Prevention of Peripheral Distal Polyneuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Participants: Patients with DM, aged ≥ 18 years.
- Interventions: Any strategy that entailed prevention or delay of DPN onset.
- Comparisons: Placebo substances, any other alternative or natural progression of the disease in the control group.
- Outcomes or results: The effectiveness of the intervention in terms of the prevention of DPN at the end of the studies in patients who did not present this condition at the beginning, or the improvement of this condition if they presented it at the beginning of the study, should be evaluated. Other outcomes may include quality of life measurements, adverse events, related costs, changes in neuropathic pain symptoms, presence of foot ulcerations and/or amputations, and events that prevented continuation of clinical trials.
2.3. Sources and Search
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction and Synthesis of Results
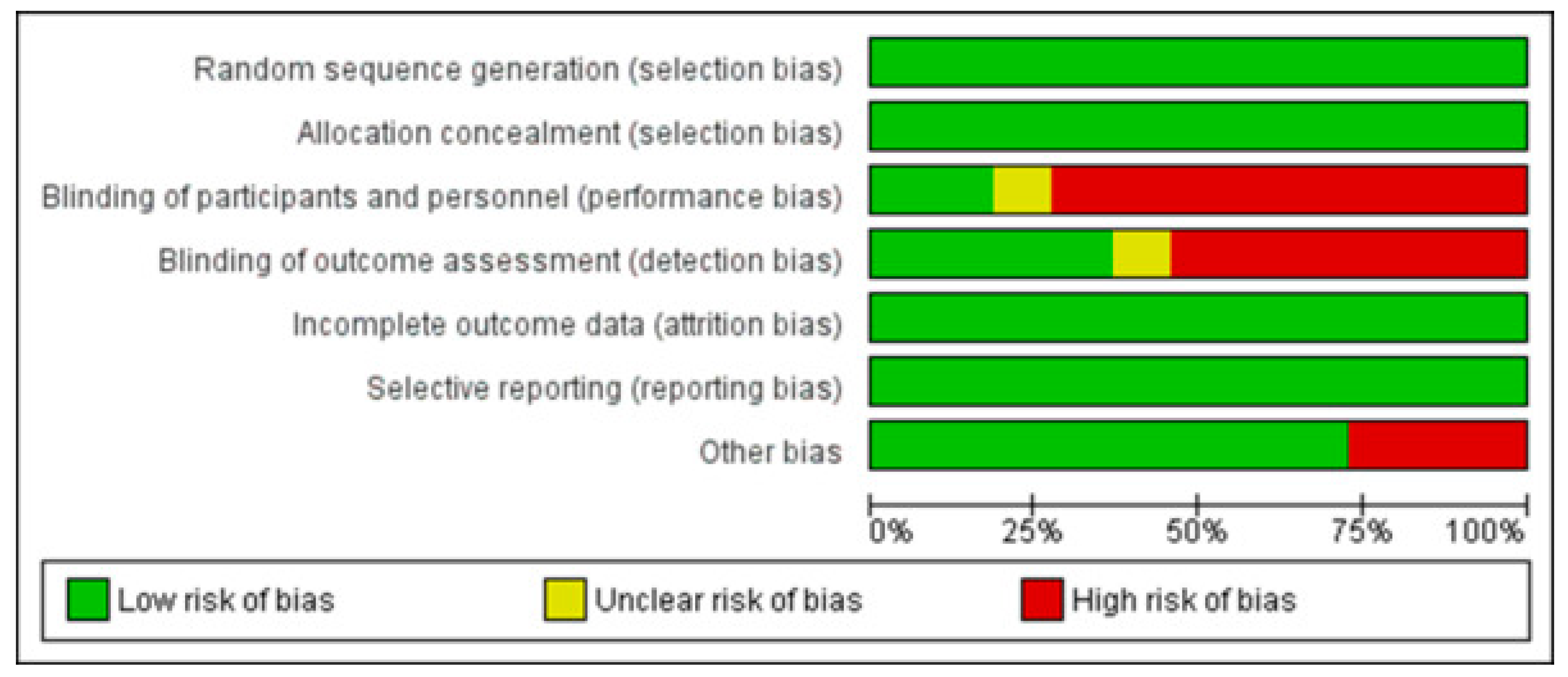
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
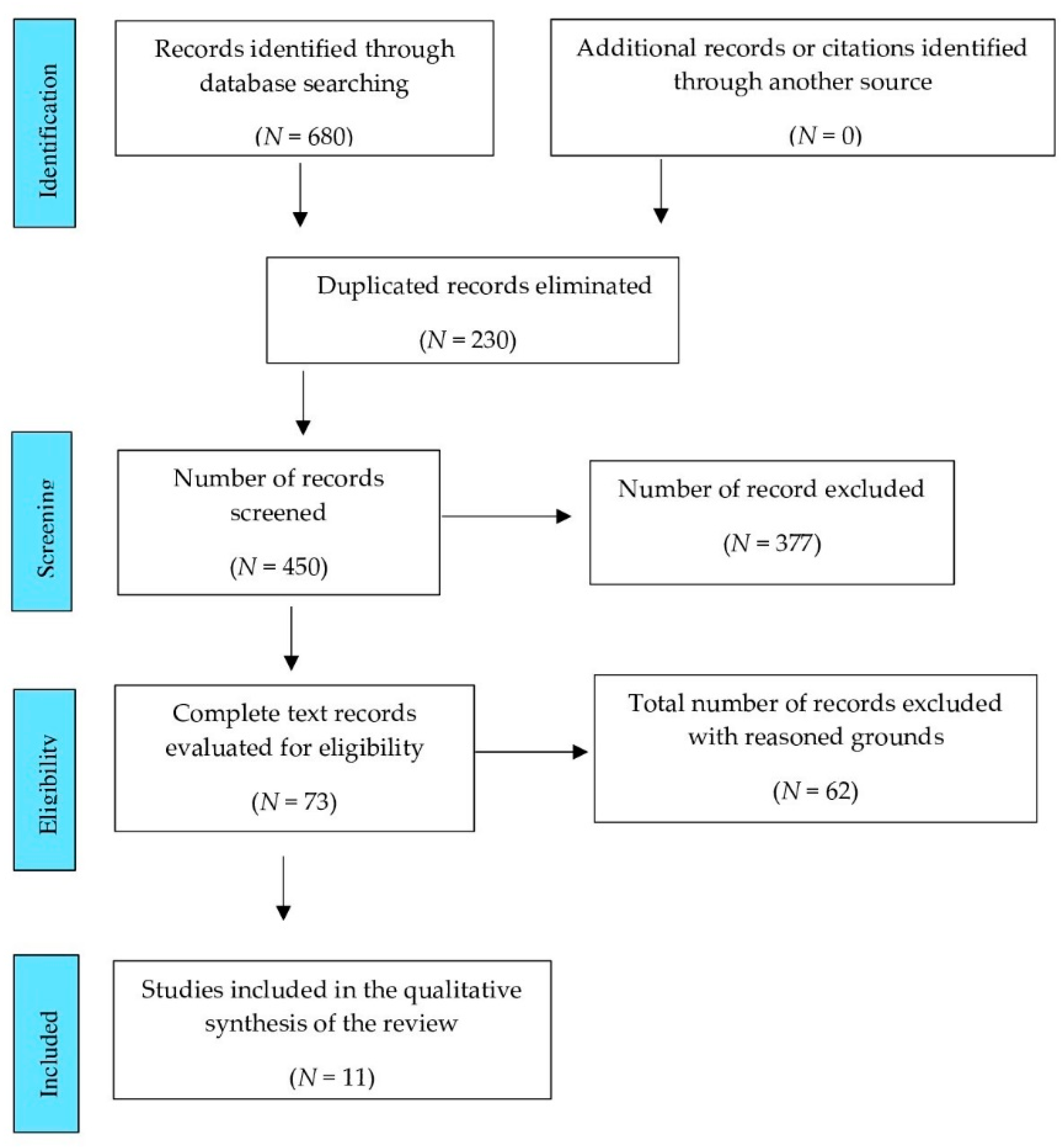
3. Results
3.1. Risk of Biases among the Studies Included
3.2. Statistical Analysis of the Quality of the Included Studies
3.3. Limitations of Included Studies
| Authors | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Ismail-Beigi et al., 2010 | Early termination of the RCT due to increased mortality among participants. |
| Charles et al., 2011 | Not all patients were evaluated with all measurements. Patients in the CASE IV subgroup were younger than the rest, so microvascular complications may have been lower in this group. |
| Gong et al., 2011 | No results were obtained for 25% of the participants who died. Low incidence of nephropathy and neuropathy due to short duration of diabetes in participants. |
| Pop-Busui et al., 2013 | Study not designed to detect an effect of the groups on DPN. A lower incidence of neuropathy was found in the IS group; however, the authors were unable to identify whether the benefit was specific to biguanides or thiazolidinediones. Small fiber neuropathy was not evaluated, as only the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI), which evaluates large fibers, was used. Subjectivity of the MNSI. |
| Dixit et al., 2014 | The effect of aerobic exercise to halt or interrupt the natural course of DPN was not studied. The study had a large number of dropouts. |
| Martin et al., 2014 | Intentional exclusion at the start of Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DDCT) of participants with severe neuropathy. Patients in the conventional insulin therapy (CON) group were switched to intensive insulin therapy (INT) group because of the benefits of intensive glycemic control in patients with TIDM. |
| Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group et al., 2015 | The combination of three different microvascular outcomes in the aggregate microvascular outcome. |
| Look AHEAD Research Group et al., 2017 | Relationship of biguanide use with vitamin B12 depletion and the development of DPN. Levels of this vitamin were not recorded. Diagnosis of DPN by questionnaire, MNSI physical examination and Semmes-Weinstein (SW) monofilament. |
| Gholami et al., 2018 | Small sample size, large number of dropouts, and only male participation. |
| Brock et al., 2019 | Severe irreversible neuropathy, more male representation. |
| Gholami et al., 2020 | Small sample size. |
3.4. Synthesis of Results
3.4.1. Studies Included
3.4.2. Participants
3.4.3. Interventions and Comparisons
3.4.4. Analysis of Results
3.4.5. Summary of Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Intensive Glycemic Control
4.2. Use of Drugs
4.3. Lifestyle Modification
4.4. Practice of Physical Exercise
4.5. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Search Strategy
Appendix A.1. PubMed
Appendix A.1.1. Clinical Trials
Appendix A.1.2. Cohort Studies
Appendix A.2. Scopus
Appendix A.3. The Cochrane Library
Appendix A.4. CINAHL
Appendix A.4.1. Clinical Trials
Appendix A.4.2. Cohort Studies
Appendix B. Individual Characteristics of the Studies Included in the Review
- Study 1: Brock et al., 2019 [53]
- Study 2: Charles et al., 2011 [62]
- Study 3: Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group et al., 2015 [57]
