Altered Resting-State Network in Adolescents with Problematic Internet Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Psychological Questionnaires
2.2.1. The Indonesian Version of Internet Addiction Test (IAT)
2.2.2. The Indonesian Version of Strength and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)
2.2.3. The Indonesian Version of Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI)
2.3. Functional Connectivity Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Psychometric Data
3.2. Comparison of Resting-State Functional Connectivity between PIU and Control Groups
3.3. Associations between Problematic Internet Use Scores, Psychological Problems, and Temperament
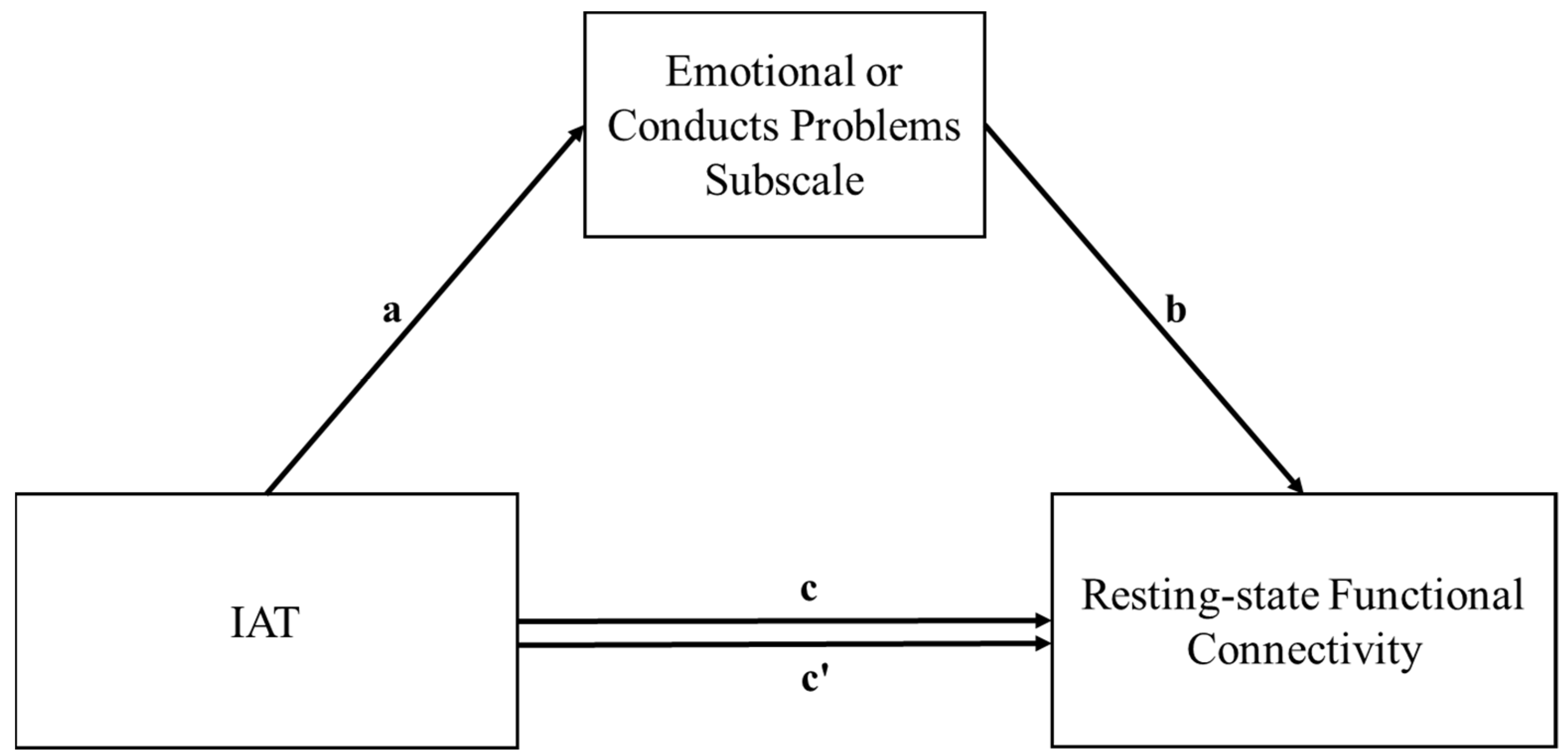
3.4. Mediation Analyses of Functional Connectivity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, C.; Li, A.Y. Internet Addiction Prevalence and Quality of (Real) Life: A Meta-Analysis of 31 Nations Across Seven World Regions. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fam, J.Y. Prevalence of Internet Gaming Disorder in Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis across Three Decades. Scand. J. Psychol. 2018, 59, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, D.X.Y.; Ng, C.W.L.; Kandasami, G.; Seow, M.Y.L.; Choo, C.C.; Chew, P.K.H.; Lee, C.; Zhang, M.W.B. Prevalence of Internet Addiction and Gaming Disorders in Southeast Asia: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaeli, N.; Farhadi, H. Prevalence of Internet-Based Addictive Behaviors during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review. J. Addict. Dis. 2021, 39, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siste, K.; Hanafi, E.; Sen, L.T.; Murtani, B.J.; Christian, H.; Limawan, A.P.; Siswidiani, L.P.; Adrian. Implications of COVID-19 and Lockdown on Internet Addiction Among Adolescents: Data From a Developing Country. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 665675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silczuk, A. Problem Internet Use among Children and Adolescents from the General Practitioner’s Perspective. Alcohol. Drug Addict. 2019, 32, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.S.; Bhang, S.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Kweon, Y.-S. Clinical Characteristics of Diagnosis for Internet Gaming Disorder: Comparison of DSM-5 IGD and ICD-11 GD Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasin, D.S.; O’Brien, C.P.; Auriacombe, M.; Borges, G.; Bucholz, K.; Budney, A.; Compton, W.M.; Crowley, T.; Ling, W.; Petry, N.M.; et al. DSM-5 Criteria for Substance Use Disorders: Recommendations and Rationale. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Moal, M.L. Drug Addiction, Dysregulation of Reward, and Allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 24, 97–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.Z.; Volkow, N.D. Drug Addiction and Its Underlying Neurobiological Basis: Neuroimaging Evidence for the Involvement of the Frontal Cortex. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, A.; Jentsch, J.D. Reversal Learning as a Measure of Impulsive and Compulsive Behavior in Addictions. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, B.J.; Jones, R.M. Neurobiology of the Adolescent Brain and Behavior: Implications for Substance Use Disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 49, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerniglia, L.; Zoratto, F.; Cimino, S.; Laviola, G.; Ammaniti, M.; Adriani, W. Internet Addiction in Adolescence: Neurobiological, Psychosocial and Clinical Issues. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 76, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zuo, X.-N.; McMahon, K.L.; Craddock, R.C.; Kelly, C.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; Hickie, I.; Bandettini, P.A.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P.; et al. Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Functional Connectivity Architecture of the Human Brain. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 2341–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, E.S.; Shen, X.; Scheinost, D.; Rosenberg, M.D.; Huang, J.; Chun, M.M.; Papademetris, X.; Constable, R.T. Functional Connectome Fingerprinting: Identifying Individuals Using Patterns of Brain Connectivity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J.S.; Rombouts, S.A.R.B.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Stam, C.J.; Smith, S.M.; Beckmann, C.F. Consistent Resting-State Networks across Healthy Subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13848–13853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavor, I.; Jones, O.P.; Mars, R.B.; Smith, S.M.; Behrens, T.E.; Jbabdi, S. Task-Free MRI Predicts Individual Differences in Brain Activity during Task Performance. Science 2016, 352, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.H.; Ma, Z.; Ciric, R.; Gu, S.; Betzel, R.F.; Kaczkurkin, A.N.; Calkins, M.E.; Cook, P.A.; García de la Garza, A.; Vandekar, S.N.; et al. Linked Dimensions of Psychopathology and Connectivity in Functional Brain Networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Wendelken, C.; Nieto-Castañón, A.; Bailey, S.K.; Anteraper, S.A.; Lee, Y.J.; Chai, X.; Hirshfeld-Becker, D.R.; Biederman, J.; Cutting, L.E.; et al. Association of Intrinsic Brain Architecture with Changes in Attentional and Mood Symptoms during Development. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-B.; Zalesky, A.; Cocchi, L.; Fornito, A.; Choi, E.-J.; Kim, H.-H.; Suh, J.-E.; Kim, C.-D.; Kim, J.-W.; Yi, S.-H. Decreased Functional Brain Connectivity in Adolescents with Internet Addiction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.M. An Update Overview on Brain Imaging Studies of Internet Gaming Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.-M.; Li, N.; Wang, C.-X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, R.-B.; Xu, H.-S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, D.-R. Abnormal Brain Default-Mode Network Functional Connectivity in Drug Addicts. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, J.; Nyberg, E.; Martin, L.F.; Martin, J.; Cordes, D.; Kronberg, E.; Tregellas, J.R. Nicotine Effects on Default Mode Network during Resting State. Psychopharmacology 2011, 216, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Cortes, C.R.; Mathur, K.; Tomasi, D.; Momenan, R. Model-Free Functional Connectivity and Impulsivity Correlates of Alcohol Dependence: A Resting-State Study. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Shin, Y.-C.; Jung, W.H.