Pain Course after Total Knee Arthroplasty within a Standardized Pain Management Concept: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
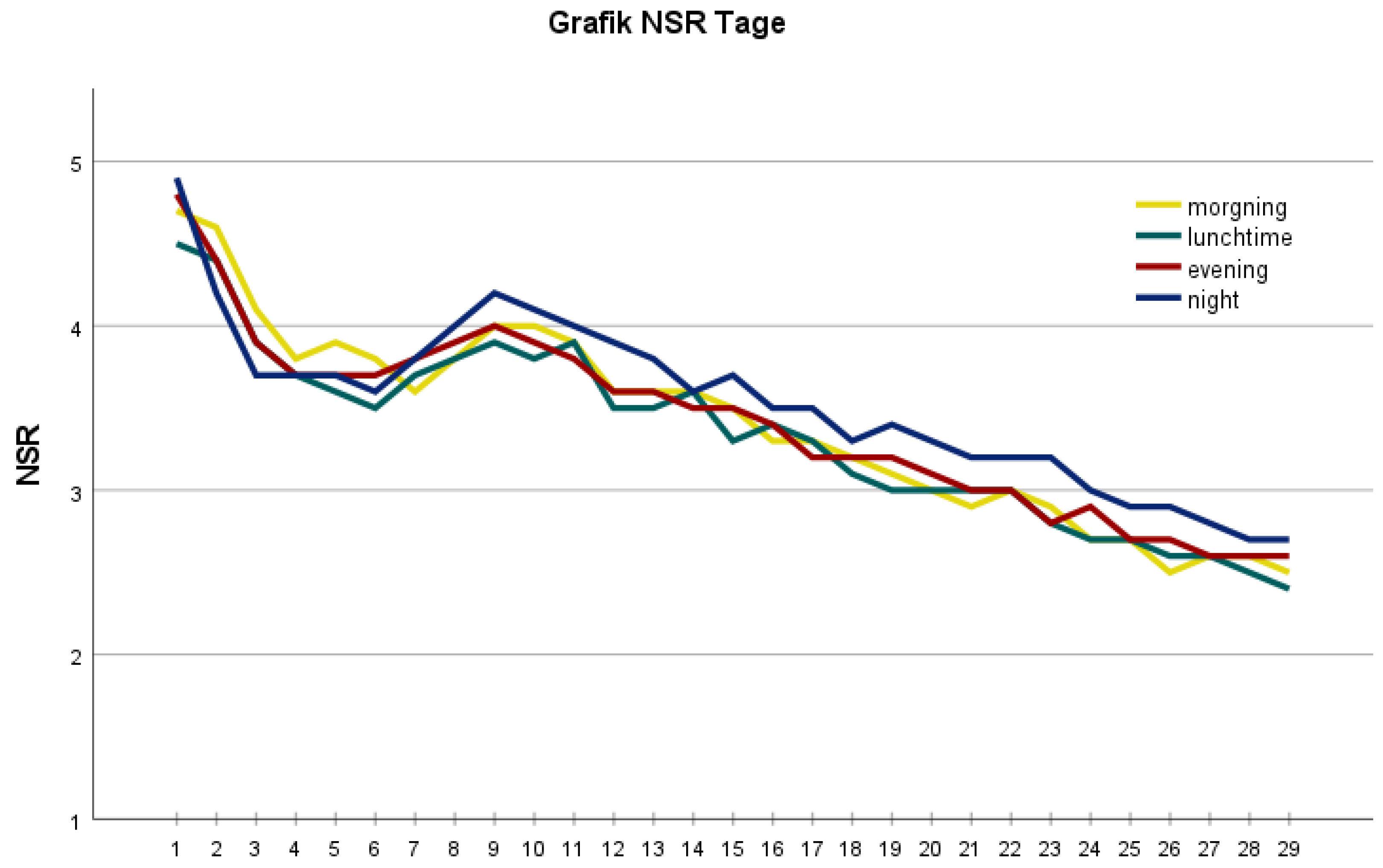
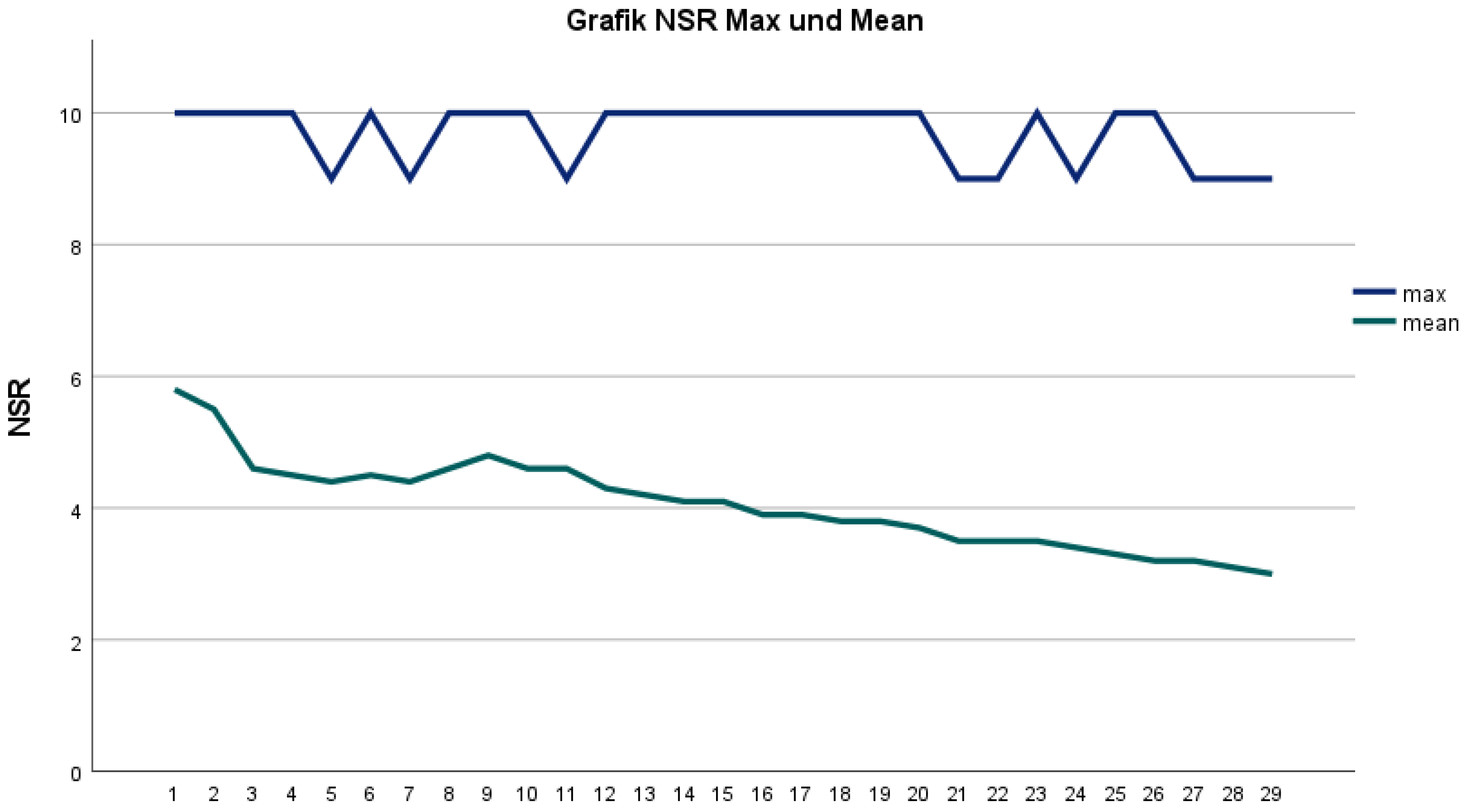
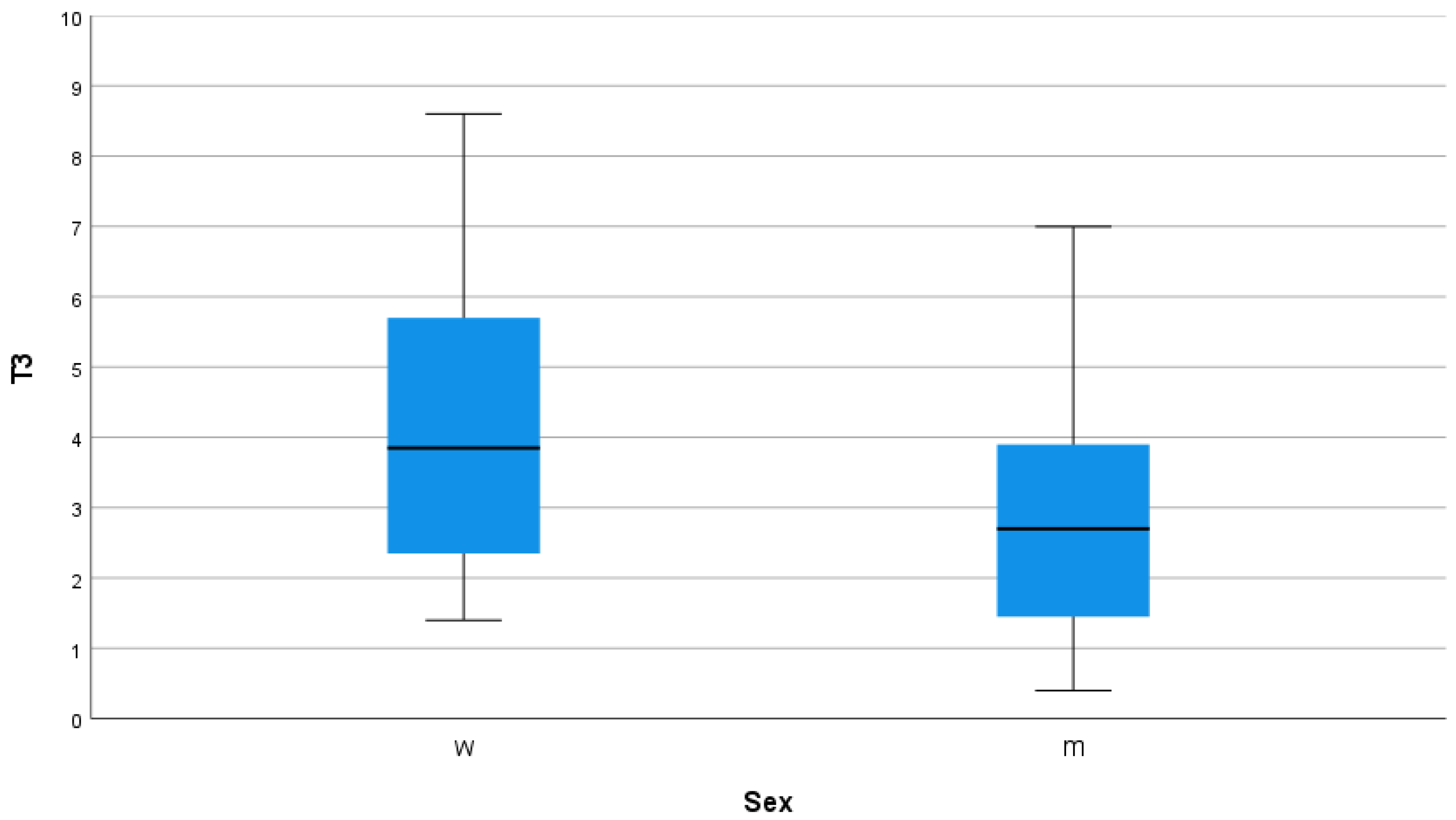
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Postoperative Pain Course
4.2. Gender of the Patient
4.3. BMI at Surgery
4.4. Age at Surgery
4.5. Operation Type
4.6. Perioperative Factors
4.7. Radiological Parameters
4.8. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, A.J.; Robertsson, O.; Graves, S.; Price, A.J.; Arden, N.K.; Judge, A.; Beard, D.J. Knee replacement. Lancet 2018, 392, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, M.; Lau, E.; Kurtz, S.M.; Alt, V. Projections of Primary TKA and THA in Germany from 2016 through 2040. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavand’homme, P.M.; Grosu, I.; France, M.N.; Thienpont, E. Pain trajectories identify patients at risk of persistent pain after knee arthroplasty: An observational study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylde, V.; Beswick, A.; Bruce, J.; Blom, A.; Howells, N.; Gooberman-Hill, R. Chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2018, 3, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmelink, K.E.M.; Dandis, R.; der Van der Wees Pj, P.J.; Zeegers, A.V.C.M.; der Sanden, M.W.; Staal, J.B. Recovery trajectories over six weeks in patients selected for a high-intensity physiotherapy program after Total knee Arthroplasty: A latent class analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021, 22, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insall, J.N.; Dorr, L.D.; Scott, R.D.; Scott, W.N. Rationale of the Knee Society Clinical Rating System. Available online: http://www.orthopaedicscore.com/scorepages/knee_society_score.html (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Benditz, A.; Drescher, J.; Greimel, F.; Zeman, F.; Grifka, J.; Meißner, W.; Völlner, F. Implementing a benchmarking and feedback concept decreases postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty: A prospective study including 256 patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benditz, A.; Völlner, F.; Baier, C.; Götz, J.; Grifka, J.; Keshmiri, A. Schmerzverlauf nach operativer orthopädischer Intervention: Charakterisierung am Beispiel der Knieendoprothetik. Schmerz 2016, 30, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greimel, F.; Dittrich, G.; Schwarz, T.; Kaiser, M.; Krieg, B.; Zeman, F.; Grifka, J.; Benditz, A. Course of pain after total hip arthroplasty within a standardized pain management concept: A prospective study examining influence, correlation, and outcome of postoperative pain on 103 consecutive patients. