Years of Potential Life Lost on Renal Replacement Therapy: Retrospective Study Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Kidney Transplantation
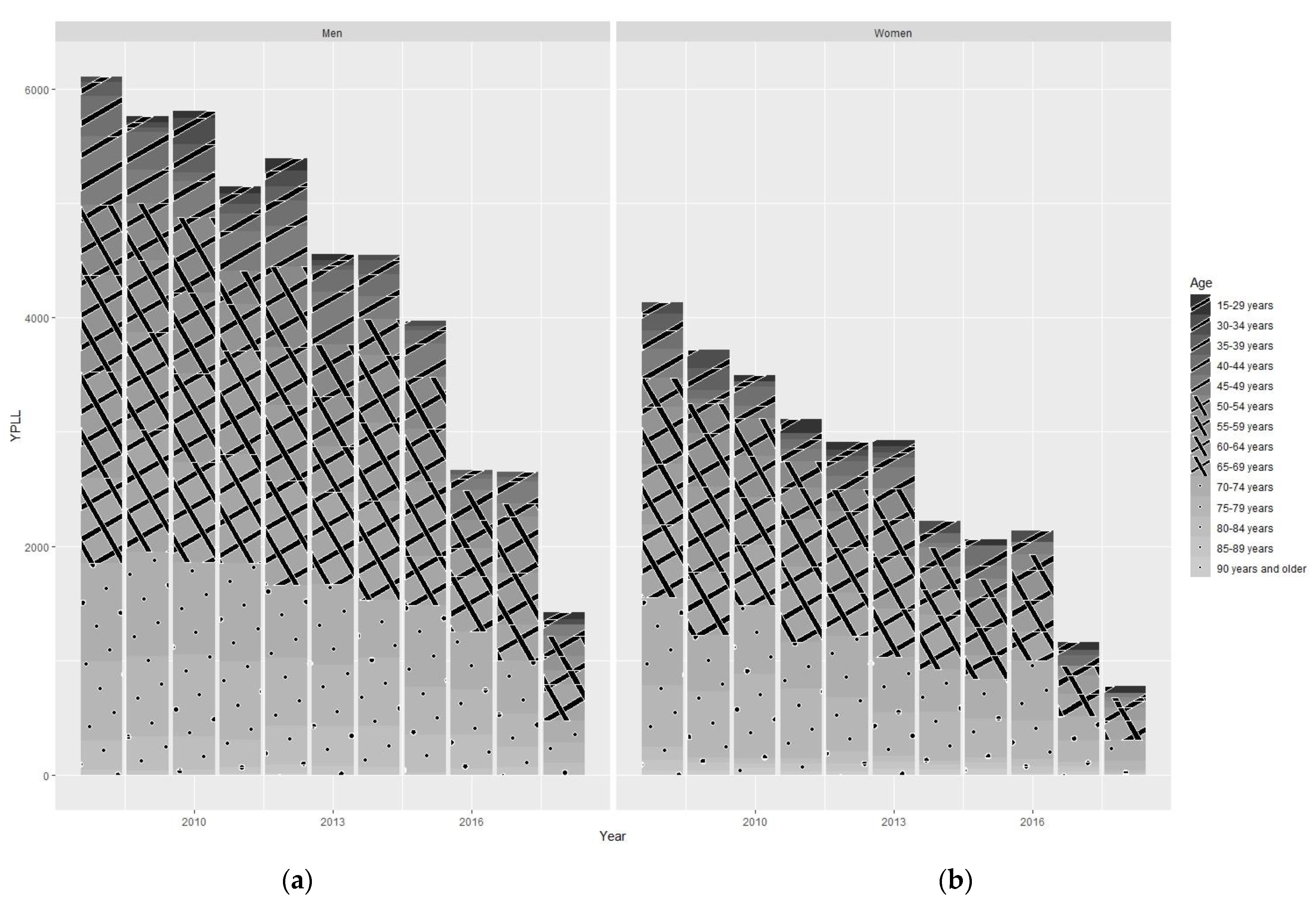
3.2. Years of Potential Life Lost
3.3. YPLL Kidney Transplantation Versus Dialysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.-H.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J.; et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbat, C.G.; Thorpe, K.E.; Russell, J.D.; Churchill, D.N. Comparison of mortality risk for dialysis patients and cadaveric first renal transplant recipients in Ontario, Canada. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA-EDTA Registry: ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2017; Amsterdam UMC, Locatie AMC, Department of Medical Informatics: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019.