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, J.-S.; Kang, D.-H.; Yi, J.-S.; Choi, C.-H.; Kwon, J.S. Decreased Connectivity of the Default Mode Network in Pathological Gambling: A Resting State Functional MRI Study. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 583, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Han, D.H.; Jung, J.; Nam, K.C.; Renshaw, P.F. Comparison of Brain Connectivity between Internet Gambling Disorder and Internet Gaming Disorder: A Preliminary Study. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsurumi, K.; Aso, T.; Kawada, R.; Murai, T.; Takahashi, H. A Positive Shift in Resting-State Functional Connectivity between the Insula and Default Mode Network Regions Reflects the Duration of Illness in Gambling Disorder Patients without Lifetime Substance Abuse. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2020, 295, 111018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V. Large-Scale Brain Networks and Psychopathology: A Unifying Triple Network Model. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 483–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Ma, S.-S.; Yan, C.-G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.-J.; Liu, B.; Yao, Y.-W.; Yang, Y.-H.; Fang, X.-Y. Altered Coupling of Default-Mode, Executive-Control and Salience Networks in Internet Gaming Disorder. Eur. Psychiatr. 2017, 45, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Lei, Y.; Zeng, L.-L.; Cao, F.; Su, L.; Yang, Z.; Yao, S.; Hu, D. Altered Default Mode, Fronto-Parietal and Salience Networks in Adolescents with Internet Addiction. Addict. Behav. 2017, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Qin, W.; Yu, D.; Bi, Y.; Xing, L.; Jin, C.; Tian, J. Core Brain Networks Interactions and Cognitive Control in Internet Gaming Disorder Individuals in Late Adolescence/Early Adulthood. Anat. Embryol. 2016, 221, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettew, D.C.; McKee, L. Temperament and Its Role in Developmental Psychopathology. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2005, 13, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.-H.; Yen, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, K.; Yen, C.-F. Tridimensional Personality of Adolescents with Internet Addiction and Substance Use Experience. Can. J. Psychiatry 2006, 51, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Bae, S.C.; Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Sim, M.; Lyoo, I.K.; Cho, S.C. Depression and Internet Addiction in Adolescents. Psychopathology 2007, 40, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, E.; Siste, K.; Wiguna, T.; Kusumadewi, I.; Nasrun, M.W. Temperament Profile and Its Association with the Vulnerability to Smartphone Addiction of Medical Students in Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, S.; Ellis, L.; Rothbart, M. The Structure of Temperament from Infancy through Adolescence. In Advances/Proceedings in Research on Temperament; Eliasz, A., Angleitner, A., Eds.; Pabst Scientist: Lengerich, Germany, 2001; pp. 165–182. ISBN 3-936142-07-6. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, A.; Stifter, C.A. Longitudinal Antecedents of Executive Function in Preschoolers: Early Antecedents of Executive Function. Child Dev. 2012, 83, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitelaar, J.K.; Huizink, A.C.; Mulder, E.J.; de Medina, P.G.R.; Visser, G.H.A. Prenatal Stress and Cognitive Development and Temperament in Infants. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, S53–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa, P.; Rodríguez-Bailón, R.; Rueda, M.R. Neurocognitive and Temperamental Systems of Self-Regulation and Early Adolescents’ Social and Academic Outcomes. Mind Brain Educ. 2008, 2, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahat, A.; Degnan, K.A.; White, L.K.; McDermott, J.M.; Henderson, H.A.; Lejuez, C.W.; Fox, N.A. Temperamental Exuberance and Executive Function Predict Propensity for Risk Taking in Childhood. Dev. Psychopathol. 2012, 24, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joormann, J.; Tanovic, E. Cognitive Vulnerability to Depression: Examining Cognitive Control and Emotion Regulation. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2015, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herba, C.M.; Tranah, T.; Rubia, K.; Yule, W. Conduct Problems in Adolescence: Three Domains of Inhibition and Effect of Gender. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2006, 30, 659–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Dai, W.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Dai, B.; Liu, X. The Mediating Role of Coping Styles on Impulsivity, Behavioral Inhibition/Approach System, and Internet Addiction in Adolescents From a Gender Perspective. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, K.; Hook, R.; Goudriaan, A.E.; Vlies, S.; Fineberg, N.A.; Grant, J.E.; Chamberlain, S.R. Cognitive Deficits in Problematic Internet Use: Meta-Analysis of 40 Studies. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 215, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siste, K.; Wiguna, T.; Bardasono, S.; Sekartini, R.; Pandelaki, J.; Sarasvita, R.; Suwartono, C.; Murtani, B.J.; Damayanti, R.; Christian, H.; et al. Internet Addiction in Adolescents: Development and Validation of Internet Addiction Diagnostic Questionnaire (KDAI). Psychiatry Res. 2021, 298, 113829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M. Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for Internet Addiction. Addiction 2010, 105, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Mental Health Mental Illness. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/mental-illness (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Humeniuk, R.; Henry-Edwards, S.; Ali, R.; Poznyak, V.; Monteiro, M.; World Health Organization. The Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-92-4-159938-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, D.V.; Sheehan, K.H.; Shytle, R.D.; Janavs, J.; Bannon, Y.; Rogers, J.E.; Milo, K.M.; Stock, S.L.; Wilkinson, B. Reliability and Validity of the Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview for Children and Adolescents (MINI-KID). J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction--and a Winning Strategy for Recovery; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-471-19159-9. [Google Scholar]
