Unconscious Conflict Adaptation of Heroin Abstainers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
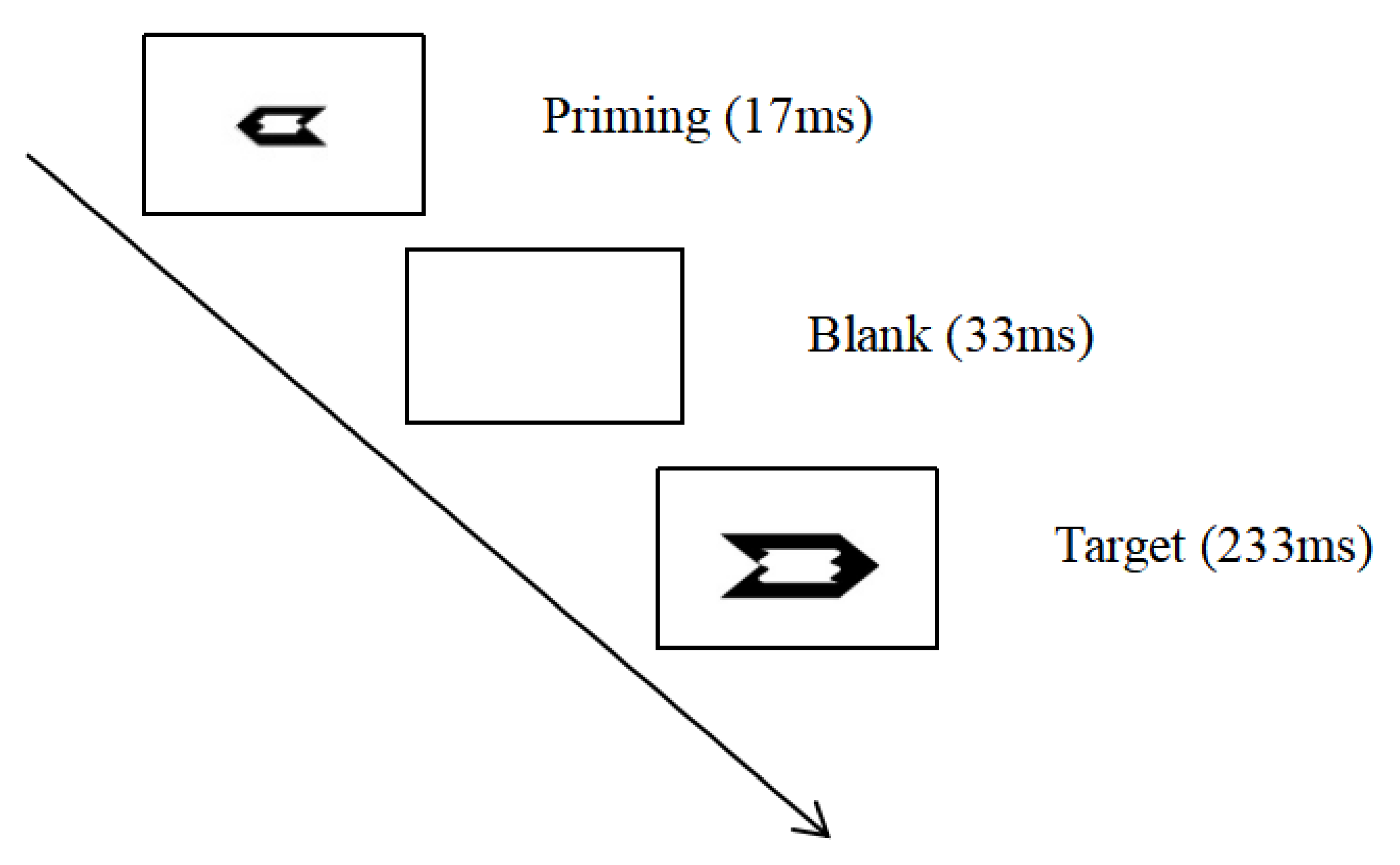
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Process
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Awareness of Primes
3.2. Emotional States and Drug Craving
3.3. Conflict Adaptation Reflected in RTs and Error Rates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gratton, G.; Coles, M.G.H.; Donchin, E. Optimizing the use of information: Strategic control of activation of responses. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1992, 121, 480–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerns, J.G. Anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex activity in an FMRI study of trial-to-trial adjustments on the Simon task. Neuroimage 2006, 33, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.J.; Kaufman, D.A.S.; Perlstein, W.M. Neural time course of conflict adaptation effects on the Stroop task. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notebaert, W.; Gevers, W.; Verbruggen, F.; Liefooghe, B. Top-down and bottom-up sequential modulations of congruency effects. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2006, 13, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notebaert, W.; Verguts, T. Conflict and error adaptation in the Simon task. Acta Psychol. 2010, 136, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, L.; Méndez, A. It is not what you expect: Dissociating conflict adaptation from expectancies in a Stroop task. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2012, 39, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayson, P.E.; Larson, M.J. Conflict adaptation and sequential trial effects: Support for the conflict monitoring theory. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, A. Conflict Adaptation Is Independent of Consciousness: Behavioral and ERP Evidence. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2014, 46, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo-Garcia, A.; Lopez-Torrecillas, F.; Gimenez, C.O.; Perez-Garcia, M. Clinical implications and methodological challenges in the study of the neuropsychological correlates of cannabis, stimulant, and opioid abuse. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2004, 14, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, W.-C.; Wang, Y.-R.; Huang, Y.-F.; Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Qin, W.; Yuan, K.; et al. Abnormal function of the posterior cingulated cortex in heroin addicted users during resting-state and drug-cue stimulation task. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Salo, R.; Nordahl, T.E.; Natsuaki, Y.; Leamon, M.H.; Galloway, G.P.; Waters, C.; Moore, C.D.; Buonocore, M.H. Attentional control and brain metabolite levels in methamphetamine abusers. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterosso, J.R.; Aron, A.R.; Cordova, X.; Xu, J.; London, E.D. Deficits in response inhibition associated with chronic methamphetamine abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2005, 79, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, R.R.; Sofuoglu, M.; Brede, E.; Robinson, C.; Waters, A.J. Attentional bias in opioid users: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 191, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, R.; Nordahl, T.E.; Buonocore, M.H.; Natsuaki, Y.; Waters, C.; Moore, C.D.; Galloway, G.P.; Leamon, M.H. Cognitive control and white matter callosal microstructure in methamphetamine-dependent subjects: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of drug-related cues on response inhibition through abstinence: A pilot study in male heroin abstainers. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2017, 43, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, R.; Fassbender, C.; Buonocore, M.H.; Ursu, S. Behavioral regulation in methamphetamine abusers: An fMRI study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2013, 211, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, D.; Zhang, H. Conflict Adaptation of Long-term Heroin Abstainers: Evidence from the ERPs. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 2017, 25, 814–819. [Google Scholar]
