Metabolic Syndrome, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
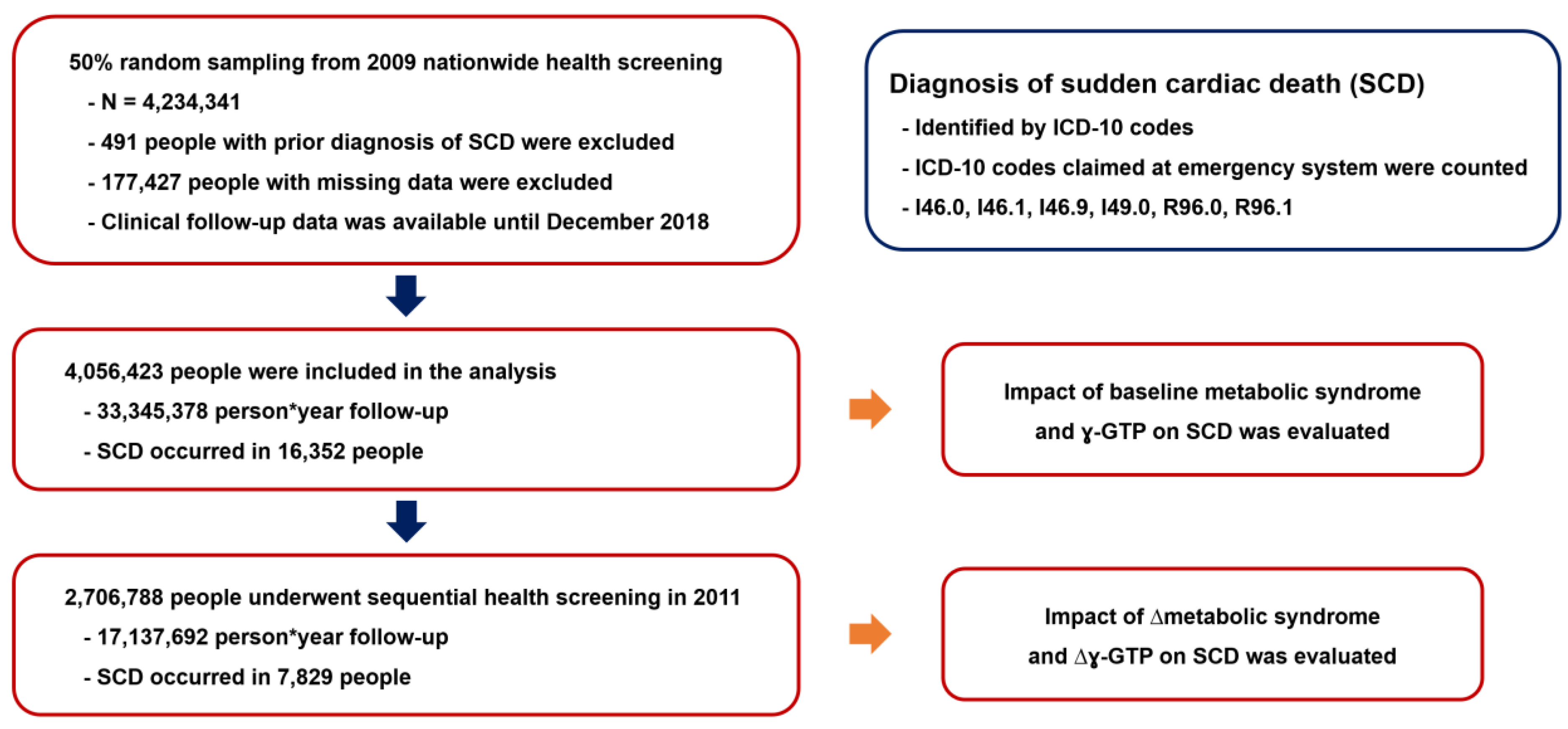
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Primary Outcome Endpoint
2.3. Metabolic Syndrome
2.4. Definitions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
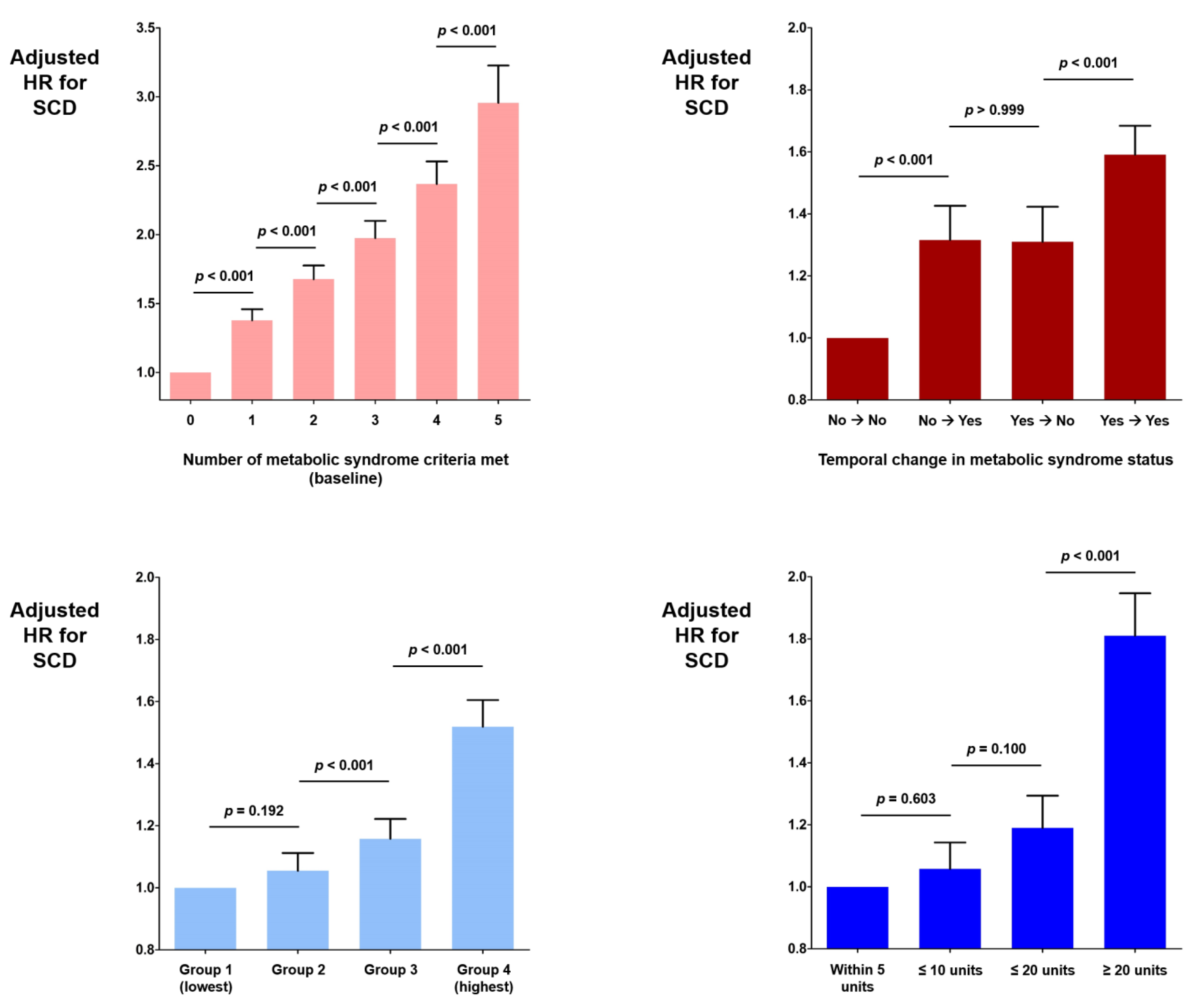
3.2. Metabolic Syndrome
3.3. ɣ-GTP
3.4. Temporal Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolic Syndrome
4.2. Gamma-GTP
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Myat, A.; Song, K.J.; Rea, T. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Current concepts. Lancet 2018, 391, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.J.; Carr, B.; Sasson, C.; Bobrow, B.J.; Callaway, C.W.; Neumar, R.W.; Ferrer, J.M.E.; Garvey, J.L.; Ornato, J.P.; Gonzales, L.; et al. Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation Systems of Care: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e645–e660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.M.; Pinto, D.S. Invasive Management of Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, e006071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, M.E.H.; Perkins, G.D.; Cariou, A. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Prehospital management. Lancet 2018, 391, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassager, C.; Nagao, K.; Hildick-Smith, D. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: In-hospital intervention strategies. Lancet 2018, 391, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, L.L.; Rea, T.D.; Murray, J.A.; Welles, B.; Fahrenbruch, C.E.; Olsufka, M.; Eisenberg, M.S.; Copass, M.K. Public access defibrillation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A community-based study. Circulation 2004, 109, 1859–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Fahrenbruch, C.E.; Cobb, L.A.; Eisenberg, M.S. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in men and women. Circulation 2001, 104, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Oh, S.K.; Choi, H.Y.; Choi, J.I. Inherited arrhythmia syndrome predisposing to sudden cardiac death. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurl, S.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Jae, S.Y.; Makikallio, T.H.; Zaccardi, F.; Kauhanen, J.; Ronkainen, K.; Laukkanen, J.A. Metabolic syndrome and the risk of sudden cardiac death in middle-aged men. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 203, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, P.L.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Friedman, D.J.; Mulder, H.; Kucharska-Newton, A.; Rosamond, W.R.; Lopes, R.D.; Gersh, B.J.; Mark, D.B.; Curtis, L.H.; et al. The Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, M.; Gonzales, C.; Baldi, S.; Posadas, R.; Williams, K.; Haffner, S.M.; Stern, M.P.; Ferrannini, E. Liver enzymes, the metabolic syndrome, and incident diabetes: The Mexico City diabetes study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, I.J.; Wannamethee, S.G.; Shaper, A.G. Prospective study of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Evans, J.C.; Robins, S.