- Siste, K.; Suwartono, C.; Nasrun, M.W.; Bardosono, S.; Sekartini, R.; Pandelaki, J.; Sarasvita, R.; Murtani, B.J.; Damayanti, R.; Wiguna, T. Validation Study of the Indonesian Internet Addiction Test among Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktaviana, M.; Wimbarti, S. Validasi Klinik Strength and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) Sebagai Instrumen Skrining Gangguan Tingkah Laku. J. Psikol. 2014, 41, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Cloninger, C.R. A Psychobiological Model of Temperament and Character. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1993, 50, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, R. Peran Biopsikososial Terhadap Perilaku Berisiko Tertular HIV Pada Remaja SLTA Di DKI, 2006. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Griffanti, L.; Salimi-Khorshidi, G.; Beckmann, C.F.; Auerbach, E.J.; Douaud, G.; Sexton, C.E.; Zsoldos, E.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Filippini, N.; Mackay, C.E.; et al. ICA-Based Artefact Removal and Accelerated FMRI Acquisition for Improved Resting State Network Imaging. NeuroImage 2014, 95, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A Functional Connectivity Toolbox for Correlated and Anticorrelated Brain Networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, Y.; Restom, K.; Liau, J.; Liu, T.T. A Component Based Noise Correction Method (CompCor) for BOLD and Perfusion Based FMRI. NeuroImage 2007, 37, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Oishi, N.; Yoshimura, S.; Ueno, T.; Miyagi, T.; Murai, T.; Fujiwara, H. Relationship between Media Multitasking and Functional Connectivity in the Dorsal Attention Network. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach, 2nd ed.; Methodology in the social sciences; Guilford Press: New York, NJ, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4625-3465-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Du, Y. Altered Default Network Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Adolescents with Internet Gaming Addiction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.N.; Grafman, J. Human Prefrontal Cortex: Processing and Representational Perspectives. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, S.D.; VanMeter, J.W. Anterior-Posterior Connectivity within the Default Mode Network Increases During Maturation. Int. J. Med. Biol. Front. 2015, 21, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.E. The Brain’s Default Mode Network. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 38, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, J.; Hoshi, E. Role of the Lateral Prefrontal Cortex in Executive Behavioral Control. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldao, A.; Nolen-Hoeksema, S.; Schweizer, S. Emotion-Regulation Strategies across Psychopathology: A Meta-Analytic Review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 30, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, M.; De Gracia, M.; Rodríguez, R.C.; Mallorquí-Bagué, N.; Sánchez-González, J.; Trujols, J.; Sánchez, I.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Menchón, J.M. Mindfulness-Based Interventions for the Treatment of Substance and Behavioral Addictions: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-Y.; Tang, R.; Posner, M.I. Mindfulness Meditation Improves Emotion Regulation and Reduces Drug Abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 163, S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, B.A.; Chun, M.M. Successful Remembering Elicits Event-Specific Activity Patterns in Lateral Parietal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8051–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northoff, G.; Heinzel, A.; de Greck, M.; Bermpohl, F.; Dobrowolny, H.; Panksepp, J. Self-Referential Processing in Our Brain—A Meta-Analysis of Imaging Studies on the Self. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 440–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.S.; Voon, V. Dimensionality of Cognitions in Behavioral Addiction. Curr. Behav. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 3, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gould, T.J. Addiction and Cognition. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2010, 5, 4–14. [Google Scholar]
- Oldrati, V.; Patricelli, J.; Colombo, B.; Antonietti, A. The Role of Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Inhibition Mechanism: A Study on Cognitive Reflection Test and Similar Tasks through Neuromodulation. Neuropsychologia 2016, 91, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Potenza, M.N. A Cognitive-Behavioral Model of Internet Gaming Disorder: Theoretical Underpinnings and Clinical Implications. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 58, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhou, H.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Dong, G. Impaired Executive Control and Reward Circuit in Internet Gaming Addicts under a Delay Discounting Task: Independent Component Analysis. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 267, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Devito, E.E.; Du, X.; Cui, Z. Impaired Inhibitory Control in “Internet Addiction Disorder”: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 203, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ying, H.; Seetohul, R.M.; Xuemei, W.; Ya, Z.; Qian, L.; Guoqing, X.; Ye, S. Brain FMRI Study of Crave Induced by Cue Pictures in Online Game Addicts (Male Adolescents). Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 233, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; Steinberg, L.; Chein, J. The Role of the Anterior Insula in Adolescent Decision Making. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V. Salience Network. In Brain Mapping: An Encylopedic Reference; Toga, A.W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 597–611. ISBN 978-0-12-397316-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pessoa, L. Emergent Processes in Cognitive-Emotional Interactions. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 12, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, H.; Yoshimura, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Ueno, T.; Oishi, N.; Murai, T. Neural Correlates of Non-Clinical Internet Use in the Motivation Network and Its Modulation by Subclinical Autistic Traits. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Uddin, L.Q. Saliency, Switching, Attention and Control: A Network Model of Insula Function. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-T.; Yao, Y.-W.; Li, C.-S.R.; Zang, Y.-F.; Shen, Z.-J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.-J.; Liu, B.; Fang, X.-Y. Altered Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Insula in Young Adults with Internet Gaming Disorder. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
