Inhaled Corticosteroids, Vitamin K Antagonists and Amlodipine Were Associated with an Increased Risk of Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Patients with Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case–Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient and Methods
2.2. Study Cohort and Controls
2.3. Cases
2.4. Data Collection and Statistical Analyses
- (1)
- A confounding factor must be an extraneous risk factor for the disease (i.e., PJI).
- (2)
- A confounding factor must be associated with the exposure (i.e., ICSs and cardiovascular drug use) under study in the source population.
- (3)
- A confounding factor must not be affected by the exposure or the disease. In particular, it cannot be an intermediate (mediator) step in the causal path between exposure and the disease.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic Joint Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gbejuade, H.O.; Lovering, A.M.; Webb, J.C. The Role of Microbial Biofilms in Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Review. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundtoft, P.H.; Pedersen, A.B.; Varnum, C.; Overgaard, S. Increased Mortality After Prosthetic Joint Infection in Primary THA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siljander, M.P.; Sobh, A.H.; Baker, K.C.; Baker, E.A.; Kaplan, L.M. Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in the Setting of Periprosthetic Joint Infection—Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmistowski, B.; Karam, J.A.; Durinka, J.B.; Casper, D.S.; Parvizi, J. Periprosthetic Joint Infection Increases the Risk of One-Year Mortality. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Whitehouse, M.R.; Blom, A.W.; Beswick, A.D.; INFORM Team. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, E.; Wiggins, A.T.; Rayens, M.K.; Morris, B.J.; Mannino, D.; Hoellein, A.; Donegan, R.P.; Crofford, L.J. Moderating Effects of Immunosuppressive Medications and Risk Factors for Post-Operative Joint Infection Following Total Joint Arthroplasty in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Osteoarthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 46, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miravitlles, M.; Vogelmeier, C.; Roche, N.; Halpin, D.; Cardoso, J.; Chuchalin, A.G.; Kankaanranta, H.; Sandström, T.; Śliwiński, P.; Zatloukal, J.; et al. A Review of National Guidelines for Management of COPD in Europe. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raherison, C.; Girodet, P.