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2018, 138, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.A.; Kluger, M.T.; McNair, P.J.; Lewis, G.N.; Somogyi, A.A.; Borotkanics, R.; Barratt, D.T.; Walker, M. Persistent postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study of potential risk factors. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, R.; Nishigami, T.; Kubo, T.; Ishigaki, T.; Yonemoto, Y.; Mibu, A.; Morioka, S.; Fujii, T. Using a postoperative pain trajectory to predict pain at 1 year after total knee arthroplasty. Knee 2021, 32, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, M.; Schreiber, K.L.; Martel, M.O.; Cornelius, M.; Campbell, C.M.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Smith, M.T.; Wright, J.; Aglio, L.S.; Edwards, R.R. Sex differences in negative affect and postoperative pain in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Biol. Sex Differ. 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lee, M.; Chong, H.C.; Ning, Y.; Lo, N.N.; Yeo, S.J. Reasons and Factors Behind Post-Total Knee Arthroplasty Dissatisfaction in an Asian Population. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2017, 46, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissolio, L.; Sabatini, L.; Risitano, S.; Bistolfi, A.; Galluzzo, U.; Massè, A.; Indelli, P.F. Is It the Surgeon, the Patient, or the Device? A Comprehensive Clinical and Radiological Evaluation of Factors Influencing Patient Satisfaction in 648 Total Knee Arthroplasties. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götz, J.S.; Benditz, A.; Reinhard, J.; Schindler, M.; Zeman, F.; Grifka, J.; Greimel, F.; Leiss, F. Influence of Anxiety/Depression, Age, Gender and ASA on 1-Year Follow-Up Outcomes Following Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in 5447 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartley, E.J.; Fillingim, R.B. Sex differences in pain: A brief review of clinical and experimental findings. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peteler, R.; Schmitz, P.; Loher, M.; Jansen, P.; Grifka, J.; Benditz, A. Sex-Dependent Differences in Symptom-Related Disability Due to Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsley, B.S.; Bertolusso, R.; Harrington, M.; Brekke, A.; Noble, P.C. Influence of gender on age of treatment with TKA and functional outcome. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, C. Body mass index and risk of knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, I.N.; Kemp, J.L.; Crossley, K.M.; Culvenor, A.G.; Hinman, R.S. Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis Affects Younger People, too. J. Orthop. Sports. Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, G.B.M.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Haftenberger, M.; Lampert, T.; Ziese, T.; Scheidt-Nave, C. Übergewicht und Adipositas in Deutschland: Ergebnisse der Studie zur Gesundheit Erwachsener in Deutschland (DEGS1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2013, 56, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasso, M.; Corona, K.; Gomberg, B.; Marullo, M. Obesity increases the risk of conversion to total knee arthroplasty after unicompartimental knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2021, 30, 3945–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Lo, N.N.; Chong, H.C.; Pang, H.N.; Tay, D.K.J.; Chia, S.L.; Yeo, S.J. The influence of body mass index on functional outcome and quality of life after total knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesinger, K.; Giesinger, J.M.; Hamilton, D.F.; Rechsteiner, J.; Ladurner, A. Higher body mass index is associated with larger postoperative improvement in patient-reported outcomes following total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021, 22, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.W.T.; Suh, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Liow, M.H.L.; Allen, J.C.; Lo, N.N.; Koh, J.S.B. Early Postoperative Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Associated with Subsequent Poorer Functional Outcomes and Lower Satisfaction. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cip, J.; Obwegeser, F.; Benesch, T.; Bach, C.; Ruckenstuhl, P.; Martin, A. Twelve-Year Follow-Up of Navigated Computer-Assisted Versus Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Comparative Trial. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.G.; Bernhard, Z.; Acuña, A.J.; Wu, V.S.; Kamath, A.F. Use of intraoperative technology in total knee arthroplasty is not associated with reductions in postoperative pain. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, J.-S. The Clinical Outcome of Computer-Navigated Compared with Conventional Knee Arthroplasty in the Same Patients: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Long-Term Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petursson, G.; Fenstad, A.M.; Gøthesen, Ø.; Dyrhovden, G.S.; Hallan, G.; Röhrl, S.M.; Aamodt, A.; Furnes, O. Computer-Assisted Compared with Conventional Total Knee Replacement: A Multicenter Parallel-Group Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benditz, A.; Maderbacher, G.; Zeman, F.; Grifka, J.; Weber, M.; von Kunow, F.; Greimel, F.; Keshmiri, A. Postoperative pain and patient satisfaction are not influenced by daytime and duration of knee and hip arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2017, 137, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, E.P.; Su, S. Strategies for reducing peri-operative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Yu, Z.-P.; Liu, L.X.; Chen, C.; Meng, W.K.; Zeng, W.N. The antifibrinolytic and anti-inflammatory effects of multiple doses of oral tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, K.; Pei, F.X.; Zhou, Z.K. Oral vs Intravenous vs Topical Tranexamic Acid in Primary Hip Arthroplasty: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappiello, G.; Camarda, L.; Pulito, G.; Tarantino, A.; Martino, D.D.; Russi, V.; Stramazzo, L.; Ragusa, C.; Guarino, G.; Ripani, U. Continuous Femoral Catheter for Postoperative Analgesia After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Med. Arch. 2020, 74, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascarella, G.; Costa, F.; Del Buono, R.; Strumia, A.; Cataldo, R.; Agrò, F.; Carassiti, M. The para-sartorial compartments (PASC) block: A new approach to the femoral triangle block for complete analgesia of the anterior knee. Anaesth. Rep. 2022, 10, e12165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, I.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, M.S.; Koh, H.J.; Kang, M.S.; In, Y. Femoral Nerve Block versus Adductor Canal Block for Analgesia after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2017, 29, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazarian, G.S.; Anthony, C.A.; Lawrie, C.M.; Barrack, R.L. The Impact of Psychological Factors and Their Treatment on the Results of Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2021, 103, 1744–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-Y.; Li, L.