- United States Renal Data System. 2021 USRD Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. 2021. Available online: https://adr.usrds.org/2021/end-stage-renal-disease/6-mortality (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Martín Escobar, E.; Registro Español de Enfermos Renales (REER). The Spanish Renal Registry: 2013 report and evolution from 2007–2013. Nefrologia 2016, 36, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organització Catalana de Trasplantaments (OCATT). Registre de Malalts Renals de Catalunya, Informe Estadístic 2018; Generalitat de Catalunya, Departament de Salut: Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Castro de la Nuez, P.; Muñoz, T.; José, M.; Egea Guerrero, J.J. Sistema de Información de la Coordinacion Autonómica de Trasplantes de Andalucia: Subsistema de Insuficiencia Renal Crónica—Informe 2017; Consejeria de Salud: Andalucia, Spain; Servicio Andaluz de Salud: Andalucia, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, S.P. Survival of recipients of cadaveric kidney transplants compared with those receiving dialysis treatment in Australia and New Zealand, 1991–2001. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnuelle, P.; Lorenz, D.; Trede, M.; Van Der Woude, F.J. Impact of renal cadaveric transplantation on survival in end-stage renal failure: Evidence for reduced mortality risk compared with hemodialysis during long-term follow-up. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, J. Evaluación económica del tratamiento sustitutivo renal (hemodiálisis, diálisis peritoneal y trasplante) en España. Nefrologia 2010, 1, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Laupacis, A.; Keown, P.; Pus, N.; Krueger, H.; Ferguson, B.; Wong, C.; Muirhead, N. A study of the quality of life and cost-utility of renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadban, S.J.; Ahn, C.; Axelrod, D.A.; Foster, B.J.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kher, V.; Kumar, D.; Oberbauer, R.; Pascual, J.; Pilmore, H.L.; et al. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Candidates for Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2020, 104, S11–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Merion, R.M.; Ashby, V.B.; Port, F.K.; Wolfe, R.A.; Kayler, L.K. Renal transplantation in elderly patients older than 70 years of age: Results from the scientific registry of transplant recipients. Transplantation 2007, 83, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, S.; Kessler, M.; Briançon, S.; Frimat, L. Survival of transplanted and dialysed patients in a French region with focus on outcomes in the elderly. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martinez, R.; Soliz, P.; Caixeta, R.; Ordunez, P. Reflection on modern methods: Years of life lost due to premature mortality—A versatile and comprehensive measure for monitoring non-communicable disease mortality. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junta de Andalucía. Orden de 27 de Septiembre de 2005, por la que se Crea el Sistema de Información de la Coordinación Autonómica de Trasplantes de Andalucía; BOJA no 200 de 13/10/2005; Junta de Andalucía: Andalucía Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddhu, S.; Bruns, F.J.; Saul, M.; Seddon, P.; Zeidel, M.L. A simple comorbidity scale predicts clinical outcomes and costs in dialysis patients. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto de Estadística y Cartografia de Andalucía. Available online: https://www.juntadeandalucia.es/institutodeestadisticaycartografia (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- R Core Team. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- ERA-EDTA Registry: ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2018; Amsterdam UMC, Locatie AMC, Department of Medical Informatics: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020.
