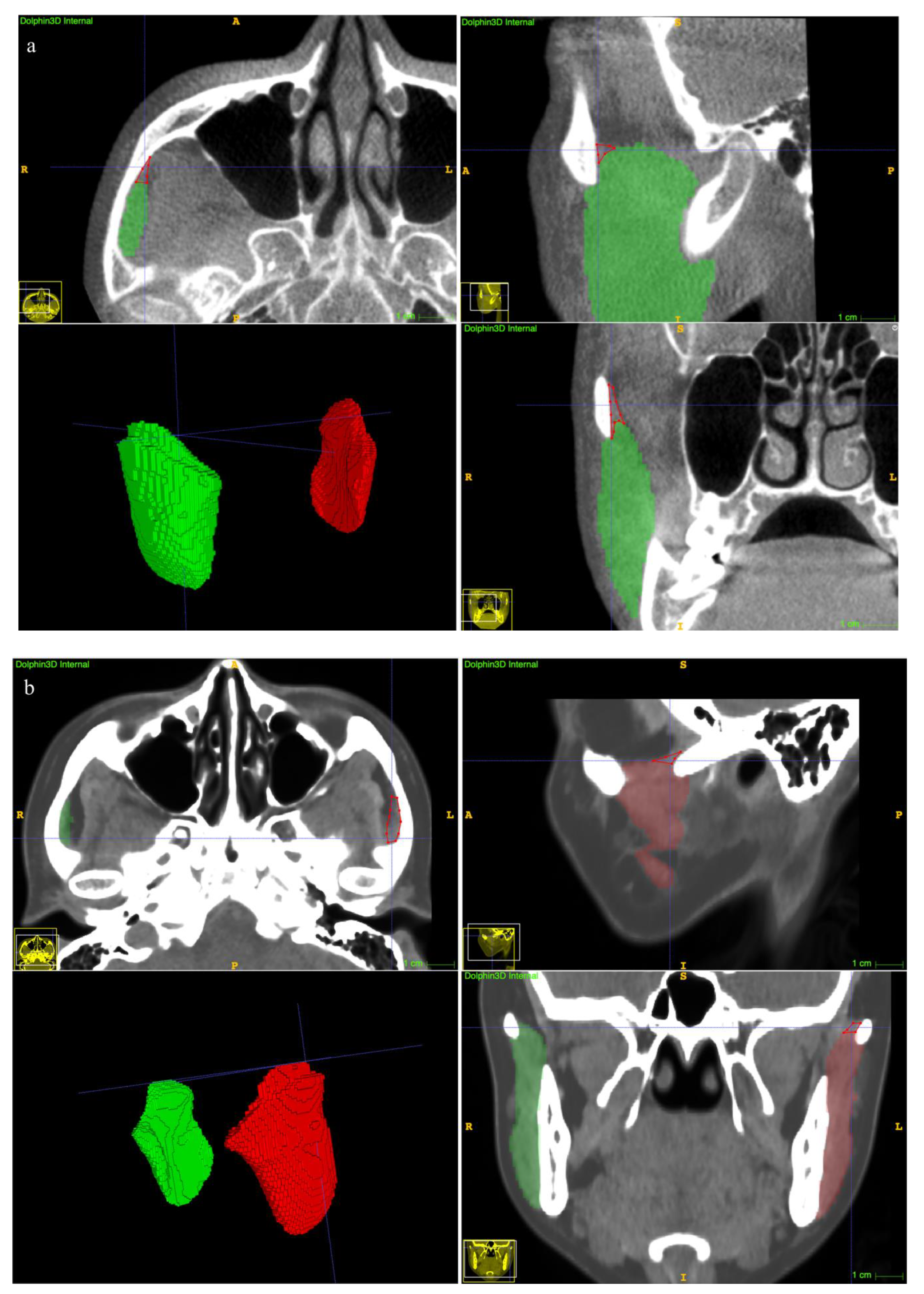
2.4. Manual Annotation of the MM
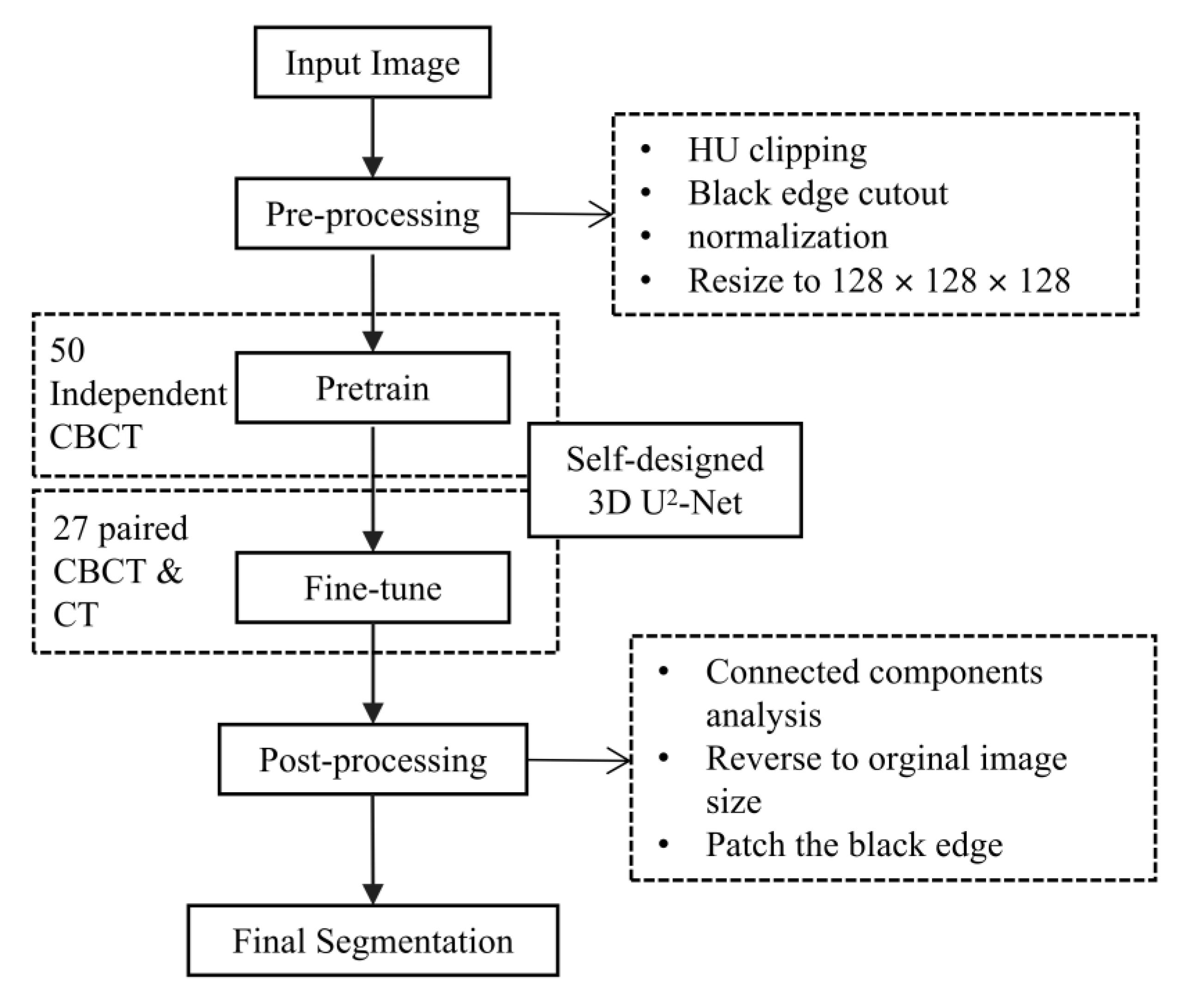
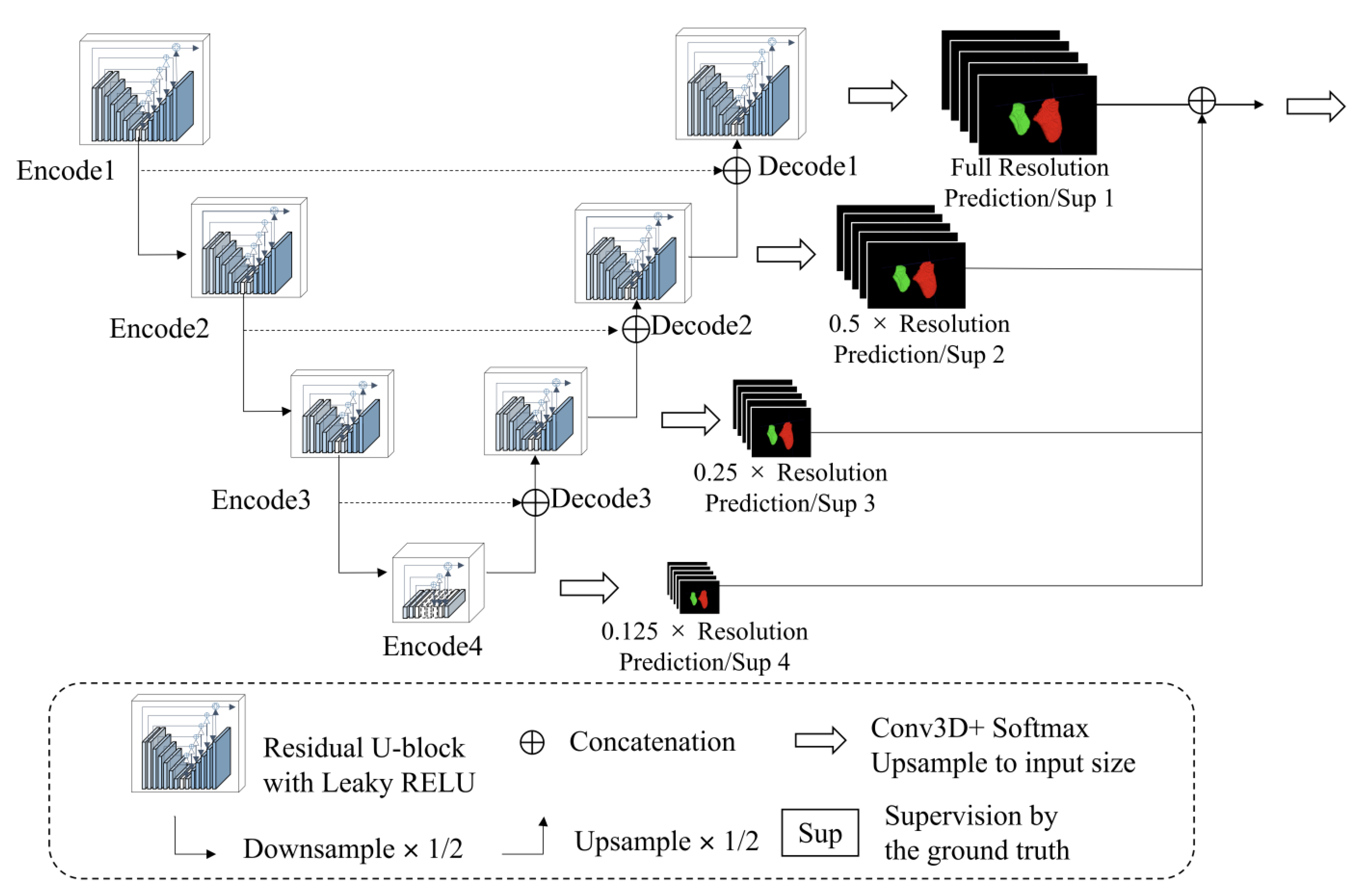
2.5. MM Auto-Segmentation
Implement Details
2.6. Evaluation of Geometric Accuracy of the Segmentations
2.7. Clinical Suitability
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Interobserver Variations
3.2. Comparison of Manual Annotation Difference between CBCT and CT
3.3. Model Performance
3.4. Time Cost
3.5. Clinical Suitability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaudy, J.F.; Zouaoui, A.; Bravetti, P.; Charrier, J.L.; Guettaf, A. Functional organization of the human masseter muscle. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2000, 22, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumata, A.; Fujishita, M.; Ariji, Y.; Ariji, E.; Langlais, R.P. 3D CT evaluation of masseter muscle morphology after setback osteotomy for mandibular prognathism. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2004, 98, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, L.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T. Thickness change of masseter muscles and the surrounding soft tissues in female patients during orthodontic treatment: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, P.S.; Park, T.H.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Yang, J.D.; Chung, H.Y.; Cho, B.C.; Choi, K.Y. The Effect of Orthognathic Surgery on Changes in Masticatory Muscle Volume in Patients with Facial Asymmetry. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2022, 33, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokaji, R.; Ooi, K.; Yahata, T.; Nakade, Y.; Kawashiri, S. Evaluation of factors related to morphological masseter muscle changes after preoperative orthodontic treatment in female patients with skeletal class III dentofacial deformities. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coclici, A.; Hedeşiu, M.; Bran, S.; Băciuţ, M.; Dinu, C.; Rotaru, H.; Roman, R. Early and long-term changes in the muscles of the mandible following orthognathic surgery. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trawitzki, L.V.V.; Dantas, R.O.; Mello-Filho, F.V.; Marques, W., Jr. Masticatory muscle function three years after surgical correction of class III dentofacial deformity. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, K.; Takazakura, D.; Marukawa, K.; Shimada, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamamoto, E. Relationship between the morphologies of the masseter muscle and the ramus and occlusal force in patients with mandibular prognathism. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Yu, H.S. Masseter muscle changes following orthognathic surgery: A long-term three-dimensional computed tomography follow-up. Angle Orthod. 2012, 82, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Yu, J.; Chen, G.; Xu, T.; Jiang, R. Changes in buccal facial depth of female patients after extraction and nonextraction orthodontic treatments: A preliminary study. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.K.; Nishida, S.; Yahagi, M.; Langenbach, G.E.; Nakamura, Y.; Tokumori, K.; Sakai, S.; Yabuuchi, H.; Yoshiura, K. Size and orientation of masticatory muscles in patients with mandibular laterognathism. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayukawa, H. Malocclusion and masticatory muscle activity: A comparison of four types of malocclusion. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 1992, 16, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becht, M.P.; Mah, J.; Martin, C.; Razmus, T.; Gunel, E.; Ngan, P. Evaluation of masseter muscle morphology in different types of malocclusions using cone beam computed tomography. Int. Orthod. 2014, 12, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.P.; Ong, S.H.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Foong, K.W.; Goh, P.S.; Nowinski, W.L. 3D segmentation and quantification of a masticatory muscle from MR data using patient-specific models and matching distributions. J. Digit. Imaging 2009, 22, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleod, I.; Heath, N. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in dental practice. Dent. Update 2008, 35, 590–592, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, K.-J.; Yu, H.-S.; Baik, H.