Can Proximal Junctional Kyphosis after Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity Be Predicted by Preoperative Dynamic Sagittal Alignment Change with 3D Gait Analysis? A Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participant Data
2.2. Radiographic Assessment
2.3. Surgical Procedure
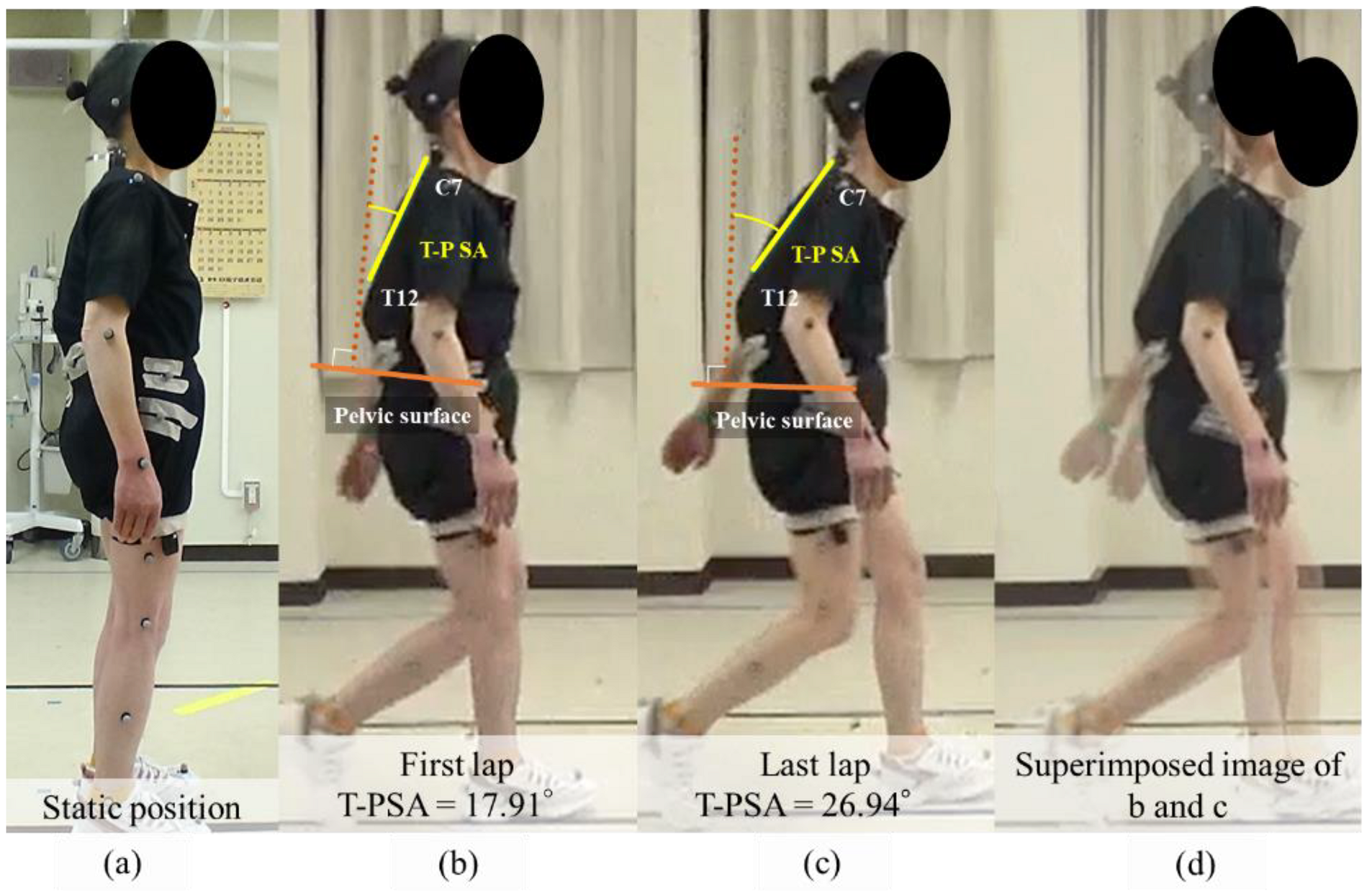
2.4. Gait Analysis and Dynamic Spinal Parameter
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
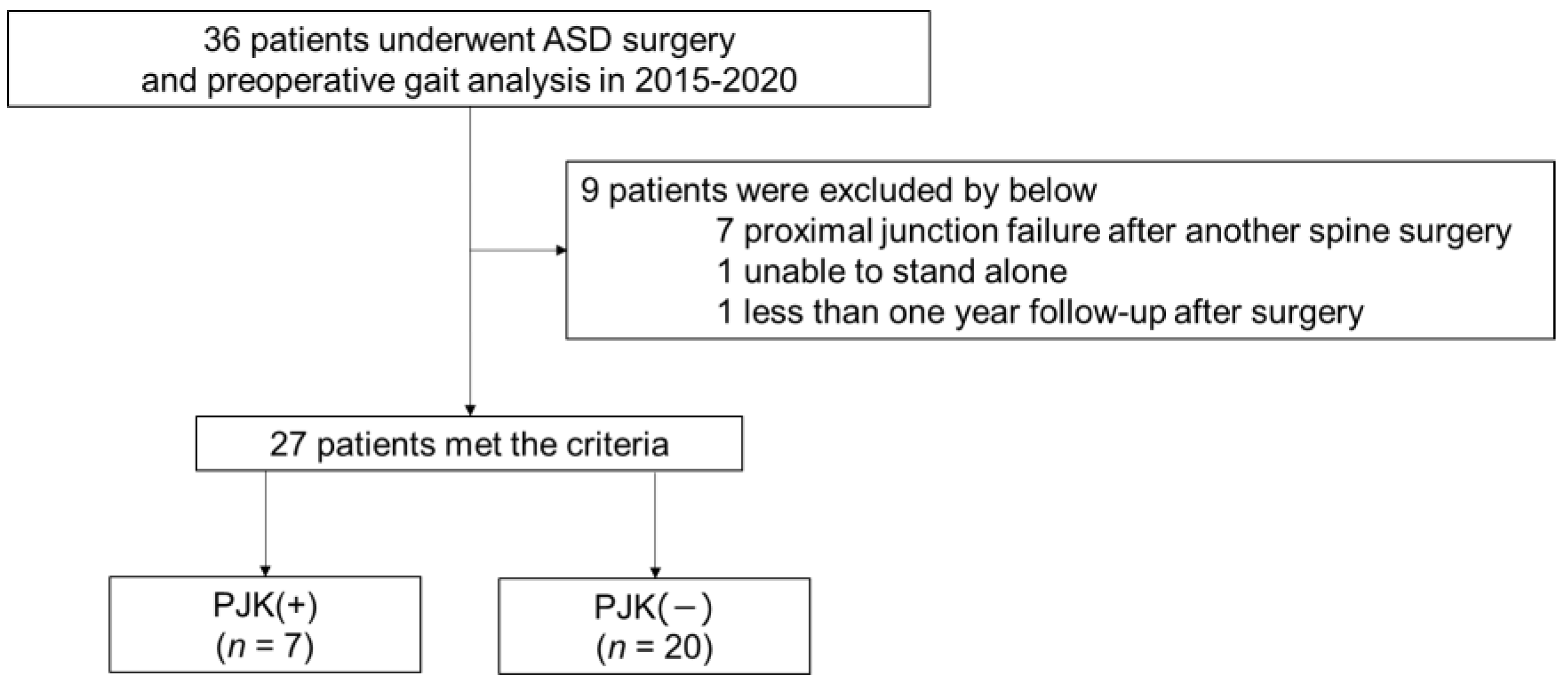
3.1. Patient Inclusion and Demographic Data
3.2. Three-Dimensional Gait Analysis (Dynamic Spinal Parameters)
3.3. Post Hoc Power Analysis of Student’s T-Test
3.4. Representative Case
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.H.; Chung, C.K.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, S.M.; Chin, D.K.; Lee, J.K.; Yoon, S.H.; Hong, J.T.; Ha, Y.; Kim, C.H.; et al. Effectiveness of deformity-correction surgery for primary degenerative sagittal imbalance: A meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 27, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.K.; Shin, J.I.; Kim, Y.J. Proximal junctional kyphosis following adult spinal deformity surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 2726–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glattes, R.C.; Bridwell, K.H.; Lenke, L.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Rinella, A.; Edwards, C.I. Proximal Junctional Kyphosis in Adult Spinal Deformity Following Long Instrumented Posterior Spinal Fusion: Incidence, Outcomes, and Risk Factor Analysis. Spine 2005, 30, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Hyun, S.-J.; Kim, K.-J.; Jahng, T.-A.; Lee, S.; Rhim, S.-C. Rod stiffness as a risk factor of proximal junctional kyphosis after adult spinal deformity surgery: Comparative study between cobalt chrome multiple-rod constructs and titanium alloy two-rod constructs. Spine J. 2017, 17, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Phan, K.; Cheung, Z.B.; Lee, N.; Vargas, L.; Arvind, V.; Merrill, R.K.; Gidumal, S.; Di Capua, J.; Overley, S.; et al. Surgical, Radiographic, and Patient-Related Risk Factors for Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: A Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2019, 9, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.; Clark, A.J.; Scheer, J.K.; Daubs, M.D.; Coe, J.D.; Paonessa, K.J.; LaGrone, M.O.; Kasten, M.D.; Amaral, R.A.; Trobisch, P.D.; et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis and failure after spinal deformity surgery: A systematic review of the literature as a background to classification development. Spine 2014, 39, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, S.D.; Wang, H.; Yang, D.L.; Ding, W.Y. Incidence and risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: A meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafage, R.; Beyer, G.; Schwab, F.; Klineberg, E.; Burton, D.; Bess, S.; Kim, H.J.; Smith, J.; Ames, C.; Hostin, R.; et al. Risk Factor Analysis for Proximal Junctional Kyphosis After Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A New Simple Scoring System to Identify High-Risk Patients. Global Spine J. 2020, 10, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Xu, G.; Xia, L. Upper Thoracic versus Lower Thoracic as Site of Upper Instrumented Vertebrae for Long Fusion Surgery in Adult Spinal Deformity: A Meta-Analysis of Proximal Junctional Kyphosis. World Neurosurg. 2017, 102, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Stopping at Sacrum Versus Nonsacral Vertebra in Long Fusion Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity: Meta-Analysis of Revision with Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2018, 124, e380–e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, T.; Miller, E.; Martin, C.T.; Kebaish, K.M. The effect of prophylactic vertebroplasty on the incidence of proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure following posterior spinal fusion in adult spinal deformity: A 5-year follow-up study. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Lee, C.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, K.-J. Should Thoracolumbar Junction Be Always Avoided as Upper Instrumented Vertebra in Long Instrumented Fusion for Adult Spinal Deformity?: Risk Factor Analysis for Proximal Junctional Failure. Spine 2020, 45, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, H.; Yamato, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Togawa, D.; Kobayashi, S.; Yasuda, T.; Banno, T.; Oe, S.; Matsuyama, Y. Discrepancy