Clinical Outcomes of Shunting in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Guidelines
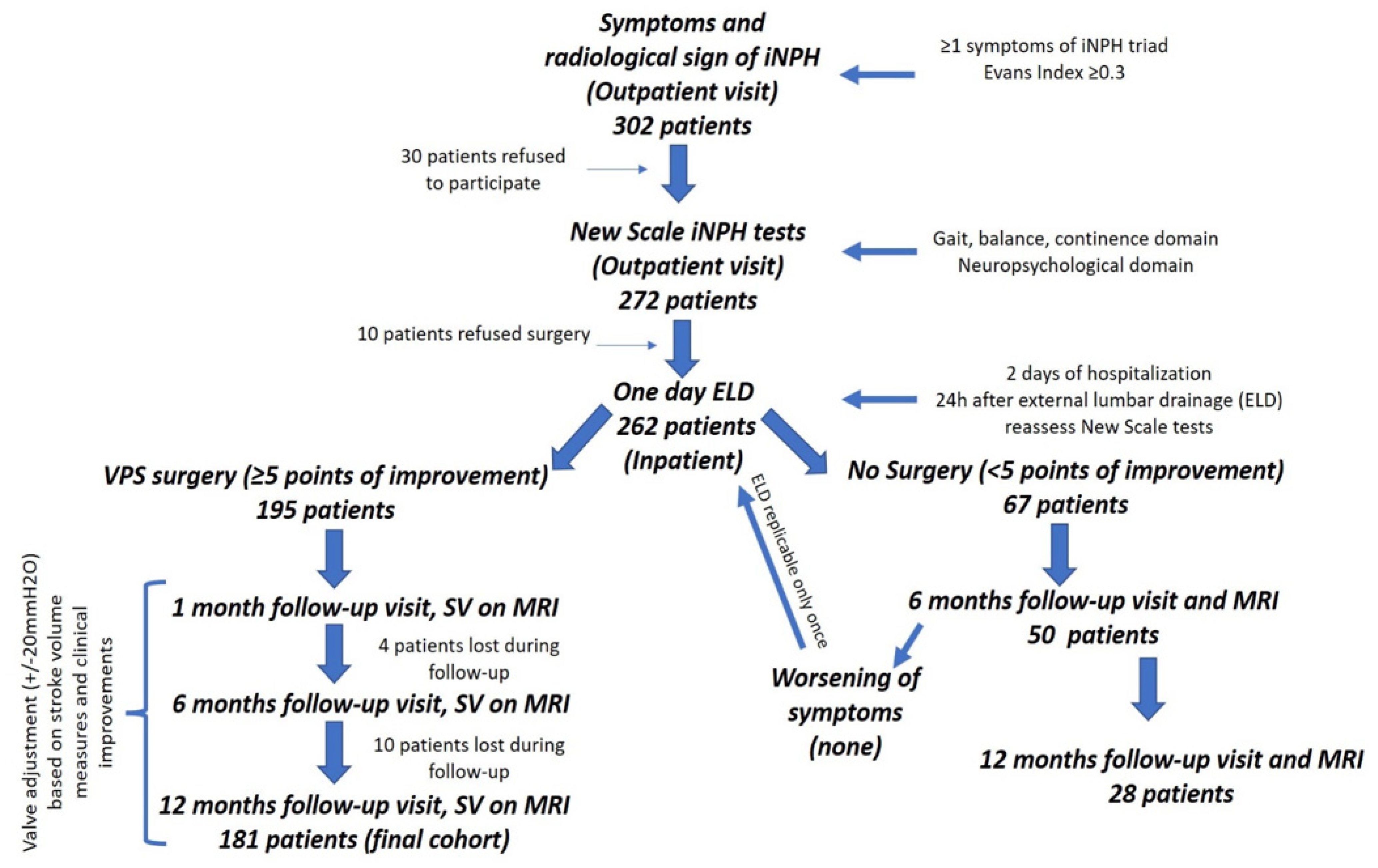
2.2. Patients’ Population
2.3. Clinical Outcomes
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographical and Surgical Data
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
3.3. Valve Pressure Setting
3.4. Complications and Reoperation Rate
3.5. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hakim, S.; Adams, R.D. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J. Neurol. Sci. 1965, 2, 272–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andren, K.; Wikkelso, C.; Tisell, M.; Hellstrom, P. Natural course of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallia, G.L.; Rigamonti, D.; Williams, M.A. The diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanneste, J.A. Diagnosis and management of normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. 2000, 247, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebb, A.O.; Cusimano, M.D. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A systematic review of diagnosis and outcome. Neurosurgery 2001, 49, 1166–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalj, M.; Dolić, K.; Kolić, K.; Ledenko, V. CSF tap test—Obsolete or appropriate test for predicting shunt responsiveness? A systemic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 362, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, M.; Kristensen, B.; Karlsson, T.; Fagerlund, M.; Elfverson, J.; Ekstedt, J. The predictive value of cerebrospinal fluid dynamic tests in patients with the idiopathic adult hydrocephalus syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 1995, 52, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, A.; Kazui, H.; Miyoshi, N.; Hashimoto, M.; Ohkawa, S.; Tokunaga, H.; Ikejiri, Y.; Takeda, M. Cognitive impairment in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2006, 21, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnet, A.; Schmitt, A.; Dufour, H.; Giorgi, R.; Grisoli, F. Differential patterns of cognitive impairment in patients with aqueductal stenosis and normal pressure. Acta Neurochir. 2004, 146, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, P.; Edsbagge, M.; Archer, T.; Tisell, M.; Tullberg, M.; Wikkelsø, C. The neuropsychology of patients with clinically diagnosed idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, P.; Hellström, P.; Tans, J.; Wikkelsø, C.; European iNPH Multicentre Study Group. One-year outcome in the European multicentre study on iNPH. European iNPH Multicentre Study Group. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikkelsø, C.; Hellström, P.; Klinge, P.M.; Tans, J.T.J.; European iNPH Multicentre Study Group. European iNPH Multicentre Study Group, the European iNPH Multicentre Study on the predictive values of resistance to CSF outflow and the CSF Tap Test in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsneider, M.; Black, P.M.; Klinge, P.; Marmarou, A.; Relkin, N. Surgical management of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, S29–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savolainen, S.; Hurskainen, H.; Paljärvi, L.; Alafuzoff, I.; Vapalahti, M. Five-year outcome of normal pressure hydrocephalus with or without a shunt: Predictive value of the clinical signs, neuropsychological evaluation and infusion test. Acta Neurochir. 