-L.; Wang, D. Preoperative sleep quality affects postoperative pain and function after total joint arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.-C.; Xu, B.; Liang, Z.-M.; Wang, H.Y.; Luo, Z.Y.; Zhou, Z.K. Limited Influence of Comorbidities on Length of Stay after Total Hip Arthroplasty: Experience of Enhanced Recovery after Surgery. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranawat, A.S.; Ranawat, C.S.; Elkus, M.; Rasquinha, V.J.; Rossi, R.; Babhulkar, S. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2005, 87 (Suppl. 1), 271–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Xie, J.; Xu, B.; Cao, G.; Pei, F. Factors influencing postoperative length of stay in an enhanced recovery after surgery program for primary total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlenberg, C.A.; Trivellas, M.; Lee, Y.Y.; Padgett, D.E. Preoperative Valgus Alignment Does Not Predict Inferior Outcome of Total Knee Arthroplasty. HSS J. 2018, 14, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Predictor | B (95% CI) | p-Value | R2 Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| T1 | −0.999 (−1.84, −0.16) | 0.020 | −0.257 |
| T2 | −1.548 (−2.41, −0.69) | 0.001 | −0.375 |
| T3 | −1.417 (−2.23, −0.61) | 0.001 | −0.362 |
| Age | |||
| T1 | −0.026 (−0.08,0.02) | 0.280 | −0.118 |
| T2 | −0.026 (−0.08, 0.02) | 0.290 | −0.112 |
| T3 | −0.027 (−0.07, 0.02) | 0.250 | −0.121 |
| BMI | |||
| T1 | −0.105 (−0.19, −0.03) | 0.010 | −0.309 |
| T2 | −0.124 (−0.21, −0.04) | 0.003 | −0.343 |
| T3 | −0.120 (−0.20, −0.04) | 0.003 | −0.349 |
| ASA Score | |||
| T1 | 0.311 (−0.44,1.06) | 0.409 | 0.089 |
| T2 | 0.669 (−0.09,1.43) | 0.085 | 0.180 |
| T3 | 0.589 (−0.13,1.31) | 0.110 | 0.166 |
| Surgical duration | |||
| T1 | 0.004 (−0.02,0.03) | 0.768 | 0.035 |
| T2 | 0.017 (−0.01,0.04) | 0.166 | 0.158 |
| T3 | 0.014 (−0.01,0.04) | 0.236 | 0.134 |
| Paincatheter duration | |||
| T1 | 0.026 (−0.50, 0.56) | 0.922 | 0.010 |
| T2 | 0.251 (−0.29, 0.79) | 0.359 | 0.087 |
| T3 | 0.203 (−0.31,0.71) | 0.432 | 0.075 |
| Previous surgery | |||
| T1 | 0.037 (−0.85, 0.92) | 0.935 | 0.009 |
| T2 | −0.413 (−1.31, 0.49) | 0.366 | −0.091 |
| T3 | −0.303 (−1.16, 0.55) | 0.483 | −0.071 |
| Operation type | |||
| T1 | 0.387 (−0.39, 1.17) | 0.328 | 0.097 |
| T2 | 0.377 (−0.45, 1.21) | 0.369 | 0.089 |
| T3 | 0.380 (−0.41, 1.17) | 0.340 | 0.095 |
| Anatomical axis 1 | |||
| T1 | 0.065 (0.01, 0.12) | 0.020 | 0.240 |