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Albano, I.; Fox, C.S.; Wang, T.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Vasan, R.S. Gamma glutamyl transferase and metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and mortality risk: The Framingham Heart Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, R.; Kohara, K.; Tabara, Y.; Miki, T.; Otsuka, N. Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase levels are associated with metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling individuals. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2009, 16, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantala, A.O.; Lilja, M.; Kauma, H.; Savolainen, M.J.; Reunanen, A.; Kesaniemi, Y.A. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 248, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.D.; Choi, J.I.; Choi, Y.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Boo, K.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, K.N.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Non-genetic risk factors for atrial fibrillation are equally important in both young and old age: A nationwide population-based study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.D.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, Y.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Roh, S.Y.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.I.; Kim, Y.H. Different Influence of Blood Pressure on New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Hypertension 2021, 77, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.D.; Choi, J.I.; Choi, Y.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Shim, J.; Kim, Y.H. Premature ventricular contraction is associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population-based study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, S.Y.; Choi, J.I.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, E.Y.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, K.N.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Incidence and etiology of sudden cardiac arrest in Koreans: A cohort from the national health insurance service database. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.D.; Choi, J.I.; Yung Boo, K.; Kim, D.Y.; Oh, S.K.; Lee, K.N.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Impact of the Duration and Degree of Hypertension and Body Weight on New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Hypertension 2019, 74, e45–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, S.