Between Standing Posture and Sagittal Balance During Walking in Adult Spinal Deformity Patients. Spine 2017, 42, E25–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Theologis, A.A.; Jang, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Deviren, V. Impact of Fatigue on Maintenance of Upright Posture: Dynamic Assessment of Sagittal Spinal Deformity Parameters After Walking 10 Minutes. Spine 2017, 42, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddas, R.; Hu, X.; Lieberman, I.H. The Correlation of Spinopelvic Parameters With Biomechanical Parameters Measured by Gait and Balance Analyses in Patients With Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Clin. Spine Surg. 2020, 33, E33–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Koda, M.; Kadone, H.; Abe, T.; Kumagai, H.; Nagashima, K.; Mataki, K.; Fujii, K.; Noguchi, H.; Funayama, T.; et al. Successful detection of postoperative improvement of dynamic sagittal balance with a newly developed three-dimensional gait motion analysis system in a patient with iatrogenic flatback syndrome: A case report. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 53, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, F.; Patel, A.; Ungar, B.; Farcy, J.-P.; Lafage, V. Adult Spinal Deformity—Postoperative Standing Imbalance: How Much Can You Tolerate? An Overview of Key Parameters in Assessing Alignment and Planning Corrective Surgery. Spine 2010, 35, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, M.; King, A.B.; Boachie-Adjei, O. Characterization of osteopenia/osteoporosis in adult scoliosis: Does bone density affect surgical outcome? Spine 2011, 36, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochmüller, E.M.; Bürklein, D.; Kuhn, V.; Glaser, C.; Müller, R.; Glüer, C.C.; Eckstein, F. Mechanical strength of the thoracolumbar spine in the elderly: Prediction from in situ dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, quantitative computed tomography (QCT), upper and lower limb peripheral QCT, and quantitative ultrasound. Bone 2002, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Kadone, H.; Koda, M.; Abe, T.; Funayama, T.; Noguchi, H.; Mataki, K.; Nagashima, K.; Kumagai, H.; Shibao, Y.; et al. Thoracic kyphosis and pelvic anteversion in patients with adult spinal deformity increase while walking: Analyses of dynamic alignment change using a three-dimensional gait motion analysis system. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, D.W.; Han, H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.M.; Chang, B.S.; Yeom, J.S. Risk factors for acute proximal junctional kyphosis after adult spinal deformity surgery in preoperative motion analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Rhim, S.-C. Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis after stopping at thoracolumbar junction have lower muscularity, fatty degeneration at the thoracolumbar area. Spine J. 2016, 16, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, T.; Kotani, T.; Akazawa, T.; Nakayama, K.; Iijima, Y.; Shiratani, Y.; Kishida, S.; Muramatsu, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Ueno, K.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Prevention Strategy for Proximal Junctional Kyphosis in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2021, 5, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafage, R.; Schwab, F.; Challier, V.; Henry, J.K.; Gum, J.; Smith, J.; Hostin, R.; Shaffrey, C.; Kim, H.J.; Ames, C.; et al. Defining Spino-Pelvic Alignment Thresholds: Should Operative Goals in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery Account for Age? Spine 2016, 41, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamato, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Togawa, D.; Yoshida, G.; Banno, T.; Arima, H.; Oe, S.; Mihara, Y.; Ushirozako, H.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Rigorous Correction of Sagittal Vertical Axis Is Correlated With Better ODI Outcomes After Extensive Corrective Fusion in Elderly or Extremely Elderly Patients With Spinal Deformity. Spine Deform. 2019, 7, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Studer, D.; Hasler, C.C.; Romkes, J.; Taylor, W.R.; Brunner, R.; Lorenzetti, S. Using Skin Markers for Spinal Curvature Quantification in Main Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: An Explorative Radiographic Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

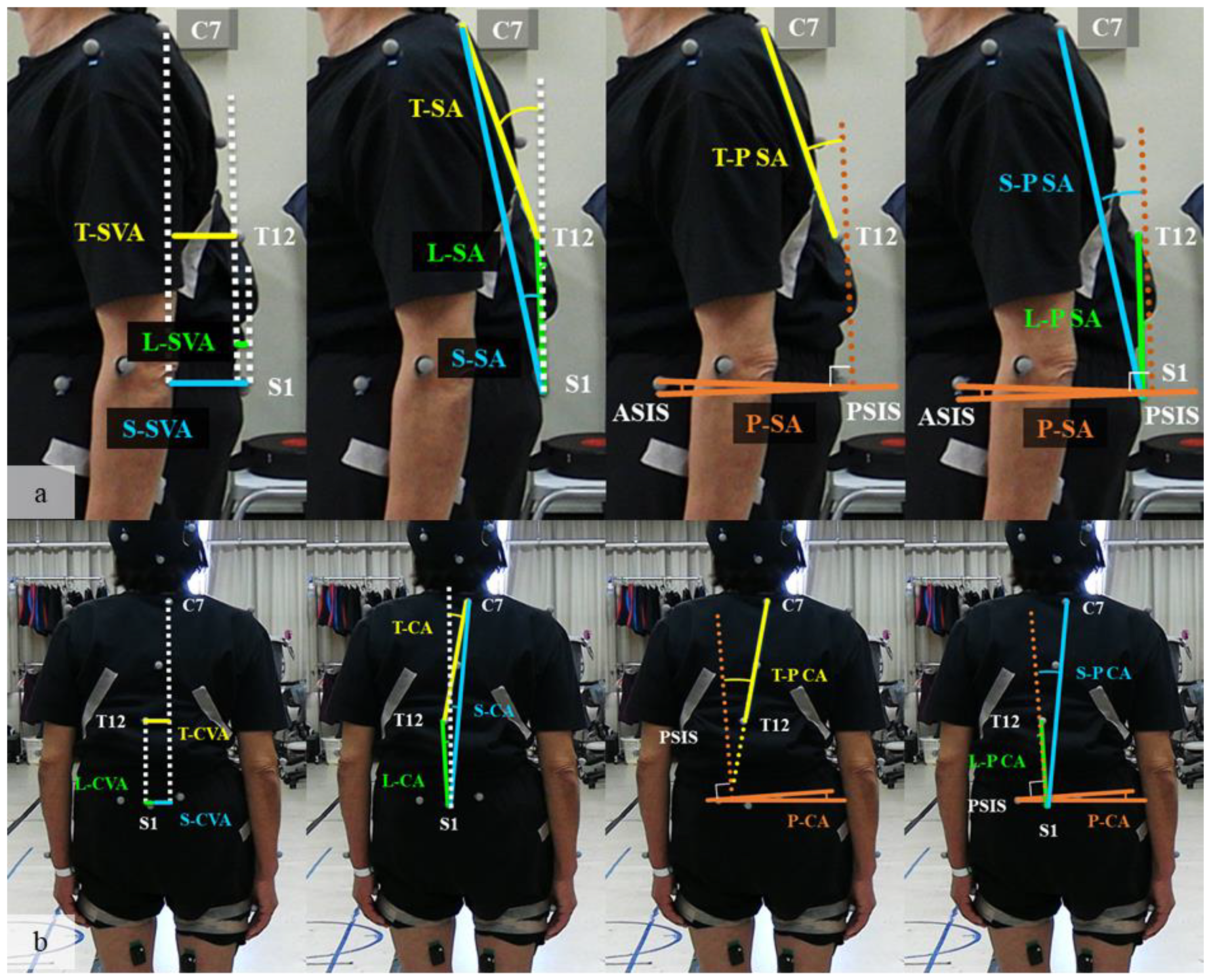


