Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics Based on the Rome III and IV Criteria of Japanese Patients with Functional Dyspepsia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Assessment
2.4. Questionnaires (Symptoms, QOL, Anxiety, and Depression)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
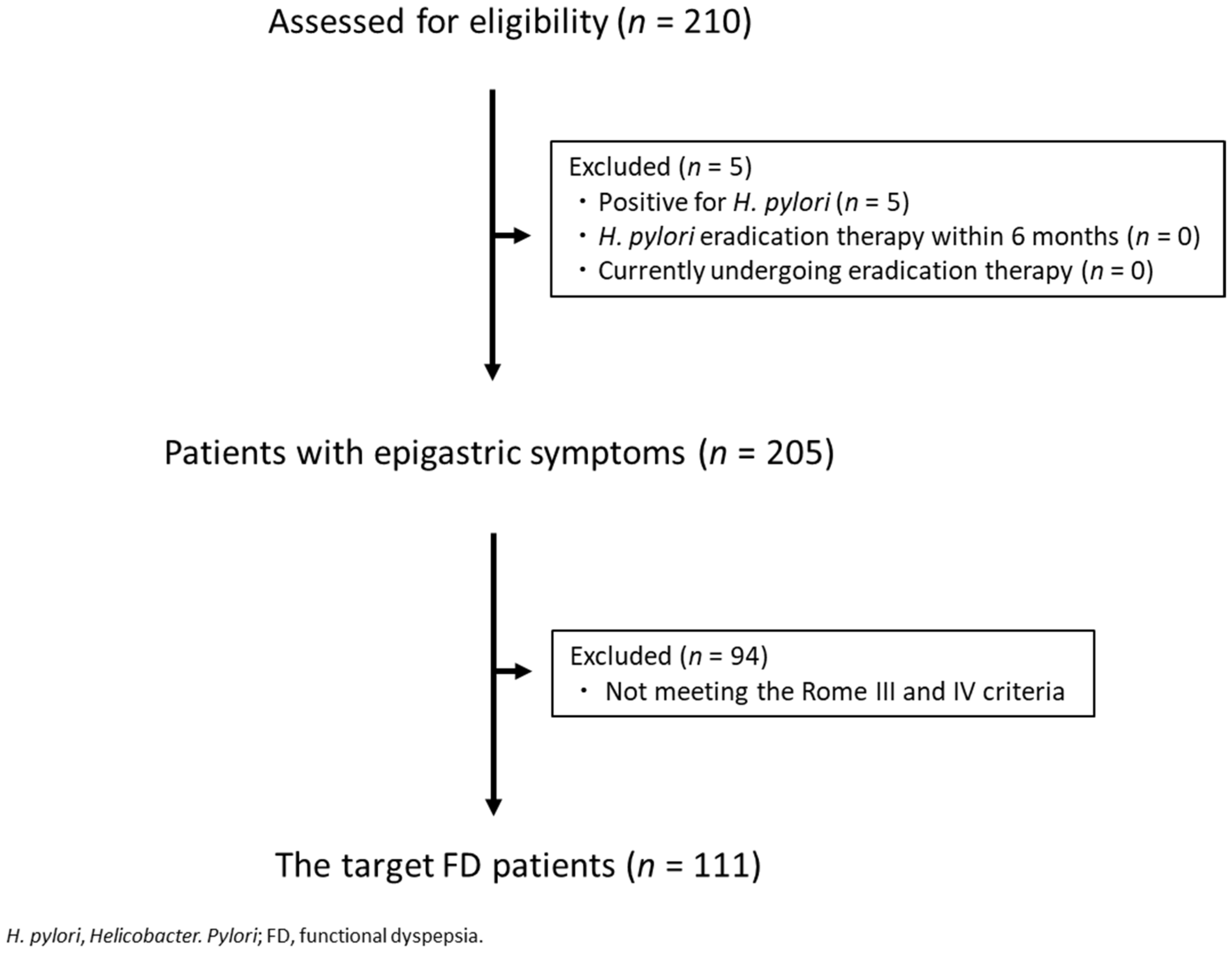
3.1. Enrolment and Baseline Characteristics of the Patients
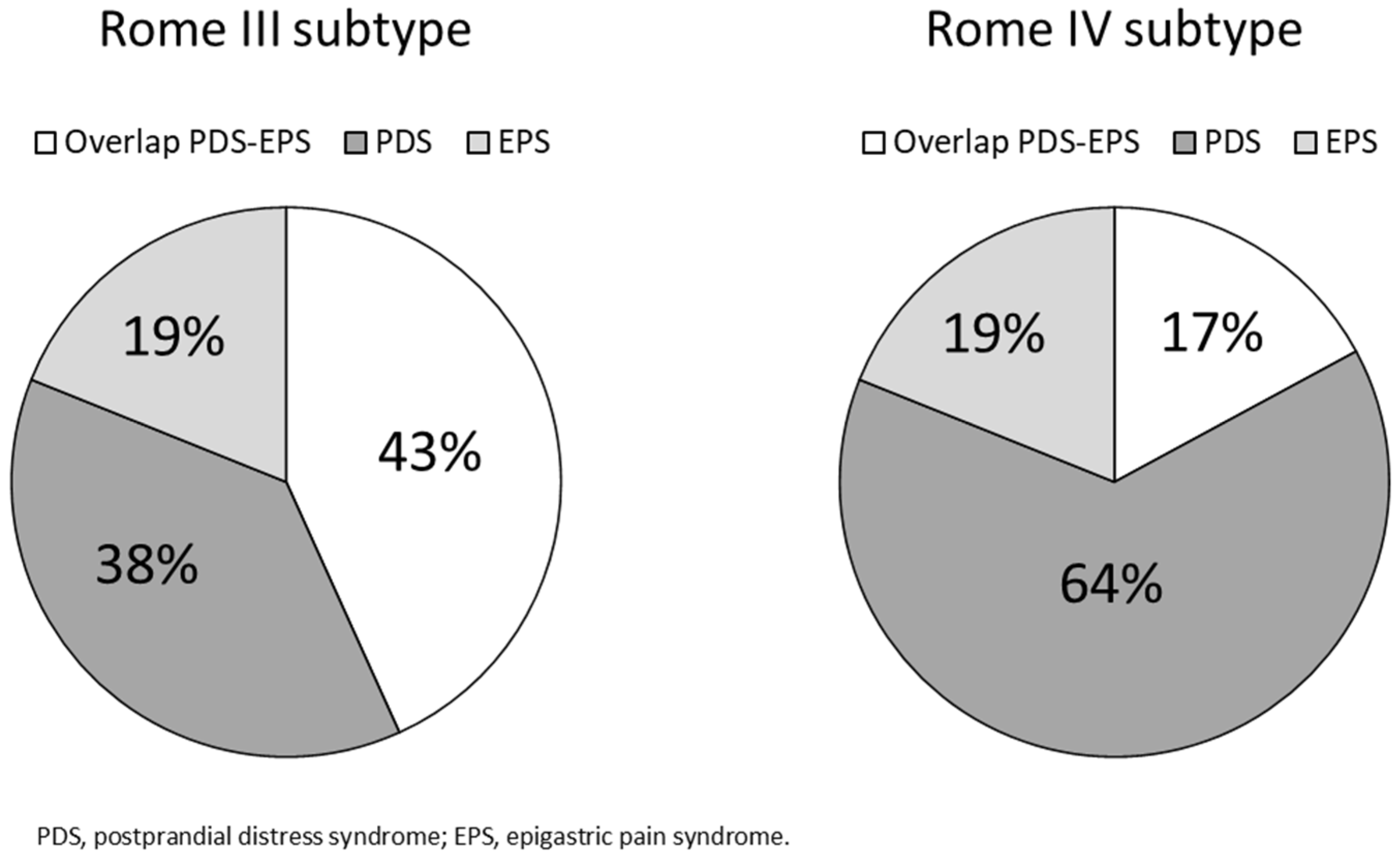
3.2. FD Subgroups under the Rome III Criteria vs. the Rome IV Criteria
3.3. Patient Background Factors for FD under the Rome III Criteria vs. the Rome IV Criteria
3.4. Characteristics of PDS to PDS vs. Overlap to PDS
3.5. QOL, Psychological Score, Gastrointestinal Symptoms (PDS to PDS vs. Overlap to PDS)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drossman, D.A. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: History, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; Miwa, H. New Approaches to Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2018, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talley, N.J. Non-ulcer dyspepsia: Myths and realities. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 5 (Suppl. S1), 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome II process. Gut 1999, 45 (Suppl. S2), II1–II5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tack, J.; Talley, N.J.; Camilleri, M.; Holtmann, G.; Hu, P.; Malagelada, J.R.; Stanghellini, V. Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmulson, M.J.; Drossman, D.A. What Is New in Rome IV. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, N.; Haruma, K.; Hata, J.; Imamura, H.; Kamada, T.; Kusunoki, H.; Sanuki, E.; Tsumaru, S.; Futagami, Y.; Sadamoto, Y.; et al. Is the Rome III classification applicable? Gastroenterology 2010, 45, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.H.; Huh, K.C.; Jung, H.K.; Yoon, Y.H.; Choi, K.D.; Song, K.H.; Keum, B.; Kim, J.W. Prevalence of uninvestigated dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux disease in Korea: A population-based study using the Rome III criteria. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Holvoet, L.; Tack, J. Rome III functional dyspepsia subdivision in PDS and EPS: Recognizing postprandial symptoms reduces overlap. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheel, H.; Carbone, F.; Valvekens, L.; Simren, M.; Tornblom, H.; Vanuytsel, T.