-Y.; Choi, J.-I.; Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Do Han, K.; Kim, Y.-H. The 10-year trend of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: A Korean nationwide population-based study. Korean Circ. J. 2021, 51, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Sterz, F.; Darby, J.M.; Padosch, S.A.; Kern, K.B.; Böttiger, B.W.; Polderman, K.H.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Holzer, M.; Bernard, S.A.; et al. Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- de Vreede-Swagemakers, J.J.; Gorgels, A.P.; Dubois-Arbouw, W.I.; van Ree, J.W.; Daemen, M.J.; Houben, L.G.; Wellens, H.J. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in the 1990’s: A population-based study in the Maastricht area on incidence, characteristics and survival. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 30, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.; Taegtmeyer, H. Epidemic obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Circulation 2003, 108, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empana, J.P.; Duciemetiere, P.; Balkau, B.; Jouven, X. Contribution of the metabolic syndrome to sudden death risk in asymptomatic men: The Paris Prospective Study I. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, R.; Tabara, Y.; Kohara, K.; Miki, T.; Kusunoki, T.; Takayama, S.; Abe, M.; Katoh, T.; Ohtsuka, N. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and gamma-glutamyl transferase levels are synergistically associated with metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling persons. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2010, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Min, H.K.; Son, S.M.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, Y.K. The association of serum gamma glutamyltransferase with components of the metabolic syndrome in the Korean adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, N.; Saitoh, S.; Shimamoto, K. Clinical diagnosis of metabolic syndrome 1. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 1283–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory pathways and insulin action. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27 (Suppl 3), S53–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicchi, A.; Minotti, G.; Tonarelli, P.; Tongiani, R.; De Cesare, D.; Mezzetti, A.; Dominici, S.; Comporti, M.; Pompella, A. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-dependent iron reduction and LDL oxidation--a potential mechanism in atherosclerosis. J. Investig. Med. 1999, 47, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.D.; Choi, J.I.; Boo, K.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Oh, S.K.; Lee, K.N.