-O. Epidemiology of COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2009, 18, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Ghanem, E.; Joshi, A.; Sharkey, P.F.; Hozack, W.J.; Rothman, R.H. Does “Excessive” Anticoagulation Predispose to Periprosthetic Infection? J. Arthroplast. 2007, 22, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, K.; Asok Kumar, K.; Dutta, N.K. Potential Role of the Cardiovascular Non-Antibiotic (Helper Compound) Amlodipine in the Treatment of Microbial Infections: Scope and Hope for the Future. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z. Evaluation of Amlodipine Inhibition and Antimicrobial Effects. IJPC 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassaji, M. The Effect of Statins Use on the Risk and Outcome of Acute Bacterial Infections in Adult Patients. JCDR 2015, 9, OC09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zeng, D. Sample Size/Power Calculation for Case-Cohort Studies. Biometrics 2004, 60, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, M.M.; Deijkers, R.L.; Bazuin, R.; Elzakker, E.M.; Pijls, B.G. Proton-Pump Inhibitors Are Associated with Increased Risk of Prosthetic Joint Infection in Patients with Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case-Cohort Study. Acta Orthop. 2021, 92, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.S. A New Comparison of Nested Case–Control and Case–Cohort Designs and Methods. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dowsey, M.M.; Choong, P.F.M. Obesity Is a Major Risk Factor for Prosthetic Infection after Primary Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douketis, J.D.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Spencer, F.A.; Mayr, M.; Jaffer, A.K.; Eckman, M.H.; Dunn, A.S.; Kunz, R. Perioperative Management of Antithrombotic Therapy. Chest 2012, 141, e326S–e350S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prentice, R.L. A Case-Cohort Design for Epidemiologic Cohort Studies and Disease Prevention Trials. Biometrika 1986, 73, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Current Concepts and Outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Zmistowski, B.; Berbari, E.F.; Bauer, T.W.; Springer, B.D.; Della Valle, C.J.; Garvin, K.L.; Mont, M.A.; Wongworawat, M.D.; Zalavras, C.G. New Definition for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: From the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2992–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Steenbergen, L.N.; Denissen, G.A.W.; Spooren, A.; van Rooden, S.M.; van Oosterhout, F.J.; Morrenhof, J.W.