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Tack, J. Pathophysiological Abnormalities in Functional Dyspepsia Subgroups According to the Rome III Criteria. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, F.; Vanuytsel, T.; Tack, J. Analysis of Postprandial Symptom Patterns in Subgroups of Patients with Rome III or Rome IV Functional Dyspepsia. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Houte, K.; Carbone, F.; Goelen, N.; Schol, J.; Masuy, I.; Arts, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Staessen, D.; Vergauwe, P.; Van Roey, G.; et al. Effects of Rome IV Definitions of Functional Dyspepsia Subgroups in Secondary Care. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperber, A.D.; Freud, T.; Aziz, I.; Palsson, O.S.; Drossman, D.A.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Fang, X.; Fukudo, S.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Kellow, J.; et al. Greater Overlap of Rome IV Disorders of Gut-Brain Interactions Leads to Increased Disease Severity and Poorer Quality of Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, S1542–S3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wulffen, M.; Talley, N.J.; Hammer, J.; McMaster, J.; Rich, G.; Shah, A.; Koloski, N.; Kendall, B.J.; Jones, M.; Holtmann, G. Overlap of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia in the Clinical Setting: Prevalence and Risk Factors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shiba, M.; Kohata, Y.; Yamagami, H.; Tanigawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Tominaga, K.; Arakawa, T. Prevalence of overlaps between GERD, FD and IBS and impact on health-related quality of life. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bortoli, N.; Tolone, S.; Frazzoni, M.; Martinucci, I.; Sgherri, G.; Albano, E.; Ceccarelli, L.; Stasi, C.; Bellini, M.; Savarino, V.; et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: Common overlapping gastrointestinal disorders. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedlund, J.; Sjödin, I.; Dotevall, G. GSRS—A clinical rating scale for gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and peptic ulcer disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1988, 33, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, Y.; Okubo, T.; Ohde, S.; Jacobs, J.; Takahashi, O.; Omata, F.; Yanai, H.; Hinohara, S.; Fukui, T. Assessing items on the SF-8 Japanese version for health-related quality of life: A psychometric analysis based on the nominal categories model of item response theory. Value Health 2009, 12, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.E. STAI Manual; Consulting Psychologist Press: California, CA, USA, 1970; pp. 23–49. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, T.; Tanno, S.; Ohhira, M.; Tanno, S. Prevalence of functional dyspepsia in an outpatient clinic with primary care physicians in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanheel, H.; Tack, J. Therapeutic options for functional dyspepsia. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsueda, K.; Hongo, M.; Tack, J.; Saito, Y.; Kato, H. A placebo-controlled trial of acotiamide for meal-related symptoms of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2012, 61, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, K.; Sakata, Y.; Kusunoki, H.; Odaka, T.; Sakurai, K.; Kawamura, O.; Nagahara, A.; Takeuchi, T.; Fujikawa, Y.; Oshima, T.; et al. Rikkunshito simultaneously improves dyspepsia correlated with anxiety in patients with functional dyspepsia: A randomized clinical trial (the DREAM study). Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Huang, J.Q.; Zheng, G.F.; Xia, H.H.; Wong, W.M.; Liu, X.G.; Karlberg, J.; Wong, B.C. Effects of proton-pump inhibitors on functional dyspepsia: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.L.; Peng, S.; Tao, J.; Wang, A.J.; Lin, J.K.; Hu, P.J.; Chen, M.H. Prevalence and symptom pattern of pathologic esophageal acid reflux in patients with functional dyspepsia based on the Rome III criteria. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2626–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Liou, J.M.; Yang, T.H.; Hsu, W.L.; Lin, H.J.; Wu, H.T.; Lin, J.T.; Wang, H.P.; Wu, M.S. Proton pump inhibitor versus prokinetic therapy in patients with functional dyspepsia: Is therapeutic response predicted by Rome III subgroups? J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kusunoki, H.; Kamiya, T.; Futagami, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nishizawa, T.; Iwasaki, E.; Matsuzaki, J.; Takahashi, S.; Sakamoto, C.; et al. Effect of lansoprazole on the epigastric symptoms of functional dyspepsia (ELF study): A multicentre, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2013, 1, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miwa, H.; Kusano, M.; Arisawa, T.; Oshima, T.; Kato, M.; Joh, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tominaga, K.; Nakada, K.; Nagahara, A.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for functional dyspepsia. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| FD | Rome III | Rome IV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlap PDS-EPS | PDS | EPS | Overlap PDS-EPS | PDS | EPS | ||