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. The impact of body weight and diabetes on new-onset atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population based study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.D.; Choi, J.I.; Boo, K.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, K.N.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Frequent drinking is a more important risk factor for new-onset atrial fibrillation than binge drinking: A nationwide population-based study. Europace 2020, 22, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SCD | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||
| 4,040,071 | 16,352 | ||
| Male sex | 2,221,898 (55.0%) | 11,633 (71.1%) | <0.001 |
| Age (year) | 47.0 ± 14.1 | 62.0 ± 13.2 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.7 ± 3.2 | 23.8 ± 3.4 | 0.138 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 80.2 ± 9.5 | 83.5 ± 8.9 | <0.001 |
| Smoking history | <0.001 | ||
| Never-smoker | 2,399,679 (59.4%) | 7916 (48.4%) | |
| Ex-smoker | 581,485 (14.4%) | 3128 (19.1%) | |
| Current-smoker | 1,058,907 (26.2%) | 5308 (32.5%) | |
| Alcohol consumption | <0.001 | ||
| Non-drinker | 2,077,053 (51.4%) | 9534 (58.3%) | |
| Mild-drinker | 1,641,427 (40.6%) | 5263 (32.2%) | |
| Heavy-drinker | 321,591 (8.0%) | 1555 (9.5%) | |
| Regular Exercise | 733,609 (18.2%) | 3148 (19.3%) | <0.001 |
| Income (lowest 20% group) | 704,587 (17.4%) | 3075 (18.8%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 349,134 (8.6%) | 4264 (26.1%) | <0.001 |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 97.2 ± 23.8 | 110.0 ± 41.5 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1,082,382 (27.0%) | 9331 (57.1%) | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 122.4 ± 15.0 | 129.3 ± 17.2 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 76.3 ± 10.0 | 78.9 ± 11.0 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 732,983 (18.1%) | 4610 (28.2%) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 195.3 ± 41.1 | 195.1 ± 44.3 | 0.549 |
| High density lipoprotein (mg/dL) | 56.5 ± 32.9 | 53.6 ± 30.9 | <0.001 |
| Low density lipoprotein (mg/dL) | 121.2 ± 214.2 | 115.0 ± 97.8 | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 275,854 (6.8%) | 2740 (16.8%) | <0.001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 87.6 ± 44.9 | 80.4 ± 34.7 | <0.001 |
| Metabolic Syndrome | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||
| 3,207,925 | 848,498 | ||
| Male sex | 1,717,481 (53.6%) | 516,050 (60.8%) | <0.001 |
| Age | 45.0 ± 13.6 | 55.0 ± 12.9 | <0.001 |
| Age group, years | <0.001 | ||
| 20–29 | 480,147 (15.0%) | 21,469 (2.5%) | |
| 30–39 | 687,795 (21.4%) | 91,015 (10.7%) | |
| 40–49 | 898,205 (28.0%) | 167,654 (19.8%) | |
| 50–59 | 627,768 (19.6%) | 233,180 (27.5%) | |
| 60–69 | 337,250 (10.5%) | 211,238 (24.9%) | |
| 70–79 | 152,342 (4.8%) | 109,341 (12.9%) | |
| 80+ | 24,418 (0.8%) | 14,601 (1.7%) | |
