Non-Physical Disease Facets in Spondyloarthritis: An ASAS Health Index-Based Analysis between Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
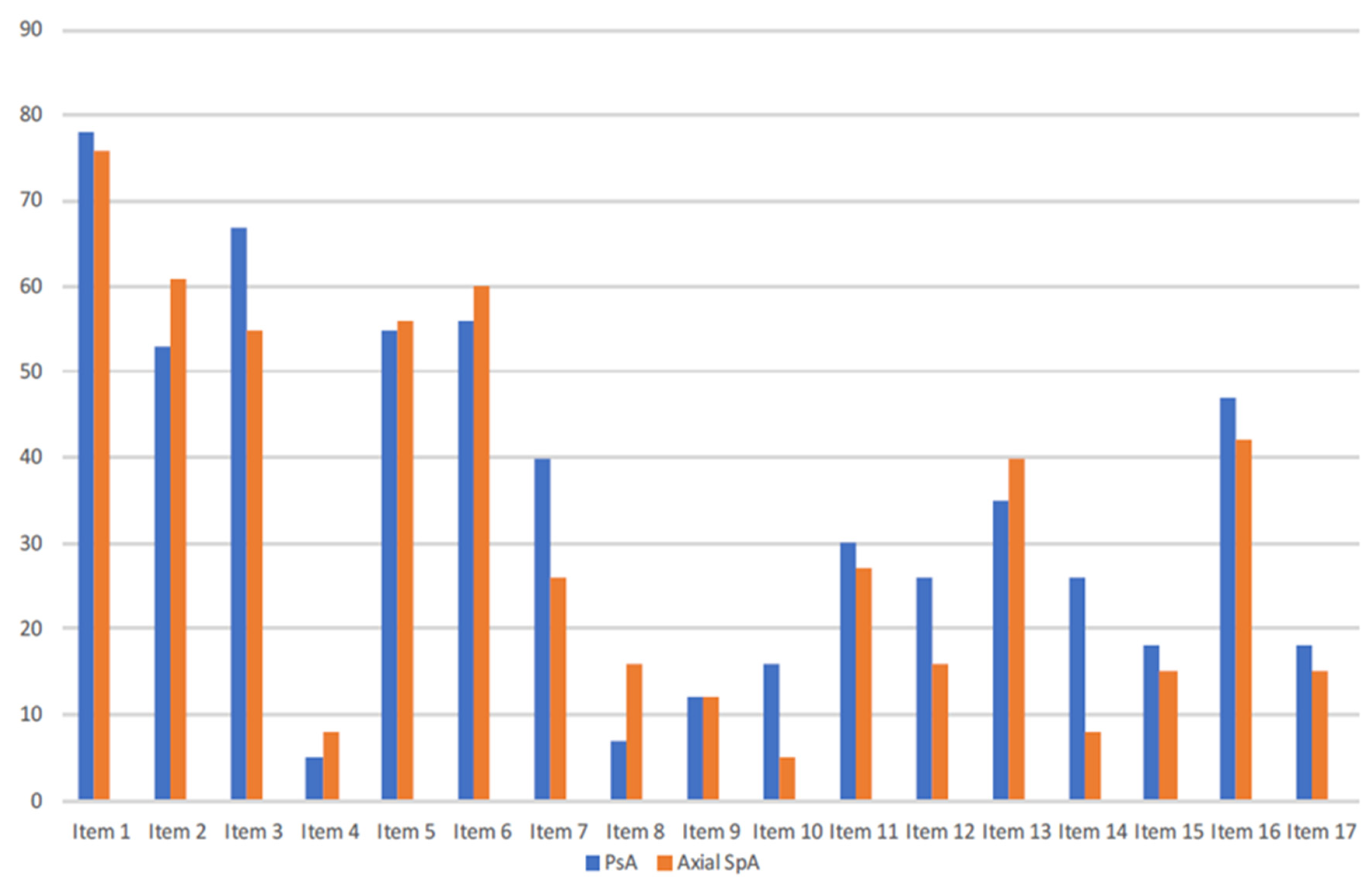
3. Results
3.1. Summary of the Study Population
3.2. Stress Handling
3.3. Frustration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre-Alonso, J.C.; Queiro, R.; Comellas, M.; Lizán, L.; Blanch, C. Patient-reported outcomes in European spondyloarthritis patients: A systematic review of the literature. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2018, 12, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, L.C.; Orbai, A.M.; Azevedo, V.F.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Steinberg, K.; Lippe, R.; Fallon, L. Results of a global, patient-based survey assessing the impact of psoriatic arthritis discussed in the context of the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID) questionnaire. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Cumbrera, M.; Poddubnyy, D.; Gossec, L.; Gálvez-Ruiz, D.; Bundy, C.; Mahapatra, R.; Navarro-Compán, V. The European Map of Axial Spondyloarthritis: Capturing the patient per-spective—An analysis of 2846 patients across 13 countries. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zusman, E.Z.; Howren, A.M.; Park, J.Y.E.; Dutz, J.; De Vera, M.A. Epidemiology of depression and anxiety in patients with psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, C.E.; Lapane, K.L.; Ferrucci, K.A.; Beccia, A.L.; Khan, S.K.; Yi, E.; Liu, S.H. Personal Experiences with Diagnostic Delay among Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients: A Qualitative Study. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 1015–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, I.; Richette, P.; Queiro-Silva, R.; Moser, J.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Ng, H.Y.; Witcombe, D. Patient Perceptions of Psoriatic Arthritis Management and Communication with Physicians in Australia: Results from a Patient Survey. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossec, L.; de Wit, M.; Kiltz, U.; Braun, J.; Kalyoncu, U.; Scrivo, R.; Kvien, T.K. A patient-derived and patient-reported outcome measure for assessing psoriatic arthritis: Elaboration and preliminary validation of the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID) questionnaire, a 13-country EULAR initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiltz, U.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Boonen, A.; Cieza, A.; Stucki, G.; Khan, M.A.; Braun, J. Development of a health index in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (ASAS HI): Final result of a global initiative based on the ICF guided by ASAS. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañete, J.D.; Tasende, J.A.P.; Laserna, F.J.R.; Castro, S.G.; Queiro, R. The Impact of Comorbidity on Patient-Reported Outcomes in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiro, R. Differentiating facets of quality of life between spondyloarthritis phenotypes: Added value of the ASAS health index. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2709–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Castro, S.; Pardo, E.; Charca, L.; Pino, M.; Fernández, S.; Alperi, M.; Queiro, R. Performance of the ASAS health index for the evaluation of spondyloarthritis in daily practice. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morante, I.; Aurrecoechea, E.; Villa, I.; Santos, M.; Riancho, L.; Queiro, R. Construct validity of the ASAS health index in psoriatic arthritis: A cross-sectional analysis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Gasparini, S.; Intorcia, M.; Grassi, W. The health-related quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis: A comparison with a selected sample of healthy people. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2009, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jajić, Z.; Rajnpreht, I.; Kovačić, N.; Lukić, I.K.; Velagić, V.; Grubišić, F.; Grčević, D. Which clinical variables have the most significant correlation with quality of life evaluated by SF-36 survey in Croatian cohort of patient with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis? Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tański, W.; Świątoniowska-Lonc, N.; Dudek, K.; Jankowska-Polańska, B. Benefit of Biological Drugs for Quality of Life in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1335, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohde, G.; Berg, K.H.; Pripp, A.H.; Prøven, A.; Haugeberg, G. No deterioration in health-related quality of life in patients with axial spondyloarthritis followed for 5 years in ordinary outpatient clinics in the biological treatment era. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husni, M.E.; Merola, J.F.; Davin, S. The psychosocial burden of psoriatic arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 47, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, J.T.; Foley, É.M.; Jadon, D.R.; Khandaker, G.M. Depression in patients with spondyloarthritis: Prevalence, incidence, risk, factors, mechanisms and management. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720X20970028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudu, T.; Gossec, L. Quality of life in psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, S.; Morante, I.; Alperi, M.; Queiro, R. The ASAS Health Index: A New Era for Health Impact Assessment in Spondyloar-thritis. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Axial Spondyloarthritis | N: 111 | Psoriatic Arthritis | N: 90 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs (mean ± SD) | 43.3 ± 10.6 | Age (yrs), (mean ± SD) | 55.3 ± 14.3 |