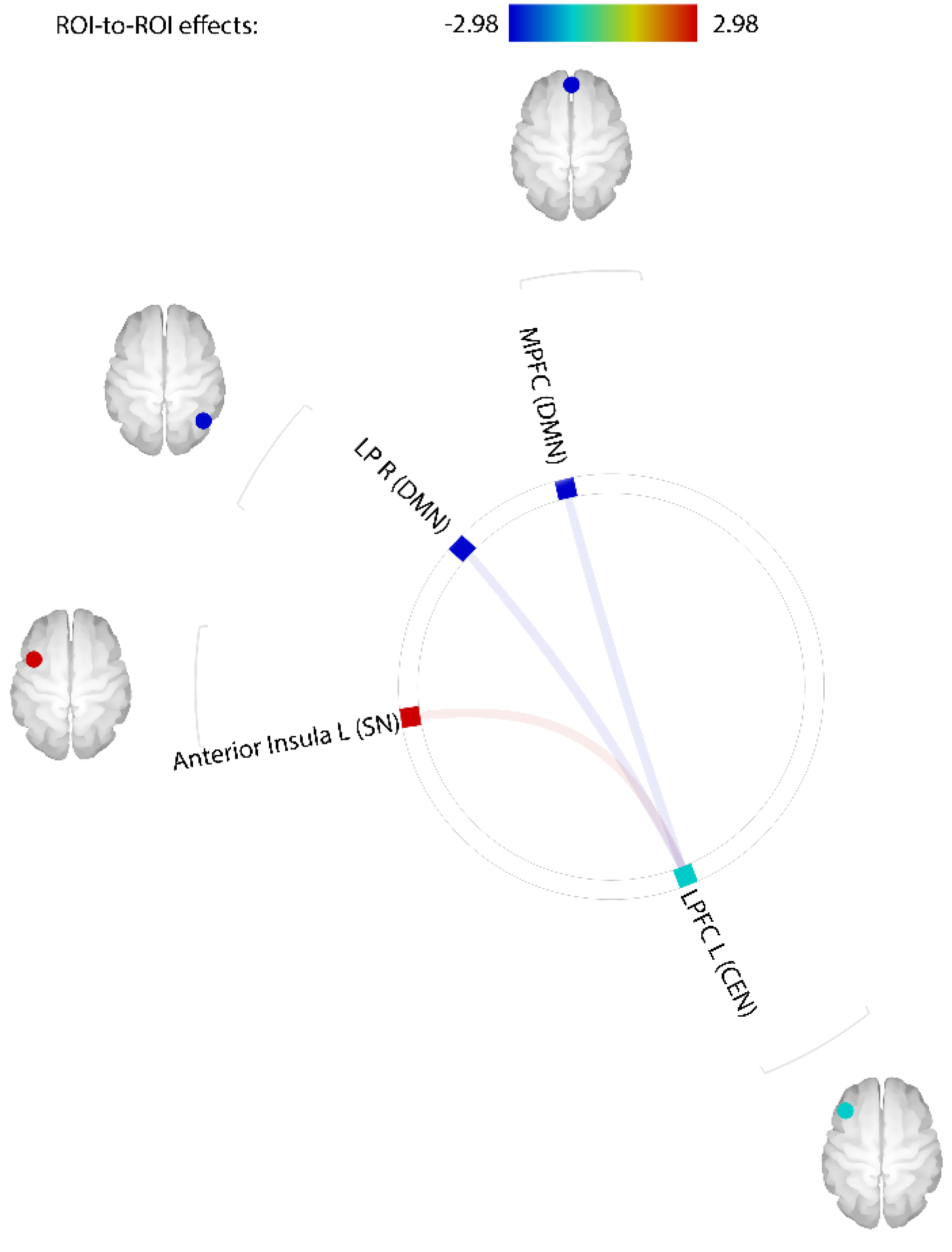
| Variables | Control (n = 29) a | PIU (n = 28) a | T/χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 13.9 ± 1.5 | 14.4 ± 1.6 | −1.061 |
| Sex (male/female) b | 11/18 | 14/14 | 0.843 |
| Weekly Internet Duration | 31.6 ± 15.1 | 41.1 ± 31.9 | −1.444 |
| IAT | 27.2 ± 5.5 | 50.8 ± 6.1 | −15.389 *** |
| Emotional Symptoms | 4.1 ± 2.1 | 5.9 ± 2.2 | −3.108 ** |
| Conduct Problems | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 3.5 ± 1.6 | −1.656 |
| Hyperactivity Symptoms | 3.9 ± 1.6 | 4.5 ± 2.0 | −1.262 |
| Peer Problems | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.9 | −7.33 |
| Prosocial Behaviours | 7.9 ± 2.2 | 7.1 ± 2.1 | 1.367 |
| NS | 11.1 ± 1.6 | 11.8 ± 1.7 | −1.682 |
| HA | 9.9 ± 1.2 | 9.1 ± 1.5 | 2.045 * |
| RD | 12.1 ± 1.2 | 12.4 ± 1.7 | −0.57 |
| Variables | Correlation with IAT (Pearson’s r) |
|---|---|
| SDQ | |
| 1. Emotional Symptoms | 0.377 ** |
| 2. Conduct Problems | 0.263 * |
| 3. Hyperactivity Symptoms | 0.198 |
| 4. Peer Problems | 0.164 |
| 5. Prosocial Behavior | −0.168 |
| TCI | |
| 6. NS | 0.289 * |
| 7. HA | −0.143 |
| 8. RD | 0.062 |
| rsFC | Effect of IAT to Emotional Symptoms Subscale (a) | Direct Effect of Emotional Symptoms Subscale (b) | Direct Effect of IAT (c’) | Total Effect of IAT (C) | Indirect Effect of IAT (ab) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | β | SE | β | SE | β | SE | β | SE | Boot 95%CI | |
| LPFC(L)-aIns(L) | 0.054 ** | 0.02 | 0.097 | 0.017 | 0.0064 ** | 0.0025 | 0.007 *** | 0.0024 | 0.0005 | 0.001 | −0.0016, 0.0024 |
| LPFC(L)-MPFC | 0.054 ** | 0.02 | −0.036 ** | 0.015 | −0.0026 | 0.0023 | −0.0045 * | 0.0022 | −0.002 | 0.0013 | (−0.0051, −0.0001) + |
| −0.12 | 0.074 | (−0.29, −0.0052) ‡ | |||||||||
| LPFC(L)-LP(R) | 0.054 ** | 0.02 | −0.0059 | 0.015 | −0.0046 * | 0.0023 | −0.0050 * | 0.0021 | −0.0003 | 0.001 | −0.0021, 0.0019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siste, K.; Pandelaki, J.; Miyata, J.; Oishi, N.; Tsurumi, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Murai, T.; Nasrun, M.W.; Wiguna, T.; Bardosono, S.; et al. Altered Resting-State Network in Adolescents with Problematic Internet Use. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195838
Siste K, Pandelaki J, Miyata J, Oishi N, Tsurumi K, Fujiwara H, Murai T, Nasrun MW, Wiguna T, Bardosono S, et al. Altered Resting-State Network in Adolescents with Problematic Internet Use. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195838
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiste, Kristiana, Jacub Pandelaki, Jun Miyata, Naoya Oishi, Kosuke Tsurumi, Hironobu Fujiwara, Toshiya Murai, Martina Wiwie Nasrun, Tjhin Wiguna, Saptawati Bardosono, and et al. 2022. "Altered Resting-State Network in Adolescents with Problematic Internet Use" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195838
APA StyleSiste, K., Pandelaki, J., Miyata, J., Oishi, N., Tsurumi, K., Fujiwara, H., Murai, T., Nasrun, M. W., Wiguna, T., Bardosono, S., Sekartini, R., Sarasvita, R., Murtani, B. J., Sen, L. T., & Firdaus, K. K. (2022). Altered Resting-State Network in Adolescents with Problematic Internet Use. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195838