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H. More than 95% Completeness of Reported Procedures in the Population-Based Dutch Arthroplasty Register: External Validation of 311,890 Procedures. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, W.E.; Ichikawa, L.; Rosner, D.; Izumi, S. Analysis of Case-Cohort Designs. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1999, 52, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, K.; Greenland, S.; Lash, T. Modern Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Svendsson, J.E.; Johnsen, S.P.; Riis, A.; Overgaard, S. Risk Factors for Revision Due to Infection after Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Population-Based Study of 80,756 Primary Procedures in the Danish Hip Arthroplasty Registry. Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eka, A.; Chen, A.F. Patient-Related Medical Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip and Knee. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derendorf, H.; Nave, R.; Drollmann, A.; Cerasoli, F.; Wurst, W. Relevance of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Inhaled Corticosteroids to Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.D.; Zakeri, R.; Quint, J.K. Defining the Relationship between COPD and CVD: What Are the Implications for Clinical Practice? Adv. Respir. Dis. 2018, 12, 175346581775052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunkler, D.; Ploner, M.; Schemper, M.; Heinze, G. Weighted Cox Regression Using the R Package Coxphw. J. Stat. Soft. 2018, 84, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gundtoft, P.H.; Pedersen, A.B.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Møller, J.K.; Overgaard, S. One-Year Incidence of Prosthetic Joint Infection in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Cohort Study with Linkage of the Danish Hip Arthroplasty Register and Danish Microbiology Databases. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, V.K.; Weintraub, S.; Klock, J.; Stachel, A.; Phillips, M.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Iorio, R.; Bosco, J.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Vigdorchik, J.M.; et al. 2019 Frank Stinchfield Award: A Comparison of Prosthetic Joint Infection Rates between Direct Anterior and Non-Anterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Single Institution Experience. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101-B, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipworth, B.J. Systemic Adverse Effects of Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinden, N.J.; Stockley, R.A. Systemic Inflammation and Comorbidity in COPD: A Result of “overspill” of Inflammatory Mediators from the Lungs? Review of the Evidence. Thorax 2010, 65, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Refaai, M.A.; Blumberg, N. Transfusion immunomodulation from a clinical perspective: An update. Expert Rev Hematol. 2013, 6, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leijtens, B.; Kremers van de Hei, K.; Jansen, J.; Koëter, S. High Complication Rate after Total Knee and Hip Replacement Due to Perioperative Bridging of Anticoagulant Therapy Based on the 2012 ACCP Guideline. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2014, 134, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.A.; Schulz, K.F. Bias and Causal Associations in Observational Research. Lancet 2002, 359, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
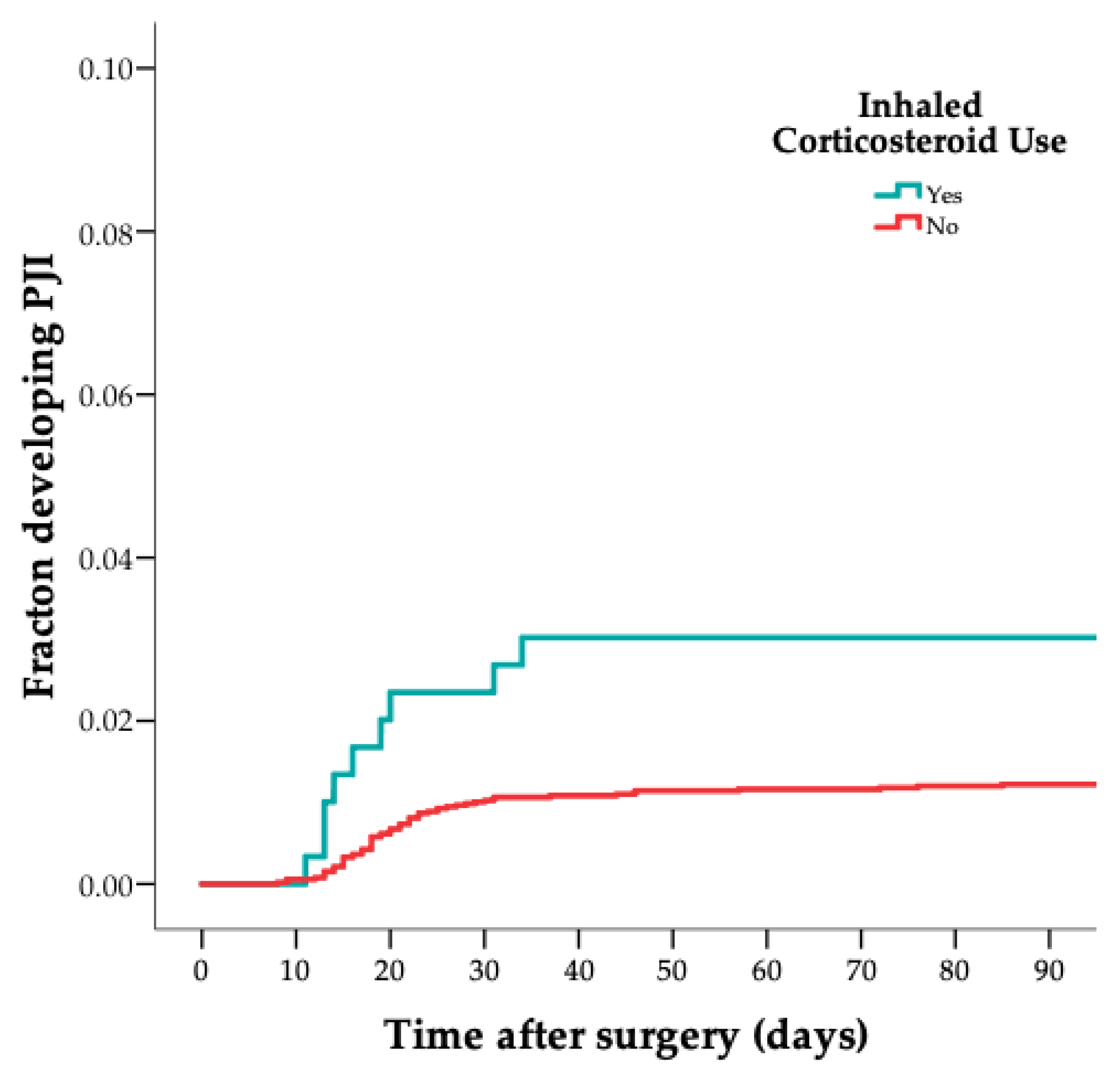
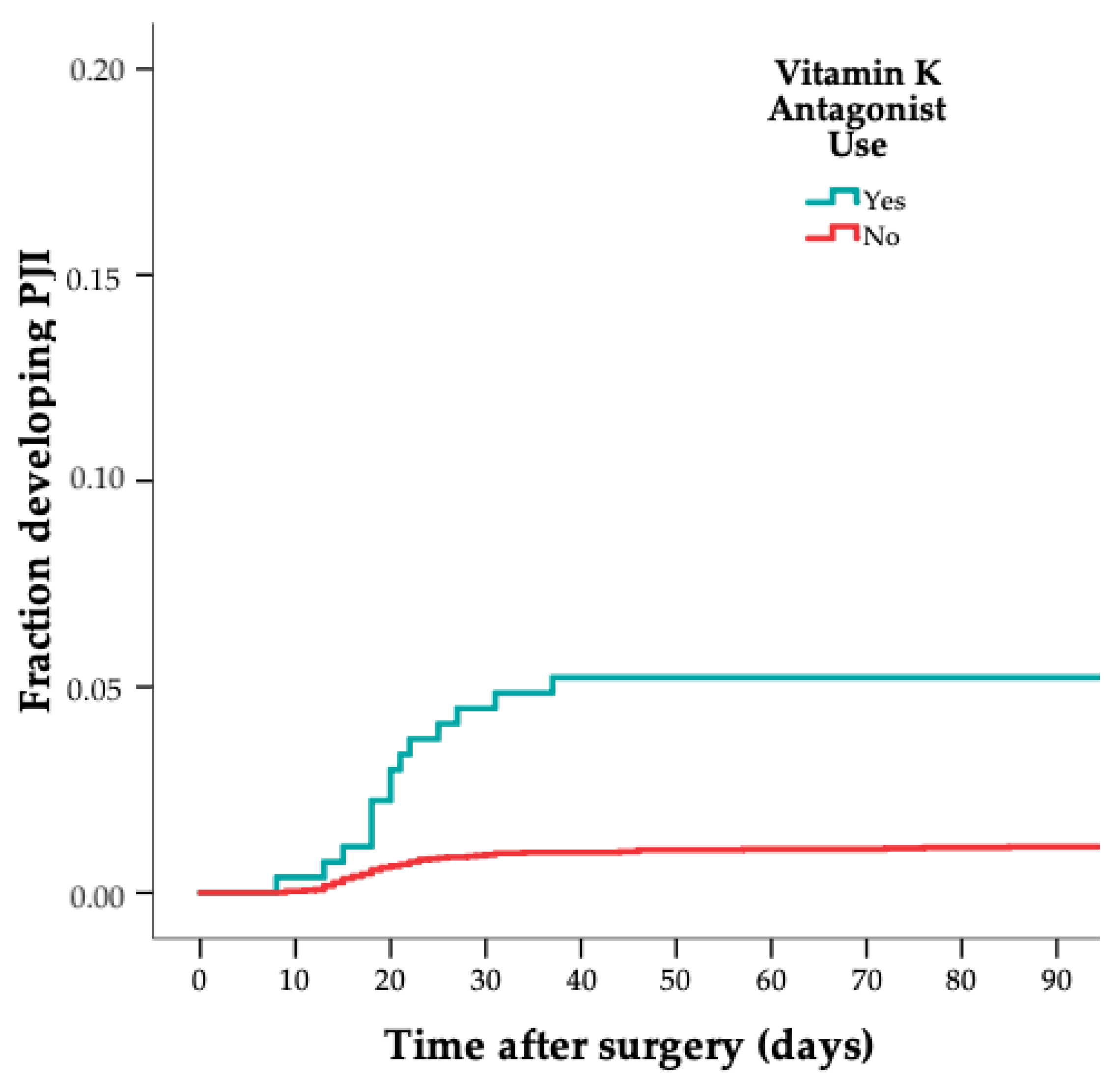

| Variable | Cases (n = 75) | Controls (n = 302) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, mean years ± SD | 68.9 ± 10.3 | 67.7 ± 10.8 |
| Sex n (%) | ||
| Female | 42 (56) | 188 (62) |
| Male | 33 (44) | 114 (38) |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 30 (5.4) | 27 (4.2) |
| Obesity (BMI > 30), yes (%) ASA score n (%) | 28 (38) | 57 (19) |
| ASA 1 | 7 (9.3) | 85 (28) |
| ASA 2 | 47 (63) | 175 (58) |
| ASA 3 | 18 (24) | 42 (14) |
| ASA 4 | 3 (4.0) | 0 (0) |
| Smoking status, yes n (%) | 19 (25) | 54 (18) |
| Inhalation corticosteroid use n (%) | 10 (13) | 16 (5) |
| COPD | 3 | 5 |
| Asthma | 4 | 7 |
| Other | 3 | 4 |
| Anticoagulant use n (%) | 35 (47) | 76 (25) |
| VKA | 16 (21) | 14 (5) |
| PAI | 19 (25) | 58 (19) |
| DOAC | 0 (0) | 4 (1) |
| Amlodipine use n (%) | 11 (15) | 17 (6) |
| Nifedipine use n (%) | 1 (1) | 4 (1) |
| Statin use n (%) | 25 (33) | 75 (25) |
| Cardiovascular disease status, yes n (%) | 28 (37) | 69 (23) |
| Pulmonary disease status, yes n (%) | 8 (11) | 24 (8) |
| Risk Factor | HR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 1.0 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Sex (male) | 0.8 | 0.5–1.1 |
| ASA score 3 and 4 | 2.4 | 1.4–3.9 |
| Smoking status, yes | 1.6 | 0.9–2.6 |
| Pulmonary disease status, yes | 1.4 | 0.7–2.9 |
| Cardiovascular disease status, yes | 1.9 | 1.2–3.1 |
| Inhalation corticosteroid use | 2.6 | 1.1–5.9 |
| VKA | 5.3 | 2.5–11 |
| PAI | 1.5 | 0.8–2.6 |
| DOAC | NA | NA |
| Amlodipine | 3.1 | 1.4–6.9 |