| Disease duration, yrs (mean ± SD) | 7.6 ± 6.8 | Arthritis duration (yrs), median (IQR) Psoriasis duration (yrs), median (IQR) | 7 (3–14) 16 (10–29) |
| Men, n (%) | 74 (66.7) | Men, n (%) | 52 (57.7) |
| AS, n (%) Peripheral involvement, n (%) | 74 (66.7) 18 (16.2) | Plaque psoriasis, n (%) Nail disease, n (%) ≥3 Affected body areas, n (%) | 75 (83.3) 33 (36.7) 61 (67.8) |
| Family history, n (%) | 16 (14.4) | Family history of psoriasis, n (%) Family history of PsA, n (%) | 37(41.1) 6 (6.7) |
| Primary education, n (%) Secondary education, n (%) University degree, n (%) | 43 (38.7) 34 (30.6) 34 (30.6) | Primary education, n (%) Secondary education, n (%) University degree, n (%) | 25 (27.8) 45 (50) 20 (22.2) |
| Tobacco, n (%) Obesity, n (%) Hypertension, n (%) Diabetes, n (%) Dyslipidemia, n (%) Cardiovascular adverse events, n (%) | 44 (39.6) 18 (16.2) 14 (12.6) 6 (5.4) 26 (23.4) 1 (0.9) | Diabetes, n (%) Hypertension, n (%) Dyslipidemia, n (%) Obesity, n (%) Smokers, n (%) Adverse cardiovascular events, n (%) | 13 (14.4) 37 (41.1) 30 (33.3) 21 (23.3) 14 (15.6) 6 (6.7) |
| Enthesitis, n (%) Anterior uveitis, n (%) Inflammatory bowel disease, n (%) | 8 (7.2) 14 (12.6) 6 (5.4) | Axial pattern, n (%) Oligoarthritis, n (%) Polyarthritis, n (%) | 14 (15.6) 42 (46.7) 34 (37.8) |
| HLA-B27, n (%) | 88 (79.3) | ||
| NSAID use, n (%) Biologic therapy, n (%) | 89 (80.2) 67 (60.4) | Conventional DMARDs, n (%) Biological therapy, n (%) | 81 (90) 37 (41.1) |
| BASDAI, mean (SD) ASDAS-CRP, mean (SD) ASAS-HI, mean (SD) | 3.4 (2.3) 2.1 (0.8) 5.4 (3.8) | DAPSA, mean (SD) PsAID, mean (SD) ASAS-HI, mean (SD) | 9.7 (7.8) 2.8 (2.3) 5.8 (4.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Queiro, R.; Alonso, S.; Morante, I.; Alperi, M. Non-Physical Disease Facets in Spondyloarthritis: An ASAS Health Index-Based Analysis between Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206094
Queiro R, Alonso S, Morante I, Alperi M. Non-Physical Disease Facets in Spondyloarthritis: An ASAS Health Index-Based Analysis between Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206094
Chicago/Turabian StyleQueiro, Rubén, Sara Alonso, Isla Morante, and Mercedes Alperi. 2022. "Non-Physical Disease Facets in Spondyloarthritis: An ASAS Health Index-Based Analysis between Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206094
APA StyleQueiro, R., Alonso, S., Morante, I., & Alperi, M. (2022). Non-Physical Disease Facets in Spondyloarthritis: An ASAS Health Index-Based Analysis between Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206094