| n | 111 | 48 | 42 | 21 | 19 | 71 | 21 |
| Age (y) | 54.3 ± 14.9 | 51.8 ± 15.5 | 57.3 ± 12.4 | 53.8 ± 16.9 | 55.5 ± 13.1 | 54.1 ± 14.7 | 53.8 ± 16.9 |
| Gender (% female) | 68.5 | 70.8 | 69 | 61.9 | 52.6 | 74.6 | 61.9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.8 ± 3.5 | 22.2 ± 3.6 | 21.4 ± 3.7 | 21.9 ± 2.6 | 22.7 ± 4.1 | 21.6 ± 3.5 | 21.9 ± 2.6 |
| Smoking | 23.4% | 25% | 16.7% | 33.3% | 31.6% | 18.3% | 33.3% |
| Drinking | 28.8% | 27.1% | 19% | 52.4% | 26.3% | 22.5% | 52.4% |
| After eradication of Helicobacter pylori | 22.5% | 22.9% | 14.3% | 33.3% | 26.3% | 18.3% | 33.3% |
| Postprandial fullness | 54.1% | 72.9% | 59.5% | 0% | 84.2% | 62% | 0% |
| Early satiation | 46.8% | 43.8% | 73.8% | 0% | 47.4% | 60.6% | 0% |
| Epigastric pain or burning | 61.3% | 100% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 40.8% | 100% |
| Postprandial epigastric pain or burning | 27% | 60.4% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 40.8% | 0% |
| Chest pain | 60.4% | 64.6% | 40.5% | 66.7% | 74% | 47.9% | 66.7% |
| Heartburn | 51.4% | 64.6% | 40.5% | 42.9% | 74% | 47.9% | 42.9% |
| Characteristics and Symptoms | Rome III to Rome IV | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDS to PDS | Overlap to PDS | ||
| Patients (n) | 42 | 29 | |
| Age (y) | 57.3 ± 12.4 | 49.3 ± 16.5 | 0.050 |
| Gender (% female) | 69 | 82.8 | 0.198 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 21.4 ± 3.7 | 21.8 ± 3.2 | 0.717 |
| Smoking | 16.7% | 20.7% | 0.675 |
| Drinking | 19% | 27.6% | 0.405 |
| After eradication of Helicobacter pylori | 14.3% | 24.1% | 0.299 |
| Postprandial fullness | 59.5% | 65.5% | 0.617 |
| Early satiation | 73.8% | 41.4% | 0.007 |
| Epigastric pain or burning | 0% | 100% | |
| Postprandial epigastric pain or burning | 0% | 100% | |
| Chest pain | 40.5% | 62.1% | 0.236 |
| Heartburn | 40.5% | 58.6% | 0.137 |
| SF-8 | PDS to PDS | Overlap to PDS | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 42 | 29 | |
| PF | 45.6 ± 9.4 | 42.8 ± 10.1 | 0.157 |
| RP | 44.0 ± 9.5 | 42.6 ± 10.2 | 0.484 |