2002, 144, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, M.J.; Woodworth, G.; Coon, A.L.; Thomas, G.; Williams, M.A.; Rigamonti, D. Diagnosis, treatment, and analysis of long-term outcomes in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, G.; Palandri, G.; Ferrari, A.; Oppi, F.; Milletti, D.; Albini-Riccioli, L.; Mantovani, P.; Magnoni, S.; Chiari, L.; Cortelli, P.; et al. A prospective evaluation of clinical and instrumental features before and after ventriculo-peritoneal shunt in patients with idiopathic Normal pressure hydrocephalus: The Bologna PRO-Hydro study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 66, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmarou, A.; Young, H.F.; Aygok, G.A.; Sawauchi, S.; Tsuji, O.; Yamamoto, T.; Dunbar, J. Diagnosis and management of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: A prospective study in 151 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudo, K.I.; Nemir, J.; Pavliša, G.; Mrak, G.; Bilić, E.; Borovečki, F. Management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH)—A retrospective study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 34, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.; Everingham, E.; Mahant, N.; Jacobson, E.; Owler, B. Clinical outcomes in the surgical treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 29, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, A.K.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Stapleton, S.; Kitchen, N.D.; Watkins, L.D. Systematic review of the outcome of shunt surgery in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1977–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavarajasingam, S.G.; El-Khatib, M.; Rea, M.; Russo, S.; Lemcke, J.; Al-Nusair, L.; Vajkoczy, P. Clinical predictors of shunt response in the diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 2641–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahr, C.V.; Dengl, M.; Nestler, U.; Reiss-Zimmermann, M.; Eichner, G.; Preuß, M.; Meixensberger, J. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Diagnostic and predictive value of clinical testing, lumbar drainage, and CSF dynamics. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poca, M.A.; Sahuquillo, J.; Barba, M.A.; Añez, J.D.; Arikan, F. Prospective study of methodological issues in intracranial pressure monitoring in patients with hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poca, M.A.; Solana, E.; Martínez-Ricarte, F.R.; Romero, M.; Gándara, G.; Sahuquillo, J. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Results of a prospective cohort of 236 shunted patients. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2012, 114, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradley, W.G.; Scalzo, D.; Queralt, J.; Nitz, W.N.; Atkinson, D.J.; Wong, P. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Evaluation with cerebrospinal fluid flow measurements at MR imaging. Radiology 1996, 198, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellström, P.; Klinge, P.; Tans, J.; Wikkelsø, C. A new scale for assessment of severity and outcome in iNPH. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallina, P.; Lastrucci, G.; Caini, S.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Porfirio, B.; Scollato, A. Accuracy and safety of 1-day external lumbar drainage of CSF for shunt selection in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scollato, A.; Trungu, S.; Forcato, S.; Ricciardi, L.; Miscusi, M.; Gallina, P.; Raco, A. Fenestration of peritoneal catheter to avoid abdominal pseudocyst formation after ventriculoperitoneal shunts: A technical note. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2021, 82, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordan, E.; Palandri, G.; Lanzino, G.; Murad, M.H.; Elder, B.D. Outcomes and complications of different surgical treatments for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krahulik, D.; Vaverka, M.; Hrabalek, L.; Hampl, M.; Halaj, M.; Jablonsky, J.; Langova, K. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt in treating of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus-single-center study. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, S.; Moran, D.; Hung, A.; Elder, B.D.; Jeon, L.; Fialho, H.; Sankey, E.W.; Jusué-Torres, I.; Goodwin, C.R.; Lu, J.; et al. Timing of surgical treatment for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Association between treatment delay and reduced short-term benefit. Neurosurg Focus. 2016, 41, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scollato, A.; Gallina, P.; Gautam, B.; Pellicanò, G.; Cavallini, C.; Tenenbaum, R.; Di Lorenzo, N. Changes in aqueductal CSF stroke volume in shunted patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchorska, B.; Kunz, M.; Schniepp, R.; Jahn, K.; Goetz, C.; Tonn, J.C.; Peraud, A. Optimized surgical treatment for normal pressure hydrocephalus: Comparison between gravitational and differential pressure valves. Acta Neurochir. 2015, 157, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.F.; Saad, F.; Reis, R.C.; Rota, J.M.; Pinto, F.C.G. Programmable valve represents an efficient and safe tool in the treatment of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus patients. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2013, 71, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemcke, J.; Meier, U.; Muller, C.; Fritsch, M.J.; Kehler, U.; Langer, N.; Kiefer, M.; Eymann, R.; Schuhmann, M.U.; Speil, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of gravitational shunt valves in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A pragmatic, randomised, open label, multicentre trial (SVASONA). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gölz, L.; Ruppert, F.H.; Meier, U.; Lemcke, J. Outcome of modern shunt therapy in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus 6 years postoperatively. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelsson, H.; Larsson, J.; Eklund, A.; Malm, J. Risk factors, comorbidities, quality of life, and complications after surgery in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Review of the INPH-CRasH study. Neurosurg. Focus. 2020, 49, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feletti, A.; d’Avella, D.; Wikkelsø, C.; Klinge, P.; Hellstrom, P.; Tans, J.; Kiefer, M.; Meier, U.; Lemcke, J.; Paternò, V.; et al. Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Complications in the European Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Multicenter Study. Oper. Neurosurg. (Hagerstown) 2019, 17, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Israelsson, H.; Eklund, A.; Malm, J. Epilepsy, headache, and abdominal pain after shunt surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: The INPH-CRasH study. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollato, A.; Caini, S.; Angelini, L.; Lastrucci, G.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Porfirio, B.; Gallina, P. Aqueductal CSF stroke volume measurements may drive management of shunted idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Number of Patients | 181 |
| Mean age, years ± SD (range) Mean follow-up, months ± SD (range) | 73.6 ± 6.7 (59–86) 38.3 ± 17.3 (13–67) |