-S. Repeated injections of botulinum toxin into the masseter muscle induce bony changes in human adults: A longitudinal study. Korean J. Orthod. 2017, 47, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Qin, H.; Guo, Y.; Zha, H. Masseter Muscle Segmentation from Cone-Beam CT Images using Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Venice, Italy, 11 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Thor, M.; Onochie, I.; Hesse, J.; Zakeri, K.; LoCastro, E.; Jiang, J.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Elguindi, S.; Lee, N.Y.; et al. Prospectively-validated deep learning model for segmenting swallowing and chewing structures in CT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Dyer, B.A.; Feng, X.; Rao, S.; Benedict, S.H.; Chen, Q.; Rong, Y. Deep learning vs. atlas-based models for fast auto-segmentation of the masticatory muscles on head and neck CT images. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Pei, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, G.; Xu, T.; Zha, H. Masseter Segmentation from Computed Tomography Using Feature-Enhanced Nested Residual Neural Network. Cham, 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Minnema, J.; Batenburg, K.J.; Forouzanfar, T.; Hu, F.J.; Wu, G. Multiclass CBCT Image Segmentation for Orthodontics with Deep Learning. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Fang, Y.; Mei, L.; Zhang, B.; Yu, B.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Huang, J.; et al. A fully automatic AI system for tooth and alveolar bone segmentation from cone-beam CT images. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Q.; Xu, Z.-N.; Mao, W.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Bai, H.-L.; Ding, P.; Fu, K.-Y. Deep learning-based evaluation of the relationship between mandibular third molar and mandibular canal on CBCT. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Tian, S.; Patel, P.; Jani, A.B.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Pelvic multi-organ segmentation on cone-beam CT for prostate adaptive radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 3415–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, N.; Alam, S.R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, T.; Yezzi, A.; Nadeem, S. Multitask 3D CBCT-to-CT translation and organs-at-risk segmentation using physics-based data augmentation. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 5130–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.P.; Luck, M.; Honari, S. Distribution Matching Losses Can Hallucinate Features in Medical Image Translation. Cham, 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Dehghan, M.; Jagersand, M. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 106, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.L. Rectifier Nonlinearities Improve Neural Network Acoustic Models. In Proceedings of the ICML Workshop on Deep Learning for Audio, Speech and Language Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, A.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A.M. VNet: An End-to-End Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Road Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179424–179436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yue, N.; Su, M.Y.; Liu, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Nie, K. Improving CBCT quality to CT level using deep learning with generative adversarial network. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Bernard, M.E.; Hunter, T.; Chen, Q. Improving accuracy and robustness of deep convolutional neural network based thoracic OAR segmentation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 07nt01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mean ± SD (95%CI) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC, %) | Average Hausdorff Distance (aHD, mm) | |||||
| Mean | Background | Left MM | Right MM | Mean | Left MM | Right MM | |
| Interobserver variations (CBCT) | 96.05 ± 2.46 (94.69, 97.42) | 99.97 ± 0.02 (99.96, 99.98) | 94.39 ± 4.20 (92.07, 96.72) | 93.78 ± 3.97 (91.59, 95.98) | 4.31 ± 1.31 (3.52, 5.09) | 4.36 ± 2.92 (2.74, 5.98) | 4.26 ± 1.31 (3.53, 4.98) |
| Interobserver variations (CT) | 95.82 ± 1.52 (94.98, 96.66) | 99.97 ± 0.02 (99.96, 99.98) | 93.95 ± 2.48 (92.58, 95.32) | 93.57 ± 2.22 (92.31, 95.76) | 3.22 ± 1.14 (2.59, 3.86) | 2.99 ± 1.03 (2.33, 3.47) | 3.55 ± 1.61 (2.66, 4.44) |