- Carrero, J.J.; de Mutsert, R.; Axelsson, J.; Dekkers, O.M.; Jager, K.J.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T.; Dekker, F.W.; NECOSAD Study Group. Sex differences in the impact of diabetes on mortality in chronic dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kang, S.W.; Yang, C.W.; Kim, N.H.; Noh, H.W.; Jeon, S.J.; Lim, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Sex disparities in mortality among patients with kidney failure receiving dialysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, E.; Remontet, L.; Labeeuw, M.; Ecochard, R. Effect of age, gender, and diabetes on excess death in end-stage renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifarré i Arolas, H.; Acosta, E.; López-Casasnovas, G.; Lo, A.; Nicodemo, C.; Riffe, T.; Myrskylä, M. Years of life lost to COVID-19 in 81 countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordio, M.; Limido, A.; Postorino, M. Present and future of kidney replacement therapy in Italy: The perspective from Italian Dialysis and Transplantation Registry (IDTR). J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Trujillo, H.; González, E.; Molina, M.; Polanco, N.; Hernández, E.; Morales, E.; Gutiérrez, E.; Mori, J.R.; et al. Kidney transplantation in the extremely elderly from extremely aged deceased donors: A kidney for each age. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network: National Data—OPTN. 2021. Available online: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Rosansky, S.J.; Schell, J.; Shega, J.; Scherer, J.; Jacobs, L.; Couchoud, C.; Crews, D.; McNabney, M. Treatment decisions for older adults with advanced chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, B.R.; Sparkes, T.M.; Masters, B.M.; Thomas, B.; Demehin, M.; Bromberg, J.S.; Haririan, A. Survival benefit of renal transplantation in octogenarians. Clin. Transplant. 2020, 34, e14074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N = 11,551 | Renal Transplantation N = 3776 | No Renal Transplantation N = 7775 | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | Mean (SD) | 95% CI | Min–Max | Mean (SD) | 95% CI | ||
| Age (years) | 15–80 | 51 (13.5) | (50.6; 51.5) | 15–94 | 68.3 (12.6) | (68.0; 68.6) | <0.001 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Women N (%) | 1371 (36.3) | (34.8; 37.9) | 2922 (37.6) | (36.5; 38.7) | 0.184 | ||
| Men N (%) | 2405 (63.7) | (62.1; 65.2) | 4853 (62.4) | (61.3; 63.5) | |||
| Charlson index | 2–13 | 3.8 (1.8) | (3.8; 3.9) | 2–20 | 7.0 (2.4) | (7.0; 7.1) | <0.001 |
| Vital status | |||||||
| Alive N (%) | 3413 (90.4) | (89.4; 91.3) | 3238 (41.6) | (40.6; 42.7) | <0.001 | ||
| Dead N (%) | 363 (9.6) | (8.7; 10.6) | 4537 (58.4) | (57.3; 59.4) | |||
| Age at death * (Years) | 15–84 | 65.4 (10.2) | (64.3; 66.5) | 19–98 | 73.3 (11.1) | (73.0; 73.6) | <0.001 |
| MEN | WOMEN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Onset RRT | Total YPLL | N Patient | YPLL/ Patient | Total YPLL | N Patient | YPLL/ Patient |
| 15–29 years | 390.3 | 218 | 1.79 | 486.6 | 166 | 2.93 |
| 30–34 years | 743.2 | 191 | 3.89 | 575.7 | 94 | 6.12 |
| 35–39 years | 904.3 | 227 | 3.98 | 567.0 | 129 | 4.40 |
| 40–44 years | 1689.5 | 336 | 5.03 | 1053.9 | 196 | 5.38 |
| 45–49 years | 3274.2 | 485 | 6.75 | 1117.1 | 257 | 4.35 |
| 50–54 years | 4517.8 | 566 | 7.98 | 2039.9 | 308 | 6.62 |
| 55–59 years | 5450.6 | 698 | 7.81 | 3096.9 | 373 | 8.30 |