- Study 4: Dixit et al., 2014 [54]
- Study 5: Gholami et al., 2018 [61]
- Study 6: Gholami et al., 2020 [59]
- Study 7: Gong et al., 2011 [58]
- Study 8: Ismail-Beigi et al., 2010 [55]
- Study 9: Look AHEAD Research Group et al., 2017 [56]
- Study 10: Martin et al., 2014 [15]
- Study 11: Pop-Busui et al., 2013 [60]
References
- Crespo, C.; Brosa, M.; Soria-Juan, A.; López-Alba, A.; López-Martínez, N.; Soria, B. Costes directos de la diabetes mellitus y de sus complicaciones en España (Estudio SECCAID): Spain estimated cost Ciberdem-Cabimer in diabetes). Av. Diabetol. 2015, 29, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Soidán, F.J.; Villoro, R.; Merino, M.; Hidalgo-Vega, A.; Hernando-Martín, T.; González-Martín-Moro, B. Estado de salud, calidad de vida y utilización de recursos sanitarios de los pacientes con diabetes mellitus en España. Semergen 2017, 43, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.C.; Lamping, D.L.; Maclaine, G.D.H. Measuring health-related quality of life in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 96, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas-Velasco, M.; Cervell-Rodríguez, D.; Rodríguez-Montalbán, S.; Jiménez, V.A.I.; Fernández-de-Valderrama-Martínez, I. Actualización en el diagnóstico, tratamiento y prevención de la neuropatía diabética periferica. Angiología 2017, 69, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.M.; Vinik, A.I.; Arezzo, J.C.; Bril, V.; Feldman, E.L.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Maser, R.E.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D.; et al. Diabetic neuropathies: A statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic neuropathy: A position statement by the American diabetes association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic neuropathies: Update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrakis, I.; Kyriopoulos, I.J.; Ginis, A.; Athanasakis, K. Losing a foot versus losing a dollar; a systematic review of cost studies in diabetic foot complications. Expert. Rev. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 2017, 17, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narres, M.; Kvitkina, T.; Claessen, H.; Droste, S.; Schuster, B.; Morbach, S.; Rümenapf, G.; Van-Acker, K.; Icks, A. Incidence of lower extremity amputation in the diabetic compared to the non-diabetic population: A systematic review protocol. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, E.J.; Liu, Z.; Khamaisi, M.; King, G.L.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Hughes, T.M.; Craft, S.; Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W.; et al. Diabetic microvascular disease: An endocrine society scientific statement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4343–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-Cerrato, J. The prevalence of clinical diabetic polyneuropathy in Spain: A study in primary care and hospital clinic groups. Diabetología 1998, 41, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreira-Do-Nascimento, O.J.; Castelo-Branco-Pupe, C.; Boiteux-Uchoa-Cavalcanti, E. Diabetic neuropathy. Neuropatia diabética. Rev. Dor. São Paulo 2016, 17, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Fatela, V.; Gutiérrez, A.; Martínez-Salio, A.; Ayan, S.; Rodríguez- Sánchez, S.; Vidal-Fernández, J. Manejo del paciente con neuropatía periférica. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2007, 207, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.L.; Albers, J.W.; Pop-Busui, R.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Neuropathy and related findings in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: Standards of medical care in diabetes 2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee; Bril, V.; Breiner, A.; Perkins, B.A.; Zochodne, D. Neuropathy. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vázquez-San-Miguel, F.; Mauricio-Puente, D.; Viadé-Julià, J. Neuropatía diabética y pie diabético. Medicine 2016, 12, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veves, A.; Giurini, J.M.; LoGerfo, F.W. The Diabetic Foot, 2nd ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Maffi, P.; Secchi, A. The Burden of Diabetes: Emerging Data. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2017, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; Da-Rocha-Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, J.H.; Pfeifer, M.A. The Diabetic Foot, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Manual Cochrane de Revisiones Sistemáticas de Intervenciones, Versión 5.1.0. Available online: https://es.cochrane.org/es (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Von-Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Declaración de la iniciativa STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology): Directrices para la comunicación de estudios observacionales. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2008, 82, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CASPe. Guías CASPe de Lectura Crítica de la Literatura Médica. 2005. Available online: http://www.redcaspe.org/ (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farvid, M.S.; Homayouni, F.; Amiri, Z.; Adelmanesh, F. Improving neuropathy scores in type 2 diabetic patients using micronutrients supplementation. Diabetes Res Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.H.; Petrofsky, J.S.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, K.J.; Yim, J.E. Effects of an exercise program on balance and trunk proprioception in older adults with diabetic neuropathies. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Tedeschi, A.; Fallani, E.; Coppelli, A.; Vallini, V.; Iacopi, E.; Piaggesi, A. Custom-made orthesis and shoes in a structured follow-up program reduces the incidence of neuropathic ulcers in high-risk diabetic foot patients. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2012, 11, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavery, L.A.; LaFontaine, J.; Higgins, K.R.; Lanctot, D.R.; Constantinides, G. Shear-reducing insoles to prevent foot ulceration in high-risk diabetic patients. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2012, 25, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.J.; Tuttle, L.J.; Lemaster, J.W.; Strube, M.J.; McGill, J.B.; Hastings, M.K.; Sinacoreet, D.R. Weight-bearing versus nonweight-bearing exercise for persons with diabetes and peripheral neuropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulbrecht, J.S.; Hurley, T.; Mauger, D.T.; Cavanagh, P.R. Prevention of recurrent foot ulcers with plantar pressure-based in-shoe orthoses: The CareFUL prevention multicenter randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixit, S.; Maiya, A.; Shastry, B.A.; Guddattu, V. Analysis of postural control during quiet standing in a population with diabetic peripheral neuropathy undergoing moderate intensity aerobic exercise training: A single blind, randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Low, P.A.; Freeman, R.; Tritschler, H.; Vinik, A.I. Predictors of improvement and progression of diabetic polyneuropathy following treatment with α-lipoic acid for 4 years in the NATHAN 1 trial. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharoni, S.K.A.; Rahman, H.A.; Minhat, H.S.; Shariff-Ghazali, S.; Ong, M.H.A. The effects of self-efficacy enhancing program on foot self-care behaviour of older adults with diabetes: A randomised controlled trial in elderly care facility, Peninsular Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkataraman, K.; Tai, B.C.; Khoo, E.Y.H.; Tavintharan, S.; Chandran, K.; Hwang, S.W.; Phua, M.S.L.A.; Wee, H.L.; Koh, G.C.H.; Tai, E.S. Short-term strength and balance training does not improve quality of life but improves functional status in individuals with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Moral, M.