| Parameter | Definition | Marker | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SVA | thoracic sagittal distance between the reflective markers | C7 | T12 | mm |
| T-CVA | thoracic coronal distance between the reflective markers | C7 | T12 | mm |
| L-SVA | lumbar sagittal distance between the reflective markers | T12 | S1 | mm |
| L-CVA | lumbar coronal distance between the reflective markers | T12 | S1 | mm |
| S-SVA | whole spinal sagittal distance between the reflective markers | C7 | S1 | mm |
| S-CVA | whole spinal coronal distance between the reflective markers | C7 | S1 | mm |
| T-SA | thoracic sagittal angle between the vertical axis and the line connecting the spinal markers | C7 | T12 | ° |
| T-CA | thoracic coronal angle between the vertical axis and the line connecting the spinal markers | C7 | T12 | ° |
| L-SA | lumbar sagittal angle between the vertical axis and the line connecting the spinal markers | T12 | S1 | ° |
| L-CA | lumbar coronal angle between the vertical axis and the line connecting the spinal markers | T12 | S1 | ° |
| S-SA | whole spinal sagittal angle between the vertical axis and the line connecting the spinal markers | C7 | S1 | ° |
| S-CA | whole spinal coronal angle between the vertical axis and the line connecting the spinal markers | C7 | S1 | ° |
| P-SA | sagittal angle between the horizontal axis and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | ASIS | PSIS | ° |
| P-CA | coronal angle between the horizontal axis and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | ASIS | PSIS | ° |
| T-P SA | thoracic sagittal angle between the line connecting the spinal markers and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | C7 | T12 | ° |
| T-P CA | thoracic coronal angle between the line connecting the spinal markers and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | C7 | T12 | ° |
| L-P SA | lumbar sagittal angle between the line connecting the spinal markers and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | T12 | S1 | ° |
| L-P CA | lumbar coronal angle between the line connecting the spinal markers and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | T12 | S1 | ° |
| S-P SA | whole spinal sagittal angle between the line connecting the spinal markers and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | C7 | S1 | ° |