| BP | 46.3 ± 8.8 | 41.5 ± 9.3 | 0.025 |
| GH | 40.2 ± 7.1 | 39.1 ± 8.2 | 0.358 |
| VT | 42.1 ± 9.0 | 43.1 ± 7.4 | 0.712 |
| SF | 41.4 ± 11.2 | 39.2 ± 12.1 | 0.469 |
| RE | 44.1 ± 9.2 | 42.3 ± 11.7 | 0.641 |
| MH | 42.7 ± 7.2 | 42.8 ± 8.2 | 0.808 |
| PCS | 43.9 ± 8.0 | 40.8 ± 9.7 | 0.124 |
| MCS | 41.6 ± 9.0 | 42.0 ± 8.5 | 0.949 |
| GSRS | PDS to PDS | Overlap to PDS | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 42 | 29 | |
| Reflux | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 3.6 ± 1.6 | 0.025 |
| Abdominal pain | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 3.7 ± 1.4 | 0.024 |
| Dyspepsia | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 2.8 ± 1.3 | 0.449 |
| Diarrhea | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 2.8 ± 1.8 | 0.138 |
| Constipation | 3.1 ± 1.4 | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 0.245 |
| Total score | 2.8 ± 0.90 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 0.259 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aono, S.; Tomita, T.; Tozawa, K.; Morishita, D.; Nakai, K.; Okugawa, T.; Fukushima, M.; Oshima, T.; Fukui, H.; Miwa, H. Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics Based on the Rome III and IV Criteria of Japanese Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092342
Aono S, Tomita T, Tozawa K, Morishita D, Nakai K, Okugawa T, Fukushima M, Oshima T, Fukui H, Miwa H. Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics Based on the Rome III and IV Criteria of Japanese Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(9):2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092342
Chicago/Turabian StyleAono, Sota, Toshihiko Tomita, Katsuyuki Tozawa, Daisuke Morishita, Keisuke Nakai, Takuya Okugawa, Masashi Fukushima, Tadayuki Oshima, Hirokazu Fukui, and Hiroto Miwa. 2022. "Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics Based on the Rome III and IV Criteria of Japanese Patients with Functional Dyspepsia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 9: 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092342
APA StyleAono, S., Tomita, T., Tozawa, K., Morishita, D., Nakai, K., Okugawa, T., Fukushima, M., Oshima, T., Fukui, H., & Miwa, H. (2022). Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics Based on the Rome III and IV Criteria of Japanese Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(9), 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092342