| 60–64 years | 6675.9 | 832 | 8.02 | 3981.9 | 450 | 8.85 |
| 65–69 years | 7762.8 | 954 | 8.14 | 4471.0 | 511 | 8.75 |
| 70–74 years | 7181.8 | 1027 | 6.99 | 4919.0 | 593 | 8.30 |
| 75–79 years | 5775.4 | 943 | 6.12 | 4694.5 | 683 | 6.87 |
| 80–84 years | 3025.3 | 619 | 4.89 | 2296.9 | 404 | 5.69 |
| 85–89 years | 567.1 | 147 | 3.86 | 495.2 | 121 | 4.09 |
| 90 years and older | 51.9 | 15 | 3.46 | 25.7 | 8 | 3.21 |
| Total | 48,010.1 | 7258 | 6.61 | 29,821.2 | 4293 | 6.95 |
| MEN | WOMEN | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dialysis | Renal Transplantation | Dialysis | Renal Transplantation | |||||||||
| Age Onset RRT | Total YPLL | N Patient | YPLL/ Patient | Total YPLL | N Patient | YPLL/ Patient | Total YPLL | N Patient | YPLL/ Patient | Total YPLL | N Patient | YPLL/ Patient |
| 15–29 years | 325.7 | 52 | 6.3 | 64.5 | 166 | 0.4 | 423.7 | 37 | 11.5 | 62.8 | 129 | 0.5 |
| 30–34 years | 696.6 | 54 | 12.9 | 46.6 | 137 | 0.3 | 470.8 | 24 | 19.6 | 104.9 | 70 | 1.5 |
| 35–39 years | 657.6 | 52 | 12.6 | 246.7 | 175 | 1.4 | 423.4 | 33 | 12.8 | 143.6 | 96 | 1.5 |
| 40–44 years | 1245.0 | 113 | 11.0 | 444.5 | 223 | 2.0 | 844.9 | 55 | 15.4 | 209.0 | 141 | 1.5 |
| 45–49 years | 2766.9 | 177 | 15.6 | 507.3 | 308 | 1.6 | 966.7 | 80 | 12.1 | 150.4 | 177 | 0.8 |
| 50–54 years | 3898.0 | 263 | 14.8 | 619.8 | 303 | 2.0 | 1644.4 | 118 | 13.9 | 395.5 | 190 | 2.1 |
| 55–59 years | 4425.1 | 360 | 12.3 | 1025.5 | 338 | 3.0 | 2734.7 | 200 | 13.7 | 362.2 | 173 | 2.1 |
| 60–64 years | 5814.7 | 519 | 11.2 | 861.2 | 313 | 2.8 | 3240.5 | 278 | 11.7 | 741.4 | 172 | 4.3 |
| 65–69 years | 6713.2 | 680 | 9.9 | 1049.6 | 274 | 3.8 | 3936.7 | 370 | 10.6 | 534.3 | 141 | 3.8 |
| 70–74 years | 6799.1 | 888 | 7.7 | 382.7 | 139 | 2.8 | 4632.3 | 523 | 8.9 | 286.7 | 70 | 4.1 |
| 75–79 years | 5743.2 | 916 | 6.3 | 32.2 | 27 | 1.2 | 4659.9 | 671 | 6.9 | 34.6 | 12 | 2.9 |
| 80–84 years | 3025.3 | 617 | 4.9 | 0.0 | 2 | 0.0 | 2296.9 | 404 | 5.7 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 85–89 years | 567.1 | 147 | 3.9 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 495.2 | 121 | 4.1 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 90 years and older | 51.9 | 15 | 3.5 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 25.7 | 8 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 42,794.0 | 4853 | 8.8 | 5280.6 | 2405 | 2.2 | 26,795.7 | 2922 | 9.2 | 3025.5 | 1371 | 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Terol, J.M.; Rocha, J.L.; Castro-de la Nuez, P.; García-Cabrera, E.; Vilches-Arenas, Á. Years of Potential Life Lost on Renal Replacement Therapy: Retrospective Study Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010051
Muñoz-Terol JM, Rocha JL, Castro-de la Nuez P, García-Cabrera E, Vilches-Arenas Á. Years of Potential Life Lost on Renal Replacement Therapy: Retrospective Study Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Terol, José Manuel, José L. Rocha, Pablo Castro-de la Nuez, Emilio García-Cabrera, and Ángel Vilches-Arenas. 2023. "Years of Potential Life Lost on Renal Replacement Therapy: Retrospective Study Cohort" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010051
APA StyleMuñoz-Terol, J. M., Rocha, J. L., Castro-de la Nuez, P., García-Cabrera, E., & Vilches-Arenas, Á. (2023). Years of Potential Life Lost on Renal Replacement Therapy: Retrospective Study Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010051