| S-P CA | whole spinal coronal angle between the line connecting the spinal markers and the line connecting the reflective markers on the ASIS and PSIS | C7 | S1 | ° |
| Parameter | PJK (+) | PJK (−) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 7 | 20 | ||||
| Sex (male, female) | 1 | 6 | 4 | 16 | ||
| Age (years) | 67.5 | ±6.24 | 68.6 | ±10.2 | 0.969 | |
| Height (cm) | 146.7 | ±7.8 | 151.1 | ±35.3 | 0.340 | |
| Body weight (kg) | 52.9 | ±12.3 | 49.6 | ±14.1 | 0.668 | |
| BMD (g/cm2) | 0.63 | ±0.1 | 0.60 | ±0.2 | 0.669 | |
| YAM (%) | 77.3 | ±8.6 | 73.6 | ±25.9 | 0.635 | |
| Preop | C7SVA (mm) | 115.9 | ±51.9 | 112.7 | ±58.1 | 0.900 |
| TK ° | 20.5 | ±11.8 | 16.3 | ±15.6 | 0.524 | |
| LL ° | 6.3 | ±16.8 | 11.7 | ±20.3 | 0.703 | |
| PT ° | 36.7 | ±9.4 | 31.6 | ±14.8 | 0.436 | |
| PI ° | 52.3 | ±12.8 | 49.6 | ±15.4 | 0.501 | |
| TPA ° | 39.7 | ±11.4 | 35.5 | ±16.7 | 0.625 | |
| PI–LL ° | 46.0 | ±19.5 | 37.8 | ±23.2 | 0.463 | |
| C7CSVL (mm) | 3.6 | ±31.3 | 4.6 | ±28.9 | 0.742 | |
| Coronal Cobb angle° | 37.4 | ±21.7 | 24.1 | ±15.5 | 0.102 | |
| Parameter | PJK (+) | PJK (−) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused levels | 10.4 | ±2.0 | 7.7 | ±3.7 | 0.069 |
| C7CSVL (mm) | 15.3 | ±22.9 | 6.5 | ±15.2 | 0.258 |
| Coronal Cobb angle ° | 10.8 | ±15.5 | 10.4 | ±13.3 | 0.638 |
| C7SVA (mm) | −8.3 | ±35.8 | 40.2 | ±48.2 | 0.023 * |
| TK ° | 49.3 | ±12.2 | 26.4 | ±15.3 | 0.002 * |
| LL ° | 54.0 | ±10.8 | 34.9 | ±18.3 | 0.015 * |
| PT ° | 19.8 | ±10.8 | 19.9 | ±12.9 | 0.978 |
| PI ° | 45.1 | ±6.6 | 43.7 | ±11.2 | 0.769 |
| TPA ° | 12.5 | ±10.8 | 17.6 | ±12.6 | 0.357 |
| PI–LL ° | −9.0 | ±12.2 | 9.4 | ±20.1 | 0.033 * |
| Parameter | PJK (+) | PJK (−) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SVA (mm) | 158.4 | ±36.8 | 118.2 | ±46.6 | 0.050 |
| L-SVA (mm) | 15.0 | ±21.3 | 27.4 | ±31.8 | 0.351 |
| S-SVA (mm) | 194.8 | ±56.2 | 165.1 | ±74.5 | 0.347 |
| T-SA ° | 33.5 | ±9.2 | 25.1 | ±12.1 | 0.107 |
| L-SA ° | 4.9 | ±8.1 | 10.0 | ±11.8 | 0.300 |
| S-SA ° | 25.0 | ±7.2 | 20.4 | ±9.9 | 0.278 |
| P-SA ° | 92.4 | ±4.4 | 90.2 | ±22.3 | 0.802 |
| T-P SA ° | 32.3 | ±8.1 | 18.7 | ±13.5 | 0.020 * |
| L-P SA ° | -1.9 | ±14.1 | 5.1 | ±11.2 | 0.193 |