- Botvinick, M.M.; Nystrom, L.E.; Fissell, K.; Carter, C.S.; Cohen, J.D. Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature 1999, 402, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botvinick, M.M.; Braver, T.S.; Barch, D.M.; Carter, C.S.; Cohen, J.D. Conflict monitoring and cognitive control. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 108, 624–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botvinick, M.M.; Cohen, J.D.; Carter, C.S. Conflict monitoring and anterior cingulate cortex: An update. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinick, M.M. Conflict monitoring and decision making: Reconciling two perspectives on anterior cingulate function. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 7, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Yan, P.; Sinha, R.; Lee, T.W. Subcortical processes of motor response inhibition during a stop signal task. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kouider, S.; Dehaene, S. Levels of processing during non-conscious perception: A critical review of visual masking. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 2007, 362, 857–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.; Velmans, M.; De Fockert, J. Unconscious priming of a no-go response. Psychophysiology 2009, 46, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gaal, S.; Ridderinkhof, K.R.; Fahrenfort, J.J.; Scholte, H.S.; Lamme, V.A. Frontal cortex mediates unconsciously triggered inhibitory control. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8053–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gaal, S.; Lamme, V.A.F.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Unconsciously triggered conflict adaptation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbruggen, F.; Logan, G.D. Models of response inhibition in the stop–signal and stop–change paradigms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gaal, S.; Lamme, V.A.; Fahrenfort, J.J.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Dissociable brain mechanisms underlying the conscious and unconscious control of behavior. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, A.G.; Draine, S.C.; Abrams, R.L. Three cognitive markers of unconscious semantic activation. Science 1996, 273, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desender, K.; Van Lierde, E.; Van den Bussche, E. Comparing conscious and unconscious conflict adaptation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, A.R.; Ehrman, R.N.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sciortino, N.; Hakun, J.; Jens, W.; Suh, J.; Listerud, J.; Marquez, K. Prelude to passion: Limbic activation by “unseen” drug and sexual cues. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, D.; Zhang, Y. The Study of Subliminal Affective Priming Effects in Heroin Abstainers. J. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 41, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Meng, J.; Wei, D.; Chen, H. Electrophysiological Evidence of Abnormal Executive Control Function among Heroin Treatment Patients. J. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 37, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis, S.; Stins, J.F.; Posthuma, D.; Polderman, T.J.; Boomsma, D.I.; de Geus, E.J. Accounting for sequential trial effects in the flanker task: Conflict adaptation or associative priming? Memoy Cogn. 2006, 34, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, A. Conflict Adaptation is Induced by the Observation of Conflict: An ERP Study. Sci. Sin. 2012, 42, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Paul, K.; Pourtois, G. Defensive motivation increases conflict adaptation through local changes in cognitive control: Evidence from ERPs and mid-frontal theta. Biol. Psychol. 