| CBCT manual annotations vs. CT manual annotations | 90.16 ± 2.23 (89.33, 91.00) | 99.93 ± 0.02 (99.92, 99,94) | 84.75 ± 3.76 (83.22, 84.80) | 85.82 ± 3.25 (84.61, 87.03) | 5.41 ± 1.63 (4.80, 6.02) | 5.28 ± 2.34 (4.41, 6.16) | 5.54 ± 1.56 (4.95, 6.12) |
| Mean ± SD (95%CI) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC, %) | Average Hausdorff Distance (aHD, mm) | |||||
| Mean | Background | Left MM | Right MM | Mean | Left MM | Right MM | |
| CBCT auto-segmentations vs. CT manual annotations | 94.15 ± 0.68 (93.90, 94.40) | 99.96 ± 0.01 (99.95, 99.96) | 91.56 ± 0.97 (91.20, 91.92) | 90.94 ± 1.33 (90.44, 91.44) | 3.68 ± 1.01 (3.30, 4.06) | 3.22 ± 1.01 (2.84, 3.59) | 4.14 ± 1.68 (3.52, 4.77) |
| CT auto-segmentations vs. CT manual annotations | 94.45 ± 0.80 (94.15, 94.75) | 99.96 ± 0.01 (99.96, 99.96) | 91.84 ± 1.26 (91.37, 91.86) | 91.55 ± 1.31 (91.06, 92.04) | 3.67 ± 1.25 (3.21, 4.14) | 3.35 ± 1.00 (2.97, 3.72) | 4.00 ± 2.00 (3.25, 4.74) |
| CBCT auto-segmentations vs. CT auto-segmentations | 94.48 ± 0.74 (94.07, 94.90) | 99.96 ± 0.01 (99.95, 99.97) | 91.89 ± 1.23 (91.21, 92.57) | 91.60 ± 1.22 (90.93, 92.27) | 2.42 ± 0.33 (2.24, 2.60) | 2.27 ± 0.38 (2.06, 2.49) | 2.57 ± 0.55 (2.26, 2.87) |
| Measurements | Mean ± SD | Mean Difference (1–2) | t | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:CBCT Auto-Segmentation | 2:CBCT Manual Annotation | |||||
| Dice similarity coefficient (DSC, %) | mean | 94.15 ± 0.68 | 90.16 ± 2.23 | 3.99 | 10.402 | 0.000 ** |
| background | 99.96 ± 0.01 | 99.93 ± 0.02 | 0.03 | 10.387 | 0.000 ** | |
| Left MM | 91.56 ± 0.97 | 84.75 ± 4.10 | 6.81 | 9.366 | 0.000 ** | |
| rightMM | 90.94 ± 1.33 | 85.82 ± 3.25 | 5.12 | 9.302 | 0.000 ** | |
| Average Hausdorff distance (aHD, mm) | mean | 3.68 ± 1.01 | 5.41 ± 1.63 | −1.73 | −5.274 | 0.000 ** |
| leftMM | 3.22 ± 1.01 | 5.28 ± 2.34 | −2.06 | −4.791 | 0.000 ** | |
| rightMM | 4.14 ± 1.68 | 5.54 ± 1.56 | −1.40 | −3.480 | 0.002 ** | |
| Mean ± SD (95%CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Segmenting CBCT | Manual Segmenting CT | Model Segmenting CBCT | Model Segmenting CT |
| 1879.80 ± 338.80 (1753.49, 2006.51) | 2245.80 ± 531.72 (2047.46, 2444.54) | 5.64 ± 0.63 (5.29, 5.99) | 6.76 ± 0.76 (6.34, 7.18) |