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L.; García-Morales, E.; García-Álvarez, Y.; Alvaro-Afonso, F.J.; Molines-Barroso, R.J. Clinical efficacy of therapeutic footwear with a rigid rocker sole in the prevention of recurrence in patients with diabetes mellitus and diabetic polineuropathy: A randomized clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, E.B.; Fisher, M.A.; Miller, C.M.; Jelinek, C.; Butler, J.; McBurney, C.; Collins, E.G. Randomized controlled trial of physical exercise in diabetic veterans with length-dependent distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 13–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, I.; Noohu, M.M.; Verma, S.; Singla, D.; Hussain, M.E. Effect of sensorimotor training on balance measures and proprioception among middle and older age adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Gait Posture 2019, 74, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Liao, Z.; Liu, R.; Du, T.; Zhu, H. Effects of cilostazol tablets combined with epalrestat tablets on serum inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and nerve conduction velocity in elderly patients with type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2019, 35, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.; Altun, Z.A.; Karaman, C.A.; Kaya, B.B.; Durmus, B. Does vitamin D affect diabetic neuropathic pain and balance? J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller-Stich, B.P.; Fischer, L.; Kenngott, H.G.; Gondan, M.; Senft, J.; Clemens, G.; Nickel, F.; Fleming, T.; Nawroth, P.P.; Büchler, M.W. Gastric bypass leads to improvement of diabetic neuropathy independent of glucose normalization—Results of a prospective cohort study (DiaSurg 1 Study). Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Sullivan, K.A.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Feldman, E.L. Identification of factors associated with sural nerve regeneration and degeneration in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 4043–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.N.; Lee, K.O.; Jeong, J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Shin, H.Y.; Hong, J.M.; Ahn, C.W.; Choi, Y.C. The role of insulin resistance in diabetic neuropathy in Koreans with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 6-year follow-up study. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishibashi, F.; Taniguchi, M.; Kosaka, A.; Uetake, H.; Tavakoli, M. Improvement in neuropathy outcomes with normalizing HbA 1c in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, R.; Johnson, E.; Haneuse, S.; Coleman, K.J.; Connor, P.J.O.; Fisher, D.P.; Sidney, S.; Bogart, A.; Theis, M.K.; Anau, J.; et al. Microvascular outcomes in patients with diabetes after bariatric surgery versus usual-care: A matched cohort study. Ann. Int. Med. 2018, 169, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Su, P.F.; Hung, J.Y.; Ou, H.T.; Kuo, S. Comparative predictive ability of visit-to-visit HbA1c variability measures for microvascular disease risk in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, A.; Hivert, M.F.; Gold, D.R.; Hauser, R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Lin, P.D.; Fleisch, A.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Webster, T.F.; et al. Associations of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances with incident diabetes and microvascular disease. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Edelstein, S.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Knowler, W.C.; Marcovina, S.M.; Orchard, T.J.; Bray, G.A.; Schade, D.S.; Temprosa, M.G.; White, N.H.; et al. Long-term metformin use and vitamin B12 deficiency in the diabetes prevention program outcomes study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gæde, P.; Oellgaard, J.; Carstensen, B.; Rossing, P.; Lund-Andersen, H.; Parving, H.H.; Pedersen, O. Years of life gained by multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: 21 years follow-up on the Steno-2 randomised trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abraham, A.; Barnett, C.; Katzberg, H.D.; Lovblom, L.E.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V. Nerve function varies with hemoglobin A1c in controls and type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braffett, B.H.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Albers, J.W.; Feldman, E.L.; Martin, C.L.; White, N.H.; Orchard, T.J.; Lopes-Virella, M.; Lachin, J.M.; Pop-Busui, R.; et al. Risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) study. Diabetes Care 2020, 69, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, C.; Hansen, C.S.; Karmisholt, J.; Møller, H.J.; Juhl, A.; Farmer, A.D.; Drewes, A.M.; Riahi, S.; Lervang, H.H.; Jakobsen, P.E.; et al. Liraglutide treatment reduced interleukin-6 in adults with type 1 diabetes but did not improve established autonomic or polyneuropathy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 2512–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixit, S.; Maiya, A.G.; Shastry, B.A. Effect of aerobic exercise on peripheral nerve functions of population with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: A single blind, parallel group randomized controlled trial. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail-Beigi, F.; Craven, T.; Banerji, M.; Basile, J.; Calles, J.; Cohen, R.; Cuddihy, R.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Grimm, R.H., Jr.; et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: An analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Look AHEAD Research Group. Effects of a long-term lifestyle modification programme on peripheral neuropathy in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes: The Look AHEAD study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group; Nathan, D.M.; Barret-Connor, E.; Crandall, J.P.J.; Edelstein, S.L.; Goldberg, R.B.R.; Horton, E.S.; Knowler, W.C.; Mather, K.J.; Orchard, T.J.; et al. Long-term effects of lifestyle intervention or metformin on diabetes development and microvascular complications: The DPP outcomes study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, Q.; Gregg, E.W.; Wang, J.; An, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shuai, Y.; et al. Long-term effects of a randomised trial of a 6-year lifestyle intervention in impaired glucose tolerance on diabetes-related microvascular complications: The China da Qing Diabetes Prevention Outcome Study. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, F.; Nazari, H.; Alimi, M. Cycle training improves vascular function and neuropathic symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes and peripheral neuropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 131, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Lu, J.; Brooks, M.M.; Albert, S.; Althouse, A.D.; Escobedo, J.; Green, J.; Palumbo, P.; Perkins, B.A.; Whitehouse, F.; et al. Impact of glycemic control strategies on the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the bypass angioplasty revascularization investigation 2 diabetes (BARI 2D) Cohort. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholami, F.; Nikookheslat, S.; Salekzamani, Y.; Boule, N.; Jafari, A. Effect of aerobic training on nerve conduction in men with type 2 diabetes and peripheral neuropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2018, 48, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, M.; Ejskjaer, N.; Witte, D.R.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Lauritzen, T.; Sandbaek, A. Prevalence of neuropathy and peripheral arterial disease and the impact of treatment in people with screen-detected type 2 diabetes: The ADDITION-Denmark study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2244–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veves, A.; Backonja, M.; Malik, R.A. Painful diabetic neuropathy: Epidemiology, natural history, early diagnosis, and treatment options. Pain Med. 2008, 9, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullerton, B.; Jeitler, K.; Seitz, M.; Horvath, K.; Berghold, A.; Siebenhofer, A. Intensive glucose control versus conventional glucose control for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2, CD009122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, J.W.; Herman, W.H.; Pop-Busui, R.; Feldman, E.L.; Martin, C.L.; Cleary, P.A.; Waberski, B.H.; Lachin, J.M.; Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group. Effect of prior intensive insulin treatment during the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) on peripheral neuropathy in type 1 diabetes during the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Brinchmann-Hansen, O.; Hanssen, K.; Ganes, T.; Kierulf, P.; Smeland, E.; Sandvik, L.; Aagenaes, Ø. Effect of near normoglycaemia for two years on progression of early diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy: The Oslo study. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1986, 293, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, D.; Behler, M.; Schroers-Teuber, M.; Roden, M. Near-normoglycaemia and development of neuropathy: A 24-year prospective study from diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. BMJ Open 2015, 24, e006559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, M.; Soedamah-Muthu, S.S.; Tesfaye, S.; Fuller, J.H.; Arezzo, J.C.; Chaturvedi, N.; Witte, D.R.; EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Investigators. Low peripheral nerve conduction velocities and amplitudes are strongly related to diabetic microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes: The EURODIAB prospective complications study. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A.W. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gæde, P.; Vedel, P.; Larsen, N.; Jensen, G.; Parving, H.H.; Pedersen, O. multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group; Patel, A.; MacMahon, S.; Chalmers, J.; Neal, B.; Billot, L.; Woodward, M.; Marre, M.; Cooper, M.; Glasziou, P.; et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group; Gerstein, H.C.; Miller, M.E.; Byington, R.P.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Bigger, J.T.; Buse, J.B.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2545–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duckworth, W.; Abraira, C.; Moritz, T.; Reda, D.; Emanuele, N.; Reaven, P.D.; Zieve, F.J.; Marks, J.; Davis, S.N.; Hayward, R.; et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohkubo, Y.; Kishikawa, H.; Arak, E.; Miyataa, T.; Isami, S.; Motoyoshi, S.; Kojima, Y.; Furuyoshi, N.; Shichiri, M. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: A randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1995, 28, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Little, A.A.; Feldman, E.L.; Hughes, R.A. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 6, CD007543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehler, A.M.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Berwanger, O.; Figueiro, M.; Laranjeira, L.N.; Zazula, A.D.; Kioshi, B.; Bugano, D.G.; Santucci, E.; Sbruzzi, G.; et al. Effect of tight blood glucose control versus conventional control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 31, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasan, R.; Firwana, B.; Elraiyah, T.; Domecq, J.P.; Prutsky, G.; Nabhan, M.; Prokop, L.J.; Henke, P.; Tsapas, A.; Montori, V.M.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of glycemic control for the prevention of diabetic foot syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 22S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M.; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Gregg, E.W.; Yang, W.; Gong, Q.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; An, Y.; et al. The long-term effect of lifestyle interventions to prevent diabetes in the China Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: A 20-year follow-up study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, S.; Iacobellis, G.; Parisi, L.; Di-Biase, N.; Calandriello, E.; Leonetti, F.; Fallucca, F. Exercise training can modify the natural history of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2006, 20, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, S.; Jeziorska, M.; Ferdousi, M.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Ponirakis, G.; Marshall, A.; Alam, U.; Asghar, O.; Atkinson, A.; Jones, W.; et al. Early nerve fibre regeneration in individuals with type 1 diabetes after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singleton, J.R.; Marcus, R.L.; Jackson, J.E.K.; Lessard, M.; Graham, T.E.; Smith, A.G. Exercise increases cutaneous nerve density in diabetic patients without neuropathy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villafaina, S.; Collado-Mateo, D.; Fuentes, J.P.; Merellano-Navarro, E.; Gusi, N. Physical exercise improves heart rate variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2017, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, P.; Shenoy, S.; Hussain, M.E. Exercise training and cardiac autonomic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Dennis, S.M.; Kiernan, M.C.; Harmer, A.R. Aerobic exercise training may improve nerve function in type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, S.; Azmi, S.; Ho, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Ferdousi, M.; Siahmansur, T.; Kalteniece, A.; Marshall, A.; Dhage, S.S.; Iqbal, Z.; et al. Improvements in diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy after bariatric surgery: A prospective cohort study. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Research Group. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP): Description of lifestyle intervention. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Look AHEAD Research Group; Wing, R.R.; Bolin, P.; Brancati, F.L.; Bray, G.A.; Clark, J.M.; Coday, M.; Crow, R.S.; Curtis, J.M.; Egan, C.M.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epidemiology of Diabetes and Complications (EDIC) Research Group. Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC): Design, implementation, and preliminary results of a long-term follow-up of the diabetes control and complications trial cohort. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, D.M.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: Overview. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaitman, B.R.; Hardison, R.M.; Adler, D.; Gebhart, S.; Grogan, M.; Ocampo, S.; Sopko, G.; Ramires, J.A.; Schneider, D.; Frye, R.L.; et al. The BARI 2D randomized trial of different treatment strategies in type 2 diabetes mellitus with stable ischemic heart disease. Impact of treatment strategy on cardiac mortality and myocardial infarction. Circulation 2009, 120, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reason for Exclusion | Authors |
|---|---|
| RCTs that specifically address treatment rather than prevention of DPN | Farvid et al., 2011 [27] Song et al., 2011 [28] Rizzo et al., 2012 [29] Lavery et al., 2012 [30] Mueller et al., 2013 [31] Ulbrecht et al., 2014 [32] Dixit et al., 2016 [33] Ziegler et al., 2016 [34] Sharoni et al., 2018 [35] Venkataraman et al., 2019 [36] López-Moral et al., 2019 [37] Stubbs et al., 2019 [38] Ahmad et al., 2019 [39] Shu et al., 2019 [40] Sari et al., 2020 [41] |
| Cohort studies not from RCTs | Müller-Stich et al., 2013 [42] Hur et al., 2013 [43] Cho et al., 2014 [44] Ishibashi et al., 2018 [45] O’Brien et al., 2018 [46] Yang et al., 2020 [47] Cárdenas et al., 2019 [48] |
| Cohort studies that do not specifically address the prevention of DPN, but from RCTs | Aroda et al., 2016 [49] |
| Gaede et al., 2016 [50] | |
| Abraham et al., 2018 [51] | |
| Braffett et al., 2020 [52] |
| Intraclass Correlation a | 95% Confidence Interval | F Test with True Value 0 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Lower Bound | Value | df1 | df2 | Sig. | ||
| Single Measures | 0.997 b | 0.995 | 0.995 | 687.400 | 10 | 10 | 0.000 |
| Average Measures | 0.999 c | 0.995 | 1.000 | 687.400 | 10 | 10 | 0.000 |
| Authors | Scale | Review 1 | Review 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ismail-Beigi et al., 2010 | CASpe | 10/11 | 10/11 |
| Charles et al., 2011 | CASpe | 6/11 | 6/11 |
| Gong et al., 2011 | STROBE | 16/22 | 16/22 |
| Pop-Busui et al., 2013 | STROBE | 17/22 | 17/22 |
| Dixit et al., 2014 | CASpe | 11/11 | 11/11 |
| Martin et al., 2014 | STROBE | 16/22 | 16/22 |
| Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group et al., 2015 | STROBE | 17/22 | 17/22 |
| Look AHEAD Research Group et al., 2017 | CASpe | 9/11 | 9/11 |
| Gholami et al., 2018 | CASpe | 9/11 | 9/11 |
| Brock et al., 2019 | CASpe | 11/11 | 11/11 |
| Gholami et al., 2020 | CASpe | 9/11 | 9/11 |
| Authors | Design | Participants (N) | Groups | Diabetes Type | Average Age (Years) | Duration of the Study | Interventions | Measured Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brock et al. (2019) | RCT, double-blind, placebo-controlled | 39 | IG (Liraglutide) N = 19 CG (placebo) N = 20 | TIDM | 50.4 | 32 weeks | Liraglutide Placebo | Changes in nerve potentials, proinflammatory cytokines, autonomic function and peripheral neurophysiological tests. MNSI |
| Charles et al. (2011) | RCT with parallel groups | 1161 | Routine Care (RC) N = 459 Intensive multifactorial treatment (IT) N = 702 | TIIDM | 59.9 | 6 years | IT: Education, medication and promotion of healthy lifestyle. CR: Danish recommendations for diabetes care. | AAI Vibration detection threshold (tuning fork) Light touch (SW) |
| Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group et al. (2015) | Cohort study of a parallel-group placebo-controlled RCT | 2776 | Placebo N = 935 Metformin N = 926 Lifestyle N = 915 | TIIDM | 51 | 15 years | Metformin Placebo Lifestyle | Diagnosis of diabetes HbA1c Albuminuria (Nephropathy) Fundus evaluation (Retinopathy) SW light touch (Neuropathy) |
| Dixit et al. (2014) | RCT of parallel groups | 87 | CG N = 47 (10 lost) EG N = 40 (11 lost) | TIIDM | CG: 59.45 EG: 54.40 | 8 weeks | EG: Moderate aerobic exercise, foot care education, healthy diet CG: Standard medical care, education | Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies in peroneal and sural nerves MDNS |
| Gholami et al. (2018) | RCT of parallel groups | 24 | Exercise N = 12 Control N = 12 | TIIDM | CG: 43 ± 6.4 EG: 42 ± 4.6 | 12 weeks | Exercise: Running, walking or treadmill 3 times/week for 20–45 min. Control: Maintain usual level of physical activity. | Weight, BMI, % fat HbA1c Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) and nerve action potential amplitude (APAN) peoneal, tibial and sural nerves |
| Gholami et al. (2020) | RCT of parallel groups | 31 | CG N = 15 EG N = 16 | TIIDM | 52.8 ± 9.6 | 12 weeks | EG: Cycling exercises CG: Maintaining the usual level of physical activity | HbA1c Fasting glucose Flow mediated dilation (FMD), changes in intima-media thickness and basal diameter in superficial femoral artery, MDNS |
| Gong et al. (2011) | Cohort study of parallel-group RCTs | 577 | CG = N = 136 (42 lost) EG = N = 441 (135 lost) | TIIDM | CG 66.7 ± 9.2 EG 64.7 ± 9.3 | 20 years | EG: diet, exercise or diet + exercise CG: Regular medical care | Plasma glucose HbA1c, oral glucose tolerance test, Examination ocular fundus Inspection extremity lower limb AAI Light touch (SW) |
| Ismail-Beigi et al. (2010) | RCT of parallel groups | 10,251 | Intensive therapy N = 5128 Standard therapy N = 5123 | TIIDM | 62.2 ± 6 | 3.5 years | Intensive therapy: HbA1c < 6.0% Standard therapy: HbA1c 7.0–7.9% | Albuminuria Creatinine Fundus examination MNSI Vibratory sensitivity (tuning fork), light touch (SW) |
| Look AHEAD Research Group et al. (2017) | RCT of parallel groups | 5145 | Intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) N = 2570 Diabetes support and education (DSE) N = 2575 | TIIDM | 58.7 | 11 years | ILI: 7% weight loss, reduced caloric intake, and increased physical activity DSE: Diabetes education focused on diet and exercise | MNSI Light touch (SW) |
| Martin et al. (2014) | Cohort study of a parallel-group RCT | 1345 | Intensive insulin therapy (INT) N = 687 Conventional insulin therapy (CON) N = 688 | TIDM | 33.6 ± 7 | 14 years | INT: insulin treatment aimed at near-normal glycemia. CON: insulin treatment according to current standards | Vibratory sensitivity Light touch (SW) MNSI Nerve conduction studies HbA1c |
| Pop-Busui et al. (2013) | Cohort study of a parallel-group RCT | 2159 | Insulin-sensitizing treatments (IS) N = 1080 Insulin-providing treatments (IP) N = 1079 | TIIDM | 62 ± 9 | 4 years | Insulin-sensitizing treatments Insulin-providing treatments | HbA1c, Duration of DM, Albuminuria Retinopathy Alcohol and tobacco consumption Blood lipids, Blood pressure, MNSI Prevalence of DPN |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvajal-Moreno, L.; Coheña-Jiménez, M.; García-Ventura, I.; Pabón-Carrasco, M.; Pérez-Belloso, A.J. Prevention of Peripheral Distal Polyneuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061723
Carvajal-Moreno L, Coheña-Jiménez M, García-Ventura I, Pabón-Carrasco M, Pérez-Belloso AJ. Prevention of Peripheral Distal Polyneuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(6):1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061723
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvajal-Moreno, Lidia, Manuel Coheña-Jiménez, Irene García-Ventura, Manuel Pabón-Carrasco, and Ana Juana Pérez-Belloso. 2022. "Prevention of Peripheral Distal Polyneuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 6: 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061723
APA StyleCarvajal-Moreno, L., Coheña-Jiménez, M., García-Ventura, I., Pabón-Carrasco, M., & Pérez-Belloso, A. J. (2022). Prevention of Peripheral Distal Polyneuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(6), 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061723








