Polychromatic Assessment of a Refractive Segmented EDOF Intraocular Lens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
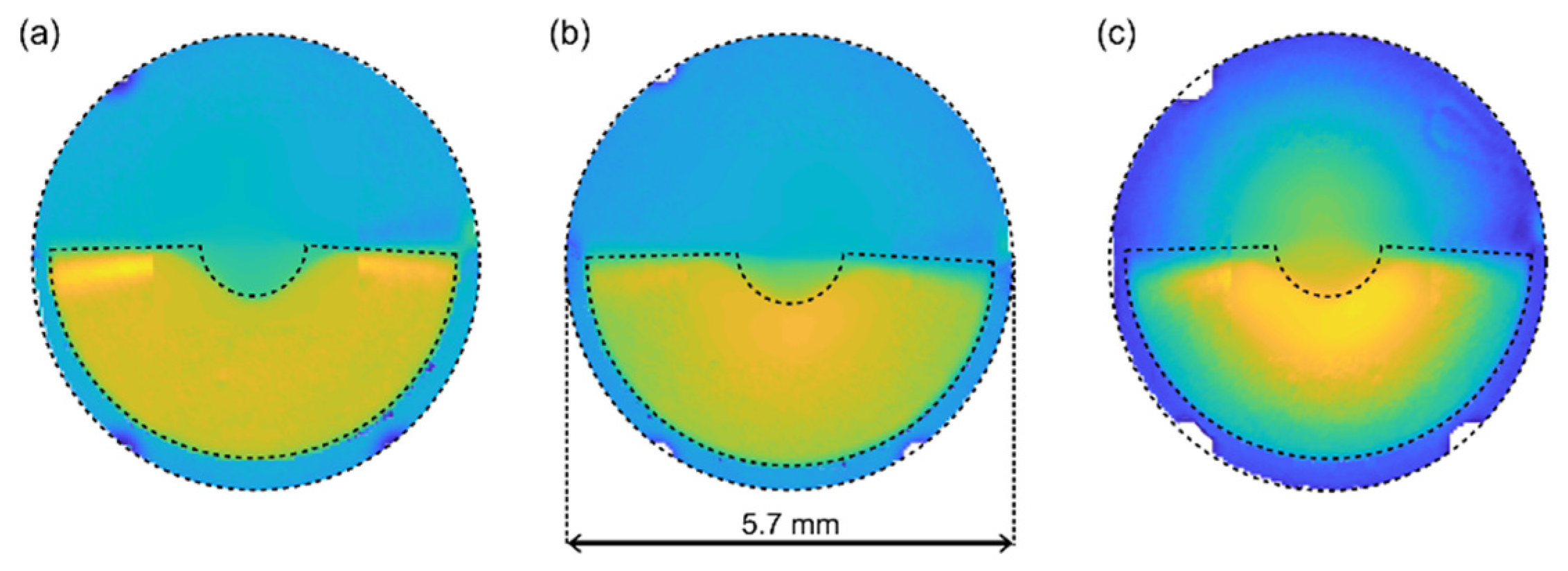
2.1. Multifocal Intraocular Lenses
2.2. Numerical Simulation
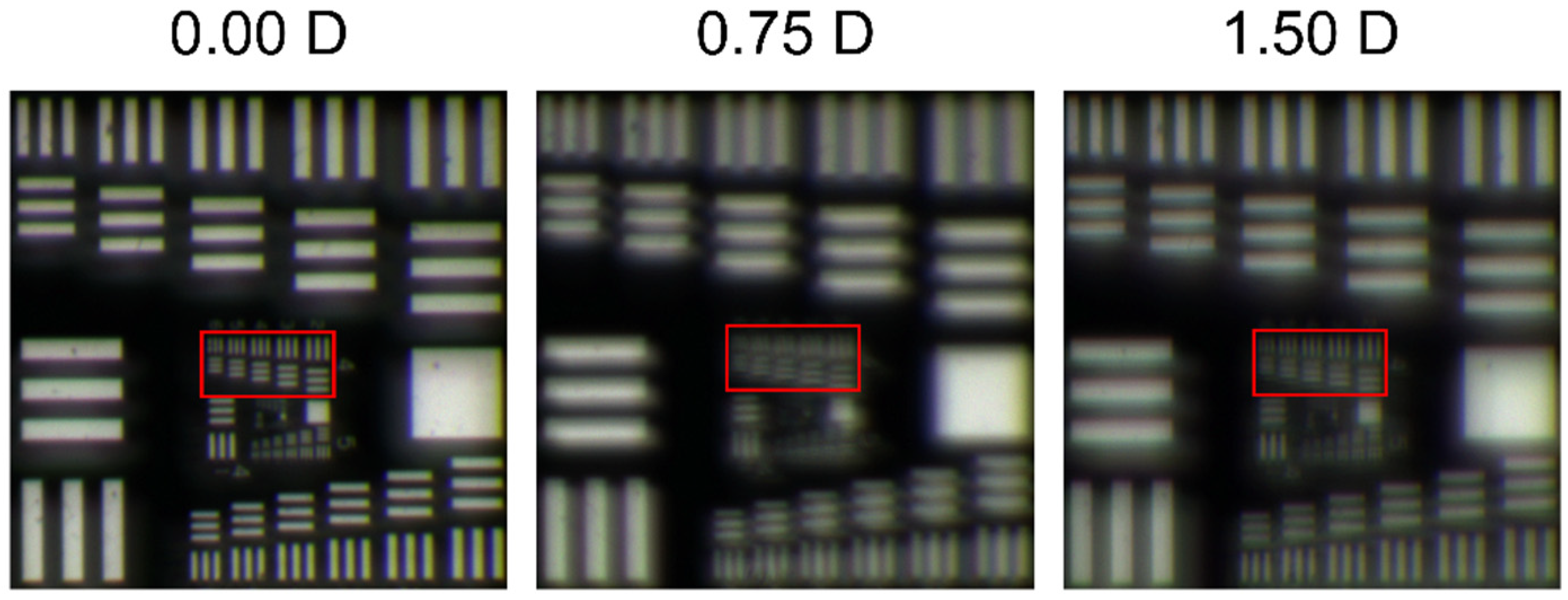
2.3. Optical Bench
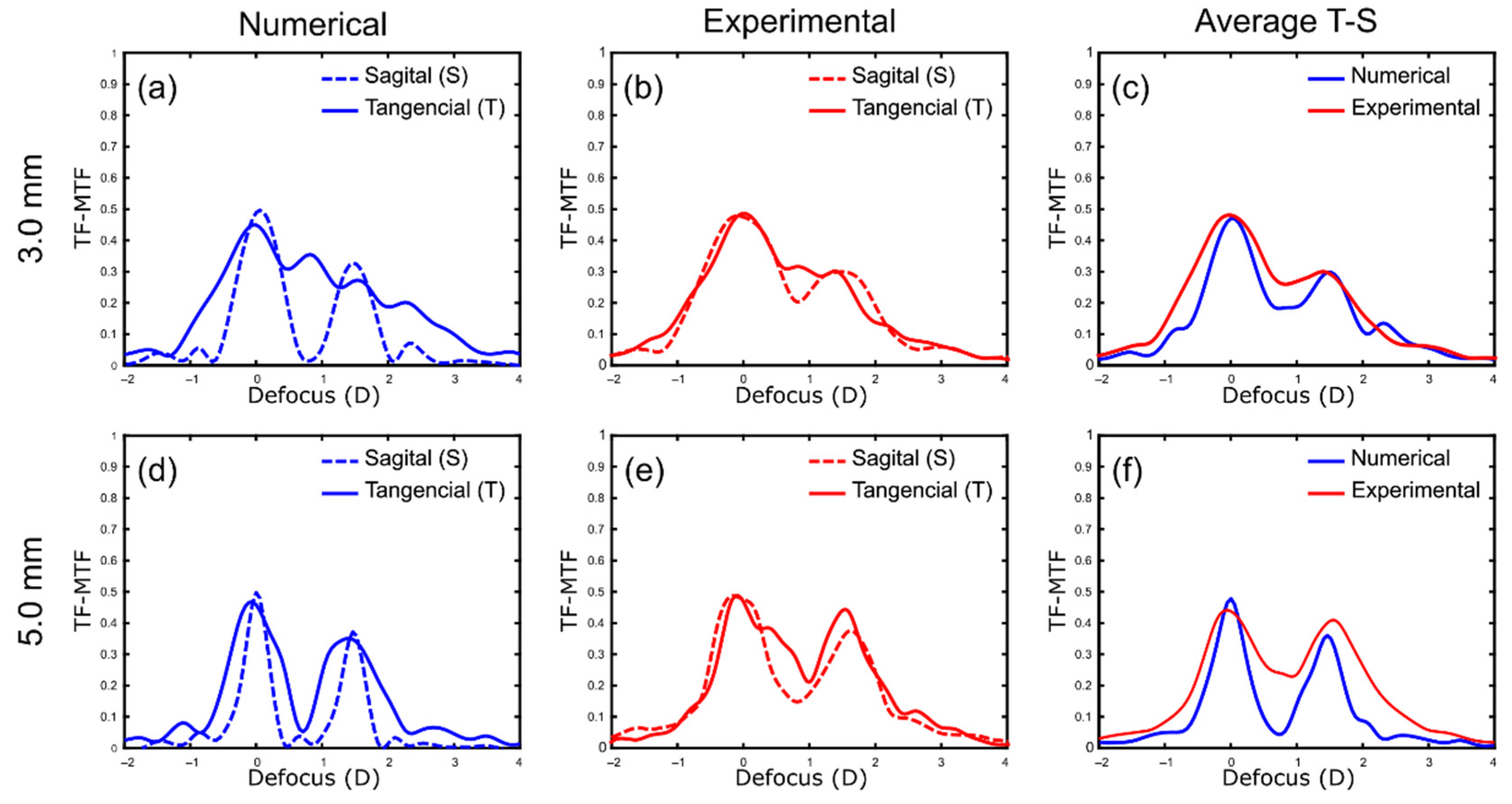
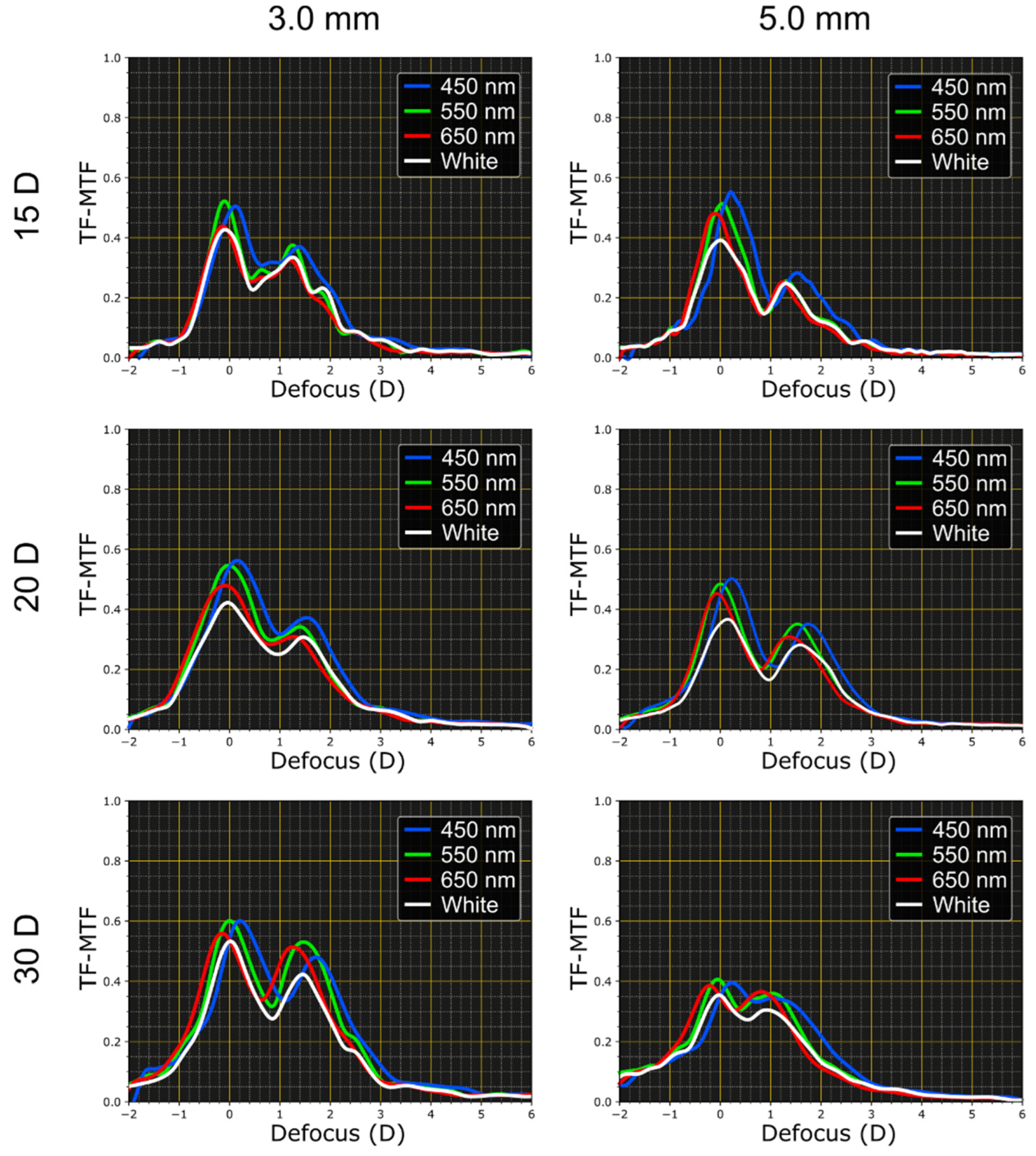
3. Results
TF-MTF Curves. Numerical vs. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacRae, S.; Holladay, J.T.; Glasser, A.; Calogero, D.; Hilmantel, G.; Masket, S.; Stark, W.; Tarver, M.E.; Nguyen, T.; Eydelman, M. Special Report: American Academy of Ophthalmology Task Force Consensus Statement for Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilbao-Calabuig, R.; Gónzalez-López, F.; Llovet-Rausell, A.; Ortega-Usobiaga, J.; Fernández, V.T.; Llovet-Osuna, F. Lens-based surgical correction of presbyopia. Where are we in 2020? Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2021, 96, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Bueno, F.; Garzón, N.; Vega, F.; Poyales, F.; Millán, M. Patient-Perceived and Laboratory-Measured Halos Associated with Diffractive Bifocal and Trifocal Intraocular Lenses. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vounotrypidis, E.; Diener, R.; Wertheimer, C.; Kreutzer, T.; Wolf, A.; Priglinger, S.; Mayer, W.J. Bifocal nondiffractive intraocular lens for enhanced depth of focus in correcting presbyopia: Clinical evaluation. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2017, 43, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, W.S. Visual Outcome and Patient Satisfaction of Low-Power-Added Multifocal Intraocular Lens. Eye Contact Lens Sci. Clin. Pract. 2018, 44, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrotti, E.; Mastropasqua, R.; Bonetto, J.; Demasi, C.; Aiello, F.; Nucci, C.; Mariotti, C.; Marchini, G. Quality of vision, patient satisfaction and long-term visual function after bilateral implantation of a low addition multifocal intraocular lens. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 38, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshika, T.; Arai, H.; Fujita, Y.; Inamura, M.; Inoue, Y.; Noda, T.; Miyata, K. One-year clinical evaluation of rotationally asymmetric multifocal intraocular lens with +1.5 diopters near addition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Lyu, D.; Shentu, X.; Xv, W.; Chen, P.; Ke, Y. Visual outcome and optical quality after implantation of zonal refractive multifocal and extended-range-of-vision IOLs: A prospective comparison. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, S.; Bradley, A.; Thibos, L.N. Chromatic aberration and polychromatic image quality with diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2014, 40, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.S.; Vega, F. Extended depth of focus intraocular lens: Chromatic performance. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4294–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loicq, J.; Willet, N.; Gatinel, D. Topography and longitudinal chromatic aberration characterizations of refractive–diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, M.S.; Vega, F. Through-Focus Energy Efficiency and Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration of Three Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagud-Martínez, D.; Ferrando, V.; Martínez-Espert, A.; Garcia-Delpech, S.; Monsoriu, J.A.; Furlan, W.D. In Vitro Chromatic Performance of Three Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses with Different Optical Designs. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.; Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Jaskulski, M.; Hong, X.; Brink, N.; Van Noy, S. The Impact of IOL Abbe Number on Polychromatic Image Quality of Pseudophakic Eyes. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Mainster, M.A. The effect of chromatic dispersion on pseudophakic optical performance. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zapata-Díaz, J.F.; Rodríguez-Izquierdo, M.A.; Ould-Amer, N.; Lajara-Blesa, J.; López-Gil, N. Total Depth of Focus of Five Premium Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, A.; Remón, L.; Martos, J.; Furlan, W.D.; Monsoriu, J.A. Imaging quality of multifocal intraocular lenses: Automated assessment setup. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2013, 33, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11979-2; International Standard, Ophthalmic Implants-Intraocular Lenses-Part 2: Optical Properties and Test Methods. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Artal, P.; Manzanera, S.; Piers, P.; Weeber, H. Visual effect of the combined correction of spherical and longitudinal chromatic aberrations. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furlan, W.D.; Remón, L.; Llorens, C.; Rodriguez-Vallejo, M.; Monsoriu, J.A. Comparison of two different devices to assess intraocular lenses. Ophthalmology 2016, 127, 10108–10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darian-Smith, E.; Versace, P. Visual performance and positional stability of a capsulorhexis-fixated extended depth-of-focus intraocular lens. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Plaza-Puche, A.B.; Javaloy, J.; Ayala, M.J.; Moreno, L.J.; Piñero, D.P. Comparison of a New Refractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens with an Inferior Segmental Near Add and a Diffractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Yuan, X.; Tang, X. Effects of intraocular lenses with different diopters on chromatic aberrations in human eye models. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Dorronsoro, C.; Marcos, S. Differences in visual quality with orientation of a rotationally asymmetric bifocal intraocular lens design. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2016, 42, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Base Power | 15 D | 20 D | 30 D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupil diameter | 3.0 mm | 5.0 mm | 3.0 mm | 5.0 mm | 3.0 mm | 5.0 mm |
| 0.0 D | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.54 |
| 1.5 D | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, S.; Salvá, L.; García-Delpech, S.; Martínez-Espert, A.; Ferrando, V.; Montagud-Martínez, D. Polychromatic Assessment of a Refractive Segmented EDOF Intraocular Lens. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061480
García S, Salvá L, García-Delpech S, Martínez-Espert A, Ferrando V, Montagud-Martínez D. Polychromatic Assessment of a Refractive Segmented EDOF Intraocular Lens. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(6):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061480
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Scott, Luís Salvá, Salvador García-Delpech, Anabel Martínez-Espert, Vicente Ferrando, and Diego Montagud-Martínez. 2022. "Polychromatic Assessment of a Refractive Segmented EDOF Intraocular Lens" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 6: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061480
APA StyleGarcía, S., Salvá, L., García-Delpech, S., Martínez-Espert, A., Ferrando, V., & Montagud-Martínez, D. (2022). Polychromatic Assessment of a Refractive Segmented EDOF Intraocular Lens. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(6), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11061480