| S-P SA ° | 22.5 | ±7.2 | 14.5 | ±12.1 | 0.116 |
| Parameter | PJK (+) | PJK (−) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-CVA (mm) | 10.8 | ±31.7 | 8.2 | ±19.9 | 0.802 |
| L-CVA (mm) | 1.4 | ±13.8 | −3.0 | ±19.5 | 0.589 |
| S-CVA (mm) | 11.2 | ±31.4 | 7.7 | ±34.6 | 0.819 |
| T-CA ° | 3.4 | ±8.4 | 2.2 | ±5.1 | 0.655 |
| L-CA ° | 0.6 | ±5.5 | 0.4 | ±9.5 | 0.960 |
| S-CA ° | 1.7 | ±4.6 | 1.4 | ±5 | 0.909 |
| P-CA ° | 88.5 | ±7.5 | 86.1 | ±20.3 | 0.764 |
| T-P CA ° | 5.1 | ±12.2 | −0.2 | ±11.1 | 0.305 |
| L-P CA ° | −4.2 | ±11.8 | −0.4 | ±10.7 | 0.435 |
| S-P CA ° | 3.1 | ±9.2 | −0.7 | ±8.2 | 0.326 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asada, T.; Miura, K.; Koda, M.; Kadone, H.; Funayama, T.; Takahashi, H.; Noguchi, H.; Shibao, Y.; Sato, K.; Eto, F.; et al. Can Proximal Junctional Kyphosis after Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity Be Predicted by Preoperative Dynamic Sagittal Alignment Change with 3D Gait Analysis? A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195871
Asada T, Miura K, Koda M, Kadone H, Funayama T, Takahashi H, Noguchi H, Shibao Y, Sato K, Eto F, et al. Can Proximal Junctional Kyphosis after Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity Be Predicted by Preoperative Dynamic Sagittal Alignment Change with 3D Gait Analysis? A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195871
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsada, Tomoyuki, Kousei Miura, Masao Koda, Hideki Kadone, Toru Funayama, Hiroshi Takahashi, Hiroshi Noguchi, Yosuke Shibao, Kosuke Sato, Fumihiko Eto, and et al. 2022. "Can Proximal Junctional Kyphosis after Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity Be Predicted by Preoperative Dynamic Sagittal Alignment Change with 3D Gait Analysis? A Case–Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195871
APA StyleAsada, T., Miura, K., Koda, M., Kadone, H., Funayama, T., Takahashi, H., Noguchi, H., Shibao, Y., Sato, K., Eto, F., Mataki, K., & Yamazaki, M. (2022). Can Proximal Junctional Kyphosis after Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity Be Predicted by Preoperative Dynamic Sagittal Alignment Change with 3D Gait Analysis? A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195871