| Body mass index | 23.1 ± 2.9 | 26.0 ± 3.2 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference | 78.3 ± 8.5 | 87.9 ± 9.0 | <0.001 |
| Smoking status | <0.001 | ||
| Non-smoker | 1,940,944 (60.5%) | 466,651 (55.0%) | |
| Ex-smoker | 428,522 (13.4%) | 156,091 (18.4%) | |
| Current smoker | 838,459 (26.1%) | 225,756 (26.6%) | |
| Alcohol consumption | <0.001 | ||
| Non-drinker | 1,639,224 (51.1%) | 447,363 (52.7%) | |
| Mild drinker | 1,341,119 (41.8%) | 305,571 (36.0%) | |
| Heavy drinker | 227,582 (7.1%) | 95,564 (11.3%) | |
| Regular exercise | 569,089 (17.7%) | 167,668 (19.8%) | <0.001 |
| Income (lower 20%) | 564,051 (17.6%) | 143,611 (16.9%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 117,925 (3.7%) | 235,473 (27.8%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus stage | <0.001 | ||
| Non-diabetic | 2,541,796 (79.2%) | 242,335 (28.6%) | |
| Impaired fasting glucose | 548,204 (17.1%) | 370,690 (43.7%) | |
| New-onset | 53,175 (1.7%) | 67,408 (7.9%) | |
| <5 years | 32,167 (1.0%) | 87,320 (10.3%) | |
| ≥5 years | 32,583 (1.0%) | 80,745 (9.5%) | |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 92.9 ± 17.7 | 113.5 ± 34.6 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 536,787 (16.7%) | 554,926 (65.4%) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension stage | <0.001 | ||
| Non-hypertensive | 1,340,278 (41.8%) | 45,699 (5.4%) | |
| Pre-hypertension | 1,330,860 (41.5%) | 247,873 (29.2%) | |
| Hypertension without medication | 210,930 (6.6%) | 125,149 (14.8%) | |
| Hypertension with medication | 325,857 (10.2%) | 429,777 (50.7%) | |
| Systolic blood pressure | 119.8 ± 14.0 | 132.4 ± 14.7 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 74.9 ± 9.5 | 81.7 ± 10.1 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 300,945 (9.4%) | 436,648 (51.5%) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia stage (mg/dL) | <0.001 | ||
| Total cholesterol < 240 | 2,906,980 (90.6%) | 411,850 (48.5%) | |
| Total cholesterol ≥ 240 | 257,907 (8.0%) | 90,765 (10.7%) | |
| Total cholesterol ≥ 240 with medication | 43,038 (1.3%) | 345,883 (40.8%) | |
| Cholesterol level (mg/dL) | 192.3 ± 38.4 | 206.5 ± 48.5 | <0.001 |
| High-density lipoprotein (mg/dL) | 57.5 ± 31.8 | 52.8 ± 36.7 | <0.001 |
| Low-density lipoprotein (mg/dL) | 122.1 ± 232.1 | 117.8 ± 122.1 | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 182,472 (5.7%) | 96,122 (11.3%) | <0.001 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 88.8 ± 46.6 | 83.0 ± 37.4 | <0.001 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (IU/L) | 23.81 (23.79-23.82) | 38.86 (38.80-38.93) | <0.001 |
| n | SCD | Follow-up Duration (Person/Years) | Incidence | Hazard Ratio with 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| Metabolic syndrome | ||||||