| Mean ± SD (95%CI) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moda-lity | Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC, %) | Average Hausdorff Distance (aHD, mm) | Revision (%) | |||||||
| Mean | Back-ground | Left MM | Right MM | Mean | Left MM | Right MM | Mean | Left MM | Right MM | |
| CBCT | 99.84 ± 0.06 (99.76, 99.92) | 100 (100,100) | 99.77 ± 0.10 (99.64, 99.90) | 99.77 ± 0.19 (99.53, 100) | 0.95 ± 0.34 (0.53, 1.37) | 0.90 ± 0.36 (0.46, 1.35) | 1.00 ± 0.53 (0.34, 1.66) | 0.56 ± 0.30 (0.20, 0.93) | 0.68 ± 0.66 (−0.14, 1.51) | 0.44 ± 0.41 (−0.07, 0.96) |
| CT | 99.84 ± 0.20 (99.59, 100.09) | 100 (100,100) | 99.72 ± 0.28 (99.38, 100.07) | 99.81 ± 0.39 (99.33, 100.29) | 0.88 ± 1.27 (−0.70, 2.46) | 1.02 ± 0.93 (−0.13, 2.17) | 0.75 ± 1.68 (−1.33, 2.83) | 0.49 ± 0.59 (−0.24, 1.21) | 0.72 ± 1.07 (−0.60, 2.05) | 0.25 ± 0.50 (−0.37, 0.86) |
| Mean ± SD | 99.84 ± 0.14 (99.72, 9.94) | 100 (100,100) | 99.75 ± 0.20 (99.60, 99.89) | 99.79 ± 0.27 (99.58, 99.99) | 0.92 ± 0.88 (0.29, 1.55) | 0.96 ± 0.66 (0.48, 1.44) | 0.87 ± 1.18 (0.03, 1.72) | 0.52 ± 0.44 (0.21, 0.84) | 0.70 ± 0.84 (0.10, 1.30) | 0.35 ± 0.44 (0.03, 0.66) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Shang, F.; Peng, J.; Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Jiang, R. Automatic Masseter Muscle Accurate Segmentation from CBCT Using Deep Learning-Based Model. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010055
Jiang Y, Shang F, Peng J, Liang J, Fan Y, Yang Z, Qi Y, Yang Y, Xu T, Jiang R. Automatic Masseter Muscle Accurate Segmentation from CBCT Using Deep Learning-Based Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yiran, Fangxin Shang, Jiale Peng, Jie Liang, Yi Fan, Zhongpeng Yang, Yuhan Qi, Yehui Yang, Tianmin Xu, and Ruoping Jiang. 2023. "Automatic Masseter Muscle Accurate Segmentation from CBCT Using Deep Learning-Based Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010055
APA StyleJiang, Y., Shang, F., Peng, J., Liang, J., Fan, Y., Yang, Z., Qi, Y., Yang, Y., Xu, T., & Jiang, R. (2023). Automatic Masseter Muscle Accurate Segmentation from CBCT Using Deep Learning-Based Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010055