| Sex | |
| Female Male | 97 (53.6%) 84 (46.4%) |
| ASA classification | |
| I II III IV V | 0 44 (24.3%) 126 (69.6%) 11 (6.1%) 0 |
| Symptoms | |
| Gait disturbance Cognitive impairment Urinary incontinence Complete triad | 173 (95.6%) 158 (87.3%) 130 (71.8%) 128 (70.7%) |
| Preoperative duration of symptoms (median) | 21 months |
| Comorbidity | |
| Cardiovascular diseases Diabetes mellitus Obesity Respiratory diseases Smokers | 109 (60.2%) 57 (31.5%) 45 (24.9%) 39 (21.5%) 56 (30.9%) |
| MEAN ± SD | |
|---|---|
| Radiological signs on MRI | |
| Evans’ Index Stroke Volume | 0.39 ± 0.11 103.2 ± 25.4 |
| Nr. (%) | |
| Type of shunt system | |
| Codman–Hakim (Integra) Pro-Gav 2.0 (B. Braun) | 49 (27.1%) 132 (72.9%) |
| Nr. (range) | |
| Mean length of surgery ± SD (range) | 44 min ± 11.4 (30–90 min) |
| Mean length of hospital stay (range) | 2 days (2–5 days) |
| Mean time of postoperative mobilization | 1 day (1–3 days) |
| Intraoperative blood loss ± SD (range) | 60 mL ± 16.5 (40–110 mL) |
| MEAN ± SD | |
|---|---|
| Gait domain | |
| Preoperative | 58.5 ± 14.3 |
| Postoperative | 66.0 ± 12.2 |
| Follow-up at 12 months | 70.1 ± 13.4 |
| p-value (pre vs. follow-up) | <0.001 |
| Balance domain | |
| Preoperative | 66.7 ± 21.5 |
| Postoperative | 72.4 ± 19.2 |
| Follow-up at 12 months | 71.7 ± 22.1 |
| p-value (pre vs. follow-up) | 0.001 |
| Neuropsychological domain | |
| Preoperative | 57.0 ± 12.0 |
| Postoperative | 62.0 ± 10.3 |
| Follow-up at 12 months | 60.2 ± 13.0 |
| p-value (pre vs. follow-up) | 0.011 |
| Continence domain | |
| Preoperative | 69.9 ± 20.5 |
| Postoperative | 78.3 ± 18.2 |
| Follow-up at 12 months | 76.0 ± 20.0 |
| p-value (pre vs. follow-up) | 0.002 |
| Nr. (%) | |
|---|---|
| Complications | |
| Subdural hematoma/hygroma | 8 (4.4%) |
| Ischemic/hemorrhage | 2 (1.1%) |
| Infection | 2 (1.1%) |
| Incisional hernia | 4 (2.2%) |
| Overall complication rate | 8.8% |
| Reoperation rate | |
| Shunt malfunctioning Incisional hernia | 17 (9.4%) 4 (2.2%) |
| Risk Factors | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | CI 95% | p-Value | OR | CI 95% | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.094 | (1.034–1.157) | 0.071 | |||
| Sex | 0.896 | (0.248–3.245) | 0.817 | |||
| Stroke volume | 1.405 | (1.198–1.647) | <0.001 | 1.463 | (1.227–1.719) | 0.0001 |
| Evans index | 1.143 | (1.037–1.219 | 0.01 | |||
| Preoperative symptoms | 1.452 | (1.271–1.741) | <0.001 | 1.265 | (1.028–1.557) | 0.037 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trungu, S.; Scollato, A.; Ricciardi, L.; Forcato, S.; Polli, F.M.; Miscusi, M.; Raco, A. Clinical Outcomes of Shunting in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051286
Trungu S, Scollato A, Ricciardi L, Forcato S, Polli FM, Miscusi M, Raco A. Clinical Outcomes of Shunting in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(5):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051286
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrungu, Sokol, Antonio Scollato, Luca Ricciardi, Stefano Forcato, Filippo Maria Polli, Massimo Miscusi, and Antonino Raco. 2022. "Clinical Outcomes of Shunting in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 5: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051286
APA StyleTrungu, S., Scollato, A., Ricciardi, L., Forcato, S., Polli, F. M., Miscusi, M., & Raco, A. (2022). Clinical Outcomes of Shunting in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(5), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051286