| T2 | 0.062 (0.01, 0.12) | 0.030 | 0.215 |
| T3 | 0.061 (0.01,0.11) | 0.022 | 0.226 |
| Anatomical axis 2 | |||
| T1 | 0.026 (−0.09, 0.14) | 0.648 | 0.044 |
| T2 | 0.008 (−0.11, 0.12) | 0.888 | 0.013 |
| T3 | 0.014 (−0.09, 0.12) | 0.794 | 0.024 |
| KSS 1 | |||
| T1 | 0.011 (−0.01,0.04) | 0.378 | 0.086 |
| T2 | −0.004 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.733 | −0.032 |
| T3 | −0.001 (−0.03,0.02) | 0.961 | −0.005 |
| FS 1 | |||
| T1 | −0.002 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.897 | −0.014 |
| T2 | −0.006 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.666 | −0.046 |
| T3 | −0.005 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.694 | −0.042 |
| KSS 2 | |||
| T1 | −0.027 (−0.06, 0.00) | 0.055 | −0.231 |
| T2 | −0.027 (−0.06, 0.00) | 0.064 | −0.214 |
| T3 | −0.027 (−0.05, 0.00) | 0.051 | −0.225 |
| FS 2 | |||
| T1 | −0.012 (−0.05, 0.02) | 0.476 | −0.073 |
| T2 | −0.018 (−0.05, 0.02) | 0.292 | −0.104 |
| T3 | −0.016 (−0.05, 0.02) | 0.319 | −0.098 |
| KSS 3 | |||
| T1 | −0.007 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.612 | −0.060 |
| T2 | −0.008 (−0.04, 0.02) | 0.577 | −0.064 |
| T3 | −0.008 (−0.03, 0.02) | 0.549 | −0.068 |
| FS 3 | |||
| T1 | 0.009 (−0.03, 0.05) | 0.655 | 0.052 |
| T2 | 0.022 (−0.02, 0.06) | 0.276 | 0.122 |
| T3 | 0.019 (−0.02, 0.06) | 0.326 | 0.109 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schindler, M.; Schmitz, S.; Reinhard, J.; Jansen, P.; Grifka, J.; Benditz, A. Pain Course after Total Knee Arthroplasty within a Standardized Pain Management Concept: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237204
Schindler M, Schmitz S, Reinhard J, Jansen P, Grifka J, Benditz A. Pain Course after Total Knee Arthroplasty within a Standardized Pain Management Concept: A Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237204
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchindler, Melanie, Stephanie Schmitz, Jan Reinhard, Petra Jansen, Joachim Grifka, and Achim Benditz. 2022. "Pain Course after Total Knee Arthroplasty within a Standardized Pain Management Concept: A Prospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237204
APA StyleSchindler, M., Schmitz, S., Reinhard, J., Jansen, P., Grifka, J., & Benditz, A. (2022). Pain Course after Total Knee Arthroplasty within a Standardized Pain Management Concept: A Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7204. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237204