2019, 148, 107738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Pourtois, G. Conflict-driven adaptive control is enhanced by integral negative emotion on a short time scale. Cogn. Emot. 2018, 32, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiffany, S.T.; Wray, J.M. The clinical significance of drug craving. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1248, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francken, J.C.; van Gaal, S.; de Lange, F.P. Immediate and long-term priming effects are independent of prime awareness. Conscious Cogn. 2011, 20, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q. Is consciousness necessary for conflict detection and conflict resolution? Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 247, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.M.; Zhou, W.H.; Luo, X.J.; Yuen, K.S.; Ruan, X.Z.; Weng, X.C. Neural activity associated with cognitive regulation in heroin users: A fMRI study. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 382, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, S.D.; Dougherty, G.G.; Casey, B.J.; Siegle, G.J.; Braver, T.S.; Barch, D.M.; Stenger, V.A.; Wick-Hull, C.; Pisarov, L.A.; Lorensen, E. Opiate addicts lack errordependent activation of rostal anterior cingulated. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyvers, M. “Loss of control” in alcoholism and drug addiction: A neuroscientific interpretation. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2000, 8, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.H.; Albert, M.V.; Jung, K.; Carter, C.S.; Anderson, J.R. Anticipation of conlict monitoring in the anterior cingulate cortex and the prefrontal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10330–10334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hekmat, S.; Mehrjerdi, Z.A.; Moradi, A.; Ekhtiari, H.; Bakhshi, S. Cognitive flexibility, attention and speed of mental processing in opioid and methamphetamine addicts in comparison with non-addicts. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.-S.; Ho, P.-S.; Yen, C.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kuo, S.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Yeh, Y.-W.; Ma, K.-H.; Huang, S.-Y. The relationship between the striatal dopamine transporter and novelty seeking and cognitive flexibility in opioid dependence. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 74, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Heroin Abstainer Group | Healthy Control Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current-Congruent | Current-Incongruent | Current-Congruent | Current-Incongruent | |
| Previous-congruent | 434.26 ± 77.56 | 462.35 ± 84.18 | 437.08 ± 95.08 | 480.43 ± 110.56 |
| Previous-incongruent | 464.99 ± 79.37 | 477.89 ± 76.74 | 438.68 ± 97.38 | 447.18 ± 91.60 |
| Heroin Abstainer Group | Healthy Control Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current-Congruent | Current-Incongruent | Current-Congruent | Current-Incongruent | |
| Previous-congruent | 0.26 ± 0.12 | 0.36 ± 0.13 | 0.34 ± 0.15 | 0.42 ± 0.14 |
| Previous-incongruent | 0.36 ± 0.15 | 0.38 ± 0.16 | 0.35 ± 0.15 | 0.36 ± 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Yan, C.; Cao, H.; Yang, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X. Unconscious Conflict Adaptation of Heroin Abstainers. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216504
Li L, Yan C, Cao H, Yang L, Luo Y, Zhao Y, Lu X. Unconscious Conflict Adaptation of Heroin Abstainers. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216504
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ling, Changhu Yan, Hua Cao, Ling Yang, Yuchen Luo, Yu Zhao, and Xiao Lu. 2022. "Unconscious Conflict Adaptation of Heroin Abstainers" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216504
APA StyleLi, L., Yan, C., Cao, H., Yang, L., Luo, Y., Zhao, Y., & Lu, X. (2022). Unconscious Conflict Adaptation of Heroin Abstainers. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216504