| Nifedipine | 1.0 | 0.2–7.2 |
| Statin | 1.5 | 0.9–2.6 |
| ICS | VKA | PAI | Amlodipine | Statin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | HR | 95% CI | |
| Crude * | 2.6 | 1.1–5.9 | 5.3 | 2.5–11 | 1.5 | 0.8–2.6 | 3.1 | 1.4–6.9 | 1.5 | 0.9–2.6 |
| Model 1 | 2.7 | 1.2–6.1 | 5.2 | 2.4–11 | 1.4 | 0.8–2.6 | 3.1 | 1.4–6.8 | 1.5 | 0.9–2.6 |
| Model 2 | 2.6 | 1.1–6.2 | 5.2 | 2.3–12 | 1.4 | 0.7–2.7 | 3.1 | 1.3–7.1 | 1.5 | 0.8–2.7 |
| Model 3 | 2.5 | 1.0–6.1 | 5.7 | 2.4–13 | 1.4 | 0.7–2.8 | 3.4 | 1.4–8.2 | 1.5 | 0.8–2.8 |
| Model 4 | - | 4.8 | 1.9–12 | 1.1 | 0.5–2.2 | 3.1 | 1.3–7.3 | 1.3 | 0.7–2.4 | |
| Model 5 | 4.5 | 0.7–30 | - | - | - | - | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruin, M.M.; Deijkers, R.L.M.; Bus, M.P.A.; van Elzakker, E.P.M.; Bazuin, R.; Nelissen, R.G.; Pijls, B.G. Inhaled Corticosteroids, Vitamin K Antagonists and Amlodipine Were Associated with an Increased Risk of Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Patients with Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case–Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071842
Bruin MM, Deijkers RLM, Bus MPA, van Elzakker EPM, Bazuin R, Nelissen RG, Pijls BG. Inhaled Corticosteroids, Vitamin K Antagonists and Amlodipine Were Associated with an Increased Risk of Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Patients with Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case–Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(7):1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071842
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruin, Maarten M., Ruud L. M. Deijkers, Michaël P. A. Bus, Erika P. M. van Elzakker, Roos Bazuin, Rob G. Nelissen, and Bart G. Pijls. 2022. "Inhaled Corticosteroids, Vitamin K Antagonists and Amlodipine Were Associated with an Increased Risk of Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Patients with Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case–Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 7: 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071842
APA StyleBruin, M. M., Deijkers, R. L. M., Bus, M. P. A., van Elzakker, E. P. M., Bazuin, R., Nelissen, R. G., & Pijls, B. G. (2022). Inhaled Corticosteroids, Vitamin K Antagonists and Amlodipine Were Associated with an Increased Risk of Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Patients with Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case–Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(7), 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071842