| No | 3,207,925 | 9806 | 26,447,770 | 0.371 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| Yes | 848,498 | 6546 | 6,897,608 | 0.949 | 2.558 (2.480–2.640) | 1.507 (1.456–1.560) |
| Number of metabolic syndrome criteria met | ||||||
| 0 | 1,261,043 | 1806 | 10,465,831 | 0.173 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| 1 | 1,127,888 | 3819 | 9,285,122 | 0.411 | 2.383 (2.254–2.521) | 1.378 (1.302–1.459) |
| 2 | 818,994 | 4181 | 6,696,816 | 0.624 | 3.619 (3.424–3.824) | 1.677 (1.583–1.776) |
| 3 | 509,764 | 3378 | 4,153,728 | 0.813 | 4.712 (4.451–4.990) | 1.975 (1.858–2.100) |
| 4 | 259,869 | 2287 | 2,107,073 | 1.085 | 6.288 (5.911–6.688) | 2.367 (2.214–2.531) |
| 5 | 78,865 | 881 | 636,807 | 1.383 | 8.008 (7.388–8.680) | 2.956 (2.707–3.227) |
| n | SCD | Follow-Up Duration (Person/Years) | Incidence | Hazard Ratio with 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| ɣ-GTP | ||||||
| Q1 (lowest) | 987,003 | 2314 | 8,162,351 | 0.284 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| Q2 | 1,066,117 | 3727 | 8,789,346 | 0.424 | 1.496 (1.420–1.575) | 1.055 (1.000–1.112) |
| Q3 | 996,270 | 4447 | 8,184,478 | 0.543 | 1.918 (1.824–2.017) | 1.158 (1.098–1.222) |
| Q4 (highest) | 1,007,033 | 5864 | 8,209,202 | 0.714 | 2.528 (2.409–2.652) | 1.519 (1.437–1.605) |
| n | SCD | Follow-Up Duration (Person/Years) | Incidence | Hazard Ratio with 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| Metabolic syndrome | ||||||
| No (in 2009) → No (in 2011) | 1,967,483 | 4,080 | 12,479,939 | 0.327 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| No → Yes | 189,148 | 733 | 1,193,749 | 0.614 | 1.877 (1.735–2.030) | 1.316 (1.215–1.426) |
| Yes → No | 169,640 | 702 | 1,068,427 | 0.657 | 2.009 (1.854–2.176) | 1.310 (1.207–1.423) |
| Yes → Yes | 380,517 | 2,314 | 2,395,577 | 0.966 | 2.946 (2.800–3.101) | 1.591 (1.503–1.684) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.G.; Han, K.; Jeong, J.H.; Roh, S.-Y.; Choi, Y.Y.; Min, K.; Shim, J.; Choi, J.-I.; Kim, Y.-H. Metabolic Syndrome, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071781
Kim YG, Han K, Jeong JH, Roh S-Y, Choi YY, Min K, Shim J, Choi J-I, Kim Y-H. Metabolic Syndrome, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(7):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071781
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yun Gi, Kyungdo Han, Joo Hee Jeong, Seung-Young Roh, Yun Young Choi, Kyongjin Min, Jaemin Shim, Jong-Il Choi, and Young-Hoon Kim. 2022. "Metabolic Syndrome, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 7: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071781
APA StyleKim, Y. G., Han, K., Jeong, J. H., Roh, S.-Y., Choi, Y. Y., Min, K., Shim, J., Choi, J.-I., & Kim, Y.-H. (2022). Metabolic Syndrome, Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(7), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071781






